Yuxia Geng
Tailored Teaching with Balanced Difficulty: Elevating Reasoning in Multimodal Chain-of-Thought via Prompt Curriculum
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The effectiveness of Multimodal Chain-of-Thought (MCoT) prompting is often limited by the use of randomly or manually selected examples. These examples fail to account for both model-specific knowledge distributions and the intrinsic complexity of the tasks, resulting in suboptimal and unstable model performance. To address this, we propose a novel framework inspired by the pedagogical principle of "tailored teaching with balanced difficulty". We reframe prompt selection as a prompt curriculum design problem: constructing a well ordered set of training examples that align with the model's current capabilities. Our approach integrates two complementary signals: (1) model-perceived difficulty, quantified through prediction disagreement in an active learning setup, capturing what the model itself finds challenging; and (2) intrinsic sample complexity, which measures the inherent difficulty of each question-image pair independently of any model. By jointly analyzing these signals, we develop a difficulty-balanced sampling strategy that ensures the selected prompt examples are diverse across both dimensions. Extensive experiments conducted on five challenging benchmarks and multiple popular Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate that our method yields substantial and consistent improvements and greatly reduces performance discrepancies caused by random sampling, providing a principled and robust approach for enhancing multimodal reasoning.
Cross-composition Feature Disentanglement for Compositional Zero-shot Learning
Aug 19, 2024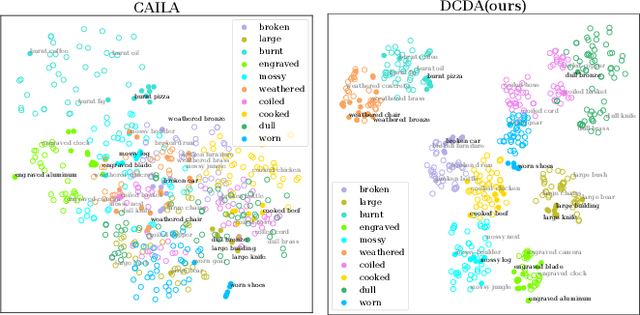
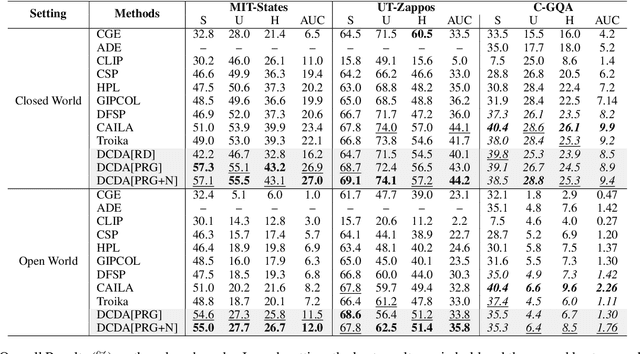
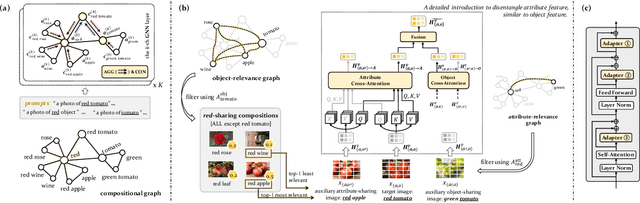
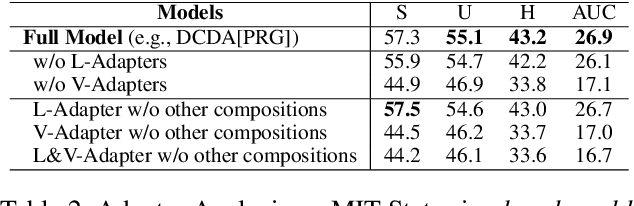
Abstract:Disentanglement of visual features of primitives (i.e., attributes and objects) has shown exceptional results in Compositional Zero-shot Learning (CZSL). However, due to the feature divergence of an attribute (resp. object) when combined with different objects (resp. attributes), it is challenging to learn disentangled primitive features that are general across different compositions. To this end, we propose the solution of cross-composition feature disentanglement, which takes multiple primitive-sharing compositions as inputs and constrains the disentangled primitive features to be general across these compositions. More specifically, we leverage a compositional graph to define the overall primitive-sharing relationships between compositions, and build a task-specific architecture upon the recently successful large pre-trained vision-language model (VLM) CLIP, with dual cross-composition disentangling adapters (called L-Adapter and V-Adapter) inserted into CLIP's frozen text and image encoders, respectively. Evaluation on three popular CZSL benchmarks shows that our proposed solution significantly improves the performance of CZSL, and its components have been verified by solid ablation studies.
Knowledge Graphs Meet Multi-Modal Learning: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) play a pivotal role in advancing various AI applications, with the semantic web community's exploration into multi-modal dimensions unlocking new avenues for innovation. In this survey, we carefully review over 300 articles, focusing on KG-aware research in two principal aspects: KG-driven Multi-Modal (KG4MM) learning, where KGs support multi-modal tasks, and Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph (MM4KG), which extends KG studies into the MMKG realm. We begin by defining KGs and MMKGs, then explore their construction progress. Our review includes two primary task categories: KG-aware multi-modal learning tasks, such as Image Classification and Visual Question Answering, and intrinsic MMKG tasks like Multi-modal Knowledge Graph Completion and Entity Alignment, highlighting specific research trajectories. For most of these tasks, we provide definitions, evaluation benchmarks, and additionally outline essential insights for conducting relevant research. Finally, we discuss current challenges and identify emerging trends, such as progress in Large Language Modeling and Multi-modal Pre-training strategies. This survey aims to serve as a comprehensive reference for researchers already involved in or considering delving into KG and multi-modal learning research, offering insights into the evolving landscape of MMKG research and supporting future work.
Prompting Disentangled Embeddings for Knowledge Graph Completion with Pre-trained Language Model
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:Both graph structures and textual information play a critical role in Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC). With the success of Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) such as BERT, they have been applied for text encoding for KGC. However, the current methods mostly prefer to fine-tune PLMs, leading to huge training costs and limited scalability to larger PLMs. In contrast, we propose to utilize prompts and perform KGC on a frozen PLM with only the prompts trained. Accordingly, we propose a new KGC method named PDKGC with two prompts -- a hard task prompt which is to adapt the KGC task to the PLM pre-training task of token prediction, and a disentangled structure prompt which learns disentangled graph representation so as to enable the PLM to combine more relevant structure knowledge with the text information. With the two prompts, PDKGC builds a textual predictor and a structural predictor, respectively, and their combination leads to more comprehensive entity prediction. Solid evaluation on two widely used KGC datasets has shown that PDKGC often outperforms the baselines including the state-of-the-art, and its components are all effective. Our codes and data are available at https://github.com/genggengcss/PDKGC.
Structure Pretraining and Prompt Tuning for Knowledge Graph Transfer
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KG) are essential background knowledge providers in many tasks. When designing models for KG-related tasks, one of the key tasks is to devise the Knowledge Representation and Fusion (KRF) module that learns the representation of elements from KGs and fuses them with task representations. While due to the difference of KGs and perspectives to be considered during fusion across tasks, duplicate and ad hoc KRF modules design are conducted among tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel knowledge graph pretraining model KGTransformer that could serve as a uniform KRF module in diverse KG-related tasks. We pretrain KGTransformer with three self-supervised tasks with sampled sub-graphs as input. For utilization, we propose a general prompt-tuning mechanism regarding task data as a triple prompt to allow flexible interactions between task KGs and task data. We evaluate pretrained KGTransformer on three tasks, triple classification, zero-shot image classification, and question answering. KGTransformer consistently achieves better results than specifically designed task models. Through experiments, we justify that the pretrained KGTransformer could be used off the shelf as a general and effective KRF module across KG-related tasks. The code and datasets are available at https://github.com/zjukg/KGTransformer.
Generalizing to Unseen Elements: A Survey on Knowledge Extrapolation for Knowledge Graphs
Feb 03, 2023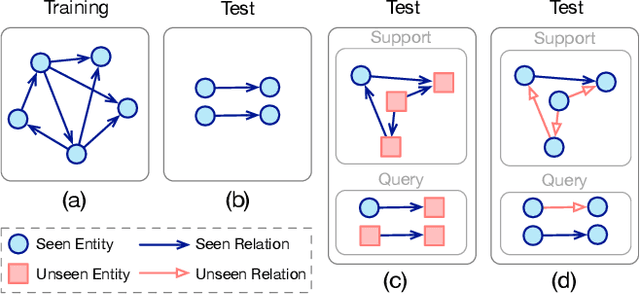
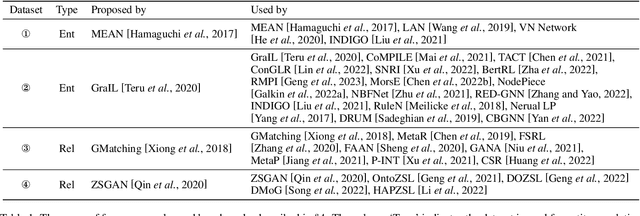
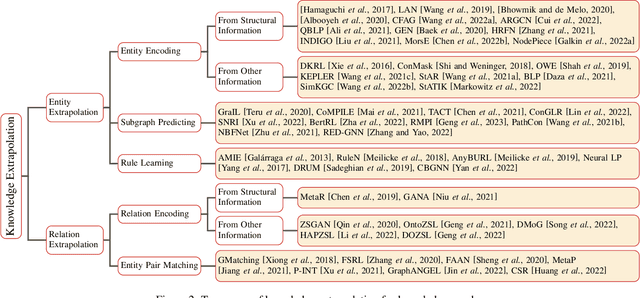
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have become effective knowledge resources in diverse applications, and knowledge graph embedding (KGE) methods have attracted increasing attention in recent years. However, it's still challenging for conventional KGE methods to handle unseen entities or relations during the model test. Much effort has been made in various fields of KGs to address this problem. In this paper, we use a set of general terminologies to unify these methods and refer to them as Knowledge Extrapolation. We comprehensively summarize these methods classified by our proposed taxonomy and describe their correlations. Next, we introduce the benchmarks and provide comparisons of these methods from aspects that are not reflected by the taxonomy. Finally, we suggest some potential directions for future research.
MEAformer: Multi-modal Entity Alignment Transformer for Meta Modality Hybrid
Dec 29, 2022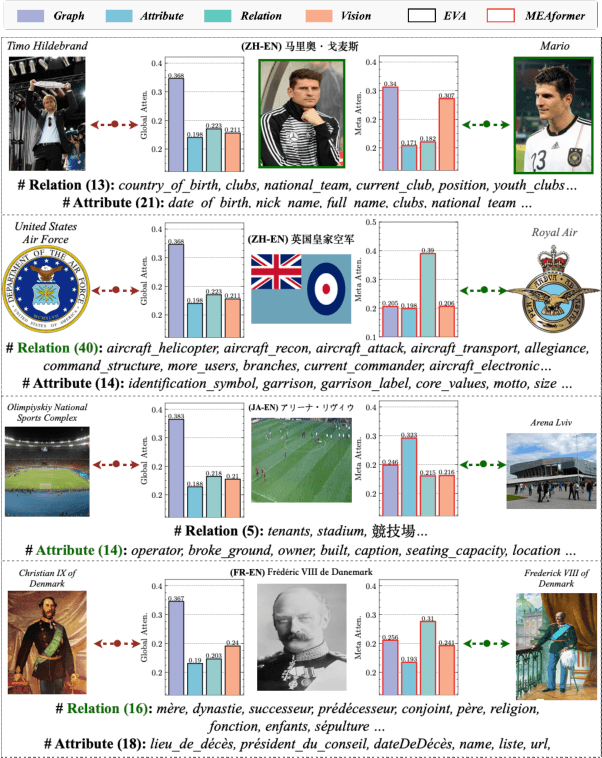
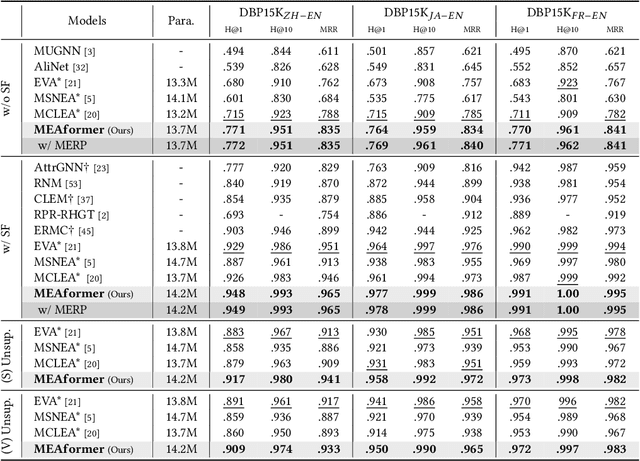
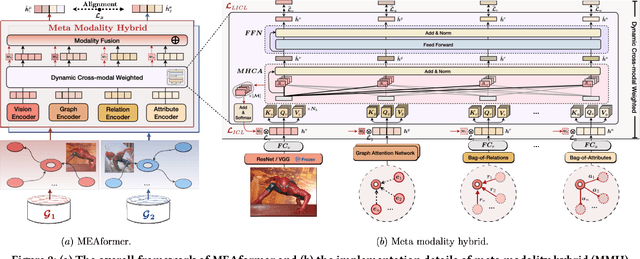
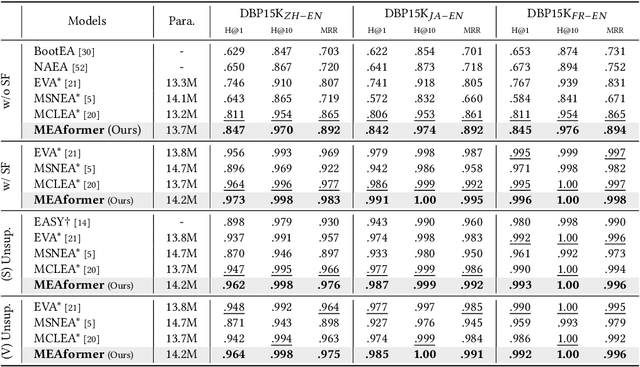
Abstract:As an important variant of entity alignment (EA), multi-modal entity alignment (MMEA) aims to discover identical entities across different knowledge graphs (KGs) with multiple modalities like images. However, current MMEA algorithms all adopt KG-level modality fusion strategies but ignore modality differences among individual entities, hurting the robustness to potential noise involved in modalities (e.g., unidentifiable images and relations). In this paper we present MEAformer, a multi-modal entity alignment transformer approach for meta modality hybrid, to dynamically predict the mutual correlation coefficients among modalities for instance-level feature fusion. A modal-aware hard entity replay strategy is also proposed for addressing vague entity details. Extensive experimental results show that our model not only achieves SOTA performance on multiple training scenarios including supervised, unsupervised, iterative, and low resource, but also has limited parameters, optimistic speed, and good interpretability. Our code will be available soon.
Tele-Knowledge Pre-training for Fault Analysis
Oct 20, 2022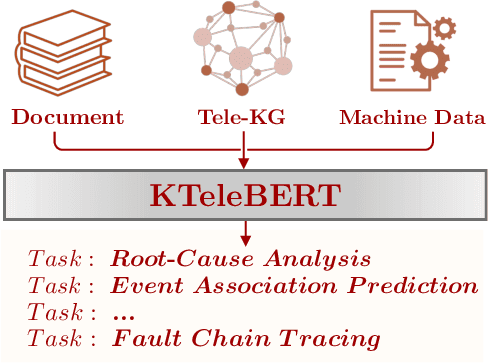


Abstract:In this work, we share our experience on tele-knowledge pre-training for fault analysis. Fault analysis is a vital task for tele-application, which should be timely and properly handled. Fault analysis is also a complex task, that has many sub-tasks. Solving each task requires diverse tele-knowledge. Machine log data and product documents contain part of the tele-knowledge. We create a Tele-KG to organize other tele-knowledge from experts uniformly. With these valuable tele-knowledge data, in this work, we propose a tele-domain pre-training model KTeleBERT and its knowledge-enhanced version KTeleBERT, which includes effective prompt hints, adaptive numerical data encoding, and two knowledge injection paradigms. We train our model in two stages: pre-training TeleBERT on 20 million telecommunication corpora and re-training TeleBERT on 1 million causal and machine corpora to get the KTeleBERT. Then, we apply our models for three tasks of fault analysis, including root-cause analysis, event association prediction, and fault chain tracing. The results show that with KTeleBERT, the performance of task models has been boosted, demonstrating the effectiveness of pre-trained KTeleBERT as a model containing diverse tele-knowledge.
Relational Message Passing for Fully Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion
Oct 08, 2022



Abstract:In knowledge graph completion (KGC), predicting triples involving emerging entities and/or relations, which are unseen when the KG embeddings are learned, has become a critical challenge. Subgraph reasoning with message passing is a promising and popular solution. Some recent methods have achieved good performance, but they (i) usually can only predict triples involving unseen entities alone, failing to address more realistic fully inductive situations with both unseen entities and unseen relations, and (ii) often conduct message passing over the entities with the relation patterns not fully utilized. In this study, we propose a new method named RMPI which uses a novel Relational Message Passing network for fully Inductive KGC. It passes messages directly between relations to make full use of the relation patterns for subgraph reasoning with new techniques on graph transformation, graph pruning, relation-aware neighborhood attention, addressing empty subgraphs, etc., and can utilize the relation semantics defined in the ontological schema of KG. Extensive evaluation on multiple benchmarks has shown the effectiveness of techniques involved in RMPI and its better performance compared with the existing methods that support fully inductive KGC. RMPI is also comparable to the state-of-the-art partially inductive KGC methods with very promising results achieved. Our codes and data are available at https://github.com/zjukg/RMPI.
LaKo: Knowledge-driven Visual Question Answering via Late Knowledge-to-Text Injection
Jul 26, 2022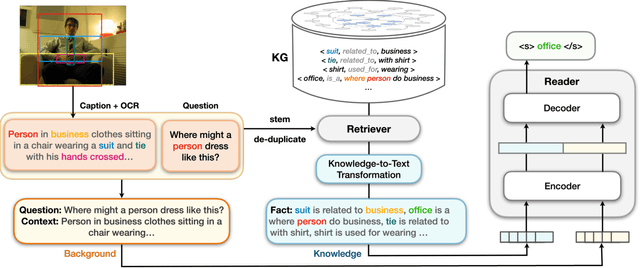

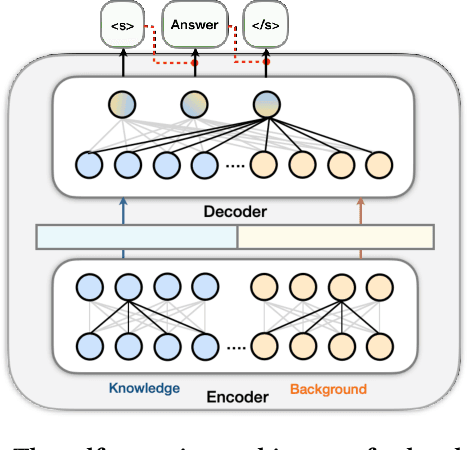

Abstract:Visual question answering (VQA) often requires an understanding of visual concepts and language semantics, which relies on external knowledge. Most existing methods exploit pre-trained language models or/and unstructured text, but the knowledge in these resources are often incomplete and noisy. Some methods prefer to use knowledge graphs (KGs) which often have intensive structured knowledge, but the research is still quite preliminary. In this paper, we propose LaKo, a knowledge-driven VQA method via Late Knowledge-to-text Injection. To effectively incorporate an external KG, we transfer triples into text and propose a late injection mechanism. Finally we address VQA as a text generation task with an effective encoder-decoder paradigm. In the evaluation with OKVQA datasets, our method achieves state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge