Xiaohui Liu
Quantum State Preparation via Large-Language-Model-Driven Evolution
May 09, 2025Abstract:We propose an automated framework for quantum circuit design by integrating large-language models (LLMs) with evolutionary optimization to overcome the rigidity, scalability limitations, and expert dependence of traditional ones in variational quantum algorithms. Our approach (FunSearch) autonomously discovers hardware-efficient ans\"atze with new features of scalability and system-size-independent number of variational parameters entirely from scratch. Demonstrations on the Ising and XY spin chains with n = 9 qubits yield circuits containing 4 parameters, achieving near-exact energy extrapolation across system sizes. Implementations on quantum hardware (Zuchongzhi chip) validate practicality, where two-qubit quantum gate noises can be effectively mitigated via zero-noise extrapolations for a spin chain system as large as 20 sites. This framework bridges algorithmic design and experimental constraints, complementing contemporary quantum architecture search frameworks to advance scalable quantum simulations.
Pseudo-Label Guided Real-World Image De-weathering: A Learning Framework with Imperfect Supervision
Apr 14, 2025
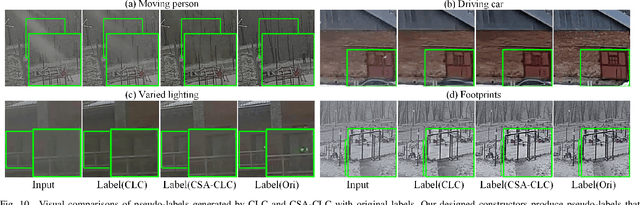
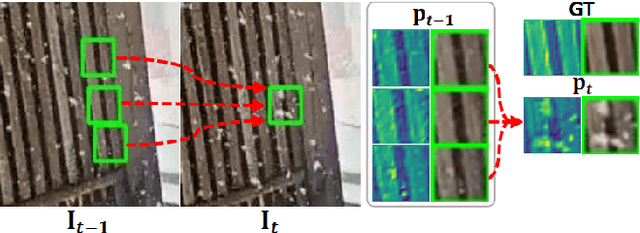
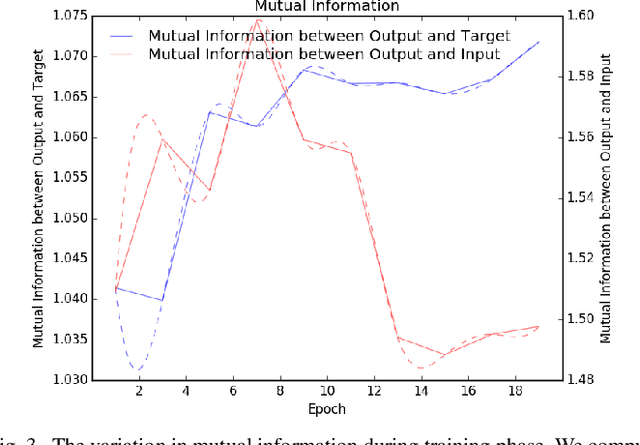
Abstract:Real-world image de-weathering aims at removingvarious undesirable weather-related artifacts, e.g., rain, snow,and fog. To this end, acquiring ideal training pairs is crucial.Existing real-world datasets are typically constructed paired databy extracting clean and degraded images from live streamsof landscape scene on the Internet. Despite the use of strictfiltering mechanisms during collection, training pairs inevitablyencounter inconsistency in terms of lighting, object position, scenedetails, etc, making de-weathering models possibly suffer fromdeformation artifacts under non-ideal supervision. In this work,we propose a unified solution for real-world image de-weatheringwith non-ideal supervision, i.e., a pseudo-label guided learningframework, to address various inconsistencies within the realworld paired dataset. Generally, it consists of a de-weatheringmodel (De-W) and a Consistent Label Constructor (CLC), bywhich restoration result can be adaptively supervised by originalground-truth image to recover sharp textures while maintainingconsistency with the degraded inputs in non-weather contentthrough the supervision of pseudo-labels. Particularly, a Crossframe Similarity Aggregation (CSA) module is deployed withinCLC to enhance the quality of pseudo-labels by exploring thepotential complementary information of multi-frames throughgraph model. Moreover, we introduce an Information AllocationStrategy (IAS) to integrate the original ground-truth imagesand pseudo-labels, thereby facilitating the joint supervision forthe training of de-weathering model. Extensive experimentsdemonstrate that our method exhibits significant advantageswhen trained on imperfectly aligned de-weathering datasets incomparison with other approaches.
AcademicGPT: Empowering Academic Research
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities across various natural language processing tasks. Yet, many of these advanced LLMs are tailored for broad, general-purpose applications. In this technical report, we introduce AcademicGPT, designed specifically to empower academic research. AcademicGPT is a continual training model derived from LLaMA2-70B. Our training corpus mainly consists of academic papers, thesis, content from some academic domain, high-quality Chinese data and others. While it may not be extensive in data scale, AcademicGPT marks our initial venture into a domain-specific GPT tailored for research area. We evaluate AcademicGPT on several established public benchmarks such as MMLU and CEval, as well as on some specialized academic benchmarks like PubMedQA, SCIEval, and our newly-created ComputerScienceQA, to demonstrate its ability from general knowledge ability, to Chinese ability, and to academic ability. Building upon AcademicGPT's foundation model, we also developed several applications catered to the academic area, including General Academic Question Answering, AI-assisted Paper Reading, Paper Review, and AI-assisted Title and Abstract Generation.
Learning Real-World Image De-Weathering with Imperfect Supervision
Oct 23, 2023
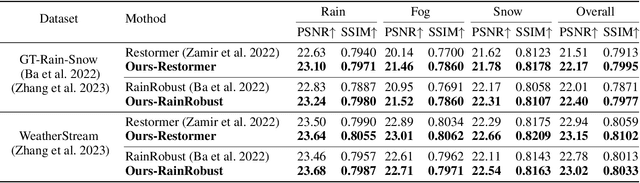
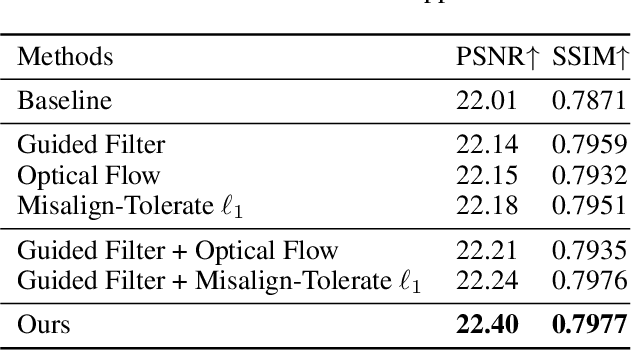
Abstract:Real-world image de-weathering aims at removing various undesirable weather-related artifacts. Owing to the impossibility of capturing image pairs concurrently, existing real-world de-weathering datasets often exhibit inconsistent illumination, position, and textures between the ground-truth images and the input degraded images, resulting in imperfect supervision. Such non-ideal supervision negatively affects the training process of learning-based de-weathering methods. In this work, we attempt to address the problem with a unified solution for various inconsistencies. Specifically, inspired by information bottleneck theory, we first develop a Consistent Label Constructor (CLC) to generate a pseudo-label as consistent as possible with the input degraded image while removing most weather-related degradations. In particular, multiple adjacent frames of the current input are also fed into CLC to enhance the pseudo-label. Then we combine the original imperfect labels and pseudo-labels to jointly supervise the de-weathering model by the proposed Information Allocation Strategy (IAS). During testing, only the de-weathering model is used for inference. Experiments on two real-world de-weathering datasets show that our method helps existing de-weathering models achieve better performance. Codes are available at https://github.com/1180300419/imperfect-deweathering.
Benchmark Dataset and Effective Inter-Frame Alignment for Real-World Video Super-Resolution
Dec 10, 2022



Abstract:Video super-resolution (VSR) aiming to reconstruct a high-resolution (HR) video from its low-resolution (LR) counterpart has made tremendous progress in recent years. However, it remains challenging to deploy existing VSR methods to real-world data with complex degradations. On the one hand, there are few well-aligned real-world VSR datasets, especially with large super-resolution scale factors, which limits the development of real-world VSR tasks. On the other hand, alignment algorithms in existing VSR methods perform poorly for real-world videos, leading to unsatisfactory results. As an attempt to address the aforementioned issues, we build a real-world 4 VSR dataset, namely MVSR4$\times$, where low- and high-resolution videos are captured with different focal length lenses of a smartphone, respectively. Moreover, we propose an effective alignment method for real-world VSR, namely EAVSR. EAVSR takes the proposed multi-layer adaptive spatial transform network (MultiAdaSTN) to refine the offsets provided by the pre-trained optical flow estimation network. Experimental results on RealVSR and MVSR4$\times$ datasets show the effectiveness and practicality of our method, and we achieve state-of-the-art performance in real-world VSR task. The dataset and code will be publicly available.
Deep Spectro-temporal Artifacts for Detecting Synthesized Speech
Oct 11, 2022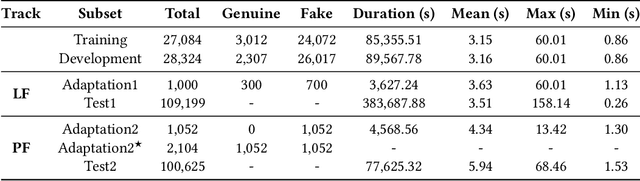
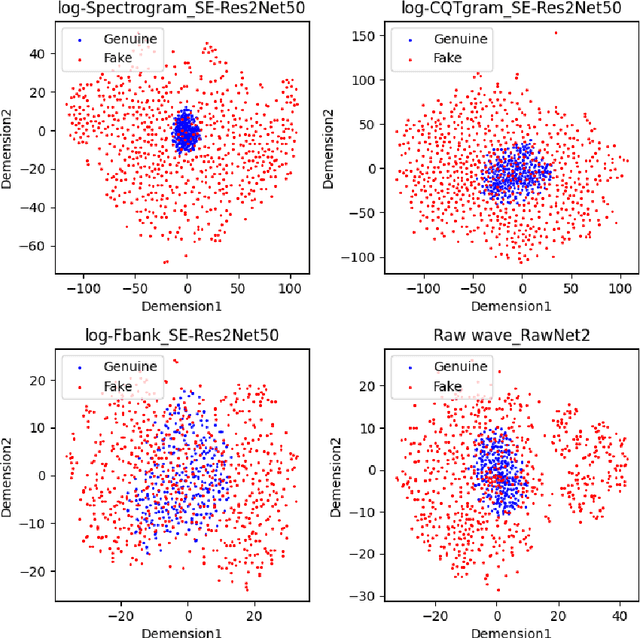
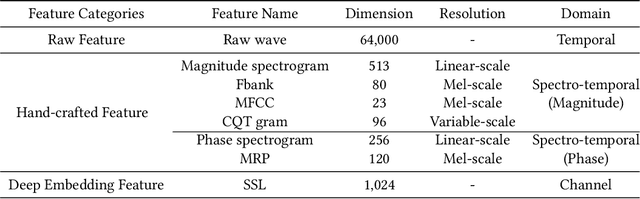
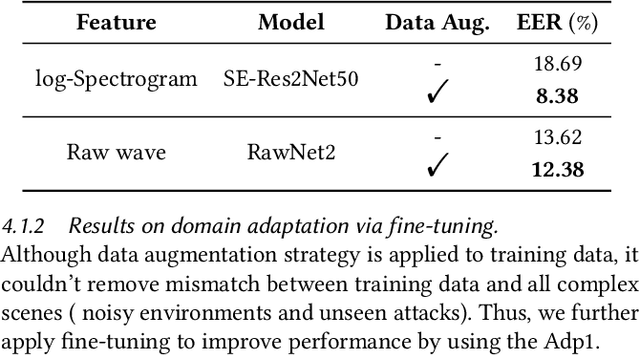
Abstract:The Audio Deep Synthesis Detection (ADD) Challenge has been held to detect generated human-like speech. With our submitted system, this paper provides an overall assessment of track 1 (Low-quality Fake Audio Detection) and track 2 (Partially Fake Audio Detection). In this paper, spectro-temporal artifacts were detected using raw temporal signals, spectral features, as well as deep embedding features. To address track 1, low-quality data augmentation, domain adaptation via finetuning, and various complementary feature information fusion were aggregated in our system. Furthermore, we analyzed the clustering characteristics of subsystems with different features by visualization method and explained the effectiveness of our proposed greedy fusion strategy. As for track 2, frame transition and smoothing were detected using self-supervised learning structure to capture the manipulation of PF attacks in the time domain. We ranked 4th and 5th in track 1 and track 2, respectively.
Symmetry-Aware Transformer-based Mirror Detection
Jul 13, 2022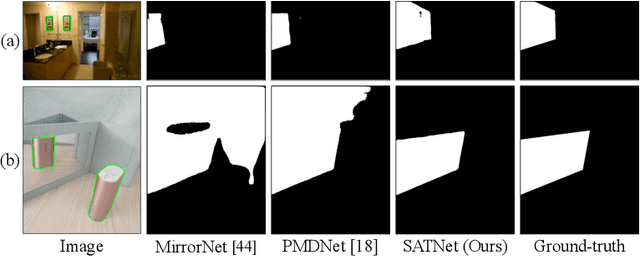
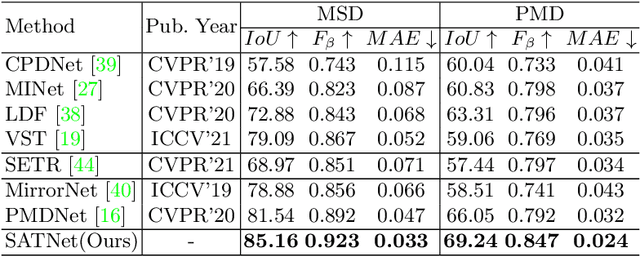
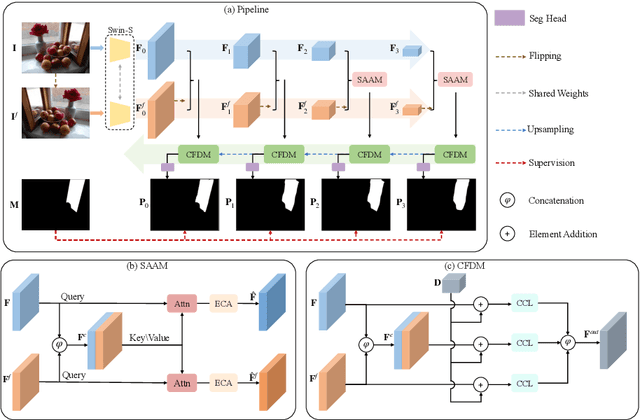
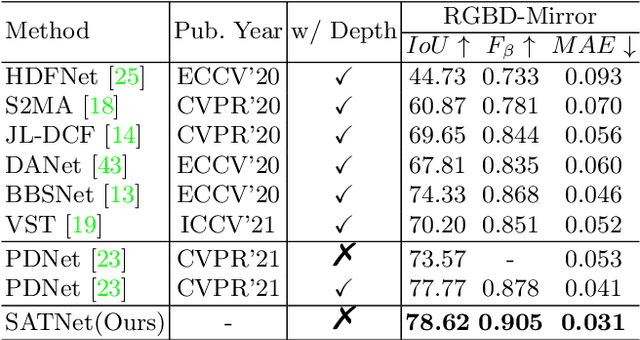
Abstract:Mirror detection aims to identify the mirror regions in the given input image. Existing works mainly focus on integrating the semantic features and structural features to mine the similarity and discontinuity between mirror and non-mirror regions, or introducing depth information to help analyze the existence of mirrors. In this work, we observe that a real object typically forms a loose symmetry relationship with its corresponding reflection in the mirror, which is beneficial in distinguishing mirrors from real objects. Based on this observation, we propose a dual-path Symmetry-Aware Transformer-based mirror detection Network (SATNet), which includes two novel modules: Symmetry-Aware Attention Module (SAAM) and Contrast and Fusion Decoder Module (CFDM). Specifically, we first introduce the transformer backbone to model global information aggregation in images, extracting multi-scale features in two paths. We then feed the high-level dual-path features to SAAMs to capture the symmetry relations. Finally, we fuse the dual-path features and refine our prediction maps progressively with CFDMs to obtain the final mirror mask. Experimental results show that SATNet outperforms both RGB and RGB-D mirror detection methods on all available mirror detection datasets.
Estimating and Mitigating the Congestion Effect of Curbside Pick-ups and Drop-offs: A Causal Inference Approach
Jun 05, 2022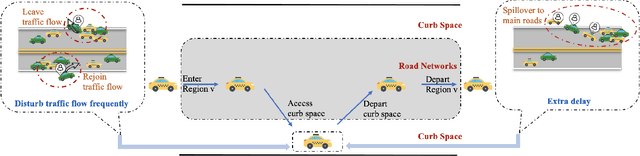
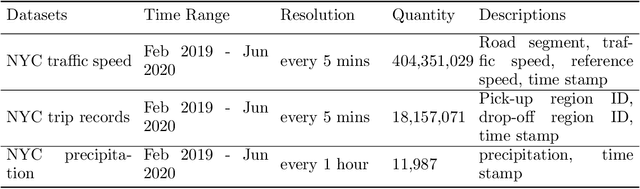
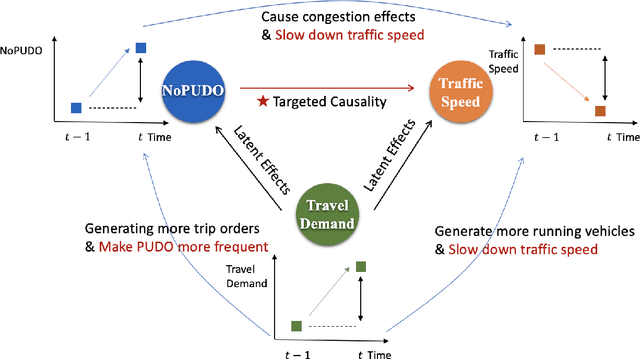
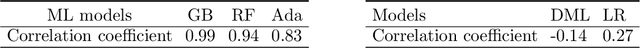
Abstract:Curb space is one of the busiest areas in urban road networks. Especially in recent years, the rapid increase of ride-hailing trips and commercial deliveries has induced massive pick-ups/drop-offs (PUDOs), which occupy the limited curb space that was designed and built decades ago. These PUDOs could jam curb utilization and disturb the mainline traffic flow, evidently leading to significant societal externalities. However, there is a lack of an analytical framework that rigorously quantifies and mitigates the congestion effect of PUDOs in the system view, particularly with little data support and involvement of confounding effects. In view of this, this paper develops a rigorous causal inference approach to estimate the congestion effect of PUDOs on general networks. A causal graph is set to represent the spatio-temporal relationship between PUDOs and traffic speed, and a double and separated machine learning (DSML) method is proposed to quantify how PUDOs affect traffic congestion. Additionally, a re-routing formulation is developed and solved to encourage passenger walking and traffic flow re-routing to achieve system optimal. Numerical experiments are conducted using real-world data in the Manhattan area. On average, 100 additional units of PUDOs in a region could reduce the traffic speed by 3.70 and 4.54 mph on weekdays and weekends, respectively. Re-routing trips with PUDOs on curbs could respectively reduce the system-wide total travel time by 2.44\% and 2.12\% in Midtown and Central Park on weekdays. Sensitivity analysis is also conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed framework.
An Effective and Efficient Evolutionary Algorithm for Many-Objective Optimization
May 31, 2022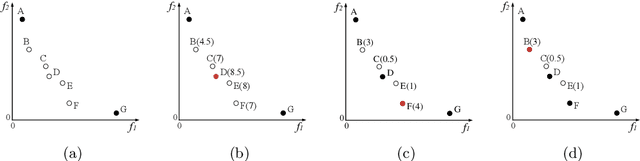
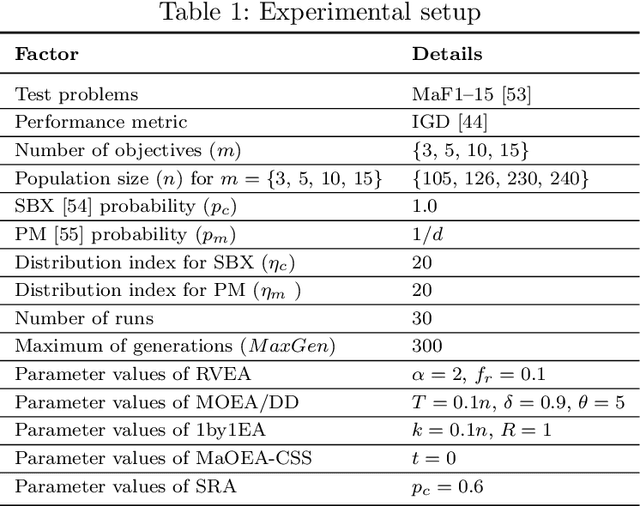
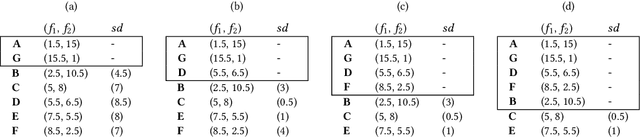
Abstract:In evolutionary multi-objective optimization, effectiveness refers to how an evolutionary algorithm performs in terms of converging its solutions into the Pareto front and also diversifying them over the front. This is not an easy job, particularly for optimization problems with more than three objectives, dubbed many-objective optimization problems. In such problems, classic Pareto-based algorithms fail to provide sufficient selection pressure towards the Pareto front, whilst recently developed algorithms, such as decomposition-based ones, may struggle to maintain a set of well-distributed solutions on certain problems (e.g., those with irregular Pareto fronts). Another issue in some many-objective optimizers is rapidly increasing computational requirement with the number of objectives, such as hypervolume-based algorithms and shift-based density estimation (SDE) methods. In this paper, we aim to address this problem and develop an effective and efficient evolutionary algorithm (E3A) that can handle various many-objective problems. In E3A, inspired by SDE, a novel population maintenance method is proposed. We conduct extensive experiments and show that E3A performs better than 11 state-of-the-art many-objective evolutionary algorithms in quickly finding a set of well-converged and well-diversified solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge