Osamu Abe
The University of Tokyo, The Department of Radiology, The University of Tokyo Hospital
ModernBERT is More Efficient than Conventional BERT for Chest CT Findings Classification in Japanese Radiology Reports
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Objective: This study aims to evaluate and compare the performance of two Japanese language models-conventional Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) and the newer ModernBERT-in classifying findings from chest CT reports, with a focus on tokenization efficiency, processing time, and classification performance. Methods: We conducted a retrospective study using the CT-RATE-JPN dataset containing 22,778 training reports and 150 test reports. Both models were fine-tuned for multi-label classification of 18 common chest CT conditions. The training data was split in 18,222:4,556 for training and validation. Performance was evaluated using F1 scores for each condition and exact match accuracy across all 18 labels. Results: ModernBERT demonstrated superior tokenization efficiency, requiring 24.0% fewer tokens per document (258.1 vs. 339.6) compared to BERT Base. This translated to significant performance improvements, with ModernBERT completing training in 1877.67 seconds versus BERT's 3090.54 seconds (39% reduction). ModernBERT processed 38.82 samples per second during training (1.65x faster) and 139.90 samples per second during inference (1.66x faster). Despite these efficiency gains, classification performance remained comparable, with ModernBERT achieving superior F1 scores in 8 conditions, while BERT performed better in 4 conditions. Overall exact match accuracy was slightly higher for ModernBERT (74.67% vs. 72.67%), though this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.6291). Conclusion: ModernBERT offers substantial improvements in tokenization efficiency and training speed without sacrificing classification performance. These results suggest that ModernBERT is a promising candidate for clinical applications in Japanese radiology reports analysis.
Development of a Large-scale Dataset of Chest Computed Tomography Reports in Japanese and a High-performance Finding Classification Model
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Background: Recent advances in large language models highlight the need for high-quality multilingual medical datasets. While Japan leads globally in CT scanner deployment and utilization, the lack of large-scale Japanese radiology datasets has hindered the development of specialized language models for medical imaging analysis. Objective: To develop a comprehensive Japanese CT report dataset through machine translation and establish a specialized language model for structured finding classification. Additionally, to create a rigorously validated evaluation dataset through expert radiologist review. Methods: We translated the CT-RATE dataset (24,283 CT reports from 21,304 patients) into Japanese using GPT-4o mini. The training dataset consisted of 22,778 machine-translated reports, while the validation dataset included 150 radiologist-revised reports. We developed CT-BERT-JPN based on "tohoku-nlp/bert-base-japanese-v3" architecture for extracting 18 structured findings from Japanese radiology reports. Results: Translation metrics showed strong performance with BLEU scores of 0.731 and 0.690, and ROUGE scores ranging from 0.770 to 0.876 for Findings and from 0.748 to 0.857 for Impression sections. CT-BERT-JPN demonstrated superior performance compared to GPT-4o in 11 out of 18 conditions, including lymphadenopathy (+14.2%), interlobular septal thickening (+10.9%), and atelectasis (+7.4%). The model maintained F1 scores exceeding 0.95 in 14 out of 18 conditions and achieved perfect scores in four conditions. Conclusions: Our study establishes a robust Japanese CT report dataset and demonstrates the effectiveness of a specialized language model for structured finding classification. The hybrid approach of machine translation and expert validation enables the creation of large-scale medical datasets while maintaining high quality.
Zero-shot 3D Segmentation of Abdominal Organs in CT Scans Using Segment Anything Model 2: Adapting Video Tracking Capabilities for 3D Medical Imaging
Aug 12, 2024

Abstract:Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the zero-shot performance of Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2) in 3D segmentation of abdominal organs in CT scans, leveraging its video tracking capabilities for volumetric medical imaging. Materials and Methods: Using a subset of the TotalSegmentator CT dataset (n=123) from 8 different institutions, we assessed SAM 2's ability to segment 8 abdominal organs. Segmentation was initiated from three different Z-coordinate levels (caudal, mid, and cranial levels) of each organ. Performance was measured using the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC). We also analyzed organ volumes to contextualize the results. Results: As a zero-shot approach, larger organs with clear boundaries demonstrated high segmentation performance, with mean(median) DSCs as follows: liver 0.821(0.898), left kidney 0.870(0.921), right kidney 0.862(0.935), and spleen 0.891(0.932). Smaller or less defined structures showed lower performance: gallbladder 0.531(0.590), pancreas 0.361(0.359), and adrenal glands 0.203-0.308(0.109-0.231). Significant differences in DSC were observed depending on the starting initial slice of segmentation for different organs. A moderate positive correlation was observed between volume size and DSCs (Spearman's rs = 0.731, P <.001 at caudal-level). DSCs exhibited high variability within organs, ranging from near 0 to almost 1.0, indicating substantial inconsistency in segmentation performance between scans. Conclusion: SAM 2 demonstrated promising zero-shot performance in segmenting certain abdominal organs in CT scans, particularly larger organs with clear boundaries. The model's ability to segment previously unseen targets without additional training highlights its potential for cross-domain generalization in medical imaging. However, improvements are needed for smaller and less defined structures.
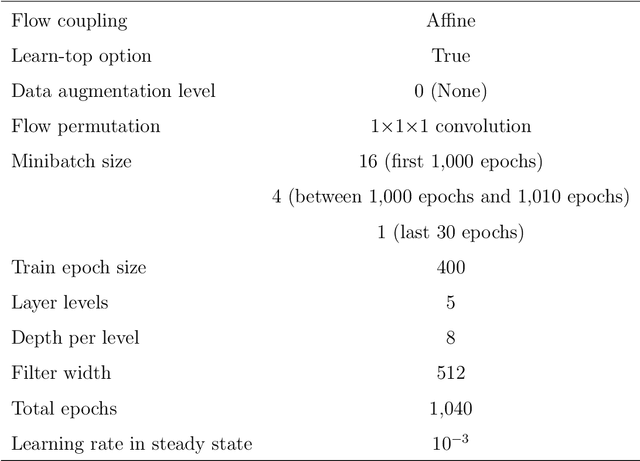
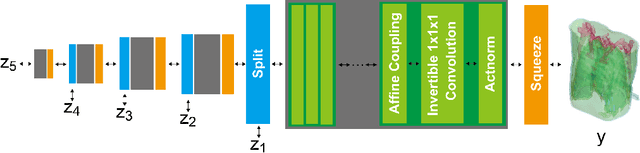
Local Differential Privacy Image Generation Using Flow-based Deep Generative Models
Dec 20, 2022



Abstract:Diagnostic radiologists need artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging, but access to medical images required for training in AI has become increasingly restrictive. To release and use medical images, we need an algorithm that can simultaneously protect privacy and preserve pathologies in medical images. To develop such an algorithm, here, we propose DP-GLOW, a hybrid of a local differential privacy (LDP) algorithm and one of the flow-based deep generative models (GLOW). By applying a GLOW model, we disentangle the pixelwise correlation of images, which makes it difficult to protect privacy with straightforward LDP algorithms for images. Specifically, we map images onto the latent vector of the GLOW model, each element of which follows an independent normal distribution, and we apply the Laplace mechanism to the latent vector. Moreover, we applied DP-GLOW to chest X-ray images to generate LDP images while preserving pathologies.
Aging prediction using deep generative model toward the development of preventive medicine
Aug 23, 2022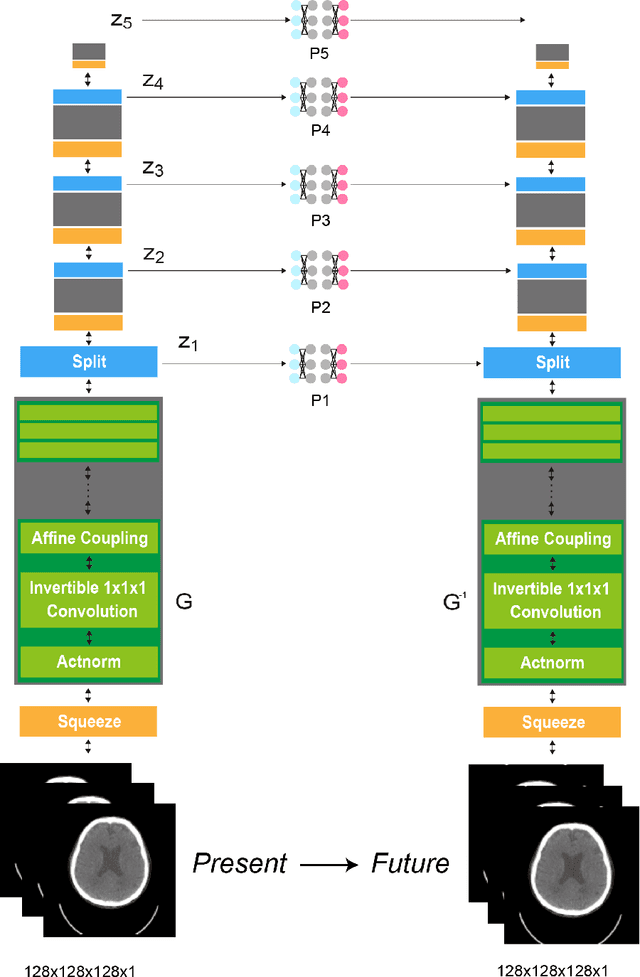

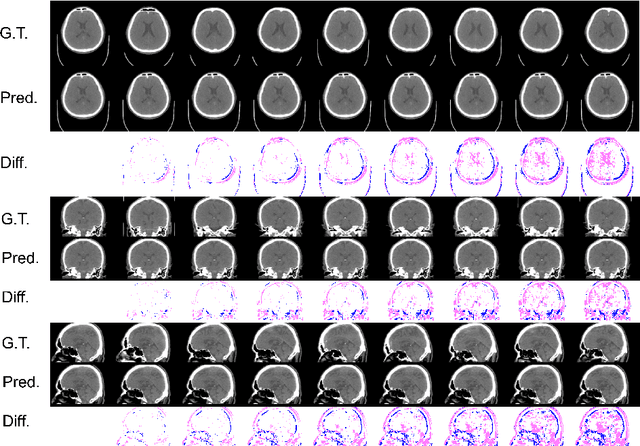
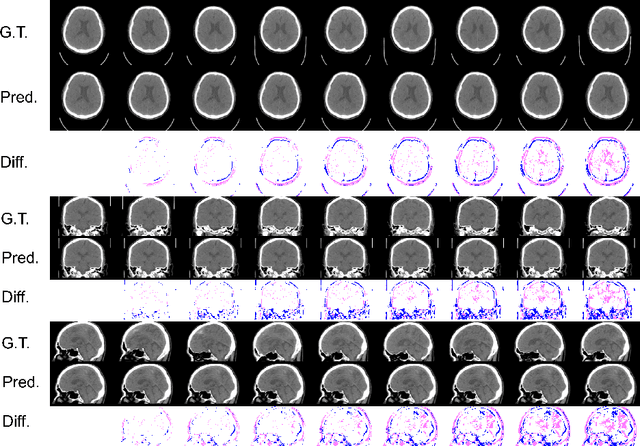
Abstract:From birth to death, we all experience surprisingly ubiquitous changes over time due to aging. If we can predict aging in the digital domain, that is, the digital twin of the human body, we would be able to detect lesions in their very early stages, thereby enhancing the quality of life and extending the life span. We observed that none of the previously developed digital twins of the adult human body explicitly trained longitudinal conversion rules between volumetric medical images with deep generative models, potentially resulting in poor prediction performance of, for example, ventricular volumes. Here, we establish a new digital twin of an adult human body that adopts longitudinally acquired head computed tomography (CT) images for training, enabling prediction of future volumetric head CT images from a single present volumetric head CT image. We, for the first time, adopt one of the three-dimensional flow-based deep generative models to realize this sequential three-dimensional digital twin. We show that our digital twin outperforms the latest methods of prediction of ventricular volumes in relatively short terms.
X2CT-FLOW: Reconstruction of multiple volumetric chest computed tomography images with different likelihoods from a uni- or biplanar chest X-ray image using a flow-based generative model
Apr 09, 2021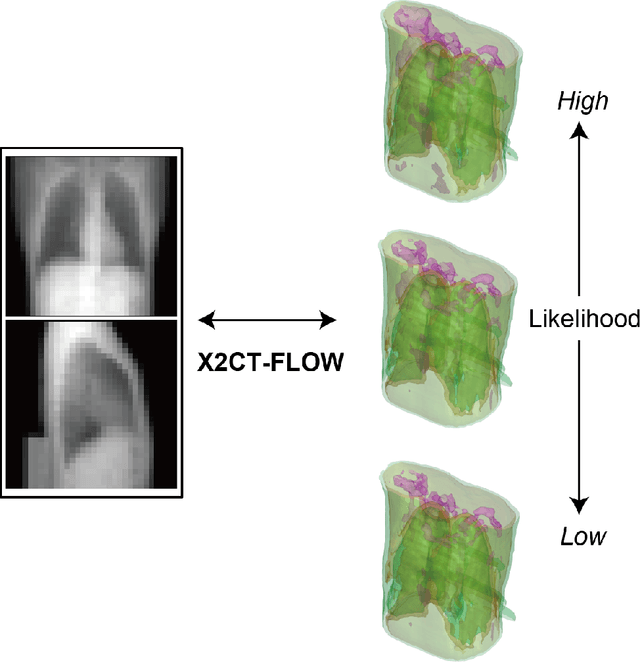
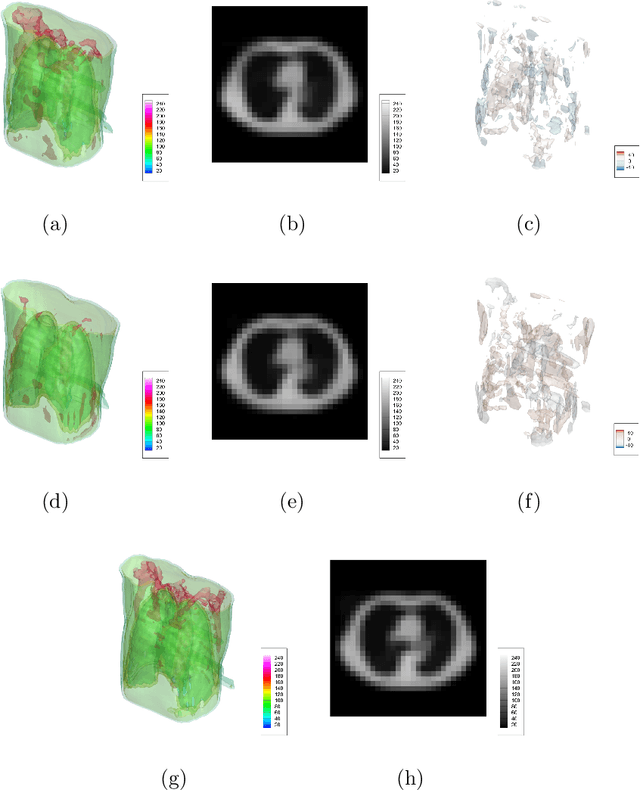
Abstract:We propose X2CT-FLOW for the reconstruction of volumetric chest computed tomography (CT) images from uni- or biplanar digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) or chest X-ray (CXR) images on the basis of a flow-based deep generative (FDG) model. With the adoption of X2CT-FLOW, all the reconstructed volumetric chest CT images satisfy the condition that each of those projected onto each plane coincides with each input DRR or CXR image. Moreover, X2CT-FLOW can reconstruct multiple volumetric chest CT images with different likelihoods. The volumetric chest CT images reconstructed from biplanar DRRs showed good agreement with ground truth images in terms of the structural similarity index (0.931 on average). Moreover, we show that X2CT-FLOW can actually reconstruct such multiple volumetric chest CT images from DRRs. Finally, we demonstrate that X2CT-FLOW can reconstruct multiple volumetric chest CT images from a real uniplanar CXR image.
KART: Privacy Leakage Framework of Language Models Pre-trained with Clinical Records
Dec 31, 2020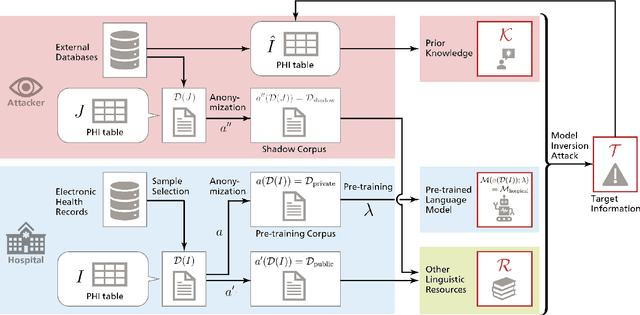
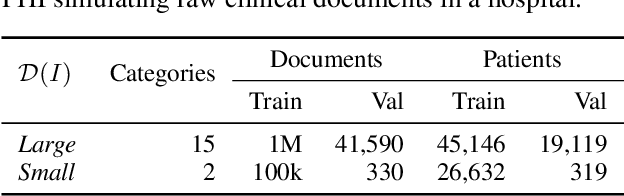
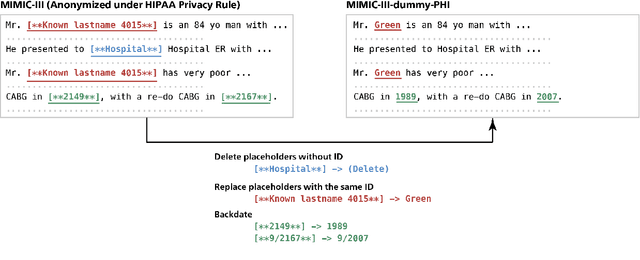
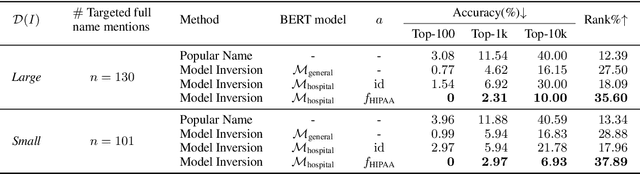
Abstract:Nowadays, mainstream natural language pro-cessing (NLP) is empowered by pre-trained language models. In the biomedical domain, only models pre-trained with anonymized data have been published. This policy is acceptable, but there are two questions: Can the privacy policy of language models be different from that of data? What happens if private language models are accidentally made public? We empirically evaluated the privacy risk of language models, using several BERT models pre-trained with MIMIC-III corpus in different data anonymity and corpus sizes. We simulated model inversion attacks to obtain the clinical information of target individuals, whose full names are already known to attackers. The BERT models were probably low-risk because the Top-100 accuracy of each attack was far below expected by chance. Moreover, most privacy leakage situations have several common primary factors; therefore, we formalized various privacy leakage scenarios under a universal novel framework named Knowledge, Anonymization, Resource, and Target (KART) framework. The KART framework helps parameterize complex privacy leakage scenarios and simplifies the comprehensive evaluation. Since the concept of the KART framework is domain agnostic, it can contribute to the establishment of privacy guidelines of language models beyond the biomedical domain.
On the Matrix-Free Generation of Adversarial Perturbations for Black-Box Attacks
Feb 18, 2020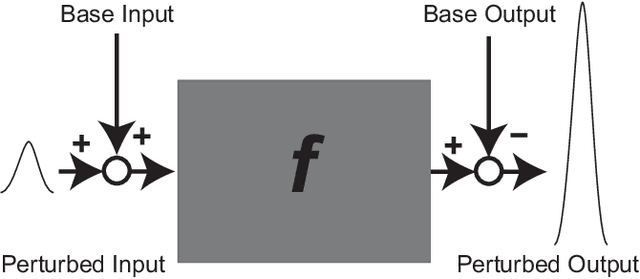

Abstract:In general, adversarial perturbations superimposed on inputs are realistic threats for a deep neural network (DNN). In this paper, we propose a practical generation method of such adversarial perturbation to be applied to black-box attacks that demand access to an input-output relationship only. Thus, the attackers generate such perturbation without invoking inner functions and/or accessing the inner states of a DNN. Unlike the earlier studies, the algorithm to generate the perturbation presented in this study requires much fewer query trials. Moreover, to show the effectiveness of the adversarial perturbation extracted, we experiment with a DNN for semantic segmentation. The result shows that the network is easily deceived with the perturbation generated than using uniformly distributed random noise with the same magnitude.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge