Thomas Lavergne
LIMSI
A Dataset for Pharmacovigilance in German, French, and Japanese: Annotating Adverse Drug Reactions across Languages
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:User-generated data sources have gained significance in uncovering Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs), with an increasing number of discussions occurring in the digital world. However, the existing clinical corpora predominantly revolve around scientific articles in English. This work presents a multilingual corpus of texts concerning ADRs gathered from diverse sources, including patient fora, social media, and clinical reports in German, French, and Japanese. Our corpus contains annotations covering 12 entity types, four attribute types, and 13 relation types. It contributes to the development of real-world multilingual language models for healthcare. We provide statistics to highlight certain challenges associated with the corpus and conduct preliminary experiments resulting in strong baselines for extracting entities and relations between these entities, both within and across languages.
Decorate the Examples: A Simple Method of Prompt Design for Biomedical Relation Extraction
Apr 21, 2022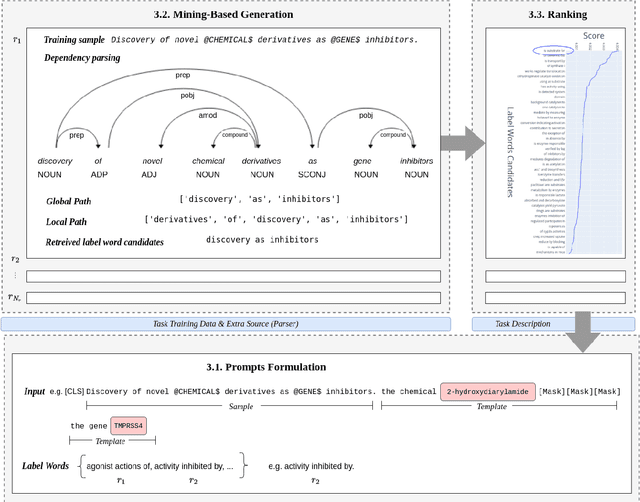
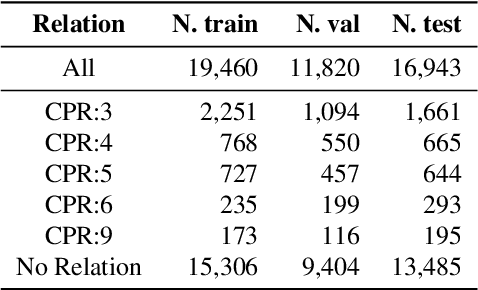
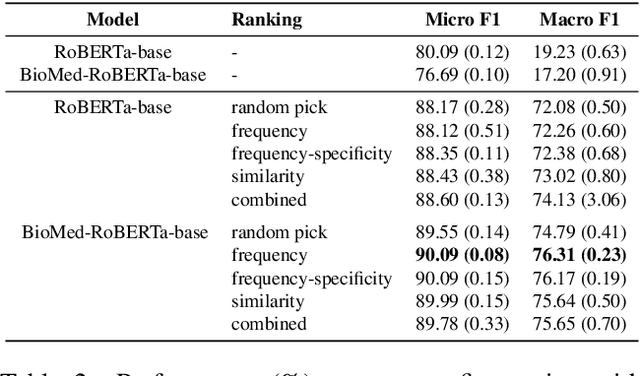
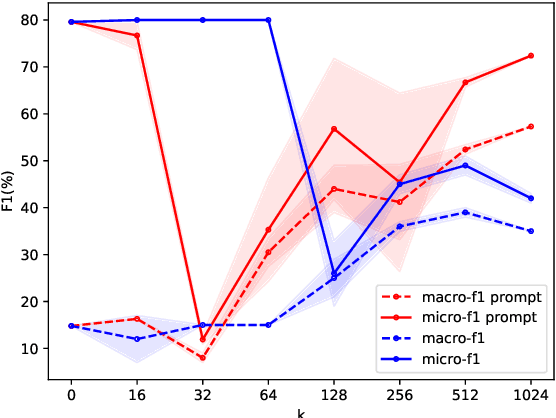
Abstract:Relation extraction is a core problem for natural language processing in the biomedical domain. Recent research on relation extraction showed that prompt-based learning improves the performance on both fine-tuning on full training set and few-shot training. However, less effort has been made on domain-specific tasks where good prompt design can be even harder. In this paper, we investigate prompting for biomedical relation extraction, with experiments on the ChemProt dataset. We present a simple yet effective method to systematically generate comprehensive prompts that reformulate the relation extraction task as a cloze-test task under a simple prompt formulation. In particular, we experiment with different ranking scores for prompt selection. With BioMed-RoBERTa-base, our results show that prompting-based fine-tuning obtains gains by 14.21 F1 over its regular fine-tuning baseline, and 1.14 F1 over SciFive-Large, the current state-of-the-art on ChemProt. Besides, we find prompt-based learning requires fewer training examples to make reasonable predictions. The results demonstrate the potential of our methods in such a domain-specific relation extraction task.
CharacterBERT: Reconciling ELMo and BERT for Word-Level Open-Vocabulary Representations From Characters
Oct 31, 2020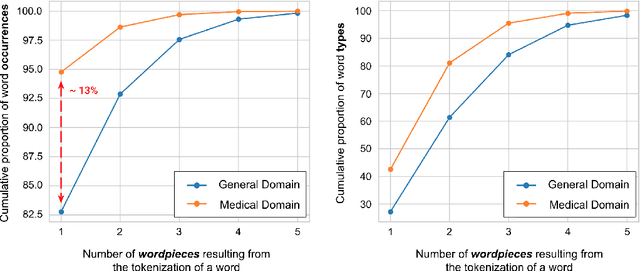

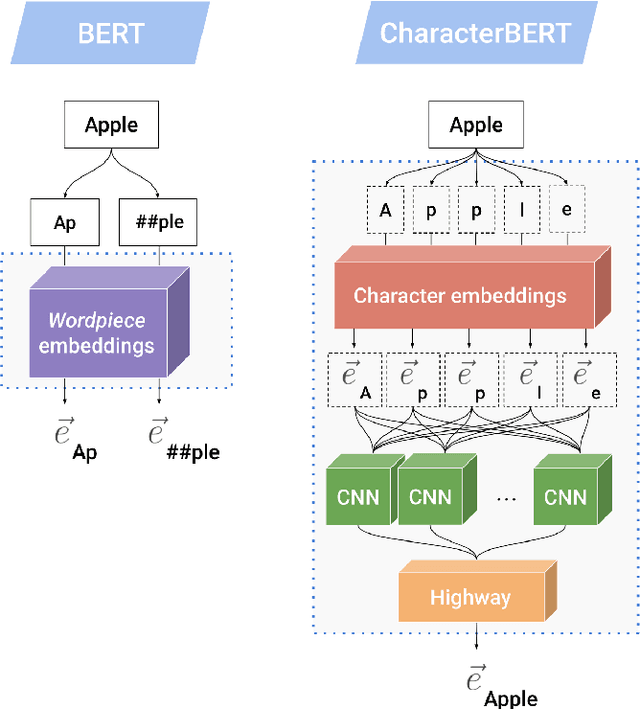
Abstract:Due to the compelling improvements brought by BERT, many recent representation models adopted the Transformer architecture as their main building block, consequently inheriting the wordpiece tokenization system despite it not being intrinsically linked to the notion of Transformers. While this system is thought to achieve a good balance between the flexibility of characters and the efficiency of full words, using predefined wordpiece vocabularies from the general domain is not always suitable, especially when building models for specialized domains (e.g., the medical domain). Moreover, adopting a wordpiece tokenization shifts the focus from the word level to the subword level, making the models conceptually more complex and arguably less convenient in practice. For these reasons, we propose CharacterBERT, a new variant of BERT that drops the wordpiece system altogether and uses a Character-CNN module instead to represent entire words by consulting their characters. We show that this new model improves the performance of BERT on a variety of medical domain tasks while at the same time producing robust, word-level and open-vocabulary representations.
DiaBLa: A Corpus of Bilingual Spontaneous Written Dialogues for Machine Translation
May 30, 2019
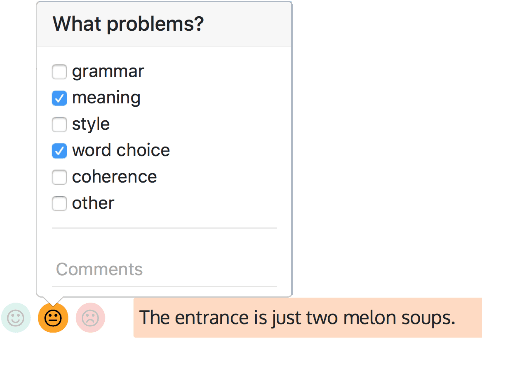
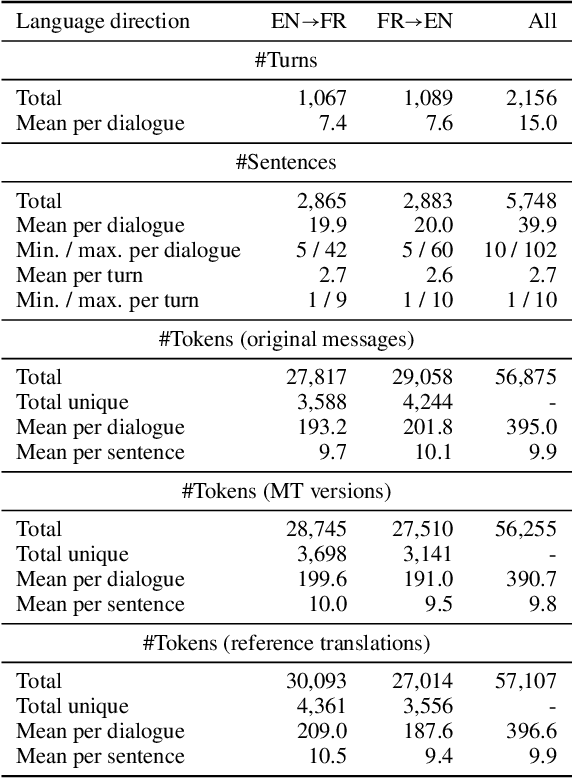
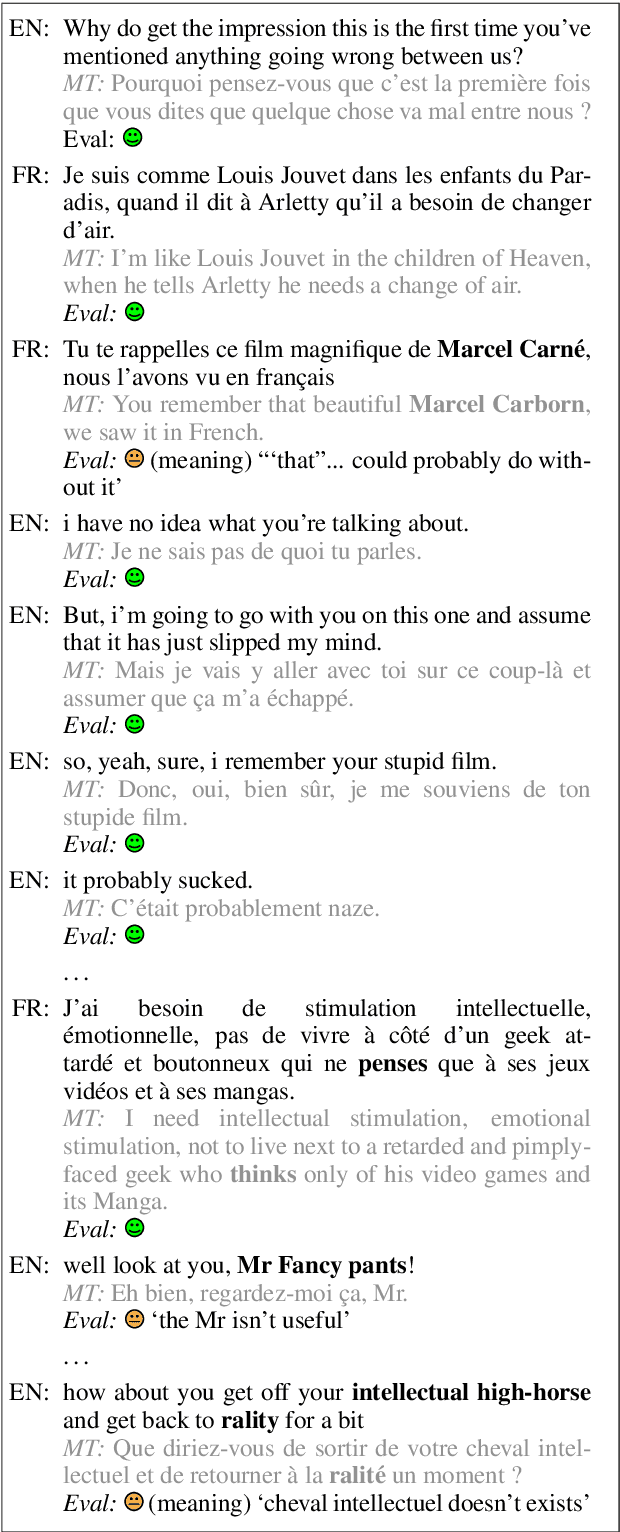
Abstract:We present a new English-French test set for the evaluation of Machine Translation (MT) for informal, written bilingual dialogue. The test set contains 144 spontaneous dialogues (5,700+ sentences) between native English and French speakers, mediated by one of two neural MT systems in a range of role-play settings. The dialogues are accompanied by fine-grained sentence-level judgments of MT quality, produced by the dialogue participants themselves, as well as by manually normalised versions and reference translations produced a posteriori. The motivation for the corpus is two-fold: to provide (i) a unique resource for evaluating MT models, and (ii) a corpus for the analysis of MT-mediated communication. We provide a preliminary analysis of the corpus to confirm that the participants' judgments reveal perceptible differences in MT quality between the two MT systems used.
Efficient Learning of Sparse Conditional Random Fields for Supervised Sequence Labelling
Jan 03, 2010

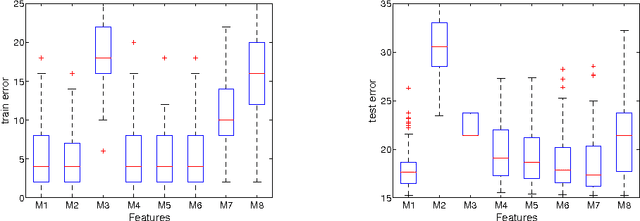
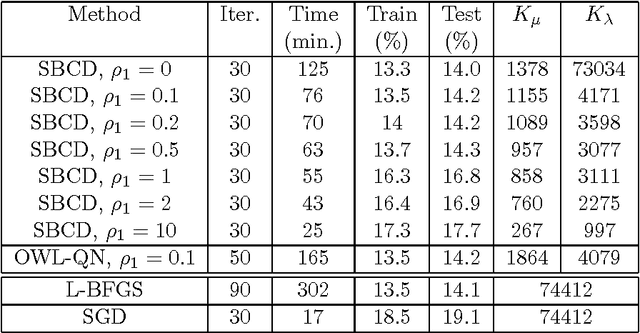
Abstract:Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) constitute a popular and efficient approach for supervised sequence labelling. CRFs can cope with large description spaces and can integrate some form of structural dependency between labels. In this contribution, we address the issue of efficient feature selection for CRFs based on imposing sparsity through an L1 penalty. We first show how sparsity of the parameter set can be exploited to significantly speed up training and labelling. We then introduce coordinate descent parameter update schemes for CRFs with L1 regularization. We finally provide some empirical comparisons of the proposed approach with state-of-the-art CRF training strategies. In particular, it is shown that the proposed approach is able to take profit of the sparsity to speed up processing and hence potentially handle larger dimensional models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge