Wanming Yu
Dynamic Robot Systems, Oxford Robotics Institute, University of Oxford
Reference Free Platform Adaptive Locomotion for Quadrupedal Robots using a Dynamics Conditioned Policy
May 21, 2025Abstract:This article presents Platform Adaptive Locomotion (PAL), a unified control method for quadrupedal robots with different morphologies and dynamics. We leverage deep reinforcement learning to train a single locomotion policy on procedurally generated robots. The policy maps proprioceptive robot state information and base velocity commands into desired joint actuation targets, which are conditioned using a latent embedding of the temporally local system dynamics. We explore two conditioning strategies - one using a GRU-based dynamics encoder and another using a morphology-based property estimator - and show that morphology-aware conditioning outperforms temporal dynamics encoding regarding velocity task tracking for our hardware test on ANYmal C. Our results demonstrate that both approaches achieve robust zero-shot transfer across multiple unseen simulated quadrupeds. Furthermore, we demonstrate the need for careful robot reference modelling during training, enabling us to reduce the velocity tracking error by up to 30% compared to the baseline method. Despite PAL not surpassing the best-performing reference-free controller in all cases, our analysis uncovers critical design choices and informs improvements to the state of the art.
Improving Trajectory Stitching with Flow Models
May 12, 2025Abstract:Generative models have shown great promise as trajectory planners, given their affinity to modeling complex distributions and guidable inference process. Previous works have successfully applied these in the context of robotic manipulation but perform poorly when the required solution does not exist as a complete trajectory within the training set. We identify that this is a result of being unable to plan via stitching, and subsequently address the architectural and dataset choices needed to remedy this. On top of this, we propose a novel addition to the training and inference procedures to both stabilize and enhance these capabilities. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach by generating plans with out of distribution boundary conditions and performing obstacle avoidance on the Franka Panda in simulation and on real hardware. In both of these tasks our method performs significantly better than the baselines and is able to avoid obstacles up to four times as large.
Discovery of skill switching criteria for learning agile quadruped locomotion
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:This paper develops a hierarchical learning and optimization framework that can learn and achieve well-coordinated multi-skill locomotion. The learned multi-skill policy can switch between skills automatically and naturally in tracking arbitrarily positioned goals and recover from failures promptly. The proposed framework is composed of a deep reinforcement learning process and an optimization process. First, the contact pattern is incorporated into the reward terms for learning different types of gaits as separate policies without the need for any other references. Then, a higher level policy is learned to generate weights for individual policies to compose multi-skill locomotion in a goal-tracking task setting. Skills are automatically and naturally switched according to the distance to the goal. The proper distances for skill switching are incorporated in reward calculation for learning the high level policy and updated by an outer optimization loop as learning progresses. We first demonstrated successful multi-skill locomotion in comprehensive tasks on a simulated Unitree A1 quadruped robot. We also deployed the learned policy in the real world showcasing trotting, bounding, galloping, and their natural transitions as the goal position changes. Moreover, the learned policy can react to unexpected failures at any time, perform prompt recovery, and resume locomotion successfully. Compared to discrete switch between single skills which failed to transition to galloping in the real world, our proposed approach achieves all the learned agile skills, with smoother and more continuous skill transitions.
Offline Adaptation of Quadruped Locomotion using Diffusion Models
Nov 13, 2024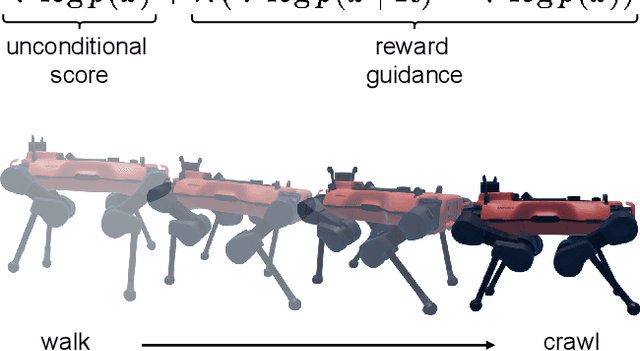
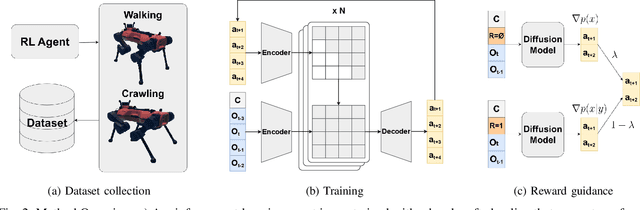
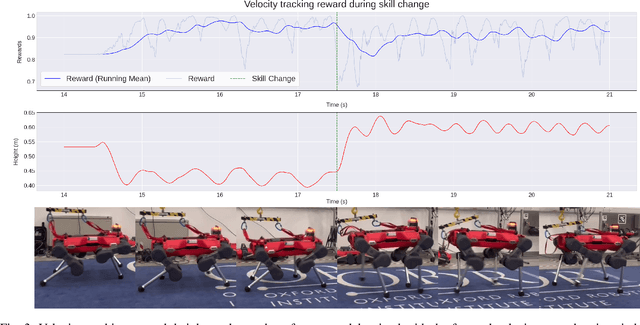
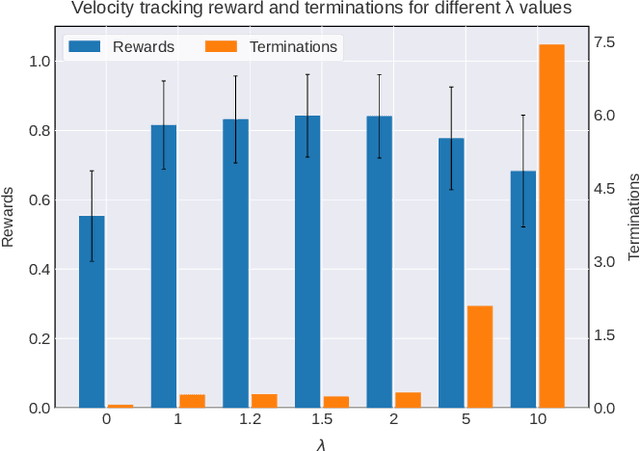
Abstract:We present a diffusion-based approach to quadrupedal locomotion that simultaneously addresses the limitations of learning and interpolating between multiple skills and of (modes) offline adapting to new locomotion behaviours after training. This is the first framework to apply classifier-free guided diffusion to quadruped locomotion and demonstrate its efficacy by extracting goal-conditioned behaviour from an originally unlabelled dataset. We show that these capabilities are compatible with a multi-skill policy and can be applied with little modification and minimal compute overhead, i.e., running entirely on the robots onboard CPU. We verify the validity of our approach with hardware experiments on the ANYmal quadruped platform.
Constrained Skill Discovery: Quadruped Locomotion with Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning
Oct 10, 2024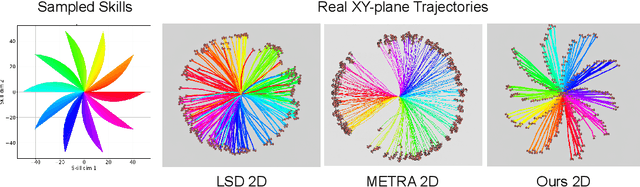
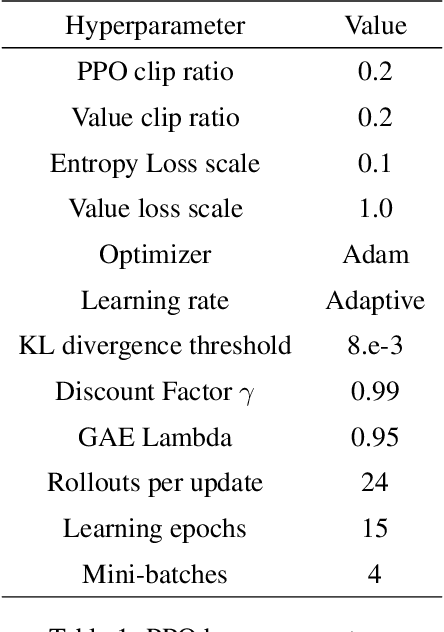
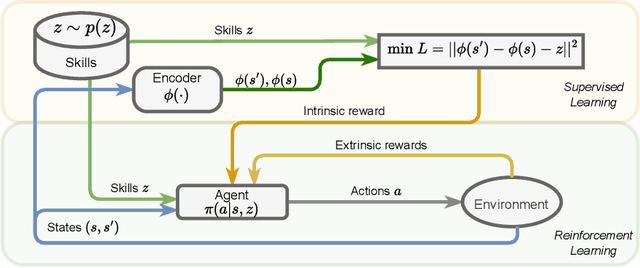
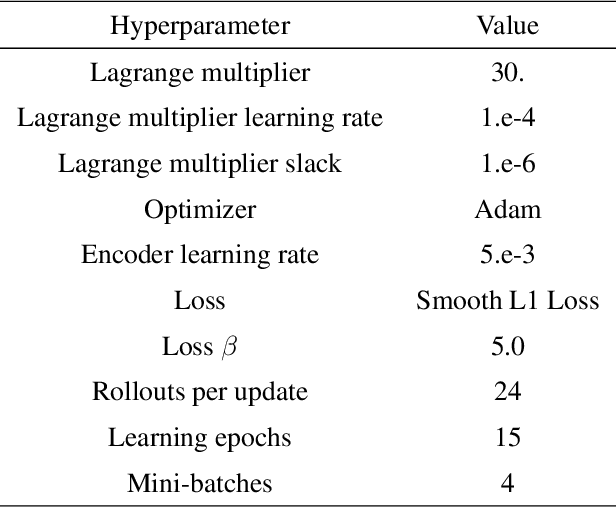
Abstract:Representation learning and unsupervised skill discovery can allow robots to acquire diverse and reusable behaviors without the need for task-specific rewards. In this work, we use unsupervised reinforcement learning to learn a latent representation by maximizing the mutual information between skills and states subject to a distance constraint. Our method improves upon prior constrained skill discovery methods by replacing the latent transition maximization with a norm-matching objective. This not only results in a much a richer state space coverage compared to baseline methods, but allows the robot to learn more stable and easily controllable locomotive behaviors. We successfully deploy the learned policy on a real ANYmal quadruped robot and demonstrate that the robot can accurately reach arbitrary points of the Cartesian state space in a zero-shot manner, using only an intrinsic skill discovery and standard regularization rewards.
Learning Fine Pinch-Grasp Skills using Tactile Sensing from Real Demonstration Data
Jul 10, 2023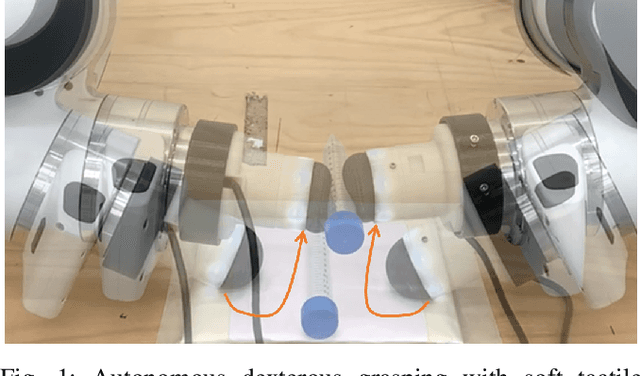
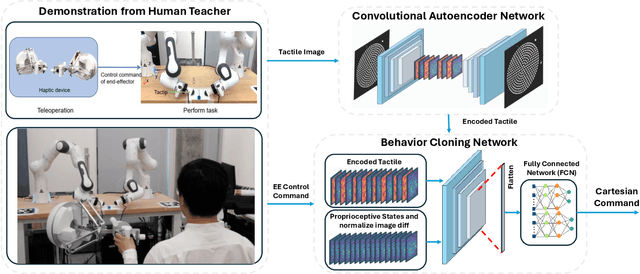
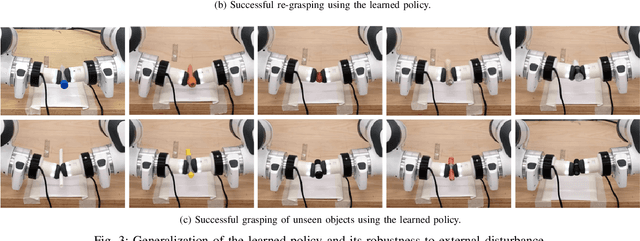
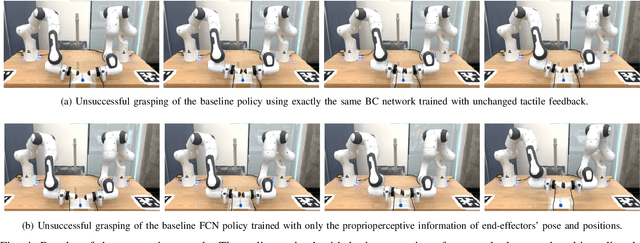
Abstract:This work develops a data-efficient learning from demonstration framework which exploits the use of rich tactile sensing and achieves fine dexterous bimanual manipulation. Specifically, we formulated a convolutional autoencoder network that can effectively extract and encode high-dimensional tactile information. Further, we developed a behaviour cloning network that can learn human-like sensorimotor skills demonstrated directly on the robot hardware in the task space by fusing both proprioceptive and tactile feedback. Our comparison study with the baseline method revealed the effectiveness of the contact information, which enabled successful extraction and replication of the demonstrated motor skills. Extensive experiments on real dual-arm robots demonstrated the robustness and effectiveness of the fine pinch grasp policy directly learned from one-shot demonstration, including grasping of the same object with different initial poses, generalizing to ten unseen new objects, robust and firm grasping against external pushes, as well as contact-aware and reactive re-grasping in case of dropping objects under very large perturbations. Moreover, the saliency map method is employed to describe the weight distribution across various modalities during pinch grasping. The video is available online at: \href{https://youtu.be/4Pg29bUBKqs}{https://youtu.be/4Pg29bUBKqs}.
Identifying Important Sensory Feedback for Learning Locomotion Skills
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Robot motor skills can be learned through deep reinforcement learning (DRL) by neural networks as state-action mappings. While the selection of state observations is crucial, there has been a lack of quantitative analysis to date. Here, we present a systematic saliency analysis that quantitatively evaluates the relative importance of different feedback states for motor skills learned through DRL. Our approach can identify the most essential feedback states for locomotion skills, including balance recovery, trotting, bounding, pacing and galloping. By using only key states including joint positions, gravity vector, base linear and angular velocities, we demonstrate that a simulated quadruped robot can achieve robust performance in various test scenarios across these distinct skills. The benchmarks using task performance metrics show that locomotion skills learned with key states can achieve comparable performance to those with all states, and the task performance or learning success rate will drop significantly if key states are missing. This work provides quantitative insights into the relationship between state observations and specific types of motor skills, serving as a guideline for robot motor learning. The proposed method is applicable to differentiable state-action mapping, such as neural network based control policies, enabling the learning of a wide range of motor skills with minimal sensing dependencies.
Accessibility-Based Clustering for Efficient Learning of Robot Fall Recovery
Sep 23, 2021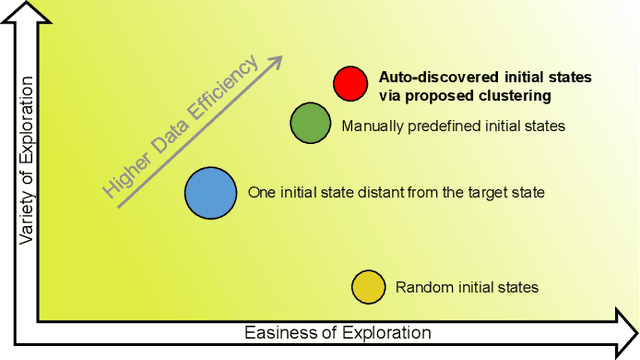
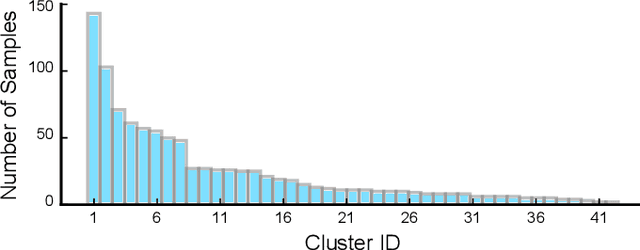
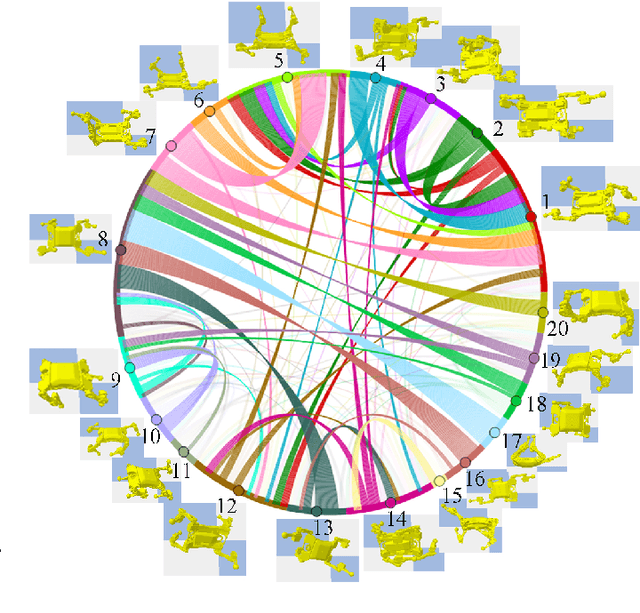
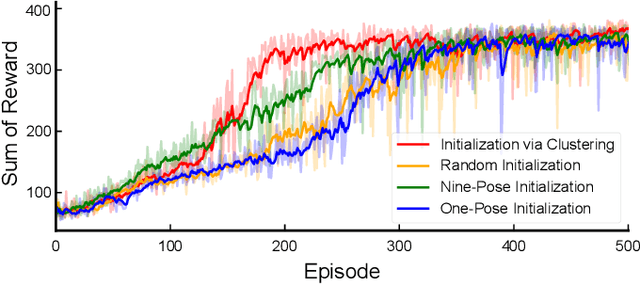
Abstract:For the model-free deep reinforcement learning of quadruped fall recovery, the initialization of robot configurations is crucial to the data efficiency and robustness. This work focuses on algorithmic improvements of data efficiency and robustness simultaneously through automatic discovery of initial states, which is achieved by our proposed K-Access algorithm based on accessibility metrics. Specifically, we formulated accessibility metrics to measure the difficulty of transitions between two arbitrary states, and proposed a novel K-Access algorithm for state-space clustering that automatically discovers the centroids of the static-pose clusters based on the accessibility metrics. By using the discovered centroidal static poses as initial states, we improve the data efficiency by reducing the redundant exploration, and enhance the robustness by easy explorations from the centroids to sampled static poses. We studied extensive validation using an 8-DOF quadrupedal robot Bittle. Compared to random initialization, the learning curve of our proposed method converges much faster, requiring only around 60% of training episodes. With our method, the robot can successfully recover standing poses in 99.4% of tests within 3 seconds.
Multi-expert learning of adaptive legged locomotion
Dec 10, 2020Abstract:Achieving versatile robot locomotion requires motor skills which can adapt to previously unseen situations. We propose a Multi-Expert Learning Architecture (MELA) that learns to generate adaptive skills from a group of representative expert skills. During training, MELA is first initialised by a distinct set of pre-trained experts, each in a separate deep neural network (DNN). Then by learning the combination of these DNNs using a Gating Neural Network (GNN), MELA can acquire more specialised experts and transitional skills across various locomotion modes. During runtime, MELA constantly blends multiple DNNs and dynamically synthesises a new DNN to produce adaptive behaviours in response to changing situations. This approach leverages the advantages of trained expert skills and the fast online synthesis of adaptive policies to generate responsive motor skills during the changing tasks. Using a unified MELA framework, we demonstrated successful multi-skill locomotion on a real quadruped robot that performed coherent trotting, steering, and fall recovery autonomously, and showed the merit of multi-expert learning generating behaviours which can adapt to unseen scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge