Yibo Zhang
SEE: Signal Embedding Energy for Quantifying Noise Interference in Large Audio Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) have been widely applied in real-time scenarios, such as in-car assistants and online meeting comprehension. In practice, audio inputs are often corrupted by device and environmental noise, leading to performance degradation. However, existing LALM studies on noise lack quantitative analysis and rely mainly on intuition and empirical observation, thus failing to understand practical robustness. To address this issue, we introduce Signal Embedding Energy (SEE), a method for quantifying the impact of noise intensity on LALM inputs, enabling the differentiation of LALM robustness in real-world deployments. SEE introduces a perspective based on structured activation subspaces derived from the model's internal representations, which more accurately captures its perception of noise than raw audio features. Across experiments, SEE exhibits a strong correlation with LALM performance, achieving a correlation of 0.98. Surprisingly, traditional audio denoising methods are only marginally effective for LALMs, and, in some cases, even increase SEE and impair performance. This suggests a mismatch between speech-centric denoising objectives and the noise sensitivity of modern LALMs. Therefore, we propose a mitigation strategy derived from SEE to denoise LALM inputs, outperforming existing denoising methods. This paper introduces a novel metric for noise quantification in LALMs, providing guidance for robustness improvements in real-world deployments.
Deep Learning-based Robust Autonomous Navigation of Aerial Robots in Dense Forests
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Autonomous aerial navigation in dense natural environments remains challenging due to limited visibility, thin and irregular obstacles, GNSS-denied operation, and frequent perceptual degradation. This work presents an improved deep learning-based navigation framework that integrates semantically enhanced depth encoding with neural motion-primitive evaluation for robust flight in cluttered forests. Several modules are incorporated on top of the original sevae-ORACLE algorithm to address limitations observed during real-world deployment, including lateral control for sharper maneuvering, a temporal consistency mechanism to suppress oscillatory planning decisions, a stereo-based visual-inertial odometry solution for drift-resilient state estimation, and a supervisory safety layer that filters unsafe actions in real time. A depth refinement stage is included to improve the representation of thin branches and reduce stereo noise, while GPU optimization increases onboard inference throughput from 4 Hz to 10 Hz. The proposed approach is evaluated against several existing learning-based navigation methods under identical environmental conditions and hardware constraints. It demonstrates higher success rates, more stable trajectories, and improved collision avoidance, particularly in highly cluttered forest settings. The system is deployed on a custom quadrotor in three boreal forest environments, achieving fully autonomous completion in all flights in moderate and dense clutter, and 12 out of 15 flights in highly dense underbrush. These results demonstrate improved reliability and safety over existing navigation methods in complex natural environments.
MMWiLoc: A Multi-Sensor Dataset and Robust Device-Free Localization Method Using Commercial Off-The-Shelf Millimeter Wave Wi-Fi Devices
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Device-free Wi-Fi sensing has numerous benefits in practical settings, as it eliminates the requirement for dedicated sensing devices and can be accomplished using current low-cost Wi-Fi devices. With the development of Wi-Fi standards, millimeter wave Wi-Fi devices with 60GHz operating frequency and up to 4GHz bandwidth have become commercially available. Although millimeter wave Wi-Fi presents great promise for Device-Free Wi-Fi sensing with increased bandwidth and beam-forming ability, there still lacks a method for localization using millimeter wave Wi-Fi. Here, we present two major contributions: First, we provide a comprehensive multi-sensor dataset that synchronously captures human movement data from millimeter wave Wi-Fi, 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, and millimeter wave radar sensors. This dataset enables direct performance comparisons across different sensing modalities and facilitates reproducible researches in indoor localization. Second, we introduce MMWiLoc, a novel localization method that achieves centimeter-level precision with low computational cost. MMWiLoc incorporates two components: beam pattern calibration using Expectation Maximization and target localization through Multi-Scale Compression Sensing. The system processes beam Signal-to-Noise Ratio (beamSNR) information from the beam-forming process to determine target Angle of Arrival (AoA), which is then fused across devices for localization. Our extensive evaluation demonstrates that MMWiLoc achieves centimeter-level precision, outperforming 2.4GHz Wi-Fi systems while maintaining competitive performance with high-precision radar systems. The dataset and examples processing code will be released after this paper is accepted at https://github.com/wowoyoho/MMWiLoc.
Lifelong Evolution: Collaborative Learning between Large and Small Language Models for Continuous Emergent Fake News Detection
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:The widespread dissemination of fake news on social media has significantly impacted society, resulting in serious consequences. Conventional deep learning methodologies employing small language models (SLMs) suffer from extensive supervised training requirements and difficulties adapting to evolving news environments due to data scarcity and distribution shifts. Large language models (LLMs), despite robust zero-shot capabilities, fall short in accurately detecting fake news owing to outdated knowledge and the absence of suitable demonstrations. In this paper, we propose a novel Continuous Collaborative Emergent Fake News Detection (C$^2$EFND) framework to address these challenges. The C$^2$EFND framework strategically leverages both LLMs' generalization power and SLMs' classification expertise via a multi-round collaborative learning framework. We further introduce a lifelong knowledge editing module based on a Mixture-of-Experts architecture to incrementally update LLMs and a replay-based continue learning method to ensure SLMs retain prior knowledge without retraining entirely. Extensive experiments on Pheme and Twitter16 datasets demonstrate that C$^2$EFND significantly outperforms existed methods, effectively improving detection accuracy and adaptability in continuous emergent fake news scenarios.
DecoupledGaussian: Object-Scene Decoupling for Physics-Based Interaction
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:We present DecoupledGaussian, a novel system that decouples static objects from their contacted surfaces captured in-the-wild videos, a key prerequisite for realistic Newtonian-based physical simulations. Unlike prior methods focused on synthetic data or elastic jittering along the contact surface, which prevent objects from fully detaching or moving independently, DecoupledGaussian allows for significant positional changes without being constrained by the initial contacted surface. Recognizing the limitations of current 2D inpainting tools for restoring 3D locations, our approach proposes joint Poisson fields to repair and expand the Gaussians of both objects and contacted scenes after separation. This is complemented by a multi-carve strategy to refine the object's geometry. Our system enables realistic simulations of decoupling motions, collisions, and fractures driven by user-specified impulses, supporting complex interactions within and across multiple scenes. We validate DecoupledGaussian through a comprehensive user study and quantitative benchmarks. This system enhances digital interaction with objects and scenes in real-world environments, benefiting industries such as VR, robotics, and autonomous driving. Our project page is at: https://wangmiaowei.github.io/DecoupledGaussian.github.io/.
KM-UNet KAN Mamba UNet for medical image segmentation
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:Medical image segmentation is a critical task in medical imaging analysis. Traditional CNN-based methods struggle with modeling long-range dependencies, while Transformer-based models, despite their success, suffer from quadratic computational complexity. To address these limitations, we propose KM-UNet, a novel U-shaped network architecture that combines the strengths of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) and state-space models (SSMs). KM-UNet leverages the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem for efficient feature representation and SSMs for scalable long-range modeling, achieving a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. We evaluate KM-UNet on five benchmark datasets: ISIC17, ISIC18, CVC, BUSI, and GLAS. Experimental results demonstrate that KM-UNet achieves competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in medical image segmentation tasks. To the best of our knowledge, KM-UNet is the first medical image segmentation framework integrating KANs and SSMs. This work provides a valuable baseline and new insights for the development of more efficient and interpretable medical image segmentation systems. The code is open source at https://github.com/2760613195/KM_UNet Keywords:KAN,Manba, state-space models,UNet, Medical image segmentation, Deep learning
PositionID: LLMs can Control Lengths, Copy and Paste with Explicit Positional Awareness
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive capabilities across various domains, including role-playing, creative writing, mathematical reasoning, and coding. Despite these advancements, LLMs still encounter challenges with length control, frequently failing to adhere to specific length constraints due to their token-level operations and insufficient training on data with strict length limitations. We identify this issue as stemming from a lack of positional awareness and propose novel approaches--PositionID Prompting and PositionID Fine-Tuning--to address it. These methods enhance the model's ability to continuously monitor and manage text length during generation. Additionally, we introduce PositionID CP Prompting to enable LLMs to perform copy and paste operations accurately. Furthermore, we develop two benchmarks for evaluating length control and copy-paste abilities. Our experiments demonstrate that our methods significantly improve the model's adherence to length constraints and copy-paste accuracy without compromising response quality.
MIO: A Foundation Model on Multimodal Tokens
Sep 26, 2024

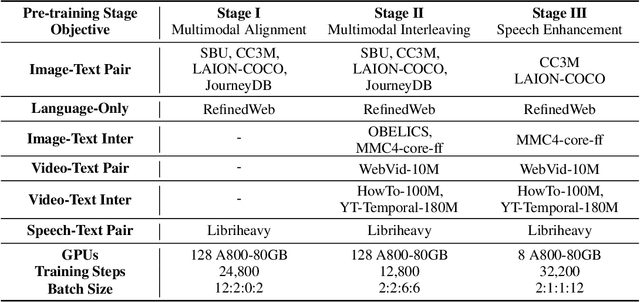

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce MIO, a novel foundation model built on multimodal tokens, capable of understanding and generating speech, text, images, and videos in an end-to-end, autoregressive manner. While the emergence of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal large language models (MM-LLMs) propels advancements in artificial general intelligence through their versatile capabilities, they still lack true any-to-any understanding and generation. Recently, the release of GPT-4o has showcased the remarkable potential of any-to-any LLMs for complex real-world tasks, enabling omnidirectional input and output across images, speech, and text. However, it is closed-source and does not support the generation of multimodal interleaved sequences. To address this gap, we present MIO, which is trained on a mixture of discrete tokens across four modalities using causal multimodal modeling. MIO undergoes a four-stage training process: (1) alignment pre-training, (2) interleaved pre-training, (3) speech-enhanced pre-training, and (4) comprehensive supervised fine-tuning on diverse textual, visual, and speech tasks. Our experimental results indicate that MIO exhibits competitive, and in some cases superior, performance compared to previous dual-modal baselines, any-to-any model baselines, and even modality-specific baselines. Moreover, MIO demonstrates advanced capabilities inherent to its any-to-any feature, such as interleaved video-text generation, chain-of-visual-thought reasoning, visual guideline generation, instructional image editing, etc.
RAG-Optimized Tibetan Tourism LLMs: Enhancing Accuracy and Personalization
Aug 21, 2024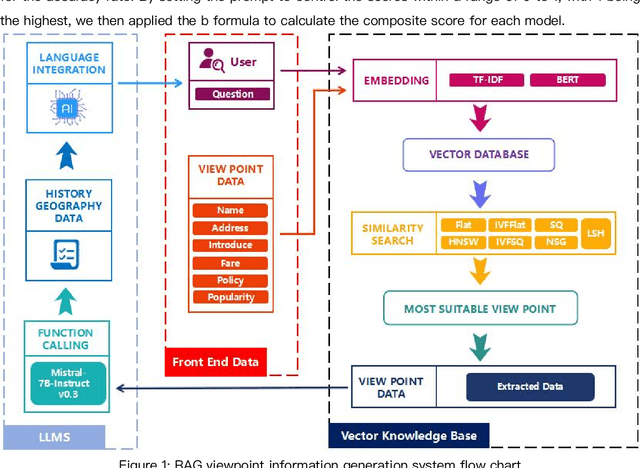
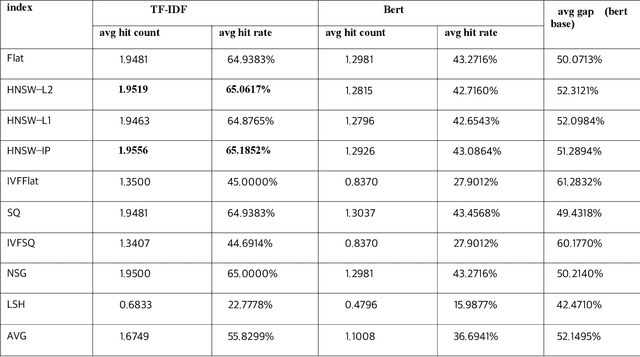
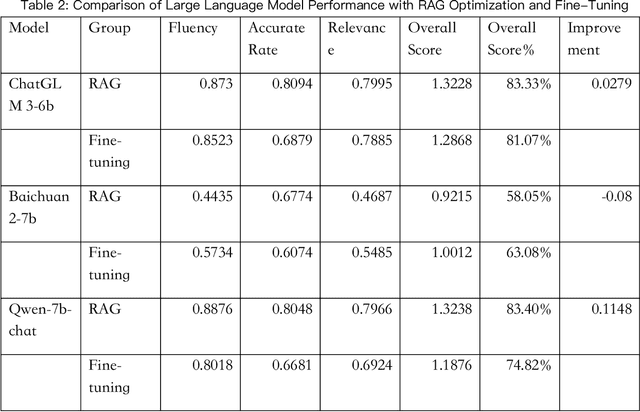
Abstract:With the development of the modern social economy, tourism has become an important way to meet people's spiritual needs, bringing development opportunities to the tourism industry. However, existing large language models (LLMs) face challenges in personalized recommendation capabilities and the generation of content that can sometimes produce hallucinations. This study proposes an optimization scheme for Tibet tourism LLMs based on retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology. By constructing a database of tourist viewpoints and processing the data using vectorization techniques, we have significantly improved retrieval accuracy. The application of RAG technology effectively addresses the hallucination problem in content generation. The optimized model shows significant improvements in fluency, accuracy, and relevance of content generation. This research demonstrates the potential of RAG technology in the standardization of cultural tourism information and data analysis, providing theoretical and technical support for the development of intelligent cultural tourism service systems.
SARA: Singular-Value Based Adaptive Low-Rank Adaption
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:With the increasing number of parameters in large pre-trained models, LoRA as a parameter-efficient fine-tuning(PEFT) method is widely used for not adding inference overhead. The LoRA method assumes that weight changes during fine-tuning can be approximated by low-rank matrices. However, the rank values need to be manually verified to match different downstream tasks, and they cannot accommodate the varying importance of different layers in the model. In this work, we first analyze the relationship between the performance of different layers and their ranks using SVD. Based on this, we design the Singular-Value Based Adaptive Low-Rank Adaption(SARA), which adaptively finds the rank during initialization by performing SVD on the pre-trained weights. Additionally, we explore the Mixture-of-SARA(Mo-SARA), which significantly reduces the number of parameters by fine-tuning only multiple parallel sets of singular values controlled by a router. Extensive experiments on various complex tasks demonstrate the simplicity and parameter efficiency of our methods. They can effectively and adaptively find the most suitable rank for each layer of each model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge