Yongchun Zhu
AdaF^2M^2: Comprehensive Learning and Responsive Leveraging Features in Recommendation System
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Feature modeling, which involves feature representation learning and leveraging, plays an essential role in industrial recommendation systems. However, the data distribution in real-world applications usually follows a highly skewed long-tail pattern due to the popularity bias, which easily leads to over-reliance on ID-based features, such as user/item IDs and ID sequences of interactions. Such over-reliance makes it hard for models to learn features comprehensively, especially for those non-ID meta features, e.g., user/item characteristics. Further, it limits the feature leveraging ability in models, getting less generalized and more susceptible to data noise. Previous studies on feature modeling focus on feature extraction and interaction, hardly noticing the problems brought about by the long-tail data distribution. To achieve better feature representation learning and leveraging on real-world data, we propose a model-agnostic framework AdaF^2M^2, short for Adaptive Feature Modeling with Feature Mask. The feature-mask mechanism helps comprehensive feature learning via multi-forward training with augmented samples, while the adapter applies adaptive weights on features responsive to different user/item states. By arming base models with AdaF^2M^2, we conduct online A/B tests on multiple recommendation scenarios, obtaining +1.37% and +1.89% cumulative improvements on user active days and app duration respectively. Besides, the extended offline experiments on different models show improvements as well. AdaF$^2$M$^2$ has been widely deployed on both retrieval and ranking tasks in multiple applications of Douyin Group, indicating its superior effectiveness and universality.
Long-Term Interest Clock: Fine-Grained Time Perception in Streaming Recommendation System
Jan 27, 2025


Abstract:User interests manifest a dynamic pattern within the course of a day, e.g., a user usually favors soft music at 8 a.m. but may turn to ambient music at 10 p.m. To model dynamic interests in a day, hour embedding is widely used in traditional daily-trained industrial recommendation systems. However, its discreteness can cause periodical online patterns and instability in recent streaming recommendation systems. Recently, Interest Clock has achieved remarkable performance in streaming recommendation systems. Nevertheless, it models users' dynamic interests in a coarse-grained manner, merely encoding users' discrete interests of 24 hours from short-term behaviors. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained method for perceiving time information for streaming recommendation systems, named Long-term Interest Clock (LIC). The key idea of LIC is adaptively calculating current user interests by taking into consideration the relevance of long-term behaviors around current time (e.g., 8 a.m.) given a candidate item. LIC consists of two modules: (1) Clock-GSU retrieves a sub-sequence by searching through long-term behaviors, using query information from a candidate item and current time, (2) Clock-ESU employs a time-gap-aware attention mechanism to aggregate sub-sequence with the candidate item. With Clock-GSU and Clock-ESU, LIC is capable of capturing users' dynamic fine-grained interests from long-term behaviors. We conduct online A/B tests, obtaining +0.122% improvements on user active days. Besides, the extended offline experiments show improvements as well. Long-term Interest Clock has been integrated into Douyin Music App's recommendation system.
Unified Dual-Intent Translation for Joint Modeling of Search and Recommendation
Jul 01, 2024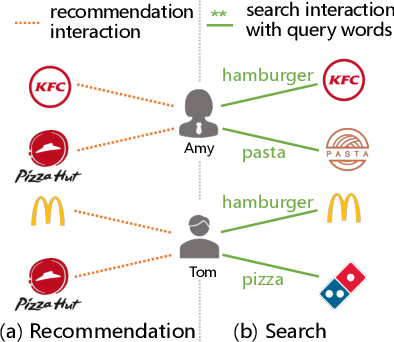
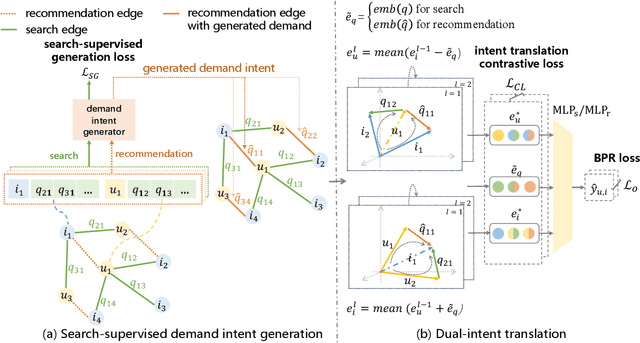
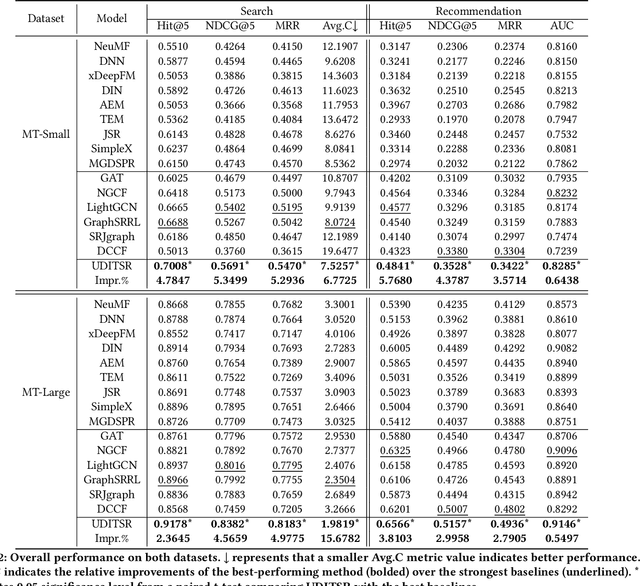
Abstract:Recommendation systems, which assist users in discovering their preferred items among numerous options, have served billions of users across various online platforms. Intuitively, users' interactions with items are highly driven by their unchanging inherent intents (e.g., always preferring high-quality items) and changing demand intents (e.g., wanting a T-shirt in summer but a down jacket in winter). However, both types of intents are implicitly expressed in recommendation scenario, posing challenges in leveraging them for accurate intent-aware recommendations. Fortunately, in search scenario, often found alongside recommendation on the same online platform, users express their demand intents explicitly through their query words. Intuitively, in both scenarios, a user shares the same inherent intent and the interactions may be influenced by the same demand intent. It is therefore feasible to utilize the interaction data from both scenarios to reinforce the dual intents for joint intent-aware modeling. But the joint modeling should deal with two problems: 1) accurately modeling users' implicit demand intents in recommendation; 2) modeling the relation between the dual intents and the interactive items. To address these problems, we propose a novel model named Unified Dual-Intents Translation for joint modeling of Search and Recommendation (UDITSR). To accurately simulate users' demand intents in recommendation, we utilize real queries from search data as supervision information to guide its generation. To explicitly model the relation among the triplet <inherent intent, demand intent, interactive item>, we propose a dual-intent translation propagation mechanism to learn the triplet in the same semantic space via embedding translations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UDITSR outperforms SOTA baselines both in search and recommendation tasks.
Interest Clock: Time Perception in Real-Time Streaming Recommendation System
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:User preferences follow a dynamic pattern over a day, e.g., at 8 am, a user might prefer to read news, while at 8 pm, they might prefer to watch movies. Time modeling aims to enable recommendation systems to perceive time changes to capture users' dynamic preferences over time, which is an important and challenging problem in recommendation systems. Especially, streaming recommendation systems in the industry, with only available samples of the current moment, present greater challenges for time modeling. There is still a lack of effective time modeling methods for streaming recommendation systems. In this paper, we propose an effective and universal method Interest Clock to perceive time information in recommendation systems. Interest Clock first encodes users' time-aware preferences into a clock (hour-level personalized features) and then uses Gaussian distribution to smooth and aggregate them into the final interest clock embedding according to the current time for the final prediction. By arming base models with Interest Clock, we conduct online A/B tests, obtaining +0.509% and +0.758% improvements on user active days and app duration respectively. Besides, the extended offline experiments show improvements as well. Interest Clock has been deployed on Douyin Music App.
Exploiting User Comments for Early Detection of Fake News Prior to Users' Commenting
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:Both accuracy and timeliness are key factors in detecting fake news on social media. However, most existing methods encounter an accuracy-timeliness dilemma: Content-only methods guarantee timeliness but perform moderately because of limited available information, while social context-based ones generally perform better but inevitably lead to latency because of social context accumulation needs. To break such a dilemma, a feasible but not well-studied solution is to leverage social contexts (e.g., comments) from historical news for training a detection model and apply it to newly emerging news without social contexts. This requires the model to (1) sufficiently learn helpful knowledge from social contexts, and (2) be well compatible with situations that social contexts are available or not. To achieve this goal, we propose to absorb and parameterize useful knowledge from comments in historical news and then inject it into a content-only detection model. Specifically, we design the Comments Assisted Fake News Detection method (CAS-FEND), which transfers useful knowledge from a comments-aware teacher model to a content-only student model during training. The student model is further used to detect newly emerging fake news. Experiments show that the CAS-FEND student model outperforms all content-only methods and even those with 1/4 comments as inputs, demonstrating its superiority for early detection.
Learn over Past, Evolve for Future: Forecasting Temporal Trends for Fake News Detection
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Fake news detection has been a critical task for maintaining the health of the online news ecosystem. However, very few existing works consider the temporal shift issue caused by the rapidly-evolving nature of news data in practice, resulting in significant performance degradation when training on past data and testing on future data. In this paper, we observe that the appearances of news events on the same topic may display discernible patterns over time, and posit that such patterns can assist in selecting training instances that could make the model adapt better to future data. Specifically, we design an effective framework FTT (Forecasting Temporal Trends), which could forecast the temporal distribution patterns of news data and then guide the detector to fast adapt to future distribution. Experiments on the real-world temporally split dataset demonstrate the superiority of our proposed framework. The code is available at https://github.com/ICTMCG/FTT-ACL23.
Modeling Dual Period-Varying Preferences for Takeaway Recommendation
Jun 16, 2023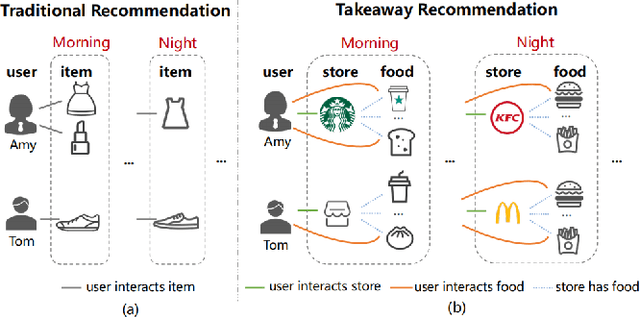

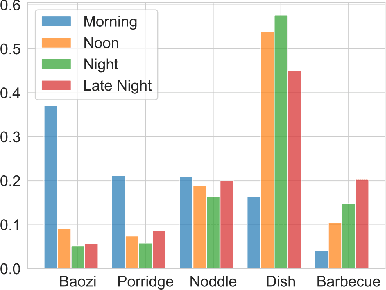

Abstract:Takeaway recommender systems, which aim to accurately provide stores that offer foods meeting users' interests, have served billions of users in our daily life. Different from traditional recommendation, takeaway recommendation faces two main challenges: (1) Dual Interaction-Aware Preference Modeling. Traditional recommendation commonly focuses on users' single preferences for items while takeaway recommendation needs to comprehensively consider users' dual preferences for stores and foods. (2) Period-Varying Preference Modeling. Conventional recommendation generally models continuous changes in users' preferences from a session-level or day-level perspective. However, in practical takeaway systems, users' preferences vary significantly during the morning, noon, night, and late night periods of the day. To address these challenges, we propose a Dual Period-Varying Preference modeling (DPVP) for takeaway recommendation. Specifically, we design a dual interaction-aware module, aiming to capture users' dual preferences based on their interactions with stores and foods. Moreover, to model various preferences in different time periods of the day, we propose a time-based decomposition module as well as a time-aware gating mechanism. Extensive offline and online experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods on real-world datasets and it is capable of modeling the dual period-varying preferences. Moreover, our model has been deployed online on Meituan Takeaway platform, leading to an average improvement in GMV (Gross Merchandise Value) of 0.70%.
Attacking Pre-trained Recommendation
May 06, 2023Abstract:Recently, a series of pioneer studies have shown the potency of pre-trained models in sequential recommendation, illuminating the path of building an omniscient unified pre-trained recommendation model for different downstream recommendation tasks. Despite these advancements, the vulnerabilities of classical recommender systems also exist in pre-trained recommendation in a new form, while the security of pre-trained recommendation model is still unexplored, which may threaten its widely practical applications. In this study, we propose a novel framework for backdoor attacking in pre-trained recommendation. We demonstrate the provider of the pre-trained model can easily insert a backdoor in pre-training, thereby increasing the exposure rates of target items to target user groups. Specifically, we design two novel and effective backdoor attacks: basic replacement and prompt-enhanced, under various recommendation pre-training usage scenarios. Experimental results on real-world datasets show that our proposed attack strategies significantly improve the exposure rates of target items to target users by hundreds of times in comparison to the clean model.
Improving Fake News Detection of Influential Domain via Domain- and Instance-Level Transfer
Oct 09, 2022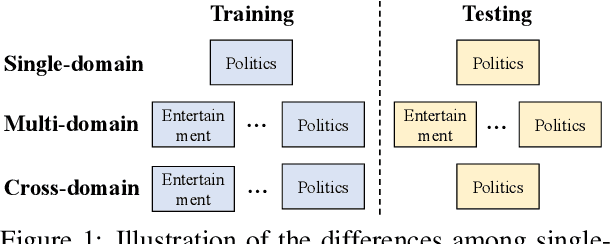
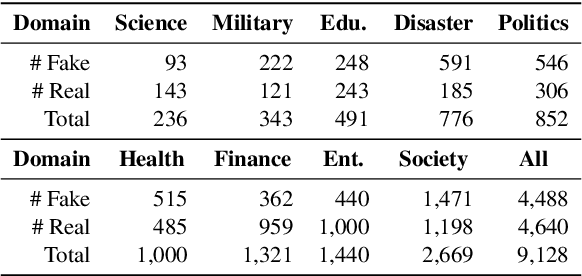
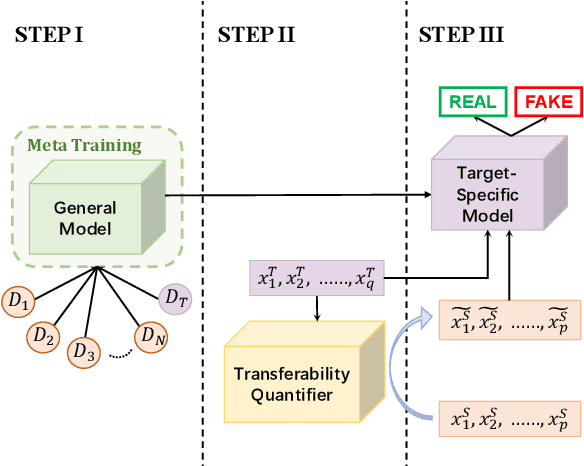
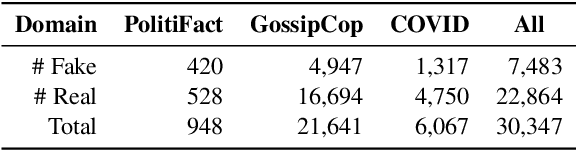
Abstract:Both real and fake news in various domains, such as politics, health, and entertainment are spread via online social media every day, necessitating fake news detection for multiple domains. Among them, fake news in specific domains like politics and health has more serious potential negative impacts on the real world (e.g., the infodemic led by COVID-19 misinformation). Previous studies focus on multi-domain fake news detection, by equally mining and modeling the correlation between domains. However, these multi-domain methods suffer from a seesaw problem: the performance of some domains is often improved at the cost of hurting the performance of other domains, which could lead to an unsatisfying performance in specific domains. To address this issue, we propose a Domain- and Instance-level Transfer Framework for Fake News Detection (DITFEND), which could improve the performance of specific target domains. To transfer coarse-grained domain-level knowledge, we train a general model with data of all domains from the meta-learning perspective. To transfer fine-grained instance-level knowledge and adapt the general model to a target domain, we train a language model on the target domain to evaluate the transferability of each data instance in source domains and re-weigh each instance's contribution. Offline experiments on two datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of DITFEND. Online experiments show that DITFEND brings additional improvements over the base models in a real-world scenario.
Customized Conversational Recommender Systems
Jun 30, 2022
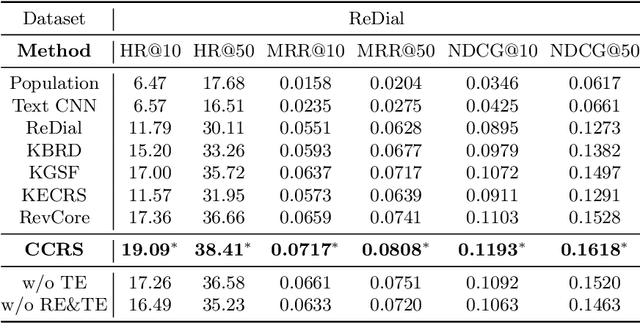
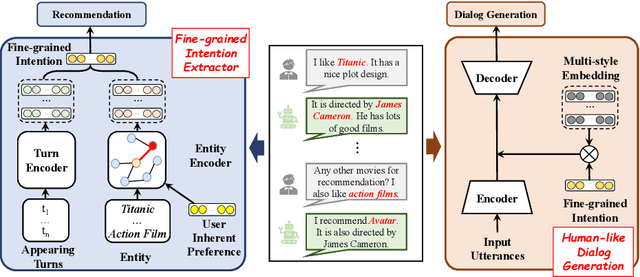
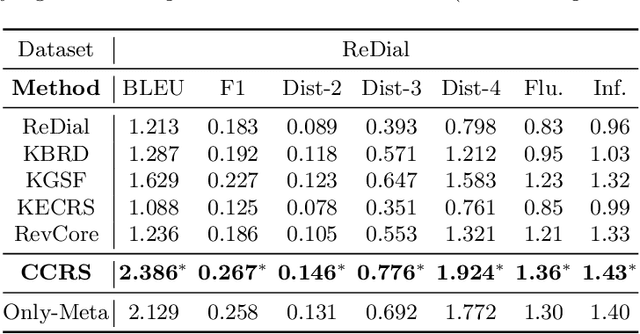
Abstract:Conversational recommender systems (CRS) aim to capture user's current intentions and provide recommendations through real-time multi-turn conversational interactions. As a human-machine interactive system, it is essential for CRS to improve the user experience. However, most CRS methods neglect the importance of user experience. In this paper, we propose two key points for CRS to improve the user experience: (1) Speaking like a human, human can speak with different styles according to the current dialogue context. (2) Identifying fine-grained intentions, even for the same utterance, different users have diverse finegrained intentions, which are related to users' inherent preference. Based on the observations, we propose a novel CRS model, coined Customized Conversational Recommender System (CCRS), which customizes CRS model for users from three perspectives. For human-like dialogue services, we propose multi-style dialogue response generator which selects context-aware speaking style for utterance generation. To provide personalized recommendations, we extract user's current fine-grained intentions from dialogue context with the guidance of user's inherent preferences. Finally, to customize the model parameters for each user, we train the model from the meta-learning perspective. Extensive experiments and a series of analyses have shown the superiority of our CCRS on both the recommendation and dialogue services.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge