Yurui Chen
From Flatland to Space: Teaching Vision-Language Models to Perceive and Reason in 3D
Mar 29, 2025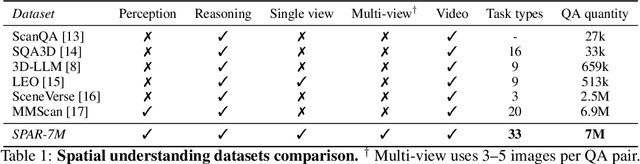
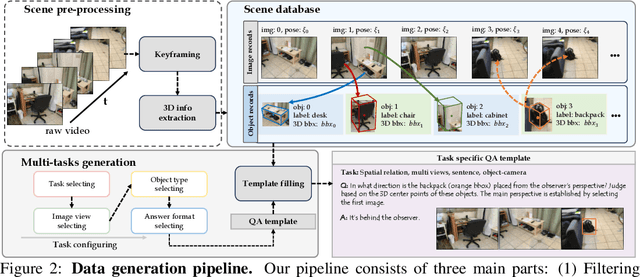
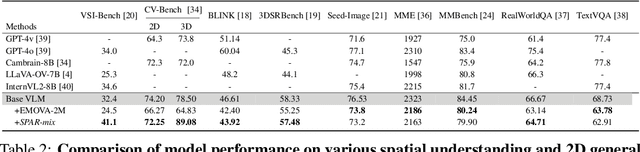
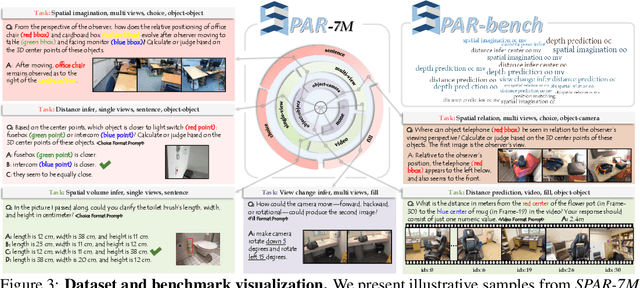
Abstract:Recent advances in LVLMs have improved vision-language understanding, but they still struggle with spatial perception, limiting their ability to reason about complex 3D scenes. Unlike previous approaches that incorporate 3D representations into models to improve spatial understanding, we aim to unlock the potential of VLMs by leveraging spatially relevant image data. To this end, we introduce a novel 2D spatial data generation and annotation pipeline built upon scene data with 3D ground-truth. This pipeline enables the creation of a diverse set of spatial tasks, ranging from basic perception tasks to more complex reasoning tasks. Leveraging this pipeline, we construct SPAR-7M, a large-scale dataset generated from thousands of scenes across multiple public datasets. In addition, we introduce SPAR-Bench, a benchmark designed to offer a more comprehensive evaluation of spatial capabilities compared to existing spatial benchmarks, supporting both single-view and multi-view inputs. Training on both SPAR-7M and large-scale 2D datasets enables our models to achieve state-of-the-art performance on 2D spatial benchmarks. Further fine-tuning on 3D task-specific datasets yields competitive results, underscoring the effectiveness of our dataset in enhancing spatial reasoning.
BANet: Bilateral Aggregation Network for Mobile Stereo Matching
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art stereo matching methods typically use costly 3D convolutions to aggregate a full cost volume, but their computational demands make mobile deployment challenging. Directly applying 2D convolutions for cost aggregation often results in edge blurring, detail loss, and mismatches in textureless regions. Some complex operations, like deformable convolutions and iterative warping, can partially alleviate this issue; however, they are not mobile-friendly, limiting their deployment on mobile devices. In this paper, we present a novel bilateral aggregation network (BANet) for mobile stereo matching that produces high-quality results with sharp edges and fine details using only 2D convolutions. Specifically, we first separate the full cost volume into detailed and smooth volumes using a spatial attention map, then perform detailed and smooth aggregations accordingly, ultimately fusing both to obtain the final disparity map. Additionally, to accurately identify high-frequency detailed regions and low-frequency smooth/textureless regions, we propose a new scale-aware spatial attention module. Experimental results demonstrate that our BANet-2D significantly outperforms other mobile-friendly methods, achieving 35.3\% higher accuracy on the KITTI 2015 leaderboard than MobileStereoNet-2D, with faster runtime on mobile devices. The extended 3D version, BANet-3D, achieves the highest accuracy among all real-time methods on high-end GPUs. Code: \textcolor{magenta}{https://github.com/gangweiX/BANet}.
StereoGen: High-quality Stereo Image Generation from a Single Image
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art supervised stereo matching methods have achieved amazing results on various benchmarks. However, these data-driven methods suffer from generalization to real-world scenarios due to the lack of real-world annotated data. In this paper, we propose StereoGen, a novel pipeline for high-quality stereo image generation. This pipeline utilizes arbitrary single images as left images and pseudo disparities generated by a monocular depth estimation model to synthesize high-quality corresponding right images. Unlike previous methods that fill the occluded area in warped right images using random backgrounds or using convolutions to take nearby pixels selectively, we fine-tune a diffusion inpainting model to recover the background. Images generated by our model possess better details and undamaged semantic structures. Besides, we propose Training-free Confidence Generation and Adaptive Disparity Selection. The former suppresses the negative effect of harmful pseudo ground truth during stereo training, while the latter helps generate a wider disparity distribution and better synthetic images. Experiments show that models trained under our pipeline achieve state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization results among all published methods. The code will be available upon publication of the paper.
MonSter: Marry Monodepth to Stereo Unleashes Power
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Stereo matching recovers depth from image correspondences. Existing methods struggle to handle ill-posed regions with limited matching cues, such as occlusions and textureless areas. To address this, we propose MonSter, a novel method that leverages the complementary strengths of monocular depth estimation and stereo matching. MonSter integrates monocular depth and stereo matching into a dual-branch architecture to iteratively improve each other. Confidence-based guidance adaptively selects reliable stereo cues for monodepth scale-shift recovery. The refined monodepth is in turn guides stereo effectively at ill-posed regions. Such iterative mutual enhancement enables MonSter to evolve monodepth priors from coarse object-level structures to pixel-level geometry, fully unlocking the potential of stereo matching. As shown in Fig.1, MonSter ranks 1st across five most commonly used leaderboards -- SceneFlow, KITTI 2012, KITTI 2015, Middlebury, and ETH3D. Achieving up to 49.5% improvements (Bad 1.0 on ETH3D) over the previous best method. Comprehensive analysis verifies the effectiveness of MonSter in ill-posed regions. In terms of zero-shot generalization, MonSter significantly and consistently outperforms state-of-the-art across the board. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/Junda24/MonSter.
S-NeRF++: Autonomous Driving Simulation via Neural Reconstruction and Generation
Feb 03, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous driving simulation system plays a crucial role in enhancing self-driving data and simulating complex and rare traffic scenarios, ensuring navigation safety. However, traditional simulation systems, which often heavily rely on manual modeling and 2D image editing, struggled with scaling to extensive scenes and generating realistic simulation data. In this study, we present S-NeRF++, an innovative autonomous driving simulation system based on neural reconstruction. Trained on widely-used self-driving datasets such as nuScenes and Waymo, S-NeRF++ can generate a large number of realistic street scenes and foreground objects with high rendering quality as well as offering considerable flexibility in manipulation and simulation. Specifically, S-NeRF++ is an enhanced neural radiance field for synthesizing large-scale scenes and moving vehicles, with improved scene parameterization and camera pose learning. The system effectively utilizes noisy and sparse LiDAR data to refine training and address depth outliers, ensuring high quality reconstruction and novel-view rendering. It also provides a diverse foreground asset bank through reconstructing and generating different foreground vehicles to support comprehensive scenario creation. Moreover, we have developed an advanced foreground-background fusion pipeline that skillfully integrates illumination and shadow effects, further enhancing the realism of our simulations. With the high-quality simulated data provided by our S-NeRF++, we found the perception methods enjoy performance boost on several autonomous driving downstream tasks, which further demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed simulator.
Periodic Vibration Gaussian: Dynamic Urban Scene Reconstruction and Real-time Rendering
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Modeling dynamic, large-scale urban scenes is challenging due to their highly intricate geometric structures and unconstrained dynamics in both space and time. Prior methods often employ high-level architectural priors, separating static and dynamic elements, resulting in suboptimal capture of their synergistic interactions. To address this challenge, we present a unified representation model, called Periodic Vibration Gaussian (PVG). PVG builds upon the efficient 3D Gaussian splatting technique, originally designed for static scene representation, by introducing periodic vibration-based temporal dynamics. This innovation enables PVG to elegantly and uniformly represent the characteristics of various objects and elements in dynamic urban scenes. To enhance temporally coherent representation learning with sparse training data, we introduce a novel flow-based temporal smoothing mechanism and a position-aware adaptive control strategy. Extensive experiments on Waymo Open Dataset and KITTI benchmarks demonstrate that PVG surpasses state-of-the-art alternatives in both reconstruction and novel view synthesis for both dynamic and static scenes. Notably, PVG achieves this without relying on manually labeled object bounding boxes or expensive optical flow estimation. Moreover, PVG exhibits 50/6000-fold acceleration in training/rendering over the best alternative.
Single-view Neural Radiance Fields with Depth Teacher
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have been proposed for photorealistic novel view rendering. However, it requires many different views of one scene for training. Moreover, it has poor generalizations to new scenes and requires retraining or fine-tuning on each scene. In this paper, we develop a new NeRF model for novel view synthesis using only a single image as input. We propose to combine the (coarse) planar rendering and the (fine) volume rendering to achieve higher rendering quality and better generalizations. We also design a depth teacher net that predicts dense pseudo depth maps to supervise the joint rendering mechanism and boost the learning of consistent 3D geometry. We evaluate our method on three challenging datasets. It outperforms state-of-the-art single-view NeRFs by achieving 5$\sim$20\% improvements in PSNR and reducing 20$\sim$50\% of the errors in the depth rendering. It also shows excellent generalization abilities to unseen data without the need to fine-tune on each new scene.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge