Yuta Nakamura
The University of Tokyo, Nara Institute of Science and Technology
Stealthy Coverage Control for Human-enabled Real-Time 3D Reconstruction
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel semi-autonomous image sampling strategy, called stealthy coverage control, for human-enabled 3D structure reconstruction. The present mission involves a fundamental problem: while the number of images required to accurately reconstruct a 3D model depends on the structural complexity of the target scene to be reconstructed, it is not realistic to assume prior knowledge of the spatially non-uniform structural complexity. We approach this issue by leveraging human flexible reasoning and situational recognition capabilities. Specifically, we design a semi-autonomous system that leaves identification of regions that need more images and navigation of the drones to such regions to a human operator. To this end, we first present a way to reflect the human intention in autonomous coverage control. Subsequently, in order to avoid operational conflicts between manual control and autonomous coverage control, we develop the stealthy coverage control that decouples the drone motion for efficient image sampling from navigation by the human. Simulation studies on a Unity/ROS2-based simulator demonstrate that the present semi-autonomous system outperforms the one without human interventions in the sense of the reconstructed model quality.
Development of a Large-scale Dataset of Chest Computed Tomography Reports in Japanese and a High-performance Finding Classification Model
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Background: Recent advances in large language models highlight the need for high-quality multilingual medical datasets. While Japan leads globally in CT scanner deployment and utilization, the lack of large-scale Japanese radiology datasets has hindered the development of specialized language models for medical imaging analysis. Objective: To develop a comprehensive Japanese CT report dataset through machine translation and establish a specialized language model for structured finding classification. Additionally, to create a rigorously validated evaluation dataset through expert radiologist review. Methods: We translated the CT-RATE dataset (24,283 CT reports from 21,304 patients) into Japanese using GPT-4o mini. The training dataset consisted of 22,778 machine-translated reports, while the validation dataset included 150 radiologist-revised reports. We developed CT-BERT-JPN based on "tohoku-nlp/bert-base-japanese-v3" architecture for extracting 18 structured findings from Japanese radiology reports. Results: Translation metrics showed strong performance with BLEU scores of 0.731 and 0.690, and ROUGE scores ranging from 0.770 to 0.876 for Findings and from 0.748 to 0.857 for Impression sections. CT-BERT-JPN demonstrated superior performance compared to GPT-4o in 11 out of 18 conditions, including lymphadenopathy (+14.2%), interlobular septal thickening (+10.9%), and atelectasis (+7.4%). The model maintained F1 scores exceeding 0.95 in 14 out of 18 conditions and achieved perfect scores in four conditions. Conclusions: Our study establishes a robust Japanese CT report dataset and demonstrates the effectiveness of a specialized language model for structured finding classification. The hybrid approach of machine translation and expert validation enables the creation of large-scale medical datasets while maintaining high quality.
Zero-shot 3D Segmentation of Abdominal Organs in CT Scans Using Segment Anything Model 2: Adapting Video Tracking Capabilities for 3D Medical Imaging
Aug 12, 2024

Abstract:Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the zero-shot performance of Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2) in 3D segmentation of abdominal organs in CT scans, leveraging its video tracking capabilities for volumetric medical imaging. Materials and Methods: Using a subset of the TotalSegmentator CT dataset (n=123) from 8 different institutions, we assessed SAM 2's ability to segment 8 abdominal organs. Segmentation was initiated from three different Z-coordinate levels (caudal, mid, and cranial levels) of each organ. Performance was measured using the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC). We also analyzed organ volumes to contextualize the results. Results: As a zero-shot approach, larger organs with clear boundaries demonstrated high segmentation performance, with mean(median) DSCs as follows: liver 0.821(0.898), left kidney 0.870(0.921), right kidney 0.862(0.935), and spleen 0.891(0.932). Smaller or less defined structures showed lower performance: gallbladder 0.531(0.590), pancreas 0.361(0.359), and adrenal glands 0.203-0.308(0.109-0.231). Significant differences in DSC were observed depending on the starting initial slice of segmentation for different organs. A moderate positive correlation was observed between volume size and DSCs (Spearman's rs = 0.731, P <.001 at caudal-level). DSCs exhibited high variability within organs, ranging from near 0 to almost 1.0, indicating substantial inconsistency in segmentation performance between scans. Conclusion: SAM 2 demonstrated promising zero-shot performance in segmenting certain abdominal organs in CT scans, particularly larger organs with clear boundaries. The model's ability to segment previously unseen targets without additional training highlights its potential for cross-domain generalization in medical imaging. However, improvements are needed for smaller and less defined structures.
Playing the Werewolf game with artificial intelligence for language understanding
Feb 21, 2023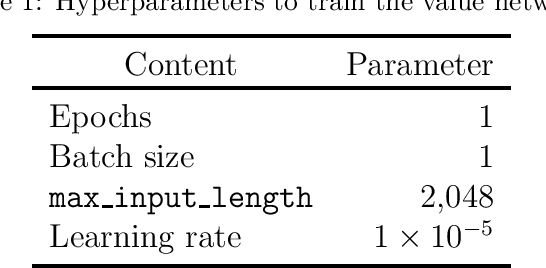
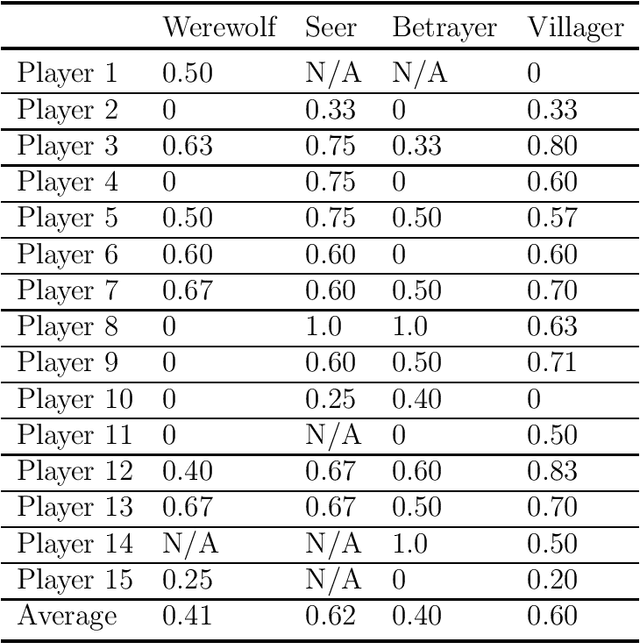
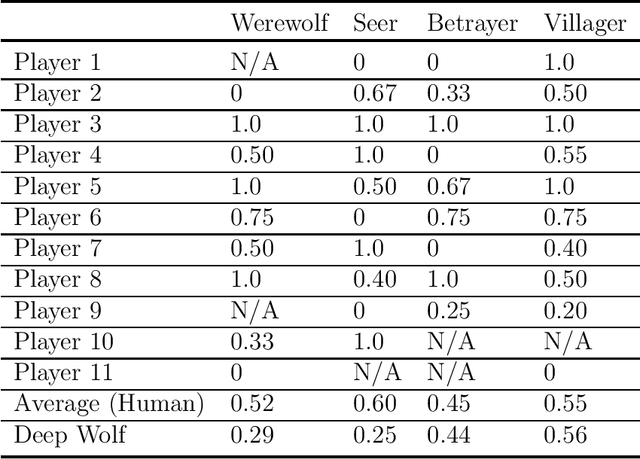
Abstract:The Werewolf game is a social deduction game based on free natural language communication, in which players try to deceive others in order to survive. An important feature of this game is that a large portion of the conversations are false information, and the behavior of artificial intelligence (AI) in such a situation has not been widely investigated. The purpose of this study is to develop an AI agent that can play Werewolf through natural language conversations. First, we collected game logs from 15 human players. Next, we fine-tuned a Transformer-based pretrained language model to construct a value network that can predict a posterior probability of winning a game at any given phase of the game and given a candidate for the next action. We then developed an AI agent that can interact with humans and choose the best voting target on the basis of its probability from the value network. Lastly, we evaluated the performance of the agent by having it actually play the game with human players. We found that our AI agent, Deep Wolf, could play Werewolf as competitively as average human players in a villager or a betrayer role, whereas Deep Wolf was inferior to human players in a werewolf or a seer role. These results suggest that current language models have the capability to suspect what others are saying, tell a lie, or detect lies in conversations.
KART: Privacy Leakage Framework of Language Models Pre-trained with Clinical Records
Dec 31, 2020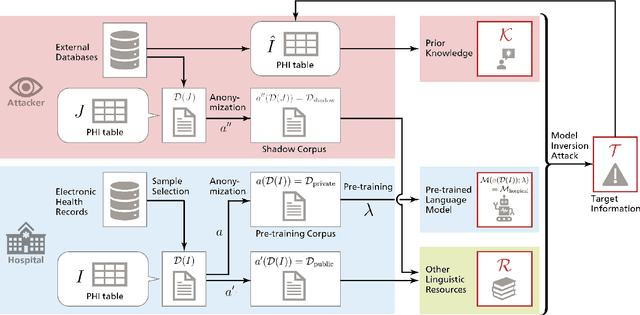
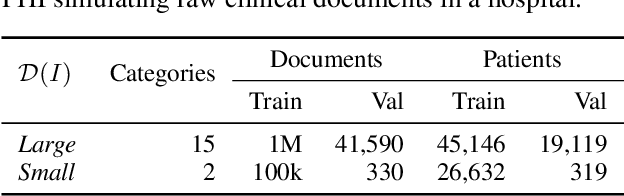
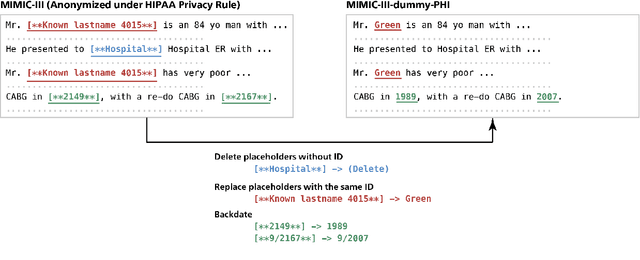
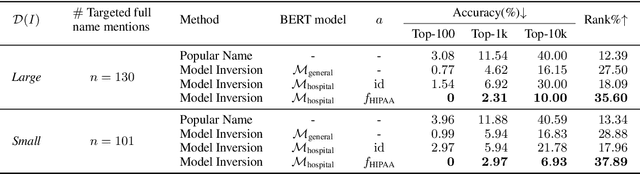
Abstract:Nowadays, mainstream natural language pro-cessing (NLP) is empowered by pre-trained language models. In the biomedical domain, only models pre-trained with anonymized data have been published. This policy is acceptable, but there are two questions: Can the privacy policy of language models be different from that of data? What happens if private language models are accidentally made public? We empirically evaluated the privacy risk of language models, using several BERT models pre-trained with MIMIC-III corpus in different data anonymity and corpus sizes. We simulated model inversion attacks to obtain the clinical information of target individuals, whose full names are already known to attackers. The BERT models were probably low-risk because the Top-100 accuracy of each attack was far below expected by chance. Moreover, most privacy leakage situations have several common primary factors; therefore, we formalized various privacy leakage scenarios under a universal novel framework named Knowledge, Anonymization, Resource, and Target (KART) framework. The KART framework helps parameterize complex privacy leakage scenarios and simplifies the comprehensive evaluation. Since the concept of the KART framework is domain agnostic, it can contribute to the establishment of privacy guidelines of language models beyond the biomedical domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge