Haipeng Fang
Attend to Not Attended: Structure-then-Detail Token Merging for Post-training DiT Acceleration
May 16, 2025Abstract:Diffusion transformers have shown exceptional performance in visual generation but incur high computational costs. Token reduction techniques that compress models by sharing the denoising process among similar tokens have been introduced. However, existing approaches neglect the denoising priors of the diffusion models, leading to suboptimal acceleration and diminished image quality. This study proposes a novel concept: attend to prune feature redundancies in areas not attended by the diffusion process. We analyze the location and degree of feature redundancies based on the structure-then-detail denoising priors. Subsequently, we introduce SDTM, a structure-then-detail token merging approach that dynamically compresses feature redundancies. Specifically, we design dynamic visual token merging, compression ratio adjusting, and prompt reweighting for different stages. Served in a post-training way, the proposed method can be integrated seamlessly into any DiT architecture. Extensive experiments across various backbones, schedulers, and datasets showcase the superiority of our method, for example, it achieves 1.55 times acceleration with negligible impact on image quality. Project page: https://github.com/ICTMCG/SDTM.
Rethinking Image Editing Detection in the Era of Generative AI Revolution
Nov 29, 2023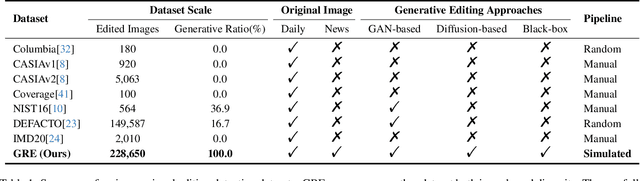
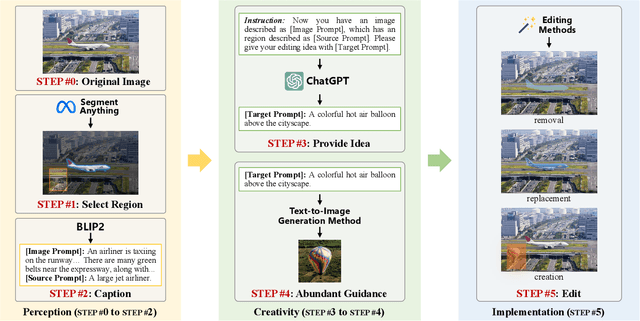


Abstract:The accelerated advancement of generative AI significantly enhance the viability and effectiveness of generative regional editing methods. This evolution render the image manipulation more accessible, thereby intensifying the risk of altering the conveyed information within original images and even propagating misinformation. Consequently, there exists a critical demand for robust capable of detecting the edited images. However, the lack of comprehensive dataset containing images edited with abundant and advanced generative regional editing methods poses a substantial obstacle to the advancement of corresponding detection methods. We endeavor to fill the vacancy by constructing the GRE dataset, a large-scale generative regional editing dataset with the following advantages: 1) Collection of real-world original images, focusing on two frequently edited scenarios. 2) Integration of a logical and simulated editing pipeline, leveraging multiple large models in various modalities. 3) Inclusion of various editing approaches with distinct architectures. 4) Provision of comprehensive analysis tasks. We perform comprehensive experiments with proposed three tasks: edited image classification, edited method attribution and edited region localization, providing analysis of distinct editing methods and evaluation of detection methods in related fields. We expect that the GRE dataset can promote further research and exploration in the field of generative region editing detection.
Dance Your Latents: Consistent Dance Generation through Spatial-temporal Subspace Attention Guided by Motion Flow
Oct 20, 2023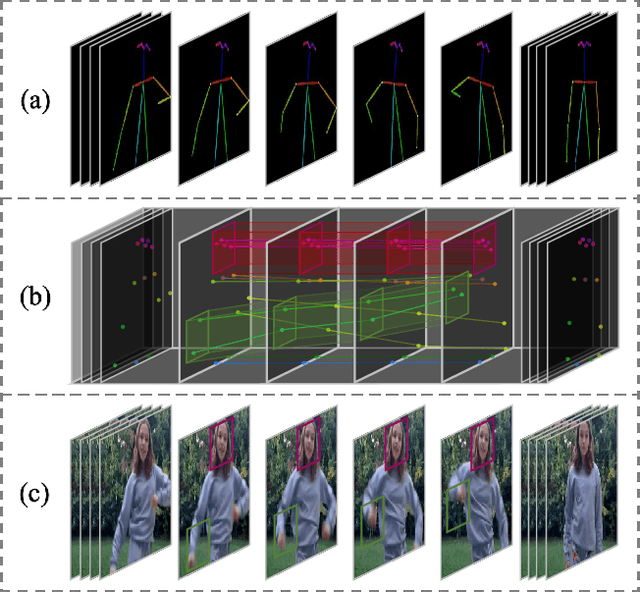
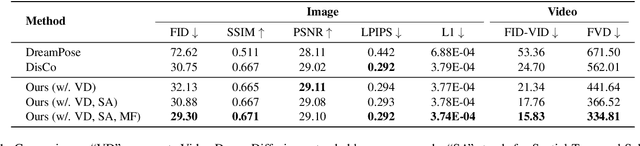
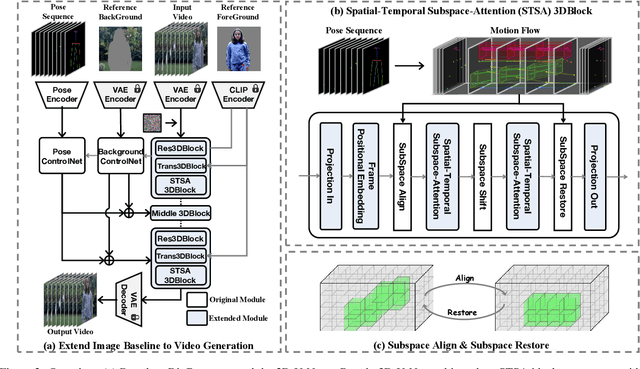
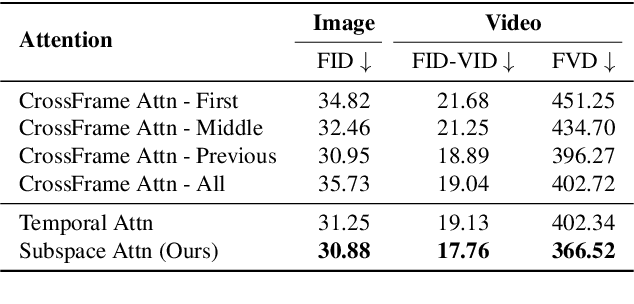
Abstract:The advancement of generative AI has extended to the realm of Human Dance Generation, demonstrating superior generative capacities. However, current methods still exhibit deficiencies in achieving spatiotemporal consistency, resulting in artifacts like ghosting, flickering, and incoherent motions. In this paper, we present Dance-Your-Latents, a framework that makes latents dance coherently following motion flow to generate consistent dance videos. Firstly, considering that each constituent element moves within a confined space, we introduce spatial-temporal subspace-attention blocks that decompose the global space into a combination of regular subspaces and efficiently model the spatiotemporal consistency within these subspaces. This module enables each patch pay attention to adjacent areas, mitigating the excessive dispersion of long-range attention. Furthermore, observing that body part's movement is guided by pose control, we design motion flow guided subspace align & restore. This method enables the attention to be computed on the irregular subspace along the motion flow. Experimental results in TikTok dataset demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances spatiotemporal consistency of the generated videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge