Ziyang Xie
Vid2Sim: Realistic and Interactive Simulation from Video for Urban Navigation
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Sim-to-real gap has long posed a significant challenge for robot learning in simulation, preventing the deployment of learned models in the real world. Previous work has primarily focused on domain randomization and system identification to mitigate this gap. However, these methods are often limited by the inherent constraints of the simulation and graphics engines. In this work, we propose Vid2Sim, a novel framework that effectively bridges the sim2real gap through a scalable and cost-efficient real2sim pipeline for neural 3D scene reconstruction and simulation. Given a monocular video as input, Vid2Sim can generate photorealistic and physically interactable 3D simulation environments to enable the reinforcement learning of visual navigation agents in complex urban environments. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Vid2Sim significantly improves the performance of urban navigation in the digital twins and real world by 31.2% and 68.3% in success rate compared with agents trained with prior simulation methods.
Automating the Diagnosis of Human Vision Disorders by Cross-modal 3D Generation
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Understanding the hidden mechanisms behind human's visual perception is a fundamental quest in neuroscience, underpins a wide variety of critical applications, e.g. clinical diagnosis. To that end, investigating into the neural responses of human mind activities, such as functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), has been a significant research vehicle. However, analyzing fMRI signals is challenging, costly, daunting, and demanding for professional training. Despite remarkable progress in artificial intelligence (AI) based fMRI analysis, existing solutions are limited and far away from being clinically meaningful. In this context, we leap forward to demonstrate how AI can go beyond the current state of the art by decoding fMRI into visually plausible 3D visuals, enabling automatic clinical analysis of fMRI data, even without healthcare professionals. Innovationally, we reformulate the task of analyzing fMRI data as a conditional 3D scene reconstruction problem. We design a novel cross-modal 3D scene representation learning method, Brain3D, that takes as input the fMRI data of a subject who was presented with a 2D object image, and yields as output the corresponding 3D object visuals. Importantly, we show that in simulated scenarios our AI agent captures the distinct functionalities of each region of human vision system as well as their intricate interplay relationships, aligning remarkably with the established discoveries of neuroscience. Non-expert diagnosis indicate that Brain3D can successfully identify the disordered brain regions, such as V1, V2, V3, V4, and the medial temporal lobe (MTL) within the human visual system. We also present results in cross-modal 3D visual construction setting, showcasing the perception quality of our 3D scene generation.
S-NeRF++: Autonomous Driving Simulation via Neural Reconstruction and Generation
Feb 03, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous driving simulation system plays a crucial role in enhancing self-driving data and simulating complex and rare traffic scenarios, ensuring navigation safety. However, traditional simulation systems, which often heavily rely on manual modeling and 2D image editing, struggled with scaling to extensive scenes and generating realistic simulation data. In this study, we present S-NeRF++, an innovative autonomous driving simulation system based on neural reconstruction. Trained on widely-used self-driving datasets such as nuScenes and Waymo, S-NeRF++ can generate a large number of realistic street scenes and foreground objects with high rendering quality as well as offering considerable flexibility in manipulation and simulation. Specifically, S-NeRF++ is an enhanced neural radiance field for synthesizing large-scale scenes and moving vehicles, with improved scene parameterization and camera pose learning. The system effectively utilizes noisy and sparse LiDAR data to refine training and address depth outliers, ensuring high quality reconstruction and novel-view rendering. It also provides a diverse foreground asset bank through reconstructing and generating different foreground vehicles to support comprehensive scenario creation. Moreover, we have developed an advanced foreground-background fusion pipeline that skillfully integrates illumination and shadow effects, further enhancing the realism of our simulations. With the high-quality simulated data provided by our S-NeRF++, we found the perception methods enjoy performance boost on several autonomous driving downstream tasks, which further demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed simulator.
Frozen Transformers in Language Models Are Effective Visual Encoder Layers
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:This paper reveals that large language models (LLMs), despite being trained solely on textual data, are surprisingly strong encoders for purely visual tasks in the absence of language. Even more intriguingly, this can be achieved by a simple yet previously overlooked strategy -- employing a frozen transformer block from pre-trained LLMs as a constituent encoder layer to directly process visual tokens. Our work pushes the boundaries of leveraging LLMs for computer vision tasks, significantly departing from conventional practices that typically necessitate a multi-modal vision-language setup with associated language prompts, inputs, or outputs. We demonstrate that our approach consistently enhances performance across a diverse range of tasks, encompassing pure 2D and 3D visual recognition tasks (e.g., image and point cloud classification), temporal modeling tasks (e.g., action recognition), non-semantic tasks (e.g., motion forecasting), and multi-modal tasks (e.g., 2D/3D visual question answering and image-text retrieval). Such improvements are a general phenomenon, applicable to various types of LLMs (e.g., LLaMA and OPT) and different LLM transformer blocks. We additionally propose the information filtering hypothesis to explain the effectiveness of pre-trained LLMs in visual encoding -- the pre-trained LLM transformer blocks discern informative visual tokens and further amplify their effect. This hypothesis is empirically supported by the observation that the feature activation, after training with LLM transformer blocks, exhibits a stronger focus on relevant regions. We hope that our work inspires new perspectives on utilizing LLMs and deepening our understanding of their underlying mechanisms. Code is available at https://github.com/ziqipang/LM4VisualEncoding.
MV-Map: Offboard HD-Map Generation with Multi-view Consistency
May 15, 2023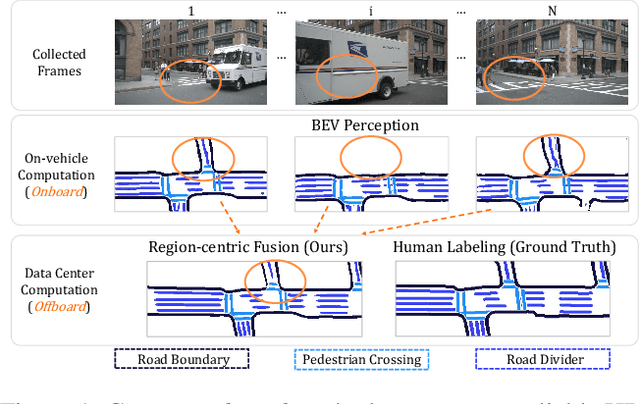



Abstract:While bird's-eye-view (BEV) perception models can be useful for building high-definition maps (HD-Maps) with less human labor, their results are often unreliable and demonstrate noticeable inconsistencies in the predicted HD-Maps from different viewpoints. This is because BEV perception is typically set up in an 'onboard' manner, which restricts the computation and consequently prevents algorithms from reasoning multiple views simultaneously. This paper overcomes these limitations and advocates a more practical 'offboard' HD-Map generation setup that removes the computation constraints, based on the fact that HD-Maps are commonly reusable infrastructures built offline in data centers. To this end, we propose a novel offboard pipeline called MV-Map that capitalizes multi-view consistency and can handle an arbitrary number of frames with the key design of a 'region-centric' framework. In MV-Map, the target HD-Maps are created by aggregating all the frames of onboard predictions, weighted by the confidence scores assigned by an 'uncertainty network'. To further enhance multi-view consistency, we augment the uncertainty network with the global 3D structure optimized by a voxelized neural radiance field (Voxel-NeRF). Extensive experiments on nuScenes show that our MV-Map significantly improves the quality of HD-Maps, further highlighting the importance of offboard methods for HD-Map generation.
S-NeRF: Neural Radiance Fields for Street Views
Mar 01, 2023



Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) aim to synthesize novel views of objects and scenes, given the object-centric camera views with large overlaps. However, we conjugate that this paradigm does not fit the nature of the street views that are collected by many self-driving cars from the large-scale unbounded scenes. Also, the onboard cameras perceive scenes without much overlapping. Thus, existing NeRFs often produce blurs, 'floaters' and other artifacts on street-view synthesis. In this paper, we propose a new street-view NeRF (S-NeRF) that considers novel view synthesis of both the large-scale background scenes and the foreground moving vehicles jointly. Specifically, we improve the scene parameterization function and the camera poses for learning better neural representations from street views. We also use the the noisy and sparse LiDAR points to boost the training and learn a robust geometry and reprojection based confidence to address the depth outliers. Moreover, we extend our S-NeRF for reconstructing moving vehicles that is impracticable for conventional NeRFs. Thorough experiments on the large-scale driving datasets (e.g., nuScenes and Waymo) demonstrate that our method beats the state-of-the-art rivals by reducing 7% to 40% of the mean-squared error in the street-view synthesis and a 45% PSNR gain for the moving vehicles rendering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge