Jingyang Huo
The Pictorial Cortex: Zero-Shot Cross-Subject fMRI-to-Image Reconstruction via Compositional Latent Modeling
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Decoding visual experiences from human brain activity remains a central challenge at the intersection of neuroscience, neuroimaging, and artificial intelligence. A critical obstacle is the inherent variability of cortical responses: neural activity elicited by the same visual stimulus differs across individuals and trials due to anatomical, functional, cognitive, and experimental factors, making fMRI-to-image reconstruction non-injective. In this paper, we tackle a challenging yet practically meaningful problem: zero-shot cross-subject fMRI-to-image reconstruction, where the visual experience of a previously unseen individual must be reconstructed without subject-specific training. To enable principled evaluation, we present a unified cortical-surface dataset -- UniCortex-fMRI, assembled from multiple visual-stimulus fMRI datasets to provide broad coverage of subjects and stimuli. Our UniCortex-fMRI is particularly processed by standardized data formats to make it possible to explore this possibility in the zero-shot scenario of cross-subject fMRI-to-image reconstruction. To tackle the modeling challenge, we propose PictorialCortex, which models fMRI activity using a compositional latent formulation that structures stimulus-driven representations under subject-, dataset-, and trial-related variability. PictorialCortex operates in a universal cortical latent space and implements this formulation through a latent factorization--composition module, reinforced by paired factorization and re-factorizing consistency regularization. During inference, surrogate latents synthesized under multiple seen-subject conditions are aggregated to guide diffusion-based image synthesis for unseen subjects. Extensive experiments show that PictorialCortex improves zero-shot cross-subject visual reconstruction, highlighting the benefits of compositional latent modeling and multi-dataset training.
DecoFuse: Decomposing and Fusing the "What", "Where", and "How" for Brain-Inspired fMRI-to-Video Decoding
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Decoding visual experiences from brain activity is a significant challenge. Existing fMRI-to-video methods often focus on semantic content while overlooking spatial and motion information. However, these aspects are all essential and are processed through distinct pathways in the brain. Motivated by this, we propose DecoFuse, a novel brain-inspired framework for decoding videos from fMRI signals. It first decomposes the video into three components - semantic, spatial, and motion - then decodes each component separately before fusing them to reconstruct the video. This approach not only simplifies the complex task of video decoding by decomposing it into manageable sub-tasks, but also establishes a clearer connection between learned representations and their biological counterpart, as supported by ablation studies. Further, our experiments show significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art methods, achieving 82.4% accuracy for semantic classification, 70.6% accuracy in spatial consistency, a 0.212 cosine similarity for motion prediction, and 21.9% 50-way accuracy for video generation. Additionally, neural encoding analyses for semantic and spatial information align with the two-streams hypothesis, further validating the distinct roles of the ventral and dorsal pathways. Overall, DecoFuse provides a strong and biologically plausible framework for fMRI-to-video decoding. Project page: https://chongjg.github.io/DecoFuse/.
NeuroPictor: Refining fMRI-to-Image Reconstruction via Multi-individual Pretraining and Multi-level Modulation
Mar 27, 2024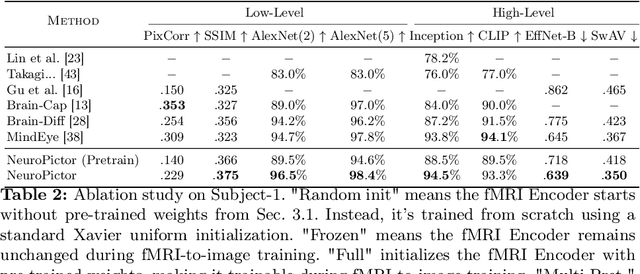

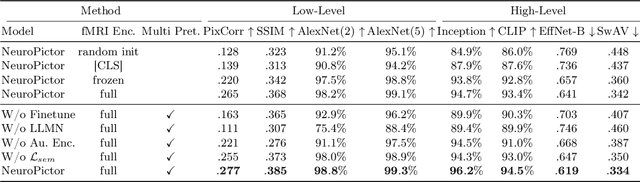
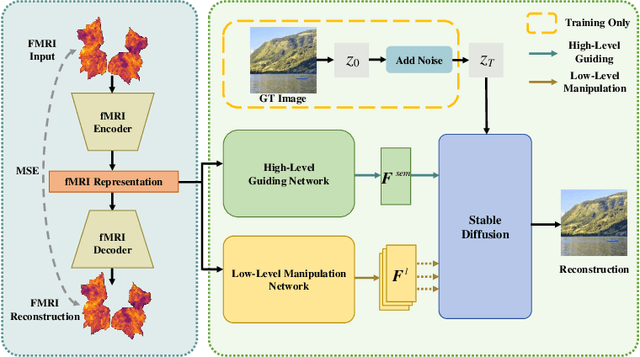
Abstract:Recent fMRI-to-image approaches mainly focused on associating fMRI signals with specific conditions of pre-trained diffusion models. These approaches, while producing high-quality images, capture only a limited aspect of the complex information in fMRI signals and offer little detailed control over image creation. In contrast, this paper proposes to directly modulate the generation process of diffusion models using fMRI signals. Our approach, NeuroPictor, divides the fMRI-to-image process into three steps: i) fMRI calibrated-encoding, to tackle multi-individual pre-training for a shared latent space to minimize individual difference and enable the subsequent cross-subject training; ii) fMRI-to-image cross-subject pre-training, perceptually learning to guide diffusion model with high- and low-level conditions across different individuals; iii) fMRI-to-image single-subject refining, similar with step ii but focus on adapting to particular individual. NeuroPictor extracts high-level semantic features from fMRI signals that characterizing the visual stimulus and incrementally fine-tunes the diffusion model with a low-level manipulation network to provide precise structural instructions. By training with over 60,000 fMRI-image pairs from various individuals, our model enjoys superior fMRI-to-image decoding capacity, particularly in the within-subject setting, as evidenced in benchmark datasets. Project page: https://jingyanghuo.github.io/neuropictor/.
Intelligent Director: An Automatic Framework for Dynamic Visual Composition using ChatGPT
Feb 24, 2024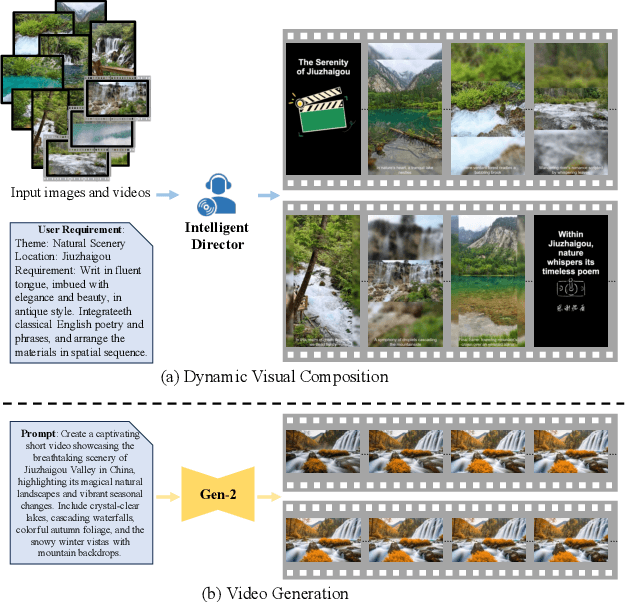
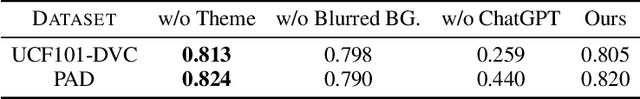
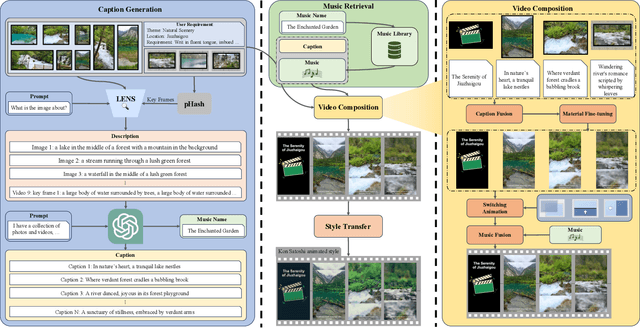
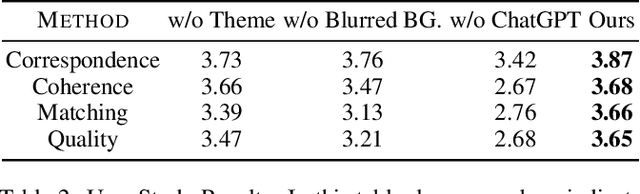
Abstract:With the rise of short video platforms represented by TikTok, the trend of users expressing their creativity through photos and videos has increased dramatically. However, ordinary users lack the professional skills to produce high-quality videos using professional creation software. To meet the demand for intelligent and user-friendly video creation tools, we propose the Dynamic Visual Composition (DVC) task, an interesting and challenging task that aims to automatically integrate various media elements based on user requirements and create storytelling videos. We propose an Intelligent Director framework, utilizing LENS to generate descriptions for images and video frames and combining ChatGPT to generate coherent captions while recommending appropriate music names. Then, the best-matched music is obtained through music retrieval. Then, materials such as captions, images, videos, and music are integrated to seamlessly synthesize the video. Finally, we apply AnimeGANv2 for style transfer. We construct UCF101-DVC and Personal Album datasets and verified the effectiveness of our framework in solving DVC through qualitative and quantitative comparisons, along with user studies, demonstrating its substantial potential.
fMRI-PTE: A Large-scale fMRI Pretrained Transformer Encoder for Multi-Subject Brain Activity Decoding
Nov 01, 2023
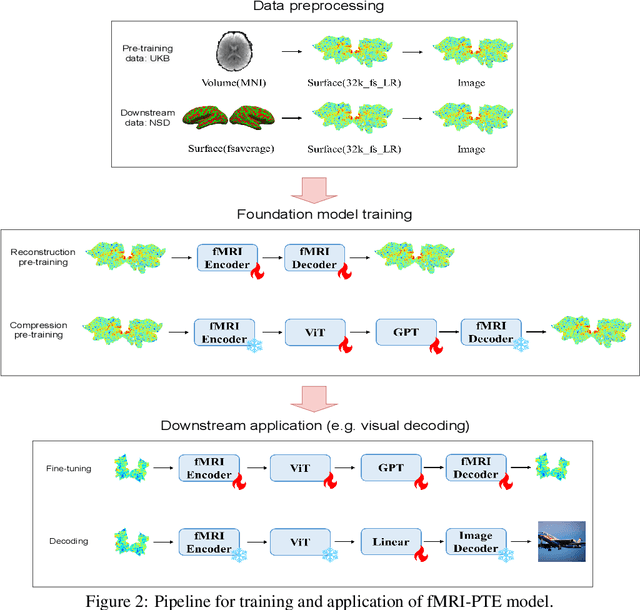
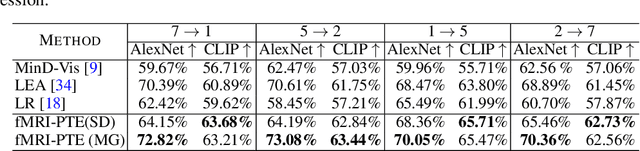
Abstract:The exploration of brain activity and its decoding from fMRI data has been a longstanding pursuit, driven by its potential applications in brain-computer interfaces, medical diagnostics, and virtual reality. Previous approaches have primarily focused on individual subject analysis, highlighting the need for a more universal and adaptable framework, which is the core motivation behind our work. In this work, we propose fMRI-PTE, an innovative auto-encoder approach for fMRI pre-training, with a focus on addressing the challenges of varying fMRI data dimensions due to individual brain differences. Our approach involves transforming fMRI signals into unified 2D representations, ensuring consistency in dimensions and preserving distinct brain activity patterns. We introduce a novel learning strategy tailored for pre-training 2D fMRI images, enhancing the quality of reconstruction. fMRI-PTE's adaptability with image generators enables the generation of well-represented fMRI features, facilitating various downstream tasks, including within-subject and cross-subject brain activity decoding. Our contributions encompass introducing fMRI-PTE, innovative data transformation, efficient training, a novel learning strategy, and the universal applicability of our approach. Extensive experiments validate and support our claims, offering a promising foundation for further research in this domain.
Pushing the Limits of 3D Shape Generation at Scale
Jun 20, 2023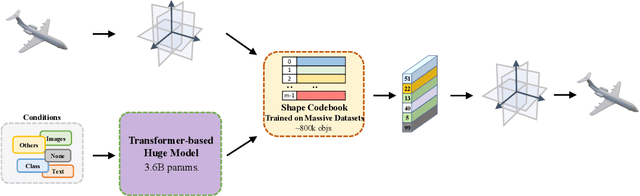
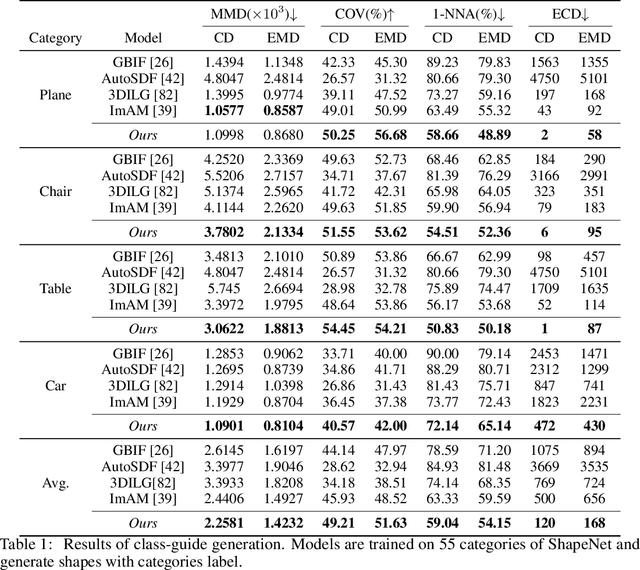
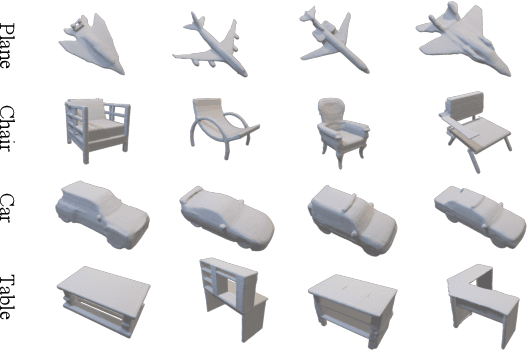

Abstract:We present a significant breakthrough in 3D shape generation by scaling it to unprecedented dimensions. Through the adaptation of the Auto-Regressive model and the utilization of large language models, we have developed a remarkable model with an astounding 3.6 billion trainable parameters, establishing it as the largest 3D shape generation model to date, named Argus-3D. Our approach addresses the limitations of existing methods by enhancing the quality and diversity of generated 3D shapes. To tackle the challenges of high-resolution 3D shape generation, our model incorporates tri-plane features as latent representations, effectively reducing computational complexity. Additionally, we introduce a discrete codebook for efficient quantization of these representations. Leveraging the power of transformers, we enable multi-modal conditional generation, facilitating the production of diverse and visually impressive 3D shapes. To train our expansive model, we leverage an ensemble of publicly-available 3D datasets, consisting of a comprehensive collection of approximately 900,000 objects from renowned repositories such as ModelNet40, ShapeNet, Pix3D, 3D-Future, and Objaverse. This diverse dataset empowers our model to learn from a wide range of object variations, bolstering its ability to generate high-quality and diverse 3D shapes. Extensive experimentation demonstrate the remarkable efficacy of our approach in significantly improving the visual quality of generated 3D shapes. By pushing the boundaries of 3D generation, introducing novel methods for latent representation learning, and harnessing the power of transformers for multi-modal conditional generation, our contributions pave the way for substantial advancements in the field. Our work unlocks new possibilities for applications in gaming, virtual reality, product design, and other domains that demand high-quality and diverse 3D objects.
GeoVLN: Learning Geometry-Enhanced Visual Representation with Slot Attention for Vision-and-Language Navigation
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Most existing works solving Room-to-Room VLN problem only utilize RGB images and do not consider local context around candidate views, which lack sufficient visual cues about surrounding environment. Moreover, natural language contains complex semantic information thus its correlations with visual inputs are hard to model merely with cross attention. In this paper, we propose GeoVLN, which learns Geometry-enhanced visual representation based on slot attention for robust Visual-and-Language Navigation. The RGB images are compensated with the corresponding depth maps and normal maps predicted by Omnidata as visual inputs. Technically, we introduce a two-stage module that combine local slot attention and CLIP model to produce geometry-enhanced representation from such input. We employ V&L BERT to learn a cross-modal representation that incorporate both language and vision informations. Additionally, a novel multiway attention module is designed, encouraging different phrases of input instruction to exploit the most related features from visual input. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our newly designed modules and show the compelling performance of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge