Jianfeng Feng
On the Nonasymptotic Scaling Guarantee of Hyperparameter Estimation in Inhomogeneous, Weakly-Dependent Complex Network Dynamical Systems
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Hierarchical Bayesian models are increasingly used in large, inhomogeneous complex network dynamical systems by modeling parameters as draws from a hyperparameter-governed distribution. However, theoretical guarantees for these estimates as the system size grows have been lacking. A critical concern is that hyperparameter estimation may diverge for larger networks, undermining the model's reliability. Formulating the system's evolution in a measure transport perspective, we propose a theoretical framework for estimating hyperparameters with mean-type observations, which are prevalent in many scientific applications. Our primary contribution is a nonasymptotic bound for the deviation of estimate of hyperparameters in inhomogeneous complex network dynamical systems with respect to network population size, which is established for a general family of optimization algorithms within a fixed observation duration. While we firstly establish a consistency result for systems with independent nodes, our main result extends this guarantee to the more challenging and realistic setting of weakly-dependent nodes. We validate our theoretical findings with numerical experiments on two representative models: a Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible model and a Spiking Neuronal Network model. In both cases, the results confirm that the estimation error decreases as the network population size increases, aligning with our theoretical guarantees. This research proposes the foundational theory to ensure that hierarchical Bayesian methods are statistically consistent for large-scale inhomogeneous systems, filling a gap in this area of theoretical research and justifying their application in practice.
The Pictorial Cortex: Zero-Shot Cross-Subject fMRI-to-Image Reconstruction via Compositional Latent Modeling
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Decoding visual experiences from human brain activity remains a central challenge at the intersection of neuroscience, neuroimaging, and artificial intelligence. A critical obstacle is the inherent variability of cortical responses: neural activity elicited by the same visual stimulus differs across individuals and trials due to anatomical, functional, cognitive, and experimental factors, making fMRI-to-image reconstruction non-injective. In this paper, we tackle a challenging yet practically meaningful problem: zero-shot cross-subject fMRI-to-image reconstruction, where the visual experience of a previously unseen individual must be reconstructed without subject-specific training. To enable principled evaluation, we present a unified cortical-surface dataset -- UniCortex-fMRI, assembled from multiple visual-stimulus fMRI datasets to provide broad coverage of subjects and stimuli. Our UniCortex-fMRI is particularly processed by standardized data formats to make it possible to explore this possibility in the zero-shot scenario of cross-subject fMRI-to-image reconstruction. To tackle the modeling challenge, we propose PictorialCortex, which models fMRI activity using a compositional latent formulation that structures stimulus-driven representations under subject-, dataset-, and trial-related variability. PictorialCortex operates in a universal cortical latent space and implements this formulation through a latent factorization--composition module, reinforced by paired factorization and re-factorizing consistency regularization. During inference, surrogate latents synthesized under multiple seen-subject conditions are aggregated to guide diffusion-based image synthesis for unseen subjects. Extensive experiments show that PictorialCortex improves zero-shot cross-subject visual reconstruction, highlighting the benefits of compositional latent modeling and multi-dataset training.
SLIM-Brain: A Data- and Training-Efficient Foundation Model for fMRI Data Analysis
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Foundation models are emerging as a powerful paradigm for fMRI analysis, but current approaches face a dual bottleneck of data- and training-efficiency. Atlas-based methods aggregate voxel signals into fixed regions of interest, reducing data dimensionality but discarding fine-grained spatial details, and requiring extremely large cohorts to train effectively as general-purpose foundation models. Atlas-free methods, on the other hand, operate directly on voxel-level information - preserving spatial fidelity but are prohibitively memory- and compute-intensive, making large-scale pre-training infeasible. We introduce SLIM-Brain (Sample-efficient, Low-memory fMRI Foundation Model for Human Brain), a new atlas-free foundation model that simultaneously improves both data- and training-efficiency. SLIM-Brain adopts a two-stage adaptive design: (i) a lightweight temporal extractor captures global context across full sequences and ranks data windows by saliency, and (ii) a 4D hierarchical encoder (Hiera-JEPA) learns fine-grained voxel-level representations only from the top-$k$ selected windows, while deleting about 70% masked patches. Extensive experiments across seven public benchmarks show that SLIM-Brain establishes new state-of-the-art performance on diverse tasks, while requiring only 4 thousand pre-training sessions and approximately 30% of GPU memory comparing to traditional voxel-level methods.
LongVie 2: Multimodal Controllable Ultra-Long Video World Model
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Building video world models upon pretrained video generation systems represents an important yet challenging step toward general spatiotemporal intelligence. A world model should possess three essential properties: controllability, long-term visual quality, and temporal consistency. To this end, we take a progressive approach-first enhancing controllability and then extending toward long-term, high-quality generation. We present LongVie 2, an end-to-end autoregressive framework trained in three stages: (1) Multi-modal guidance, which integrates dense and sparse control signals to provide implicit world-level supervision and improve controllability; (2) Degradation-aware training on the input frame, bridging the gap between training and long-term inference to maintain high visual quality; and (3) History-context guidance, which aligns contextual information across adjacent clips to ensure temporal consistency. We further introduce LongVGenBench, a comprehensive benchmark comprising 100 high-resolution one-minute videos covering diverse real-world and synthetic environments. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LongVie 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance in long-range controllability, temporal coherence, and visual fidelity, and supports continuous video generation lasting up to five minutes, marking a significant step toward unified video world modeling.
Stochastic Forward-Forward Learning through Representational Dimensionality Compression
May 22, 2025Abstract:The Forward-Forward (FF) algorithm provides a bottom-up alternative to backpropagation (BP) for training neural networks, relying on a layer-wise "goodness" function to guide learning. Existing goodness functions, inspired by energy-based learning (EBL), are typically defined as the sum of squared post-synaptic activations, neglecting the correlations between neurons. In this work, we propose a novel goodness function termed dimensionality compression that uses the effective dimensionality (ED) of fluctuating neural responses to incorporate second-order statistical structure. Our objective minimizes ED for clamped inputs when noise is considered while maximizing it across the sample distribution, promoting structured representations without the need to prepare negative samples. We demonstrate that this formulation achieves competitive performance compared to other non-BP methods. Moreover, we show that noise plays a constructive role that can enhance generalization and improve inference when predictions are derived from the mean of squared outputs, which is equivalent to making predictions based on the energy term. Our findings contribute to the development of more biologically plausible learning algorithms and suggest a natural fit for neuromorphic computing, where stochasticity is a computational resource rather than a nuisance. The code is available at https://github.com/ZhichaoZhu/StochasticForwardForward
DecoFuse: Decomposing and Fusing the "What", "Where", and "How" for Brain-Inspired fMRI-to-Video Decoding
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Decoding visual experiences from brain activity is a significant challenge. Existing fMRI-to-video methods often focus on semantic content while overlooking spatial and motion information. However, these aspects are all essential and are processed through distinct pathways in the brain. Motivated by this, we propose DecoFuse, a novel brain-inspired framework for decoding videos from fMRI signals. It first decomposes the video into three components - semantic, spatial, and motion - then decodes each component separately before fusing them to reconstruct the video. This approach not only simplifies the complex task of video decoding by decomposing it into manageable sub-tasks, but also establishes a clearer connection between learned representations and their biological counterpart, as supported by ablation studies. Further, our experiments show significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art methods, achieving 82.4% accuracy for semantic classification, 70.6% accuracy in spatial consistency, a 0.212 cosine similarity for motion prediction, and 21.9% 50-way accuracy for video generation. Additionally, neural encoding analyses for semantic and spatial information align with the two-streams hypothesis, further validating the distinct roles of the ventral and dorsal pathways. Overall, DecoFuse provides a strong and biologically plausible framework for fMRI-to-video decoding. Project page: https://chongjg.github.io/DecoFuse/.
CineBrain: A Large-Scale Multi-Modal Brain Dataset During Naturalistic Audiovisual Narrative Processing
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce CineBrain, the first large-scale dataset featuring simultaneous EEG and fMRI recordings during dynamic audiovisual stimulation. Recognizing the complementary strengths of EEG's high temporal resolution and fMRI's deep-brain spatial coverage, CineBrain provides approximately six hours of narrative-driven content from the popular television series The Big Bang Theory for each of six participants. Building upon this unique dataset, we propose CineSync, an innovative multimodal decoding framework integrates a Multi-Modal Fusion Encoder with a diffusion-based Neural Latent Decoder. Our approach effectively fuses EEG and fMRI signals, significantly improving the reconstruction quality of complex audiovisual stimuli. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we introduce Cine-Benchmark, a comprehensive evaluation protocol that assesses reconstructions across semantic and perceptual dimensions. Experimental results demonstrate that CineSync achieves state-of-the-art video reconstruction performance and highlight our initial success in combining fMRI and EEG for reconstructing both video and audio stimuli. Project Page: https://jianxgao.github.io/CineBrain.
Making Your Dreams A Reality: Decoding the Dreams into a Coherent Video Story from fMRI Signals
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:This paper studies the brave new idea for Multimedia community, and proposes a novel framework to convert dreams into coherent video narratives using fMRI data. Essentially, dreams have intrigued humanity for centuries, offering glimpses into our subconscious minds. Recent advancements in brain imaging, particularly functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), have provided new ways to explore the neural basis of dreaming. By combining subjective dream experiences with objective neurophysiological data, we aim to understand the visual aspects of dreams and create complete video narratives. Our process involves three main steps: reconstructing visual perception, decoding dream imagery, and integrating dream stories. Using innovative techniques in fMRI analysis and language modeling, we seek to push the boundaries of dream research and gain deeper insights into visual experiences during sleep. This technical report introduces a novel approach to visually decoding dreams using fMRI signals and weaving dream visuals into narratives using language models. We gather a dataset of dreams along with descriptions to assess the effectiveness of our framework.
Uncertainty Quantification in Working Memory via Moment Neural Networks
Nov 21, 2024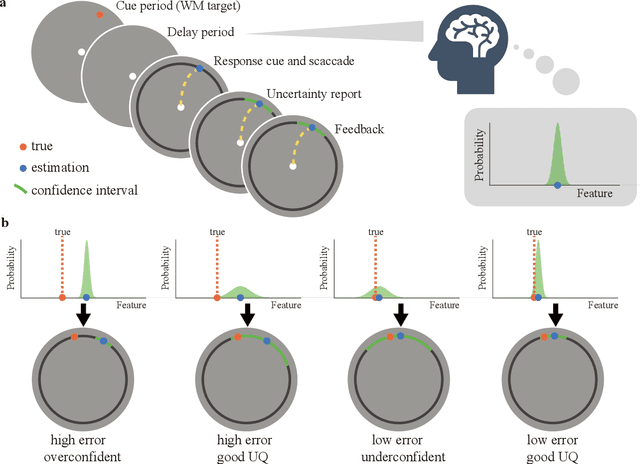
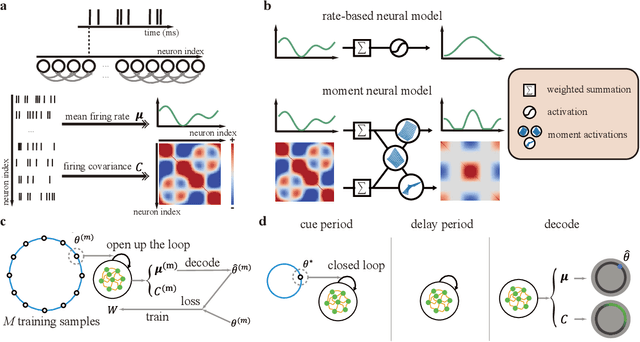
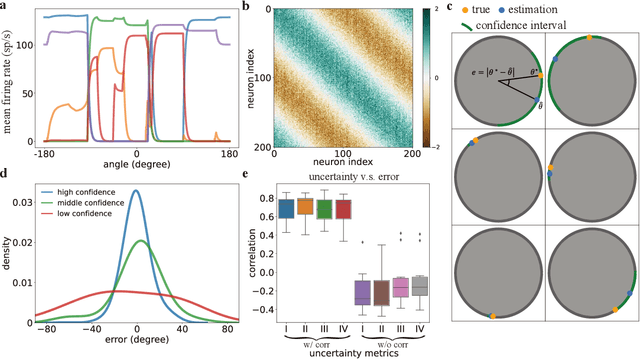
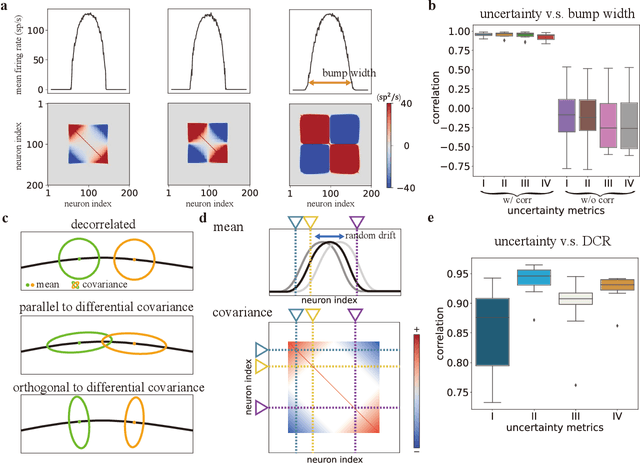
Abstract:Humans possess a finely tuned sense of uncertainty that helps anticipate potential errors, vital for adaptive behavior and survival. However, the underlying neural mechanisms remain unclear. This study applies moment neural networks (MNNs) to explore the neural mechanism of uncertainty quantification in working memory (WM). The MNN captures nonlinear coupling of the first two moments in spiking neural networks (SNNs), identifying firing covariance as a key indicator of uncertainty in encoded information. Trained on a WM task, the model demonstrates coding precision and uncertainty quantification comparable to human performance. Analysis reveals a link between the probabilistic and sampling-based coding for uncertainty representation. Transferring the MNN's weights to an SNN replicates these results. Furthermore, the study provides testable predictions demonstrating how noise and heterogeneity enhance WM performance, highlighting their beneficial role rather than being mere biological byproducts. These findings offer insights into how the brain effectively manages uncertainty with exceptional accuracy.
DG-SLAM: Robust Dynamic Gaussian Splatting SLAM with Hybrid Pose Optimization
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Achieving robust and precise pose estimation in dynamic scenes is a significant research challenge in Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). Recent advancements integrating Gaussian Splatting into SLAM systems have proven effective in creating high-quality renderings using explicit 3D Gaussian models, significantly improving environmental reconstruction fidelity. However, these approaches depend on a static environment assumption and face challenges in dynamic environments due to inconsistent observations of geometry and photometry. To address this problem, we propose DG-SLAM, the first robust dynamic visual SLAM system grounded in 3D Gaussians, which provides precise camera pose estimation alongside high-fidelity reconstructions. Specifically, we propose effective strategies, including motion mask generation, adaptive Gaussian point management, and a hybrid camera tracking algorithm to improve the accuracy and robustness of pose estimation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DG-SLAM delivers state-of-the-art performance in camera pose estimation, map reconstruction, and novel-view synthesis in dynamic scenes, outperforming existing methods meanwhile preserving real-time rendering ability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge