Shuntaro Yada
Nara Institute of Science and Technology
LLM-jp: A Cross-organizational Project for the Research and Development of Fully Open Japanese LLMs
Jul 04, 2024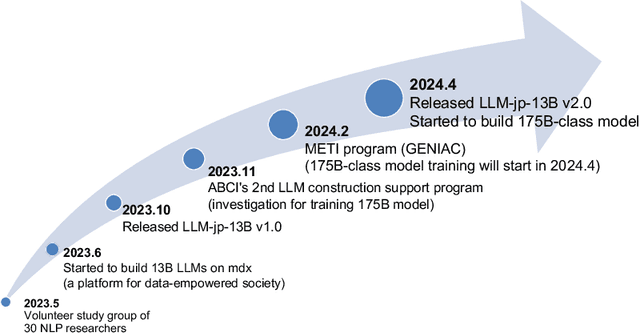
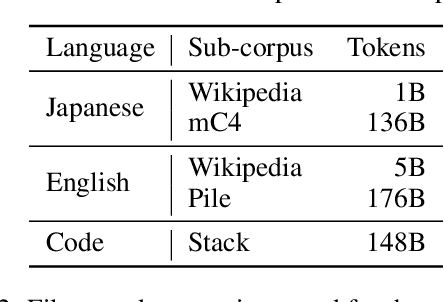

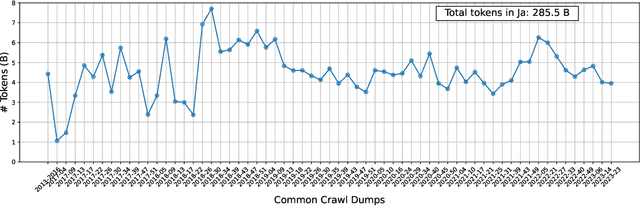
Abstract:This paper introduces LLM-jp, a cross-organizational project for the research and development of Japanese large language models (LLMs). LLM-jp aims to develop open-source and strong Japanese LLMs, and as of this writing, more than 1,500 participants from academia and industry are working together for this purpose. This paper presents the background of the establishment of LLM-jp, summaries of its activities, and technical reports on the LLMs developed by LLM-jp. For the latest activities, visit https://llm-jp.nii.ac.jp/en/.
A Dataset for Pharmacovigilance in German, French, and Japanese: Annotating Adverse Drug Reactions across Languages
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:User-generated data sources have gained significance in uncovering Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs), with an increasing number of discussions occurring in the digital world. However, the existing clinical corpora predominantly revolve around scientific articles in English. This work presents a multilingual corpus of texts concerning ADRs gathered from diverse sources, including patient fora, social media, and clinical reports in German, French, and Japanese. Our corpus contains annotations covering 12 entity types, four attribute types, and 13 relation types. It contributes to the development of real-world multilingual language models for healthcare. We provide statistics to highlight certain challenges associated with the corpus and conduct preliminary experiments resulting in strong baselines for extracting entities and relations between these entities, both within and across languages.
JaMIE: A Pipeline Japanese Medical Information Extraction System
Nov 08, 2021



Abstract:We present an open-access natural language processing toolkit for Japanese medical information extraction. We first propose a novel relation annotation schema for investigating the medical and temporal relations between medical entities in Japanese medical reports. We experiment with the practical annotation scenarios by separately annotating two different types of reports. We design a pipeline system with three components for recognizing medical entities, classifying entity modalities, and extracting relations. The empirical results show accurate analyzing performance and suggest the satisfactory annotation quality, the effective annotation strategy for targeting report types, and the superiority of the latest contextual embedding models.
End-to-end Biomedical Entity Linking with Span-based Dictionary Matching
Apr 21, 2021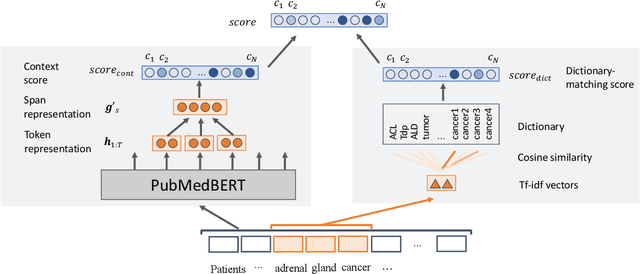
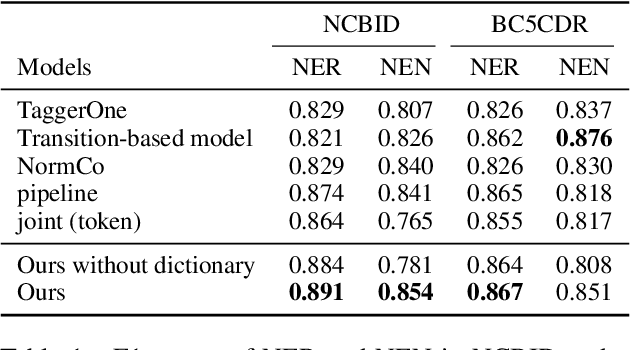
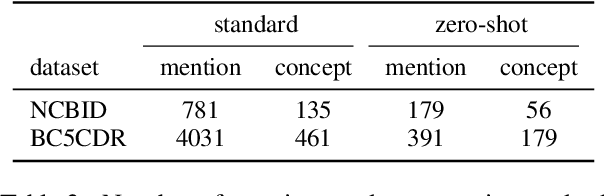
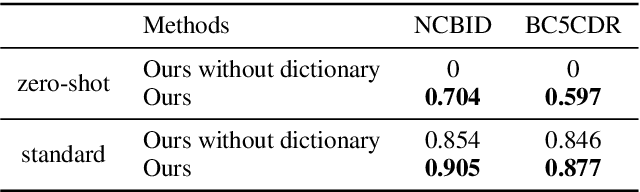
Abstract:Disease name recognition and normalization, which is generally called biomedical entity linking, is a fundamental process in biomedical text mining. Recently, neural joint learning of both tasks has been proposed to utilize the mutual benefits. While this approach achieves high performance, disease concepts that do not appear in the training dataset cannot be accurately predicted. This study introduces a novel end-to-end approach that combines span representations with dictionary-matching features to address this problem. Our model handles unseen concepts by referring to a dictionary while maintaining the performance of neural network-based models, in an end-to-end fashion. Experiments using two major datasets demonstrate that our model achieved competitive results with strong baselines, especially for unseen concepts during training.
KART: Privacy Leakage Framework of Language Models Pre-trained with Clinical Records
Dec 31, 2020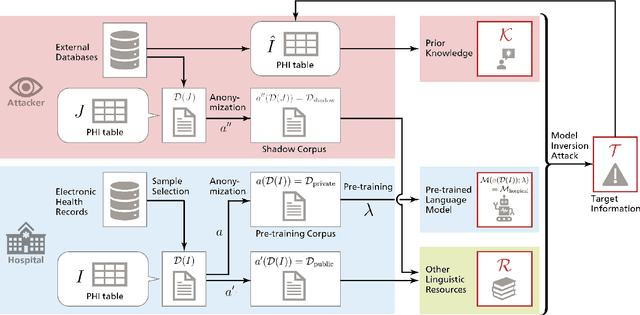
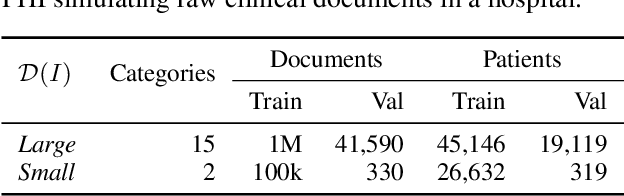
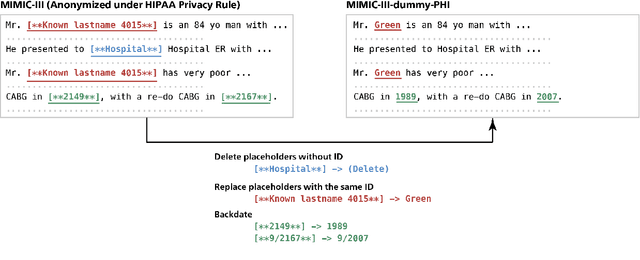
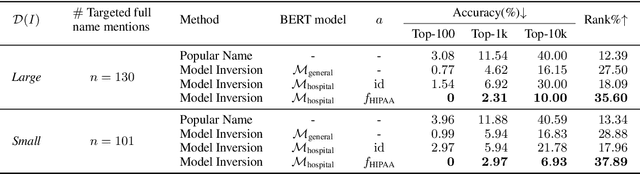
Abstract:Nowadays, mainstream natural language pro-cessing (NLP) is empowered by pre-trained language models. In the biomedical domain, only models pre-trained with anonymized data have been published. This policy is acceptable, but there are two questions: Can the privacy policy of language models be different from that of data? What happens if private language models are accidentally made public? We empirically evaluated the privacy risk of language models, using several BERT models pre-trained with MIMIC-III corpus in different data anonymity and corpus sizes. We simulated model inversion attacks to obtain the clinical information of target individuals, whose full names are already known to attackers. The BERT models were probably low-risk because the Top-100 accuracy of each attack was far below expected by chance. Moreover, most privacy leakage situations have several common primary factors; therefore, we formalized various privacy leakage scenarios under a universal novel framework named Knowledge, Anonymization, Resource, and Target (KART) framework. The KART framework helps parameterize complex privacy leakage scenarios and simplifies the comprehensive evaluation. Since the concept of the KART framework is domain agnostic, it can contribute to the establishment of privacy guidelines of language models beyond the biomedical domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge