Danding Wang
Forewarned is Forearmed: Pre-Synthesizing Jailbreak-like Instructions to Enhance LLM Safety Guardrail to Potential Attacks
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in improving large language model (LLM) to refuse to answer malicious instructions, widely used LLMs remain vulnerable to jailbreak attacks where attackers generate instructions with distributions differing from safety alignment corpora. New attacks expose LLMs' inability to recognize unseen malicious instructions, highlighting a critical distributional mismatch between training data and real-world attacks that forces developers into reactive patching cycles. To tackle this challenge, we propose IMAGINE, a synthesis framework that leverages embedding space distribution analysis to generate jailbreak-like instructions. This approach effectively fills the distributional gap between authentic jailbreak patterns and safety alignment corpora. IMAGINE follows an iterative optimization process that dynamically evolves text generation distributions across iterations, thereby augmenting the coverage of safety alignment data distributions through synthesized data examples. Based on the safety-aligned corpus enhanced through IMAGINE, our framework demonstrates significant decreases in attack success rate on Qwen2.5, Llama3.1, and Llama3.2 without compromising their utility.
Enhancing the Comprehensibility of Text Explanations via Unsupervised Concept Discovery
May 26, 2025Abstract:Concept-based explainable approaches have emerged as a promising method in explainable AI because they can interpret models in a way that aligns with human reasoning. However, their adaption in the text domain remains limited. Most existing methods rely on predefined concept annotations and cannot discover unseen concepts, while other methods that extract concepts without supervision often produce explanations that are not intuitively comprehensible to humans, potentially diminishing user trust. These methods fall short of discovering comprehensible concepts automatically. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{ECO-Concept}, an intrinsically interpretable framework to discover comprehensible concepts with no concept annotations. ECO-Concept first utilizes an object-centric architecture to extract semantic concepts automatically. Then the comprehensibility of the extracted concepts is evaluated by large language models. Finally, the evaluation result guides the subsequent model fine-tuning to obtain more understandable explanations. Experiments show that our method achieves superior performance across diverse tasks. Further concept evaluations validate that the concepts learned by ECO-Concept surpassed current counterparts in comprehensibility.
The Staircase of Ethics: Probing LLM Value Priorities through Multi-Step Induction to Complex Moral Dilemmas
May 23, 2025Abstract:Ethical decision-making is a critical aspect of human judgment, and the growing use of LLMs in decision-support systems necessitates a rigorous evaluation of their moral reasoning capabilities. However, existing assessments primarily rely on single-step evaluations, failing to capture how models adapt to evolving ethical challenges. Addressing this gap, we introduce the Multi-step Moral Dilemmas (MMDs), the first dataset specifically constructed to evaluate the evolving moral judgments of LLMs across 3,302 five-stage dilemmas. This framework enables a fine-grained, dynamic analysis of how LLMs adjust their moral reasoning across escalating dilemmas. Our evaluation of nine widely used LLMs reveals that their value preferences shift significantly as dilemmas progress, indicating that models recalibrate moral judgments based on scenario complexity. Furthermore, pairwise value comparisons demonstrate that while LLMs often prioritize the value of care, this value can sometimes be superseded by fairness in certain contexts, highlighting the dynamic and context-dependent nature of LLM ethical reasoning. Our findings call for a shift toward dynamic, context-aware evaluation paradigms, paving the way for more human-aligned and value-sensitive development of LLMs.
LLM-Generated Fake News Induces Truth Decay in News Ecosystem: A Case Study on Neural News Recommendation
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Online fake news moderation now faces a new challenge brought by the malicious use of large language models (LLMs) in fake news production. Though existing works have shown LLM-generated fake news is hard to detect from an individual aspect, it remains underexplored how its large-scale release will impact the news ecosystem. In this study, we develop a simulation pipeline and a dataset with ~56k generated news of diverse types to investigate the effects of LLM-generated fake news within neural news recommendation systems. Our findings expose a truth decay phenomenon, where real news is gradually losing its advantageous position in news ranking against fake news as LLM-generated news is involved in news recommendation. We further provide an explanation about why truth decay occurs from a familiarity perspective and show the positive correlation between perplexity and news ranking. Finally, we discuss the threats of LLM-generated fake news and provide possible countermeasures. We urge stakeholders to address this emerging challenge to preserve the integrity of news ecosystems.
FakingRecipe: Detecting Fake News on Short Video Platforms from the Perspective of Creative Process
Jul 23, 2024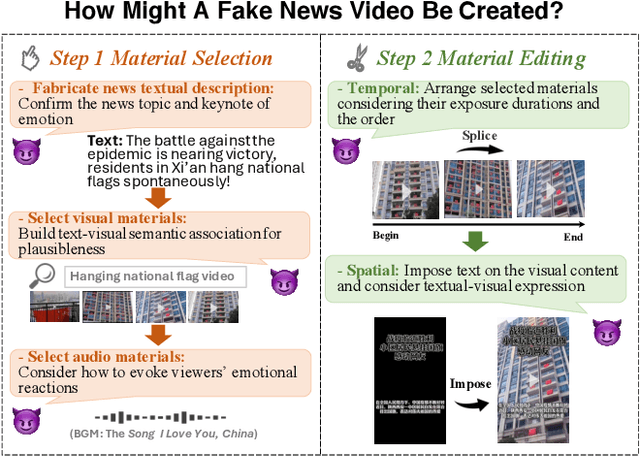
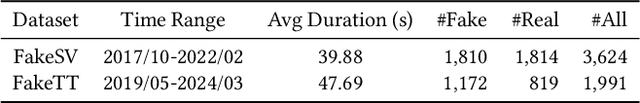
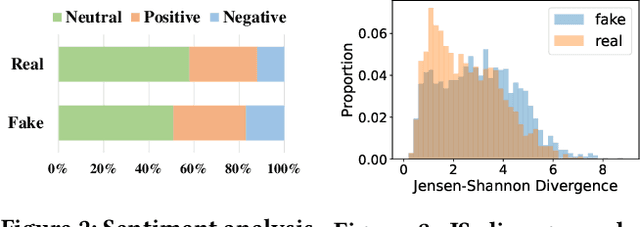
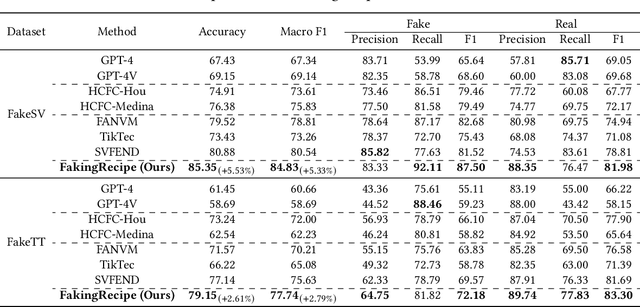
Abstract:As short-form video-sharing platforms become a significant channel for news consumption, fake news in short videos has emerged as a serious threat in the online information ecosystem, making developing detection methods for this new scenario an urgent need. Compared with that in text and image formats, fake news on short video platforms contains rich but heterogeneous information in various modalities, posing a challenge to effective feature utilization. Unlike existing works mostly focusing on analyzing what is presented, we introduce a novel perspective that considers how it might be created. Through the lens of the creative process behind news video production, our empirical analysis uncovers the unique characteristics of fake news videos in material selection and editing. Based on the obtained insights, we design FakingRecipe, a creative process-aware model for detecting fake news short videos. It captures the fake news preferences in material selection from sentimental and semantic aspects and considers the traits of material editing from spatial and temporal aspects. To improve evaluation comprehensiveness, we first construct FakeTT, an English dataset for this task, and conduct experiments on both FakeTT and the existing Chinese FakeSV dataset. The results show FakingRecipe's superiority in detecting fake news on short video platforms.
Let Silence Speak: Enhancing Fake News Detection with Generated Comments from Large Language Models
May 26, 2024



Abstract:Fake news detection plays a crucial role in protecting social media users and maintaining a healthy news ecosystem. Among existing works, comment-based fake news detection methods are empirically shown as promising because comments could reflect users' opinions, stances, and emotions and deepen models' understanding of fake news. Unfortunately, due to exposure bias and users' different willingness to comment, it is not easy to obtain diverse comments in reality, especially for early detection scenarios. Without obtaining the comments from the ``silent'' users, the perceived opinions may be incomplete, subsequently affecting news veracity judgment. In this paper, we explore the possibility of finding an alternative source of comments to guarantee the availability of diverse comments, especially those from silent users. Specifically, we propose to adopt large language models (LLMs) as a user simulator and comment generator, and design GenFEND, a generated feedback-enhanced detection framework, which generates comments by prompting LLMs with diverse user profiles and aggregating generated comments from multiple subpopulation groups. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of GenFEND and further analysis shows that the generated comments cover more diverse users and could even be more effective than actual comments.
Ten Words Only Still Help: Improving Black-Box AI-Generated Text Detection via Proxy-Guided Efficient Re-Sampling
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:With the rapidly increasing application of large language models (LLMs), their abuse has caused many undesirable societal problems such as fake news, academic dishonesty, and information pollution. This makes AI-generated text (AIGT) detection of great importance. Among existing methods, white-box methods are generally superior to black-box methods in terms of performance and generalizability, but they require access to LLMs' internal states and are not applicable to black-box settings. In this paper, we propose to estimate word generation probabilities as pseudo white-box features via multiple re-sampling to help improve AIGT detection under the black-box setting. Specifically, we design POGER, a proxy-guided efficient re-sampling method, which selects a small subset of representative words (e.g., 10 words) for performing multiple re-sampling in black-box AIGT detection. Experiments on datasets containing texts from humans and seven LLMs show that POGER outperforms all baselines in macro F1 under black-box, partial white-box, and out-of-distribution settings and maintains lower re-sampling costs than its existing counterparts.
Understanding News Creation Intents: Frame, Dataset, and Method
Dec 27, 2023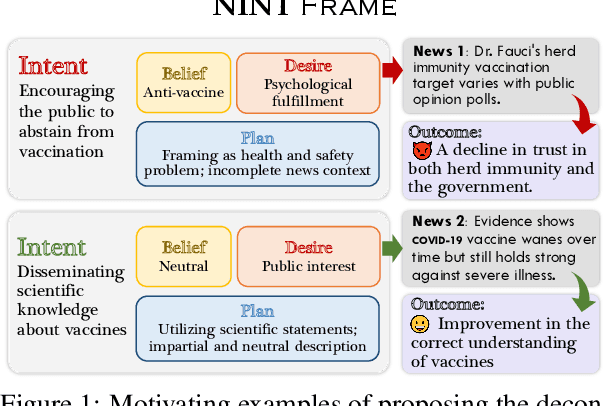
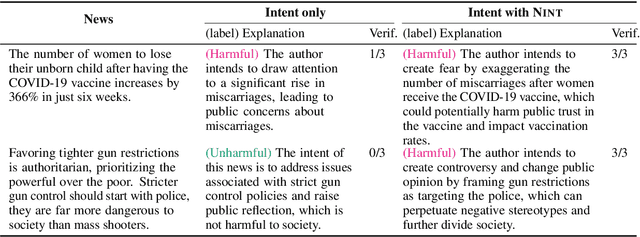
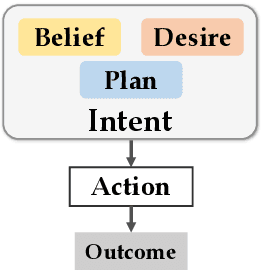
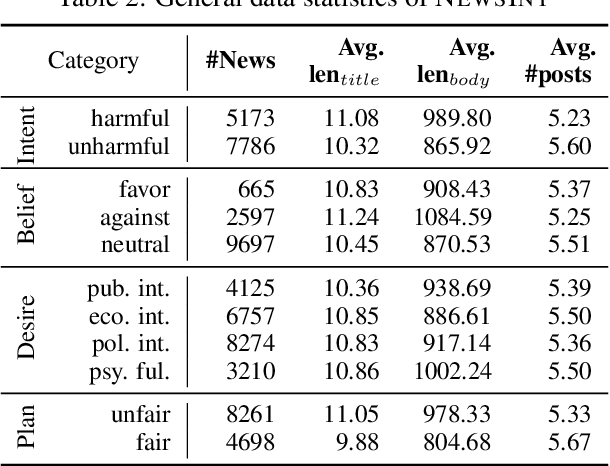
Abstract:As the disruptive changes in the media economy and the proliferation of alternative news media outlets, news intent has progressively deviated from ethical standards that serve the public interest. News intent refers to the purpose or intention behind the creation of a news article. While the significance of research on news intent has been widely acknowledged, the absence of a systematic news intent understanding framework hinders further exploration of news intent and its downstream applications. To bridge this gap, we propose News INTent (NINT) frame, the first component-aware formalism for understanding the news creation intent based on research in philosophy, psychology, and cognitive science. Within this frame, we define the news intent identification task and provide a benchmark dataset with fine-grained labels along with an efficient benchmark method. Experiments demonstrate that NINT is beneficial in both the intent identification task and downstream tasks that demand a profound understanding of news. This work marks a foundational step towards a more systematic exploration of news creation intents.
Rethinking Image Editing Detection in the Era of Generative AI Revolution
Nov 29, 2023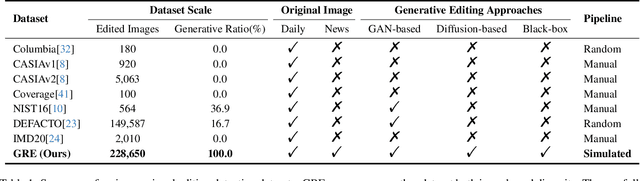
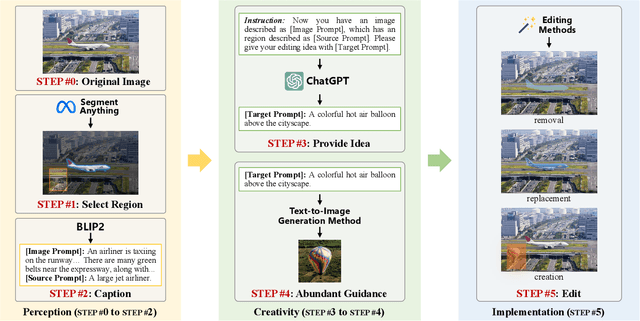


Abstract:The accelerated advancement of generative AI significantly enhance the viability and effectiveness of generative regional editing methods. This evolution render the image manipulation more accessible, thereby intensifying the risk of altering the conveyed information within original images and even propagating misinformation. Consequently, there exists a critical demand for robust capable of detecting the edited images. However, the lack of comprehensive dataset containing images edited with abundant and advanced generative regional editing methods poses a substantial obstacle to the advancement of corresponding detection methods. We endeavor to fill the vacancy by constructing the GRE dataset, a large-scale generative regional editing dataset with the following advantages: 1) Collection of real-world original images, focusing on two frequently edited scenarios. 2) Integration of a logical and simulated editing pipeline, leveraging multiple large models in various modalities. 3) Inclusion of various editing approaches with distinct architectures. 4) Provision of comprehensive analysis tasks. We perform comprehensive experiments with proposed three tasks: edited image classification, edited method attribution and edited region localization, providing analysis of distinct editing methods and evaluation of detection methods in related fields. We expect that the GRE dataset can promote further research and exploration in the field of generative region editing detection.
Topology-Preserving Adversarial Training
Nov 29, 2023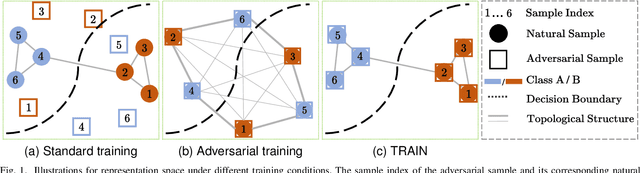
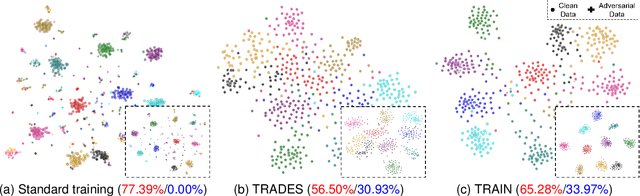
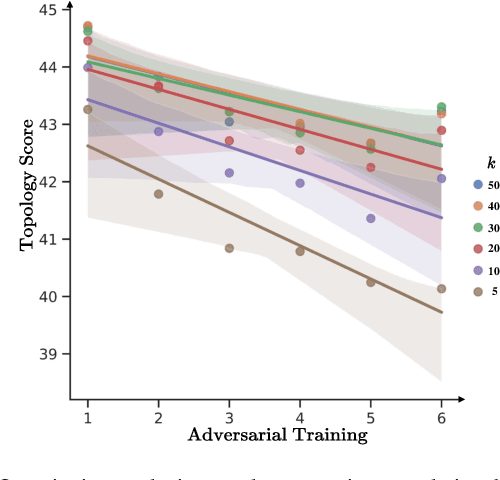
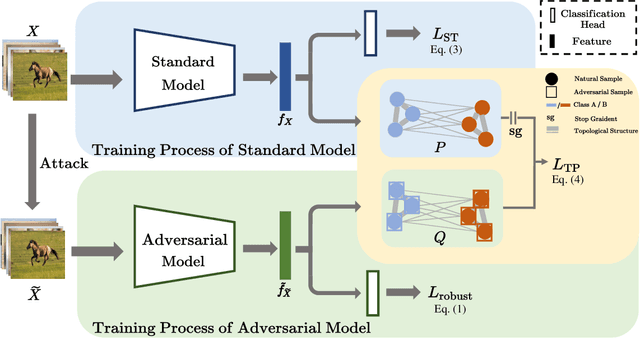
Abstract:Despite the effectiveness in improving the robustness of neural networks, adversarial training has suffered from the natural accuracy degradation problem, i.e., accuracy on natural samples has reduced significantly. In this study, we reveal that natural accuracy degradation is highly related to the disruption of the natural sample topology in the representation space by quantitative and qualitative experiments. Based on this observation, we propose Topology-pReserving Adversarial traINing (TRAIN) to alleviate the problem by preserving the topology structure of natural samples from a standard model trained only on natural samples during adversarial training. As an additional regularization, our method can easily be combined with various popular adversarial training algorithms in a plug-and-play manner, taking advantage of both sides. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny ImageNet show that our proposed method achieves consistent and significant improvements over various strong baselines in most cases. Specifically, without additional data, our proposed method achieves up to 8.78% improvement in natural accuracy and 4.50% improvement in robust accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge