Vishal Patel
PosSAM: Panoptic Open-vocabulary Segment Anything
Mar 14, 2024
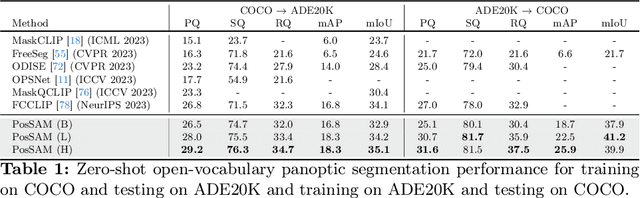
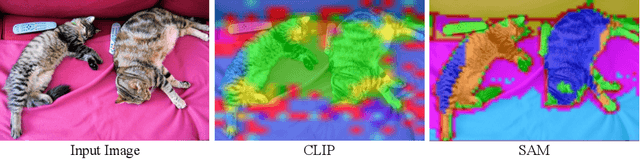
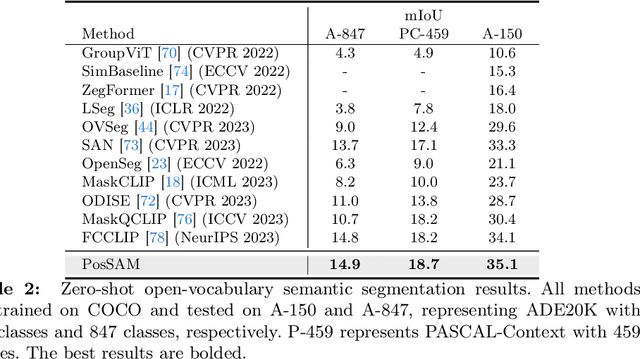
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce an open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation model that effectively unifies the strengths of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) with the vision-language CLIP model in an end-to-end framework. While SAM excels in generating spatially-aware masks, it's decoder falls short in recognizing object class information and tends to oversegment without additional guidance. Existing approaches address this limitation by using multi-stage techniques and employing separate models to generate class-aware prompts, such as bounding boxes or segmentation masks. Our proposed method, PosSAM is an end-to-end model which leverages SAM's spatially rich features to produce instance-aware masks and harnesses CLIP's semantically discriminative features for effective instance classification. Specifically, we address the limitations of SAM and propose a novel Local Discriminative Pooling (LDP) module leveraging class-agnostic SAM and class-aware CLIP features for unbiased open-vocabulary classification. Furthermore, we introduce a Mask-Aware Selective Ensembling (MASE) algorithm that adaptively enhances the quality of generated masks and boosts the performance of open-vocabulary classification during inference for each image. We conducted extensive experiments to demonstrate our methods strong generalization properties across multiple datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance with substantial improvements over SOTA open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation methods. In both COCO to ADE20K and ADE20K to COCO settings, PosSAM outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods by a large margin, 2.4 PQ and 4.6 PQ, respectively. Project Website: https://vibashan.github.io/possam-web/.
Self-Supervised MRI Reconstruction with Unrolled Diffusion Models
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) produces excellent soft tissue contrast, albeit it is an inherently slow imaging modality. Promising deep learning methods have recently been proposed to reconstruct accelerated MRI scans. However, existing methods still suffer from various limitations regarding image fidelity, contextual sensitivity, and reliance on fully-sampled acquisitions for model training. To comprehensively address these limitations, we propose a novel self-supervised deep reconstruction model, named Self-Supervised Diffusion Reconstruction (SSDiffRecon). SSDiffRecon expresses a conditional diffusion process as an unrolled architecture that interleaves cross-attention transformers for reverse diffusion steps with data-consistency blocks for physics-driven processing. Unlike recent diffusion methods for MRI reconstruction, a self-supervision strategy is adopted to train SSDiffRecon using only undersampled k-space data. Comprehensive experiments on public brain MR datasets demonstrates the superiority of SSDiffRecon against state-of-the-art supervised, and self-supervised baselines in terms of reconstruction speed and quality. Implementation will be available at https://github.com/yilmazkorkmaz1/SSDiffRecon.
Trends in Workplace Wearable Technologies and Connected-Worker Solutions for Next-Generation Occupational Safety, Health, and Productivity
May 24, 2022Abstract:The workplace influences the safety, health, and productivity of workers at multiple levels. To protect and promote total worker health, smart hardware, and software tools have emerged for the identification, elimination, substitution, and control of occupational hazards. Wearable devices enable constant monitoring of individual workers and the environment, whereas connected worker solutions provide contextual information and decision support. Here, the recent trends in commercial workplace technologies to monitor and manage occupational risks, injuries, accidents, and diseases are reviewed. Workplace safety wearables for safe lifting, ergonomics, hazard identification, sleep monitoring, fatigue management, and heat and cold stress are discussed. Examples of workplace productivity wearables for asset tracking, augmented reality, gesture and motion control, brain wave sensing, and work stress management are given. Workplace health wearables designed for work-related musculoskeletal disorders, functional movement disorders, respiratory hazards, cardiovascular health, outdoor sun exposure, and continuous glucose monitoring are shown. Connected worker platforms are discussed with information about the architecture, system modules, intelligent operations, and industry applications. Predictive analytics provide contextual information about occupational safety risks, resource allocation, equipment failure, and predictive maintenance. Altogether, these examples highlight the ground-level benefits of real-time visibility about frontline workers, work environment, distributed assets, workforce efficiency, and safety compliance
ART-SS: An Adaptive Rejection Technique for Semi-Supervised restoration for adverse weather-affected images
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:In recent years, convolutional neural network-based single image adverse weather removal methods have achieved significant performance improvements on many benchmark datasets. However, these methods require large amounts of clean-weather degraded image pairs for training, which is often difficult to obtain in practice. Although various weather degradation synthesis methods exist in the literature, the use of synthetically generated weather degraded images often results in sub-optimal performance on the real weather degraded images due to the domain gap between synthetic and real-world images. To deal with this problem, various semi-supervised restoration (SSR) methods have been proposed for deraining or dehazing which learn to restore the clean image using synthetically generated datasets while generalizing better using unlabeled real-world images. The performance of a semi-supervised method is essentially based on the quality of the unlabeled data. In particular, if the unlabeled data characteristics are very different from that of the labeled data, then the performance of a semi-supervised method degrades significantly. We theoretically study the effect of unlabeled data on the performance of an SSR method and develop a technique that rejects the unlabeled images that degrade the performance. Extensive experiments and ablation study show that the proposed sample rejection method increases the performance of existing SSR deraining and dehazing methods significantly. Code is available at :https://github.com/rajeevyasarla/ART-SS
Towards performant and reliable undersampled MR reconstruction via diffusion model sampling
Mar 11, 2022



Abstract:Magnetic Resonance (MR) image reconstruction from under-sampled acquisition promises faster scanning time. To this end, current State-of-The-Art (SoTA) approaches leverage deep neural networks and supervised training to learn a recovery model. While these approaches achieve impressive performances, the learned model can be fragile on unseen degradation, e.g. when given a different acceleration factor. These methods are also generally deterministic and provide a single solution to an ill-posed problem; as such, it can be difficult for practitioners to understand the reliability of the reconstruction. We introduce DiffuseRecon, a novel diffusion model-based MR reconstruction method. DiffuseRecon guides the generation process based on the observed signals and a pre-trained diffusion model, and does not require additional training on specific acceleration factors. DiffuseRecon is stochastic in nature and generates results from a distribution of fully-sampled MR images; as such, it allows us to explicitly visualize different potential reconstruction solutions. Lastly, DiffuseRecon proposes an accelerated, coarse-to-fine Monte-Carlo sampling scheme to approximate the most likely reconstruction candidate. The proposed DiffuseRecon achieves SoTA performances reconstructing from raw acquisition signals in fastMRI and SKM-TEA. Code will be open-sourced at www.github.com/cpeng93/DiffuseRecon.
3SD: Self-Supervised Saliency Detection With No Labels
Mar 09, 2022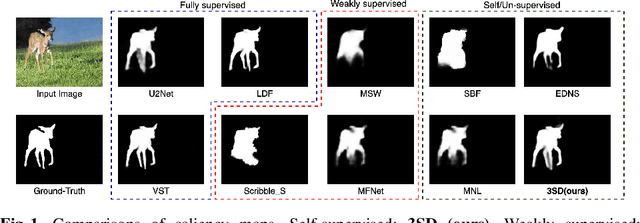
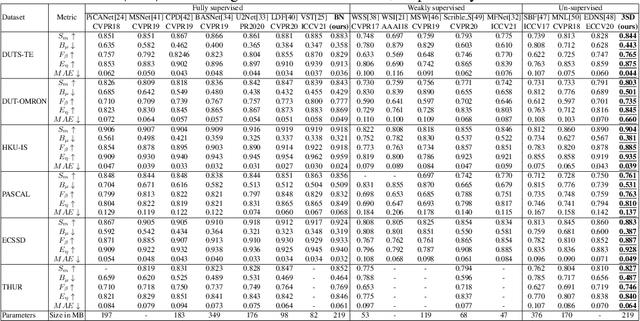
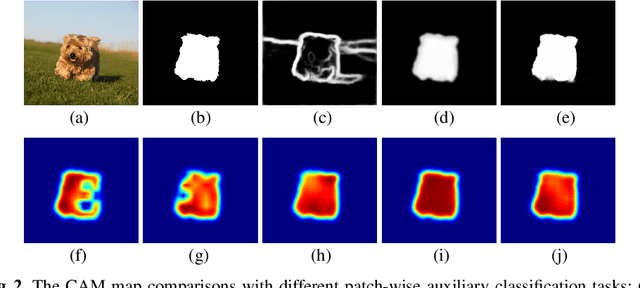

Abstract:We present a conceptually simple self-supervised method for saliency detection. Our method generates and uses pseudo-ground truth labels for training. The generated pseudo-GT labels don't require any kind of human annotations (e.g., pixel-wise labels or weak labels like scribbles). Recent works show that features extracted from classification tasks provide important saliency cues like structure and semantic information of salient objects in the image. Our method, called 3SD, exploits this idea by adding a branch for a self-supervised classification task in parallel with salient object detection, to obtain class activation maps (CAM maps). These CAM maps along with the edges of the input image are used to generate the pseudo-GT saliency maps to train our 3SD network. Specifically, we propose a contrastive learning-based training on multiple image patches for the classification task. We show the multi-patch classification with contrastive loss improves the quality of the CAM maps compared to naive classification on the entire image. Experiments on six benchmark datasets demonstrate that without any labels, our 3SD method outperforms all existing weakly supervised and unsupervised methods, and its performance is on par with the fully-supervised methods. Code is available at :https://github.com/rajeevyasarla/3SD
Uncertainty-aware Mean Teacher for Source-free Unsupervised Domain Adaptive 3D Object Detection
Sep 29, 2021

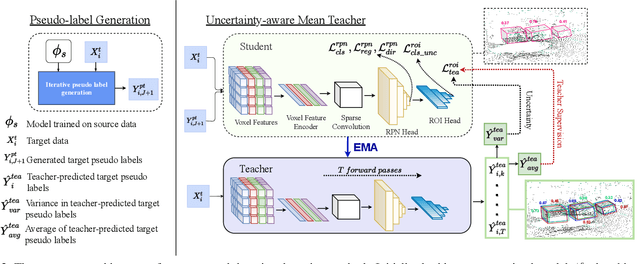

Abstract:Pseudo-label based self training approaches are a popular method for source-free unsupervised domain adaptation. However, their efficacy depends on the quality of the labels generated by the source trained model. These labels may be incorrect with high confidence, rendering thresholding methods ineffective. In order to avoid reinforcing errors caused by label noise, we propose an uncertainty-aware mean teacher framework which implicitly filters incorrect pseudo-labels during training. Leveraging model uncertainty allows the mean teacher network to perform implicit filtering by down-weighing losses corresponding uncertain pseudo-labels. Effectively, we perform automatic soft-sampling of pseudo-labeled data while aligning predictions from the student and teacher networks. We demonstrate our method on several domain adaptation scenarios, from cross-dataset to cross-weather conditions, and achieve state-of-the-art performance in these cases, on the KITTI lidar target dataset.
A Joint Representation Learning and Feature Modeling Approach for One-class Recognition
Jan 24, 2021



Abstract:One-class recognition is traditionally approached either as a representation learning problem or a feature modeling problem. In this work, we argue that both of these approaches have their own limitations; and a more effective solution can be obtained by combining the two. The proposed approach is based on the combination of a generative framework and a one-class classification method. First, we learn generative features using the one-class data with a generative framework. We augment the learned features with the corresponding reconstruction errors to obtain augmented features. Then, we qualitatively identify a suitable feature distribution that reduces the redundancy in the chosen classifier space. Finally, we force the augmented features to take the form of this distribution using an adversarial framework. We test the effectiveness of the proposed method on three one-class classification tasks and obtain state-of-the-art results.
Few Is Enough: Task-Augmented Active Meta-Learning for Brain Cell Classification
Jul 09, 2020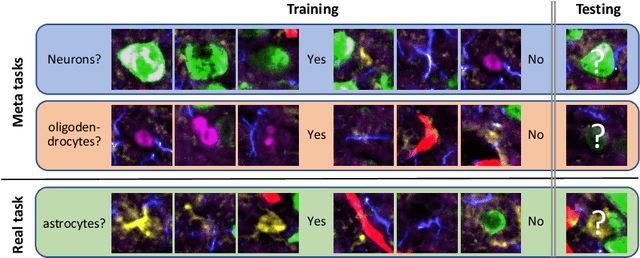
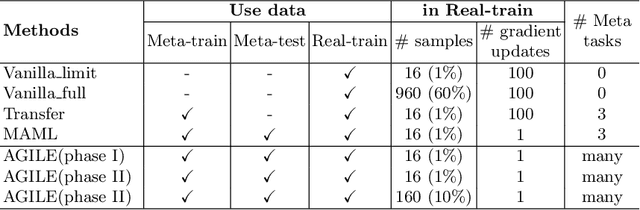
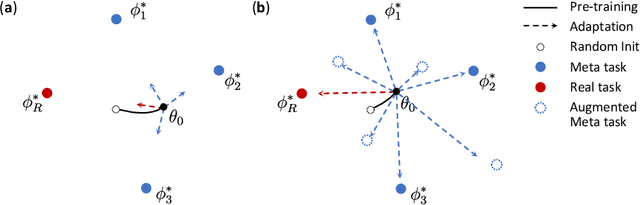
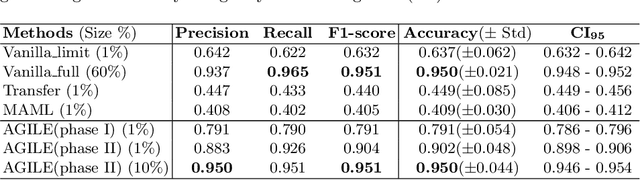
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (or DNNs) must constantly cope with distribution changes in the input data when the task of interest or the data collection protocol changes. Retraining a network from scratch to combat this issue poses a significant cost. Meta-learning aims to deliver an adaptive model that is sensitive to these underlying distribution changes, but requires many tasks during the meta-training process. In this paper, we propose a tAsk-auGmented actIve meta-LEarning (AGILE) method to efficiently adapt DNNs to new tasks by using a small number of training examples. AGILE combines a meta-learning algorithm with a novel task augmentation technique which we use to generate an initial adaptive model. It then uses Bayesian dropout uncertainty estimates to actively select the most difficult samples when updating the model to a new task. This allows AGILE to learn with fewer tasks and a few informative samples, achieving high performance with a limited dataset. We perform our experiments using the brain cell classification task and compare the results to a plain meta-learning model trained from scratch. We show that the proposed task-augmented meta-learning framework can learn to classify new cell types after a single gradient step with a limited number of training samples. We show that active learning with Bayesian uncertainty can further improve the performance when the number of training samples is extremely small. Using only 1% of the training data and a single update step, we achieved 90% accuracy on the new cell type classification task, a 50% points improvement over a state-of-the-art meta-learning algorithm.
Lesion Mask-based Simultaneous Synthesis of Anatomic and MolecularMR Images using a GAN
Jul 05, 2020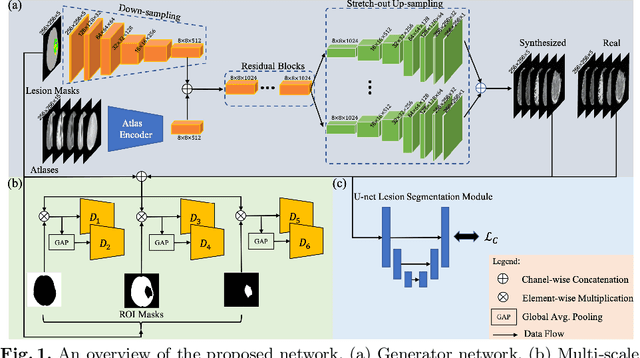

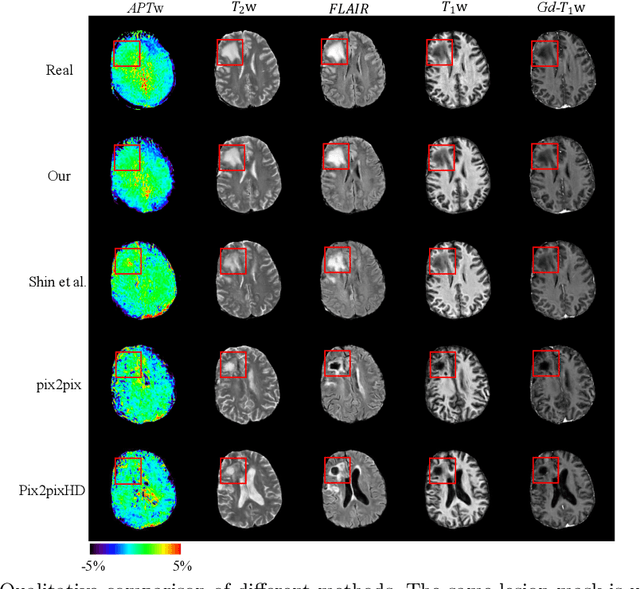
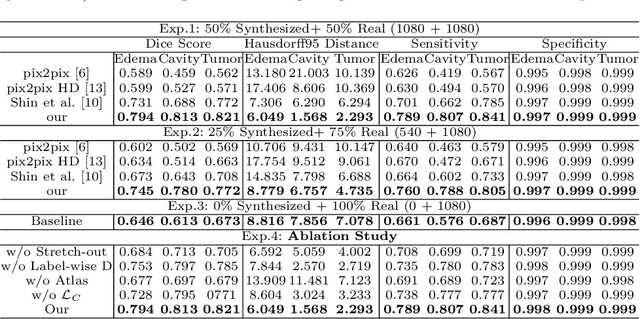
Abstract:Data-driven automatic approaches have demonstrated their great potential in resolving various clinical diagnostic dilemmas for patients with malignant gliomas in neuro-oncology with the help of conventional and advanced molecular MR images. However, the lack of sufficient annotated MRI data has vastly impeded the development of such automatic methods. Conventional data augmentation approaches, including flipping, scaling, rotation, and distortion are not capable of generating data with diverse image content. In this paper, we propose a generative adversarial network (GAN), which can simultaneously synthesize data from arbitrary manipulated lesion information on multiple anatomic and molecular MRI sequences, including T1-weighted (T1w), gadolinium enhanced T1w (Gd-T1w), T2-weighted (T2w), fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR), and amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw). The proposed framework consists of a stretch-out up-sampling module, a brain atlas encoder, a segmentation consistency module, and multi-scale labelwise discriminators. Extensive experiments on real clinical data demonstrate that the proposed model can perform significantly better than the state-of-the-art synthesis methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge