Kai Yuan
Unifying Ranking and Generation in Query Auto-Completion via Retrieval-Augmented Generation and Multi-Objective Alignment
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Query Auto-Completion (QAC) suggests query completions as users type, helping them articulate intent and reach results more efficiently. Existing approaches face fundamental challenges: traditional retrieve-and-rank pipelines have limited long-tail coverage and require extensive feature engineering, while recent generative methods suffer from hallucination and safety risks. We present a unified framework that reformulates QAC as end-to-end list generation through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and multi-objective Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). Our approach combines three key innovations: (1) reformulating QAC as end-to-end list generation with multi-objective optimization; (2) defining and deploying a suite of rule-based, model-based, and LLM-as-judge verifiers for QAC, and using them in a comprehensive methodology that combines RAG, multi-objective DPO, and iterative critique-revision for high-quality synthetic data; (3) a hybrid serving architecture enabling efficient production deployment under strict latency constraints. Evaluation on a large-scale commercial search platform demonstrates substantial improvements: offline metrics show gains across all dimensions, human evaluation yields +0.40 to +0.69 preference scores, and a controlled online experiment achieves 5.44\% reduction in keystrokes and 3.46\% increase in suggestion adoption, validating that unified generation with RAG and multi-objective alignment provides an effective solution for production QAC. This work represents a paradigm shift to end-to-end generation powered by large language models, RAG, and multi-objective alignment, establishing a production-validated framework that can benefit the broader search and recommendation industry.
Best-of-Q: Improving VLM agents with Q-function Action Ranking at Inference
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have become powerful backbones for agents to autonomously operate in digital environments like the web and operating systems. However, these models suffer from inadaptability to fast-changing environments like the web, which can be alleviated by fine-tuning requiring expansive model training and data collection. In this work, we introduce a novel paradigm for enhancing agentic VLM policies at inference without policy retraining. Fundamentally, our approach decouples the VLM's role as a high-capacity action proposer from the final action selection mechanism. We keep the VLM policy frozen and use it to generate a set of candidate actions for a given state. Then, a lightweight, offline-trained Q-function reranks these candidates, and the agent executes the action with the highest estimated value. The main contribution is to apply the Q-function directly during inference for immediate policy improvement, and not offline to relabel data for policy retraining. We demonstrate on the academic WebVoyager benchmark that our method significantly boosts agent success rates, improving a Qwen2.5-VL-7B agent from 38.8% to 55.7% and a proprietary GPT-4.1 agent from 82.4% to 88.8%.
Adaptive Source-Channel Coding for Semantic Communications
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Semantic communications (SemComs) have emerged as a promising paradigm for joint data and task-oriented transmissions, combining the demands for both the bit-accurate delivery and end-to-end (E2E) distortion minimization. However, current joint source-channel coding (JSCC) in SemComs is not compatible with the existing communication systems and cannot adapt to the variations of the sources or the channels, while separate source-channel coding (SSCC) is suboptimal in the finite blocklength regime. To address these issues, we propose an adaptive source-channel coding (ASCC) scheme for SemComs over parallel Gaussian channels, where the deep neural network (DNN)-based semantic source coding and conventional digital channel coding are separately deployed and adaptively designed. To enable efficient adaptation between the source and channel coding, we first approximate the E2E data and semantic distortions as functions of source coding rate and bit error ratio (BER) via logistic regression, where BER is further modeled as functions of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and channel coding rate. Then, we formulate the weighted sum E2E distortion minimization problem for joint source-channel coding rate and power allocation over parallel channels, which is solved by the successive convex approximation. Finally, simulation results demonstrate that the proposed ASCC scheme outperforms typical deep JSCC and SSCC schemes for both the single- and parallel-channel scenarios while maintaining full compatibility with practical digital systems.
Generating Physically Realistic and Directable Human Motions from Multi-Modal Inputs
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:This work focuses on generating realistic, physically-based human behaviors from multi-modal inputs, which may only partially specify the desired motion. For example, the input may come from a VR controller providing arm motion and body velocity, partial key-point animation, computer vision applied to videos, or even higher-level motion goals. This requires a versatile low-level humanoid controller that can handle such sparse, under-specified guidance, seamlessly switch between skills, and recover from failures. Current approaches for learning humanoid controllers from demonstration data capture some of these characteristics, but none achieve them all. To this end, we introduce the Masked Humanoid Controller (MHC), a novel approach that applies multi-objective imitation learning on augmented and selectively masked motion demonstrations. The training methodology results in an MHC that exhibits the key capabilities of catch-up to out-of-sync input commands, combining elements from multiple motion sequences, and completing unspecified parts of motions from sparse multimodal input. We demonstrate these key capabilities for an MHC learned over a dataset of 87 diverse skills and showcase different multi-modal use cases, including integration with planning frameworks to highlight MHC's ability to solve new user-defined tasks without any finetuning.
AHSG: Adversarial Attacks on High-level Semantics in Graph Neural Networks
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have garnered significant interest among researchers due to their impressive performance in graph learning tasks. However, like other deep neural networks, GNNs are also vulnerable to adversarial attacks. In existing adversarial attack methods for GNNs, the metric between the attacked graph and the original graph is usually the attack budget or a measure of global graph properties. However, we have found that it is possible to generate attack graphs that disrupt the primary semantics even within these constraints. To address this problem, we propose a Adversarial Attacks on High-level Semantics in Graph Neural Networks (AHSG), which is a graph structure attack model that ensures the retention of primary semantics. The latent representations of each node can extract rich semantic information by applying convolutional operations on graph data. These representations contain both task-relevant primary semantic information and task-irrelevant secondary semantic information. The latent representations of same-class nodes with the same primary semantics can fulfill the objective of modifying secondary semantics while preserving the primary semantics. Finally, the latent representations with attack effects is mapped to an attack graph using Projected Gradient Descent (PGD) algorithm. By attacking graph deep learning models with some advanced defense strategies, we validate that AHSG has superior attack effectiveness compared to other attack methods. Additionally, we employ Contextual Stochastic Block Models (CSBMs) as a proxy for the primary semantics to detect the attacked graph, confirming that AHSG almost does not disrupt the original primary semantics of the graph.
Can Large Language Models Logically Predict Myocardial Infarction? Evaluation based on UK Biobank Cohort
Sep 22, 2024Abstract:Background: Large language models (LLMs) have seen extraordinary advances with applications in clinical decision support. However, high-quality evidence is urgently needed on the potential and limitation of LLMs in providing accurate clinical decisions based on real-world medical data. Objective: To evaluate quantitatively whether universal state-of-the-art LLMs (ChatGPT and GPT-4) can predict the incidence risk of myocardial infarction (MI) with logical inference, and to further make comparison between various models to assess the performance of LLMs comprehensively. Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, 482,310 participants recruited from 2006 to 2010 were initially included in UK Biobank database and later on resampled into a final cohort of 690 participants. For each participant, tabular data of the risk factors of MI were transformed into standardized textual descriptions for ChatGPT recognition. Responses were generated by asking ChatGPT to select a score ranging from 0 to 10 representing the risk. Chain of Thought (CoT) questioning was used to evaluate whether LLMs make prediction logically. The predictive performance of ChatGPT was compared with published medical indices, traditional machine learning models and other large language models. Conclusions: Current LLMs are not ready to be applied in clinical medicine fields. Future medical LLMs are suggested to be expert in medical domain knowledge to understand both natural languages and quantified medical data, and further make logical inferences.
IENE: Identifying and Extrapolating the Node Environment for Out-of-Distribution Generalization on Graphs
Jun 02, 2024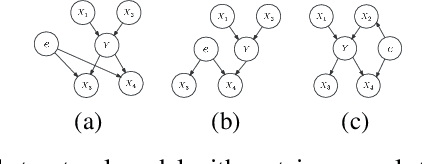
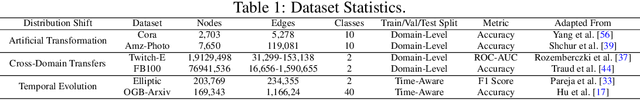
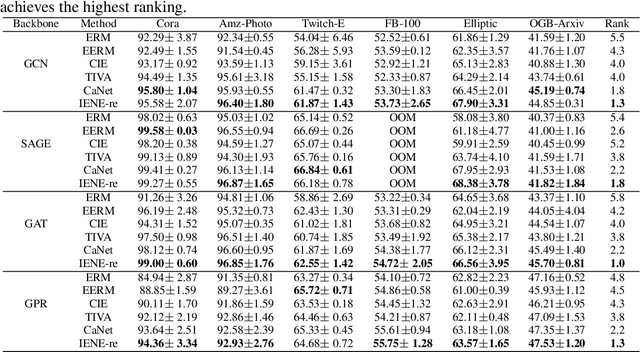
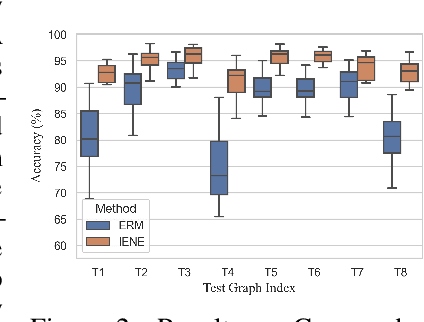
Abstract:Due to the performance degradation of graph neural networks (GNNs) under distribution shifts, the work on out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization on graphs has received widespread attention. A novel perspective involves distinguishing potential confounding biases from different environments through environmental identification, enabling the model to escape environmentally-sensitive correlations and maintain stable performance under distribution shifts. However, in graph data, confounding factors not only affect the generation process of node features but also influence the complex interaction between nodes. We observe that neglecting either aspect of them will lead to a decrease in performance. In this paper, we propose IENE, an OOD generalization method on graphs based on node-level environmental identification and extrapolation techniques. It strengthens the model's ability to extract invariance from two granularities simultaneously, leading to improved generalization. Specifically, to identify invariance in features, we utilize the disentangled information bottleneck framework to achieve mutual promotion between node-level environmental estimation and invariant feature learning. Furthermore, we extrapolate topological environments through graph augmentation techniques to identify structural invariance. We implement the conceptual method with specific algorithms and provide theoretical analysis and proofs for our approach. Extensive experimental evaluations on two synthetic and four real-world OOD datasets validate the superiority of IENE, which outperforms existing techniques and provides a flexible framework for enhancing the generalization of GNNs.
Video-Language Critic: Transferable Reward Functions for Language-Conditioned Robotics
May 30, 2024Abstract:Natural language is often the easiest and most convenient modality for humans to specify tasks for robots. However, learning to ground language to behavior typically requires impractical amounts of diverse, language-annotated demonstrations collected on each target robot. In this work, we aim to separate the problem of what to accomplish from how to accomplish it, as the former can benefit from substantial amounts of external observation-only data, and only the latter depends on a specific robot embodiment. To this end, we propose Video-Language Critic, a reward model that can be trained on readily available cross-embodiment data using contrastive learning and a temporal ranking objective, and use it to score behavior traces from a separate reinforcement learning actor. When trained on Open X-Embodiment data, our reward model enables 2x more sample-efficient policy training on Meta-World tasks than a sparse reward only, despite a significant domain gap. Using in-domain data but in a challenging task generalization setting on Meta-World, we further demonstrate more sample-efficient training than is possible with prior language-conditioned reward models that are either trained with binary classification, use static images, or do not leverage the temporal information present in video data.
Fully-fused Multi-Layer Perceptrons on Intel Data Center GPUs
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a SYCL implementation of Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs), which targets and is optimized for the Intel Data Center GPU Max 1550. To increase the performance, our implementation minimizes the slow global memory accesses by maximizing the data reuse within the general register file and the shared local memory by fusing the operations in each layer of the MLP. We show with a simple roofline model that this results in a significant increase in the arithmetic intensity, leading to improved performance, especially for inference. We compare our approach to a similar CUDA implementation for MLPs and show that our implementation on the Intel Data Center GPU outperforms the CUDA implementation on Nvidia's H100 GPU by a factor up to 2.84 in inference and 1.75 in training. The paper also showcases the efficiency of our SYCL implementation in three significant areas: Image Compression, Neural Radiance Fields, and Physics-Informed Machine Learning. In all cases, our implementation outperforms the off-the-shelf Intel Extension for PyTorch (IPEX) implementation on the same Intel GPU by up to a factor of 30 and the CUDA PyTorch version on Nvidia's H100 GPU by up to a factor 19. The code can be found at https://github.com/intel/tiny-dpcpp-nn.
D$^2$-JSCC: Digital Deep Joint Source-channel Coding for Semantic Communications
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Semantic communications (SemCom) have emerged as a new paradigm for supporting sixth-generation applications, where semantic features of data are transmitted using artificial intelligence algorithms to attain high communication efficiencies. Most existing SemCom techniques utilize deep neural networks (DNNs) to implement analog source-channel mappings, which are incompatible with existing digital communication architectures. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel framework of digital deep joint source-channel coding (D$^2$-JSCC) targeting image transmission in SemCom. The framework features digital source and channel codings that are jointly optimized to reduce the end-to-end (E2E) distortion. First, deep source coding with an adaptive density model is designed to encode semantic features according to their distributions. Second, digital channel coding is employed to protect encoded features against channel distortion. To facilitate their joint design, the E2E distortion is characterized as a function of the source and channel rates via the analysis of the Bayesian model and Lipschitz assumption on the DNNs. Then to minimize the E2E distortion, a two-step algorithm is proposed to control the source-channel rates for a given channel signal-to-noise ratio. Simulation results reveal that the proposed framework outperforms classic deep JSCC and mitigates the cliff and leveling-off effects, which commonly exist for separation-based approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge