Zeqi Tan
GaVaMoE: Gaussian-Variational Gated Mixture of Experts for Explainable Recommendation
Oct 15, 2024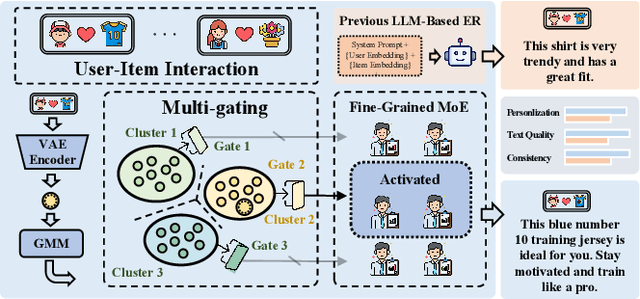
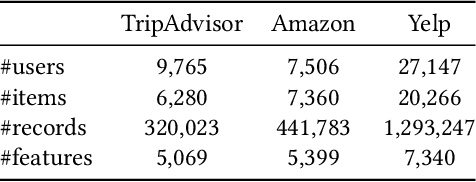
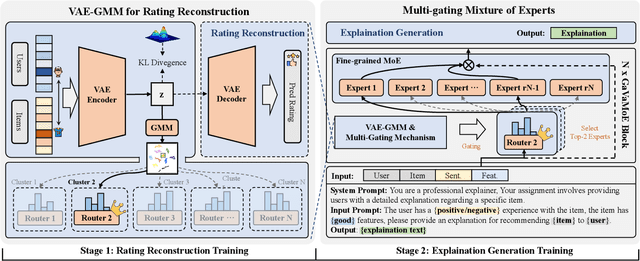
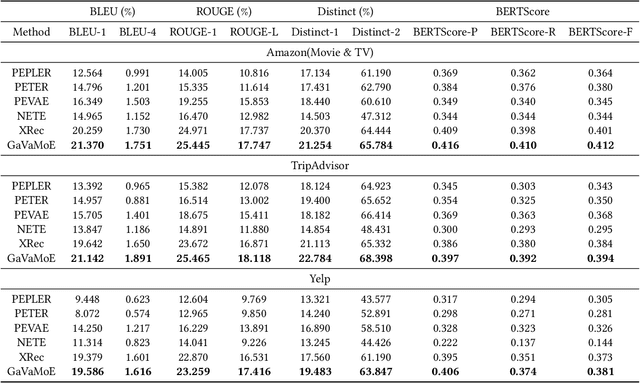
Abstract:Large language model-based explainable recommendation (LLM-based ER) systems show promise in generating human-like explanations for recommendations. However, they face challenges in modeling user-item collaborative preferences, personalizing explanations, and handling sparse user-item interactions. To address these issues, we propose GaVaMoE, a novel Gaussian-Variational Gated Mixture of Experts framework for explainable recommendation. GaVaMoE introduces two key components: (1) a rating reconstruction module that employs Variational Autoencoder (VAE) with a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to capture complex user-item collaborative preferences, serving as a pre-trained multi-gating mechanism; and (2) a set of fine-grained expert models coupled with the multi-gating mechanism for generating highly personalized explanations. The VAE component models latent factors in user-item interactions, while the GMM clusters users with similar behaviors. Each cluster corresponds to a gate in the multi-gating mechanism, routing user-item pairs to appropriate expert models. This architecture enables GaVaMoE to generate tailored explanations for specific user types and preferences, mitigating data sparsity by leveraging user similarities. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that GaVaMoE significantly outperforms existing methods in explanation quality, personalization, and consistency. Notably, GaVaMoE exhibits robust performance in scenarios with sparse user-item interactions, maintaining high-quality explanations even for users with limited historical data.
Entering Real Social World! Benchmarking the Theory of Mind and Socialization Capabilities of LLMs from a First-person Perspective
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:In the social world, humans possess the capability to infer and reason about others mental states (such as emotions, beliefs, and intentions), known as the Theory of Mind (ToM). Simultaneously, humans own mental states evolve in response to social situations, a capability we refer to as socialization. Together, these capabilities form the foundation of human social interaction. In the era of artificial intelligence (AI), especially with the development of large language models (LLMs), we raise an intriguing question: How do LLMs perform in terms of ToM and socialization capabilities? And more broadly, can these AI models truly enter and navigate the real social world? Existing research evaluating LLMs ToM and socialization capabilities by positioning LLMs as passive observers from a third person perspective, rather than as active participants. However, compared to the third-person perspective, observing and understanding the world from an egocentric first person perspective is a natural approach for both humans and AI agents. The ToM and socialization capabilities of LLMs from a first person perspective, a crucial attribute for advancing embodied AI agents, remain unexplored. To answer the aforementioned questions and bridge the research gap, we introduce EgoSocialArena, a novel framework designed to evaluate and investigate the ToM and socialization capabilities of LLMs from a first person perspective. It encompasses two evaluation environments: static environment and interactive environment, with seven scenarios: Daily Life, Counterfactual, New World, Blackjack, Number Guessing, and Limit Texas Hold em, totaling 2,195 data entries. With EgoSocialArena, we have conducted a comprehensive evaluation of nine advanced LLMs and observed some key insights regarding the future development of LLMs as well as the capabilities levels of the most advanced LLMs currently available.
Multimodal Self-Instruct: Synthetic Abstract Image and Visual Reasoning Instruction Using Language Model
Jul 10, 2024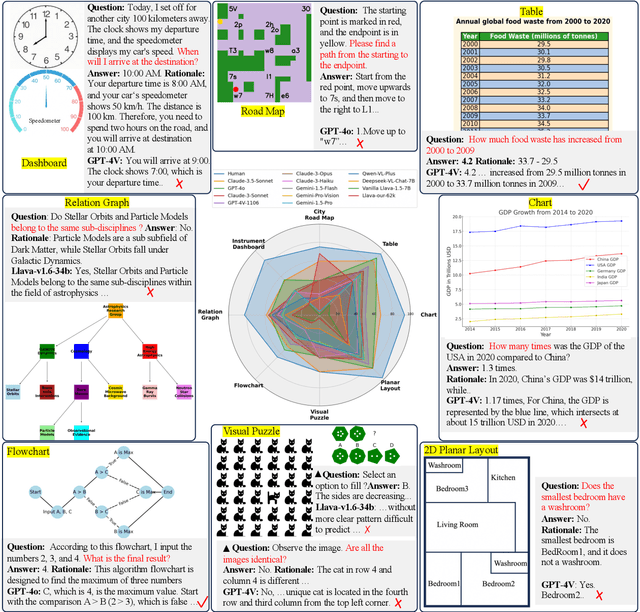
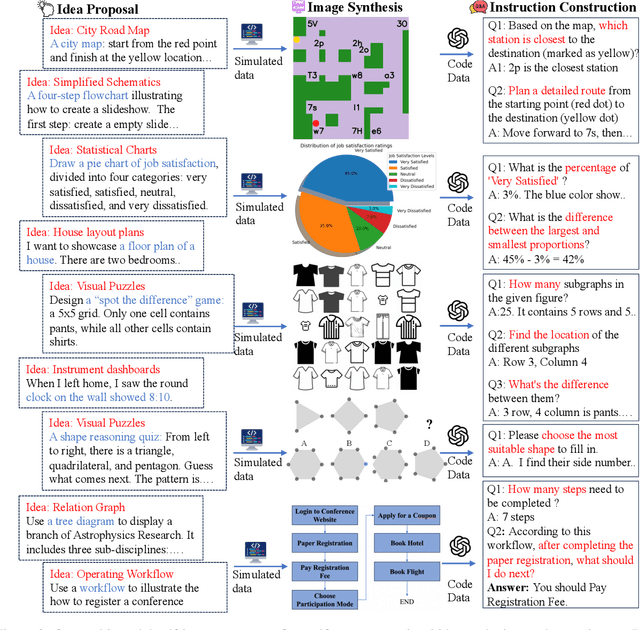
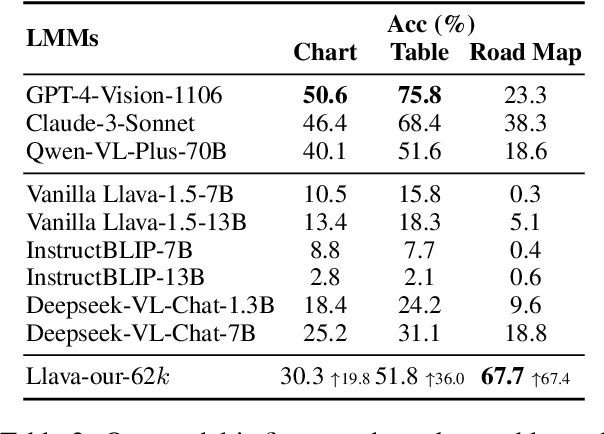
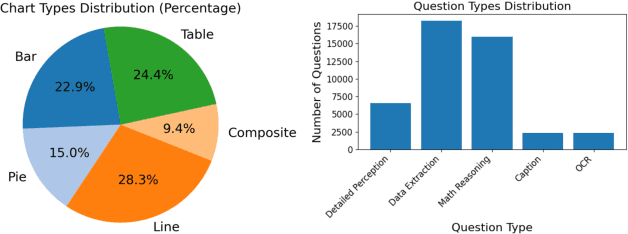
Abstract:Although most current large multimodal models (LMMs) can already understand photos of natural scenes and portraits, their understanding of abstract images, e.g., charts, maps, or layouts, and visual reasoning capabilities remains quite rudimentary. They often struggle with simple daily tasks, such as reading time from a clock, understanding a flowchart, or planning a route using a road map. In light of this, we design a multi-modal self-instruct, utilizing large language models and their code capabilities to synthesize massive abstract images and visual reasoning instructions across daily scenarios. Our strategy effortlessly creates a multimodal benchmark with 11,193 instructions for eight visual scenarios: charts, tables, simulated maps, dashboards, flowcharts, relation graphs, floor plans, and visual puzzles. \textbf{This benchmark, constructed with simple lines and geometric elements, exposes the shortcomings of most advanced LMMs} like Claude-3.5-Sonnet and GPT-4o in abstract image understanding, spatial relations reasoning, and visual element induction. Besides, to verify the quality of our synthetic data, we fine-tune an LMM using 62,476 synthetic chart, table and road map instructions. The results demonstrate improved chart understanding and map navigation performance, and also demonstrate potential benefits for other visual reasoning tasks. Our code is available at: \url{https://github.com/zwq2018/Multi-modal-Self-instruct}.
Advancing Process Verification for Large Language Models via Tree-Based Preference Learning
Jun 29, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in handling complex reasoning tasks by generating step-by-step rationales.Some methods have proven effective in boosting accuracy by introducing extra verifiers to assess these paths. However, existing verifiers, typically trained on binary-labeled reasoning paths, fail to fully utilize the relative merits of intermediate steps, thereby limiting the effectiveness of the feedback provided. To overcome this limitation, we propose Tree-based Preference Learning Verifier (Tree-PLV), a novel approach that constructs reasoning trees via a best-first search algorithm and collects step-level paired data for preference training. Compared to traditional binary classification, step-level preferences more finely capture the nuances between reasoning steps, allowing for a more precise evaluation of the complete reasoning path. We empirically evaluate Tree-PLV across a range of arithmetic and commonsense reasoning tasks, where it significantly outperforms existing benchmarks. For instance, Tree-PLV achieved substantial performance gains over the Mistral-7B self-consistency baseline on GSM8K (67.55% to 82.79%), MATH (17.00% to 26.80%), CSQA (68.14% to 72.97%), and StrategyQA (82.86% to 83.25%).Additionally, our study explores the appropriate granularity for applying preference learning, revealing that step-level guidance provides feedback that better aligns with the evaluation of the reasoning process.
Information Re-Organization Improves Reasoning in Large Language Models
Apr 22, 2024
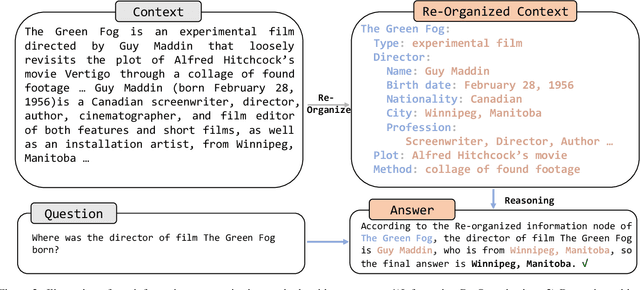
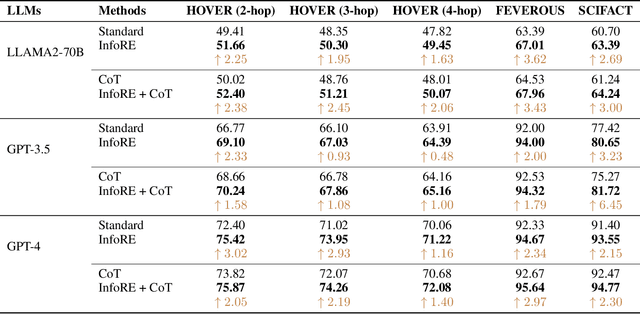
Abstract:Improving the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) has attracted considerable interest. Recent approaches primarily focus on improving the reasoning process to yield a more precise final answer. However, in scenarios involving contextually aware reasoning, these methods neglect the importance of first identifying logical relationships from the context before proceeding with the reasoning. This oversight could lead to a superficial understanding and interaction with the context, potentially undermining the quality and reliability of the reasoning outcomes. In this paper, we propose an information re-organization (InfoRE) method before proceeding with the reasoning to enhance the reasoning ability of LLMs. We first perform a re-organization processing of the contextual content, e.g., documents or paragraphs, to obtain logical relationships. Then, we utilize the re-organized information in the reasoning process. This enables LLMs to deeply understand the contextual content by clearly perceiving these logical relationships. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in improving the reasoning ability, we conduct experiments using Llama2-70B, GPT-3.5, and GPT-4 on various contextually aware multi-hop reasoning tasks. Using only a zero-shot setting, our method achieves an average improvement of 3\% across all tasks, highlighting its potential to improve the reasoning performance of LLMs. Our source code is available at https://github.com/hustcxx/InfoRE.
Agent-Pro: Learning to Evolve via Policy-Level Reflection and Optimization
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models exhibit robust problem-solving capabilities for diverse tasks. However, most LLM-based agents are designed as specific task solvers with sophisticated prompt engineering, rather than agents capable of learning and evolving through interactions. These task solvers necessitate manually crafted prompts to inform task rules and regulate LLM behaviors, inherently incapacitating to address complex dynamic scenarios e.g., large interactive games. In light of this, we propose Agent-Pro: an LLM-based Agent with Policy-level Reflection and Optimization that can learn a wealth of expertise from interactive experiences and progressively elevate its behavioral policy. Specifically, it involves a dynamic belief generation and reflection process for policy evolution. Rather than action-level reflection, Agent-Pro iteratively reflects on past trajectories and beliefs, fine-tuning its irrational beliefs for a better policy. Moreover, a depth-first search is employed for policy optimization, ensuring continual enhancement in policy payoffs. Agent-Pro is evaluated across two games: Blackjack and Texas Hold'em, outperforming vanilla LLM and specialized models. Our results show Agent-Pro can learn and evolve in complex and dynamic scenes, which also benefits numerous LLM-based applications.
An Expression Tree Decoding Strategy for Mathematical Equation Generation
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:Generating mathematical equations from natural language requires an accurate understanding of the relations among math expressions. Existing approaches can be broadly categorized into token-level and expression-level generation. The former treats equations as a mathematical language, sequentially generating math tokens. Expression-level methods generate each expression one by one. However, each expression represents a solving step, and there naturally exist parallel or dependent relations between these steps, which are ignored by current sequential methods. Therefore, we integrate tree structure into the expression-level generation and advocate an expression tree decoding strategy. To generate a tree with expression as its node, we employ a layer-wise parallel decoding strategy: we decode multiple independent expressions (leaf nodes) in parallel at each layer and repeat parallel decoding layer by layer to sequentially generate these parent node expressions that depend on others. Besides, a bipartite matching algorithm is adopted to align multiple predictions with annotations for each layer. Experiments show our method outperforms other baselines, especially for these equations with complex structures.
MProto: Multi-Prototype Network with Denoised Optimal Transport for Distantly Supervised Named Entity Recognition
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Distantly supervised named entity recognition (DS-NER) aims to locate entity mentions and classify their types with only knowledge bases or gazetteers and unlabeled corpus. However, distant annotations are noisy and degrade the performance of NER models. In this paper, we propose a noise-robust prototype network named MProto for the DS-NER task. Different from previous prototype-based NER methods, MProto represents each entity type with multiple prototypes to characterize the intra-class variance among entity representations. To optimize the classifier, each token should be assigned an appropriate ground-truth prototype and we consider such token-prototype assignment as an optimal transport (OT) problem. Furthermore, to mitigate the noise from incomplete labeling, we propose a novel denoised optimal transport (DOT) algorithm. Specifically, we utilize the assignment result between Other class tokens and all prototypes to distinguish unlabeled entity tokens from true negatives. Experiments on several DS-NER benchmarks demonstrate that our MProto achieves state-of-the-art performance. The source code is now available on Github.
GDA: Generative Data Augmentation Techniques for Relation Extraction Tasks
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Relation extraction (RE) tasks show promising performance in extracting relations from two entities mentioned in sentences, given sufficient annotations available during training. Such annotations would be labor-intensive to obtain in practice. Existing work adopts data augmentation techniques to generate pseudo-annotated sentences beyond limited annotations. These techniques neither preserve the semantic consistency of the original sentences when rule-based augmentations are adopted, nor preserve the syntax structure of sentences when expressing relations using seq2seq models, resulting in less diverse augmentations. In this work, we propose a dedicated augmentation technique for relational texts, named GDA, which uses two complementary modules to preserve both semantic consistency and syntax structures. We adopt a generative formulation and design a multi-tasking solution to achieve synergies. Furthermore, GDA adopts entity hints as the prior knowledge of the generative model to augment diverse sentences. Experimental results in three datasets under a low-resource setting showed that GDA could bring {\em 2.0\%} F1 improvements compared with no augmentation technique. Source code and data are available.
* Accepted to ACL 2023 (Findings), Long Paper, 12 pages
PromptNER: Prompt Locating and Typing for Named Entity Recognition
May 26, 2023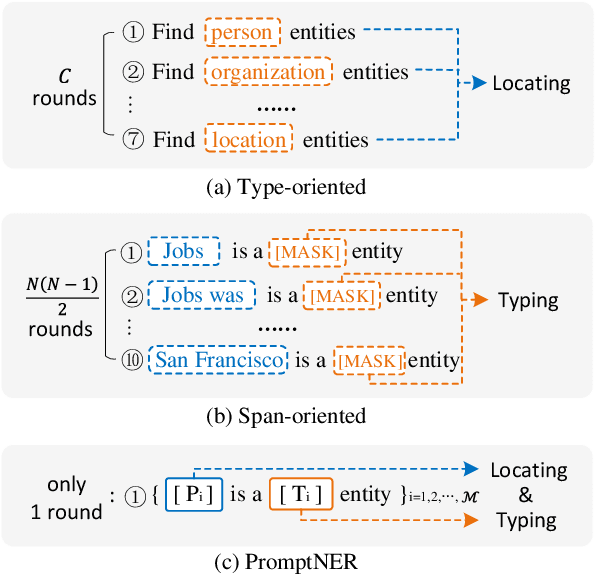
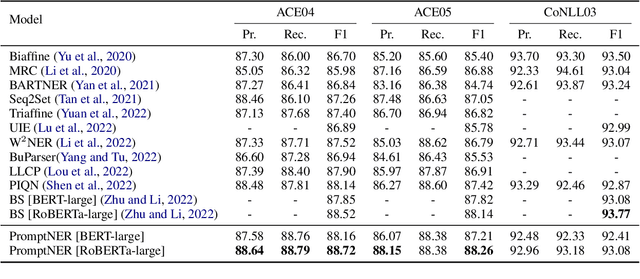
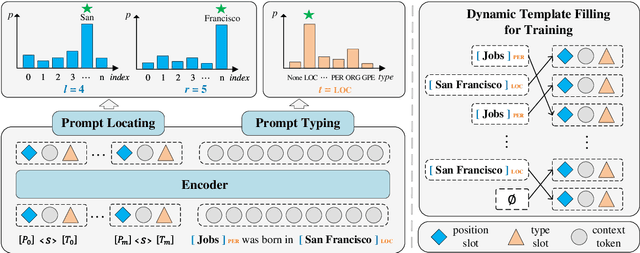
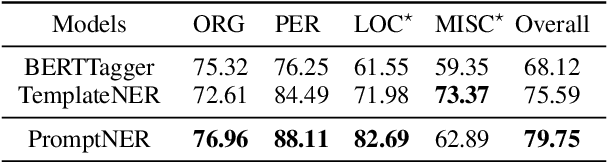
Abstract:Prompt learning is a new paradigm for utilizing pre-trained language models and has achieved great success in many tasks. To adopt prompt learning in the NER task, two kinds of methods have been explored from a pair of symmetric perspectives, populating the template by enumerating spans to predict their entity types or constructing type-specific prompts to locate entities. However, these methods not only require a multi-round prompting manner with a high time overhead and computational cost, but also require elaborate prompt templates, that are difficult to apply in practical scenarios. In this paper, we unify entity locating and entity typing into prompt learning, and design a dual-slot multi-prompt template with the position slot and type slot to prompt locating and typing respectively. Multiple prompts can be input to the model simultaneously, and then the model extracts all entities by parallel predictions on the slots. To assign labels for the slots during training, we design a dynamic template filling mechanism that uses the extended bipartite graph matching between prompts and the ground-truth entities. We conduct experiments in various settings, including resource-rich flat and nested NER datasets and low-resource in-domain and cross-domain datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves a significant performance improvement, especially in the cross-domain few-shot setting, which outperforms the state-of-the-art model by +7.7% on average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge