Yilin Li
Zhejiang University
Subset Selection for Stratified Sampling in Online Controlled Experiments
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:Online controlled experiments, also known as A/B testing, are the digital equivalent of randomized controlled trials for estimating the impact of marketing campaigns on website visitors. Stratified sampling is a traditional technique for variance reduction to improve the sensitivity (or statistical power) of controlled experiments; this technique first divides the population into strata (homogeneous subgroups) based on stratification variables and then draws samples from each stratum to avoid sampling bias. To enhance the estimation accuracy of stratified sampling, we focus on the problem of selecting a subset of stratification variables that are effective in variance reduction. We design an efficient algorithm that selects stratification variables one by one by simulating a series of stratified sampling processes. We also estimate the computational complexity of our subset selection algorithm. Computational experiments using synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our method can outperform other variance reduction techniques especially when multiple variables have a certain correlation with the outcome variable. Our subset selection method for stratified sampling can improve the sensitivity of online controlled experiments, thus enabling more reliable marketing decisions.
Harnessing Rule-Based Reinforcement Learning for Enhanced Grammatical Error Correction
Aug 26, 2025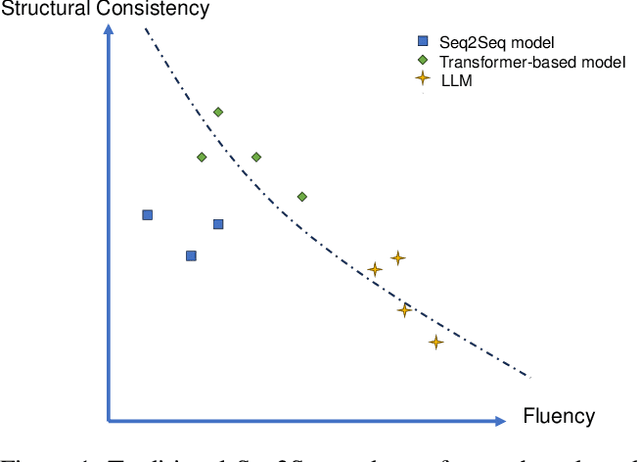


Abstract:Grammatical error correction is a significant task in NLP. Traditional methods based on encoder-decoder models have achieved certain success, but the application of LLMs in this field is still underexplored. Current research predominantly relies on supervised fine-tuning to train LLMs to directly generate the corrected sentence, which limits the model's powerful reasoning ability. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework based on Rule-Based RL. Through experiments on the Chinese datasets, our Rule-Based RL framework achieves \textbf{state-of-the-art }performance, with a notable increase in \textbf{recall}. This result clearly highlights the advantages of using RL to steer LLMs, offering a more controllable and reliable paradigm for future development in GEC.
Artificial Intelligence-Based Multiscale Temporal Modeling for Anomaly Detection in Cloud Services
Aug 20, 2025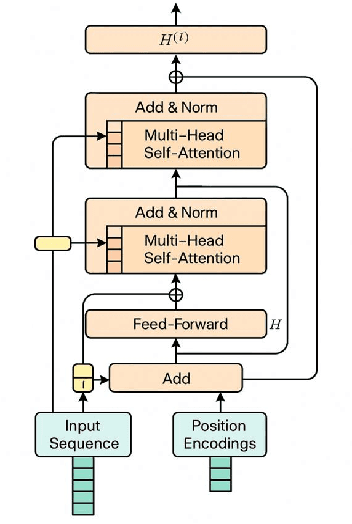
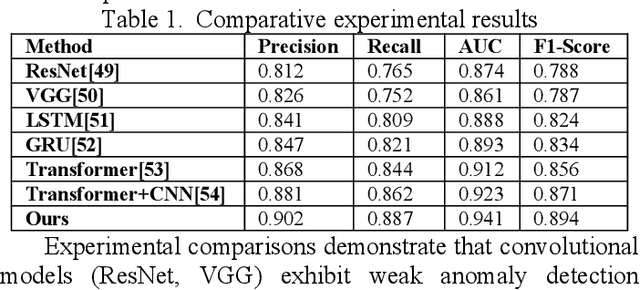
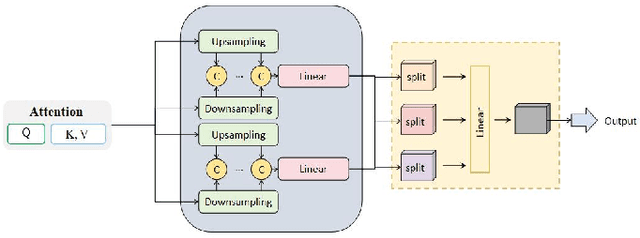
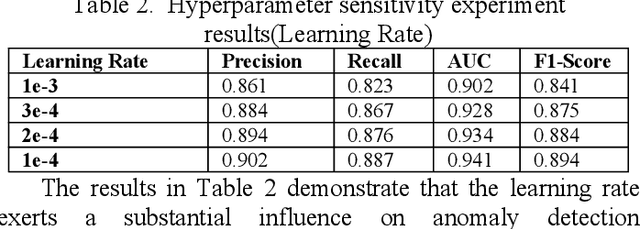
Abstract:This study proposes an anomaly detection method based on the Transformer architecture with integrated multiscale feature perception, aiming to address the limitations of temporal modeling and scale-aware feature representation in cloud service environments. The method first employs an improved Transformer module to perform temporal modeling on high-dimensional monitoring data, using a self-attention mechanism to capture long-range dependencies and contextual semantics. Then, a multiscale feature construction path is introduced to extract temporal features at different granularities through downsampling and parallel encoding. An attention-weighted fusion module is designed to dynamically adjust the contribution of each scale to the final decision, enhancing the model's robustness in anomaly pattern modeling. In the input modeling stage, standardized multidimensional time series are constructed, covering core signals such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and task scheduling states, while positional encoding is used to strengthen the model's temporal awareness. A systematic experimental setup is designed to evaluate performance, including comparative experiments and hyperparameter sensitivity analysis, focusing on the impact of optimizers, learning rates, anomaly ratios, and noise levels. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms mainstream baseline models in key metrics, including precision, recall, AUC, and F1-score, and maintains strong stability and detection performance under various perturbation conditions, demonstrating its superior capability in complex cloud environments.
Representation Learning with Mutual Influence of Modalities for Node Classification in Multi-Modal Heterogeneous Networks
May 12, 2025Abstract:Nowadays, numerous online platforms can be described as multi-modal heterogeneous networks (MMHNs), such as Douban's movie networks and Amazon's product review networks. Accurately categorizing nodes within these networks is crucial for analyzing the corresponding entities, which requires effective representation learning on nodes. However, existing multi-modal fusion methods often adopt either early fusion strategies which may lose the unique characteristics of individual modalities, or late fusion approaches overlooking the cross-modal guidance in GNN-based information propagation. In this paper, we propose a novel model for node classification in MMHNs, named Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network with Inter-Modal Attention (HGNN-IMA). It learns node representations by capturing the mutual influence of multiple modalities during the information propagation process, within the framework of heterogeneous graph transformer. Specifically, a nested inter-modal attention mechanism is integrated into the inter-node attention to achieve adaptive multi-modal fusion, and modality alignment is also taken into account to encourage the propagation among nodes with consistent similarities across all modalities. Moreover, an attention loss is augmented to mitigate the impact of missing modalities. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of the model in the node classification task, providing an innovative view to handle multi-modal data, especially when accompanied with network structures.
LLaVA-CMoE: Towards Continual Mixture of Experts for Large Vision-Language Models
Mar 27, 2025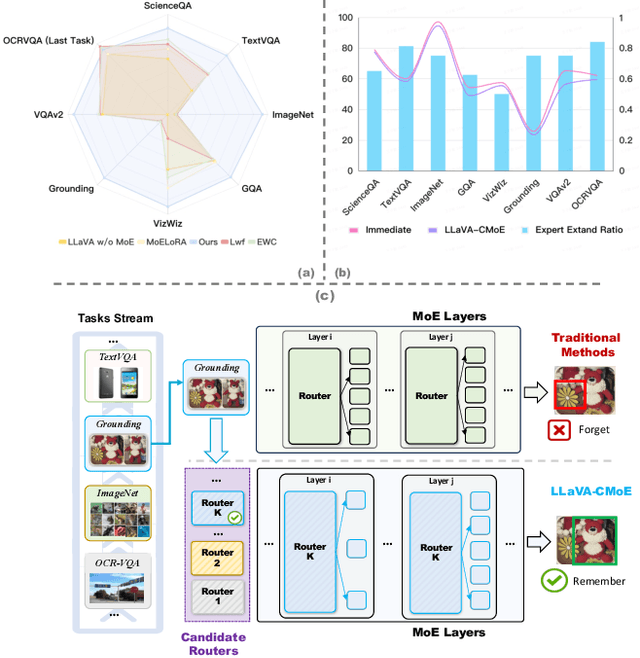
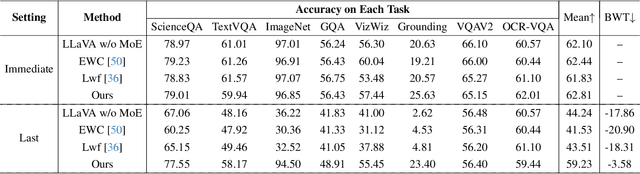
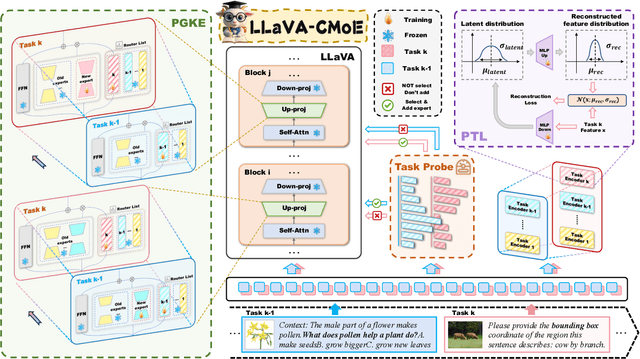
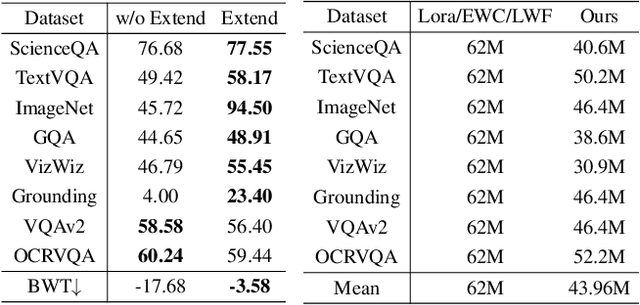
Abstract:Although applying Mixture of Experts to large language models for learning new tasks is widely regarded as an effective strategy for continuous learning, there still remain two major challenges: (1) As the number of tasks grows, simple parameter expansion strategies can lead to excessively large models. (2) Modifying the parameters of the existing router results in the erosion of previously acquired knowledge. In this paper, we present an innovative framework named LLaVA-CMoE, which is a continuous Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture without any replay data. Specifically, we have developed a method called Probe-Guided Knowledge Extension (PGKE), which employs probe experts to assess whether additional knowledge is required for a specific layer. This approach enables the model to adaptively expand its network parameters based on task distribution, thereby significantly improving the efficiency of parameter expansion. Additionally, we introduce a hierarchical routing algorithm called Probabilistic Task Locator (PTL), where high-level routing captures inter-task information and low-level routing focuses on intra-task details, ensuring that new task experts do not interfere with existing ones. Our experiments shows that our efficient architecture has substantially improved model performance on the Coin benchmark while maintaining a reasonable parameter count.
AIstorian lets AI be a historian: A KG-powered multi-agent system for accurate biography generation
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Huawei has always been committed to exploring the AI application in historical research. Biography generation, as a specialized form of abstractive summarization, plays a crucial role in historical research but faces unique challenges that existing large language models (LLMs) struggle to address. These challenges include maintaining stylistic adherence to historical writing conventions, ensuring factual fidelity, and handling fragmented information across multiple documents. We present AIstorian, a novel end-to-end agentic system featured with a knowledge graph (KG)-powered retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and anti-hallucination multi-agents. Specifically, AIstorian introduces an in-context learning based chunking strategy and a KG-based index for accurate and efficient reference retrieval. Meanwhile, AIstorian orchestrates multi-agents to conduct on-the-fly hallucination detection and error-type-aware correction. Additionally, to teach LLMs a certain language style, we finetune LLMs based on a two-step training approach combining data augmentation-enhanced supervised fine-tuning with stylistic preference optimization. Extensive experiments on a real-life historical Jinshi dataset demonstrate that AIstorian achieves a 3.8x improvement in factual accuracy and a 47.6% reduction in hallucination rate compared to existing baselines. The data and code are available at: https://github.com/ZJU-DAILY/AIstorian.
From Images to Detection: Machine Learning for Blood Pattern Classification
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:Bloodstain Pattern Analysis (BPA) helps us understand how bloodstains form, with a focus on their size, shape, and distribution. This aids in crime scene reconstruction and provides insight into victim positions and crime investigation. One challenge in BPA is distinguishing between different types of bloodstains, such as those from firearms, impacts, or other mechanisms. Our study focuses on differentiating impact spatter bloodstain patterns from gunshot bloodstain patterns. We distinguish patterns by extracting well-designed individual stain features, applying effective data consolidation methods, and selecting boosting classifiers. As a result, we have developed a model that excels in both accuracy and efficiency. In addition, we use outside data sources from previous studies to discuss the challenges and future directions for BPA.
DSGram: Dynamic Weighting Sub-Metrics for Grammatical Error Correction in the Era of Large Language Models
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Evaluating the performance of Grammatical Error Correction (GEC) models has become increasingly challenging, as large language model (LLM)-based GEC systems often produce corrections that diverge from provided gold references. This discrepancy undermines the reliability of traditional reference-based evaluation metrics. In this study, we propose a novel evaluation framework for GEC models, DSGram, integrating Semantic Coherence, Edit Level, and Fluency, and utilizing a dynamic weighting mechanism. Our framework employs the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in conjunction with large language models to ascertain the relative importance of various evaluation criteria. Additionally, we develop a dataset incorporating human annotations and LLM-simulated sentences to validate our algorithms and fine-tune more cost-effective models. Experimental results indicate that our proposed approach enhances the effectiveness of GEC model evaluations.
Optimizing Item-based Marketing Promotion Efficiency in C2C Marketplace with Dynamic Sequential Coupon Allocation Framework
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:In e-commerce platforms, coupons play a crucial role in boosting transactions. In the customer-to-customer (C2C) marketplace, ensuring the satisfaction of both buyers and sellers is essential. While buyer-focused marketing strategies often receive more attention, addressing the needs of sellers is equally important. Additionally, the existing strategies tend to optimize each promotion independently, resulting in a lack of continuity between promotions and unnecessary costs in the pursuit of short-term impact within each promotion period. We introduce a Dynamic Sequential Coupon Allocation Framework (DSCAF) to optimize item coupon allocation strategies across a series of promotions. DSCAF provides sequential recommendations for coupon configurations and timing to target items. In cases where initial suggestions do not lead to sales, it dynamically adjusts the strategy and offers subsequent solutions. It integrates two predictors for estimating the sale propensity in the current and subsequent rounds of coupon allocation, and a decision-making process to determine the coupon allocation solution. It runs iteratively until the item is sold. The goal of the framework is to maximize Return on Investment (ROI) while ensuring lift Sell-through Rate (STR) remains above a specified threshold. DSCAF aims to optimize sequential coupon efficiency with a long-term perspective rather than solely focusing on the lift achieved in each individual promotion. It has been applied for item coupon allocation in Mercari.
Stochastic Parrots or ICU Experts? Large Language Models in Critical Care Medicine: A Scoping Review
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI), large language models (LLMs) have shown strong capabilities in natural language understanding, reasoning, and generation, attracting amounts of research interest in applying LLMs to health and medicine. Critical care medicine (CCM) provides diagnosis and treatment for critically ill patients who often require intensive monitoring and interventions in intensive care units (ICUs). Can LLMs be applied to CCM? Are LLMs just like stochastic parrots or ICU experts in assisting clinical decision-making? This scoping review aims to provide a panoramic portrait of the application of LLMs in CCM. Literature in seven databases, including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL, IEEE Xplore, and ACM Digital Library, were searched from January 1, 2019, to June 10, 2024. Peer-reviewed journal and conference articles that discussed the application of LLMs in critical care settings were included. From an initial 619 articles, 24 were selected for final review. This review grouped applications of LLMs in CCM into three categories: clinical decision support, medical documentation and reporting, and medical education and doctor-patient communication. LLMs have advantages in handling unstructured data and do not require manual feature engineering. Meanwhile, applying LLMs to CCM faces challenges, including hallucinations, poor interpretability, bias and alignment challenges, and privacy and ethics issues. Future research should enhance model reliability and interpretability, integrate up-to-date medical knowledge, and strengthen privacy and ethical guidelines. As LLMs evolve, they could become key tools in CCM to help improve patient outcomes and optimize healthcare delivery. This study is the first review of LLMs in CCM, aiding researchers, clinicians, and policymakers to understand the current status and future potentials of LLMs in CCM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge