Yosuke Yamagishi
Automated Classification of Normal and Atypical Mitotic Figures Using ConvNeXt V2: MIDOG 2025 Track 2
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:This paper presents our solution for the MIDOG 2025 Challenge Track 2, which focuses on binary classification of normal mitotic figures (NMFs) versus atypical mitotic figures (AMFs) in histopathological images. Our approach leverages a ConvNeXt V2 base model with center cropping preprocessing and 5-fold cross-validation ensemble strategy. The method addresses key challenges including severe class imbalance, high morphological variability, and domain heterogeneity across different tumor types, species, and scanners. Through strategic preprocessing with 60% center cropping and mixed precision training, our model achieved robust performance on the diverse MIDOG 2025 dataset. The solution demonstrates the effectiveness of modern convolutional architectures for mitotic figure subtyping while maintaining computational efficiency through careful architectural choices and training optimizations.
CXR-LT 2024: A MICCAI challenge on long-tailed, multi-label, and zero-shot disease classification from chest X-ray
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:The CXR-LT series is a community-driven initiative designed to enhance lung disease classification using chest X-rays (CXR). It tackles challenges in open long-tailed lung disease classification and enhances the measurability of state-of-the-art techniques. The first event, CXR-LT 2023, aimed to achieve these goals by providing high-quality benchmark CXR data for model development and conducting comprehensive evaluations to identify ongoing issues impacting lung disease classification performance. Building on the success of CXR-LT 2023, the CXR-LT 2024 expands the dataset to 377,110 chest X-rays (CXRs) and 45 disease labels, including 19 new rare disease findings. It also introduces a new focus on zero-shot learning to address limitations identified in the previous event. Specifically, CXR-LT 2024 features three tasks: (i) long-tailed classification on a large, noisy test set, (ii) long-tailed classification on a manually annotated "gold standard" subset, and (iii) zero-shot generalization to five previously unseen disease findings. This paper provides an overview of CXR-LT 2024, detailing the data curation process and consolidating state-of-the-art solutions, including the use of multimodal models for rare disease detection, advanced generative approaches to handle noisy labels, and zero-shot learning strategies for unseen diseases. Additionally, the expanded dataset enhances disease coverage to better represent real-world clinical settings, offering a valuable resource for future research. By synthesizing the insights and innovations of participating teams, we aim to advance the development of clinically realistic and generalizable diagnostic models for chest radiography.
ModernBERT is More Efficient than Conventional BERT for Chest CT Findings Classification in Japanese Radiology Reports
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Objective: This study aims to evaluate and compare the performance of two Japanese language models-conventional Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) and the newer ModernBERT-in classifying findings from chest CT reports, with a focus on tokenization efficiency, processing time, and classification performance. Methods: We conducted a retrospective study using the CT-RATE-JPN dataset containing 22,778 training reports and 150 test reports. Both models were fine-tuned for multi-label classification of 18 common chest CT conditions. The training data was split in 18,222:4,556 for training and validation. Performance was evaluated using F1 scores for each condition and exact match accuracy across all 18 labels. Results: ModernBERT demonstrated superior tokenization efficiency, requiring 24.0% fewer tokens per document (258.1 vs. 339.6) compared to BERT Base. This translated to significant performance improvements, with ModernBERT completing training in 1877.67 seconds versus BERT's 3090.54 seconds (39% reduction). ModernBERT processed 38.82 samples per second during training (1.65x faster) and 139.90 samples per second during inference (1.66x faster). Despite these efficiency gains, classification performance remained comparable, with ModernBERT achieving superior F1 scores in 8 conditions, while BERT performed better in 4 conditions. Overall exact match accuracy was slightly higher for ModernBERT (74.67% vs. 72.67%), though this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.6291). Conclusion: ModernBERT offers substantial improvements in tokenization efficiency and training speed without sacrificing classification performance. These results suggest that ModernBERT is a promising candidate for clinical applications in Japanese radiology reports analysis.
KVC-onGoing: Keystroke Verification Challenge
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:This article presents the Keystroke Verification Challenge - onGoing (KVC-onGoing), on which researchers can easily benchmark their systems in a common platform using large-scale public databases, the Aalto University Keystroke databases, and a standard experimental protocol. The keystroke data consist of tweet-long sequences of variable transcript text from over 185,000 subjects, acquired through desktop and mobile keyboards simulating real-life conditions. The results on the evaluation set of KVC-onGoing have proved the high discriminative power of keystroke dynamics, reaching values as low as 3.33% of Equal Error Rate (EER) and 11.96% of False Non-Match Rate (FNMR) @1% False Match Rate (FMR) in the desktop scenario, and 3.61% of EER and 17.44% of FNMR @1% at FMR in the mobile scenario, significantly improving previous state-of-the-art results. Concerning demographic fairness, the analyzed scores reflect the subjects' age and gender to various extents, not negligible in a few cases. The framework runs on CodaLab.
Development of a Large-scale Dataset of Chest Computed Tomography Reports in Japanese and a High-performance Finding Classification Model
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Background: Recent advances in large language models highlight the need for high-quality multilingual medical datasets. While Japan leads globally in CT scanner deployment and utilization, the lack of large-scale Japanese radiology datasets has hindered the development of specialized language models for medical imaging analysis. Objective: To develop a comprehensive Japanese CT report dataset through machine translation and establish a specialized language model for structured finding classification. Additionally, to create a rigorously validated evaluation dataset through expert radiologist review. Methods: We translated the CT-RATE dataset (24,283 CT reports from 21,304 patients) into Japanese using GPT-4o mini. The training dataset consisted of 22,778 machine-translated reports, while the validation dataset included 150 radiologist-revised reports. We developed CT-BERT-JPN based on "tohoku-nlp/bert-base-japanese-v3" architecture for extracting 18 structured findings from Japanese radiology reports. Results: Translation metrics showed strong performance with BLEU scores of 0.731 and 0.690, and ROUGE scores ranging from 0.770 to 0.876 for Findings and from 0.748 to 0.857 for Impression sections. CT-BERT-JPN demonstrated superior performance compared to GPT-4o in 11 out of 18 conditions, including lymphadenopathy (+14.2%), interlobular septal thickening (+10.9%), and atelectasis (+7.4%). The model maintained F1 scores exceeding 0.95 in 14 out of 18 conditions and achieved perfect scores in four conditions. Conclusions: Our study establishes a robust Japanese CT report dataset and demonstrates the effectiveness of a specialized language model for structured finding classification. The hybrid approach of machine translation and expert validation enables the creation of large-scale medical datasets while maintaining high quality.
Ensemble of ConvNeXt V2 and MaxViT for Long-Tailed CXR Classification with View-Based Aggregation
Oct 15, 2024

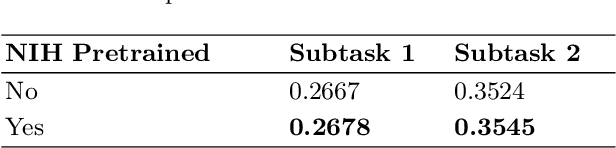
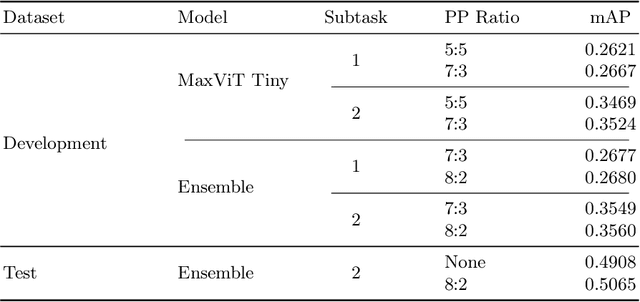
Abstract:In this work, we present our solution for the MICCAI 2024 CXR-LT challenge, achieving 4th place in Subtask 2 and 5th in Subtask 1. We leveraged an ensemble of ConvNeXt V2 and MaxViT models, pretrained on an external chest X-ray dataset, to address the long-tailed distribution of chest findings. The proposed method combines state-of-the-art image classification techniques, asymmetric loss for handling class imbalance, and view-based prediction aggregation to enhance classification performance. Through experiments, we demonstrate the advantages of our approach in improving both detection accuracy and the handling of the long-tailed distribution in CXR findings. The code is available at https://github.com/yamagishi0824/cxrlt24-multiview-pp.
Zero-shot 3D Segmentation of Abdominal Organs in CT Scans Using Segment Anything Model 2: Adapting Video Tracking Capabilities for 3D Medical Imaging
Aug 12, 2024

Abstract:Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the zero-shot performance of Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2) in 3D segmentation of abdominal organs in CT scans, leveraging its video tracking capabilities for volumetric medical imaging. Materials and Methods: Using a subset of the TotalSegmentator CT dataset (n=123) from 8 different institutions, we assessed SAM 2's ability to segment 8 abdominal organs. Segmentation was initiated from three different Z-coordinate levels (caudal, mid, and cranial levels) of each organ. Performance was measured using the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC). We also analyzed organ volumes to contextualize the results. Results: As a zero-shot approach, larger organs with clear boundaries demonstrated high segmentation performance, with mean(median) DSCs as follows: liver 0.821(0.898), left kidney 0.870(0.921), right kidney 0.862(0.935), and spleen 0.891(0.932). Smaller or less defined structures showed lower performance: gallbladder 0.531(0.590), pancreas 0.361(0.359), and adrenal glands 0.203-0.308(0.109-0.231). Significant differences in DSC were observed depending on the starting initial slice of segmentation for different organs. A moderate positive correlation was observed between volume size and DSCs (Spearman's rs = 0.731, P <.001 at caudal-level). DSCs exhibited high variability within organs, ranging from near 0 to almost 1.0, indicating substantial inconsistency in segmentation performance between scans. Conclusion: SAM 2 demonstrated promising zero-shot performance in segmenting certain abdominal organs in CT scans, particularly larger organs with clear boundaries. The model's ability to segment previously unseen targets without additional training highlights its potential for cross-domain generalization in medical imaging. However, improvements are needed for smaller and less defined structures.
IEEE BigData 2023 Keystroke Verification Challenge (KVC)
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:This paper describes the results of the IEEE BigData 2023 Keystroke Verification Challenge (KVC), that considers the biometric verification performance of Keystroke Dynamics (KD), captured as tweet-long sequences of variable transcript text from over 185,000 subjects. The data are obtained from two of the largest public databases of KD up to date, the Aalto Desktop and Mobile Keystroke Databases, guaranteeing a minimum amount of data per subject, age and gender annotations, absence of corrupted data, and avoiding excessively unbalanced subject distributions with respect to the considered demographic attributes. Several neural architectures were proposed by the participants, leading to global Equal Error Rates (EERs) as low as 3.33% and 3.61% achieved by the best team respectively in the desktop and mobile scenario, outperforming the current state of the art biometric verification performance for KD. Hosted on CodaLab, the KVC will be made ongoing to represent a useful tool for the research community to compare different approaches under the same experimental conditions and to deepen the knowledge of the field.
Towards long-tailed, multi-label disease classification from chest X-ray: Overview of the CXR-LT challenge
Oct 24, 2023



Abstract:Many real-world image recognition problems, such as diagnostic medical imaging exams, are "long-tailed" $\unicode{x2013}$ there are a few common findings followed by many more relatively rare conditions. In chest radiography, diagnosis is both a long-tailed and multi-label problem, as patients often present with multiple findings simultaneously. While researchers have begun to study the problem of long-tailed learning in medical image recognition, few have studied the interaction of label imbalance and label co-occurrence posed by long-tailed, multi-label disease classification. To engage with the research community on this emerging topic, we conducted an open challenge, CXR-LT, on long-tailed, multi-label thorax disease classification from chest X-rays (CXRs). We publicly release a large-scale benchmark dataset of over 350,000 CXRs, each labeled with at least one of 26 clinical findings following a long-tailed distribution. We synthesize common themes of top-performing solutions, providing practical recommendations for long-tailed, multi-label medical image classification. Finally, we use these insights to propose a path forward involving vision-language foundation models for few- and zero-shot disease classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge