Venet Osmani
Identifying Key Challenges of Hardness-Based Resampling
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Performance gap across classes remains a persistent challenge in machine learning, often attributed to variations in class hardness. One way to quantify class hardness is through sample complexity - the minimum number of samples required to effectively learn a given class. Sample complexity theory suggests that class hardness is driven by differences in the amount of data required for generalization. That is, harder classes need substantially more samples to achieve generalization. Therefore, hardness-based resampling is a promising approach to mitigate these performance disparities. While resampling has been studied extensively in data-imbalanced settings, its impact on balanced datasets remains unexplored. This raises the fundamental question whether resampling is effective because it addresses data imbalance or hardness imbalance. We begin addressing this question by introducing class imbalance into balanced datasets and evaluate its effect on performance disparities. We oversample hard classes and undersample easy classes to bring hard classes closer to their sample complexity requirements while maintaining a constant dataset size for fairness. We estimate class-level hardness using the Area Under the Margin (AUM) hardness estimator and leverage it to compute resampling ratios. Using these ratios, we perform hardness-based resampling on the well-known CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets. Contrary to theoretical expectations, our results show that hardness-based resampling does not meaningfully affect class-wise performance disparities. To explain this discrepancy, we conduct detailed analyses to identify key challenges unique to hardness-based imbalance, distinguishing it from traditional data-based imbalance. Our insights help explain why theoretical sample complexity expectations fail to translate into practical performance gains and we provide guidelines for future research.
Multimodal Variational Autoencoder for Low-cost Cardiac Hemodynamics Instability Detection
Mar 20, 2024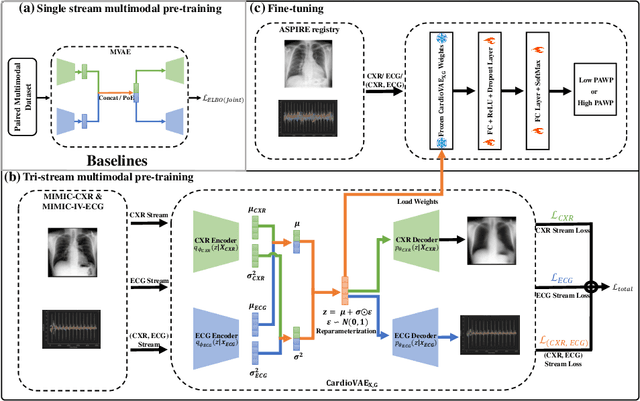
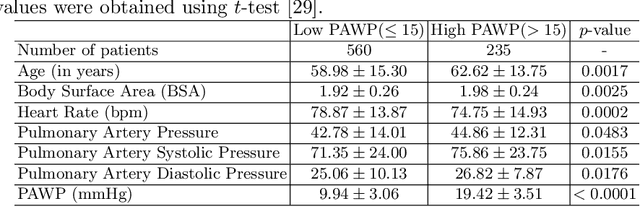
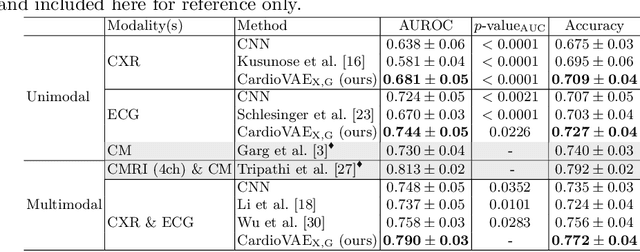
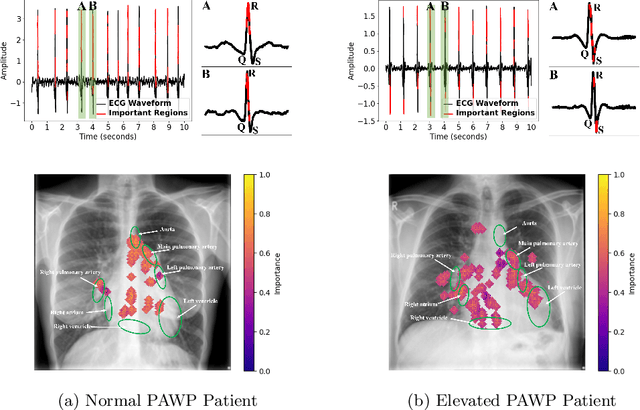
Abstract:Recent advancements in non-invasive detection of cardiac hemodynamic instability (CHDI) primarily focus on applying machine learning techniques to a single data modality, e.g. cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Despite their potential, these approaches often fall short especially when the size of labeled patient data is limited, a common challenge in the medical domain. Furthermore, only a few studies have explored multimodal methods to study CHDI, which mostly rely on costly modalities such as cardiac MRI and echocardiogram. In response to these limitations, we propose a novel multimodal variational autoencoder ($\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$) to integrate low-cost chest X-ray (CXR) and electrocardiogram (ECG) modalities with pre-training on a large unlabeled dataset. Specifically, $\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$ introduces a novel tri-stream pre-training strategy to learn both shared and modality-specific features, thus enabling fine-tuning with both unimodal and multimodal datasets. We pre-train $\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$ on a large, unlabeled dataset of $50,982$ subjects from a subset of MIMIC database and then fine-tune the pre-trained model on a labeled dataset of $795$ subjects from the ASPIRE registry. Comprehensive evaluations against existing methods show that $\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$ offers promising performance (AUROC $=0.79$ and Accuracy $=0.77$), representing a significant step forward in non-invasive prediction of CHDI. Our model also excels in producing fine interpretations of predictions directly associated with clinical features, thereby supporting clinical decision-making.
MeDSLIP: Medical Dual-Stream Language-Image Pre-training for Fine-grained Alignment
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Vision-language pre-training (VLP) models have shown significant advancements in the medical domain. Yet, most VLP models align raw reports to images at a very coarse level, without modeling fine-grained relationships between anatomical and pathological concepts outlined in reports and the corresponding semantic counterparts in images. To address this problem, we propose a Medical Dual-Stream Language-Image Pre-training (MeDSLIP) framework. Specifically, MeDSLIP establishes vision-language fine-grained alignments via disentangling visual and textual representations into anatomy-relevant and pathology-relevant streams. Moreover, a novel vision-language Prototypical Contr-astive Learning (ProtoCL) method is adopted in MeDSLIP to enhance the alignment within the anatomical and pathological streams. MeDSLIP further employs cross-stream Intra-image Contrastive Learning (ICL) to ensure the consistent coexistence of paired anatomical and pathological concepts within the same image. Such a cross-stream regularization encourages the model to exploit the synchrony between two streams for a more comprehensive representation learning. MeDSLIP is evaluated under zero-shot and supervised fine-tuning settings on three public datasets: NIH CXR14, RSNA Pneumonia, and SIIM-ACR Pneumothorax. Under these settings, MeDSLIP outperforms six leading CNN-based models on classification, grounding, and segmentation tasks.
Mitigating Health Data Poverty: Generative Approaches versus Resampling for Time-series Clinical Data
Oct 26, 2022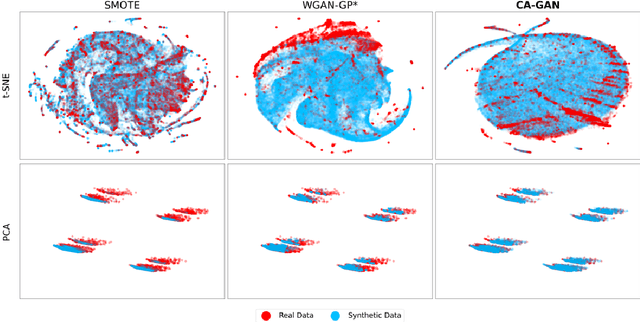
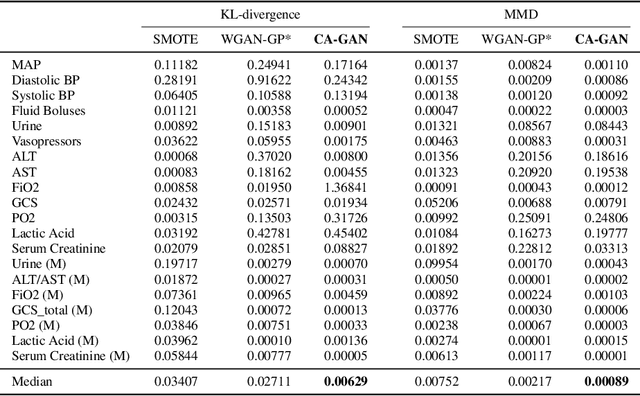
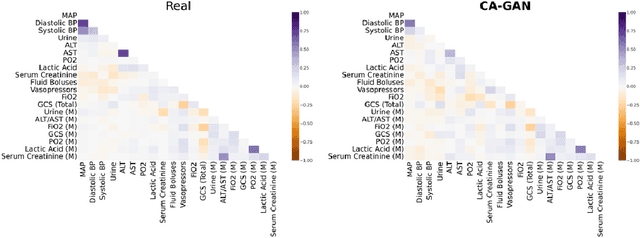
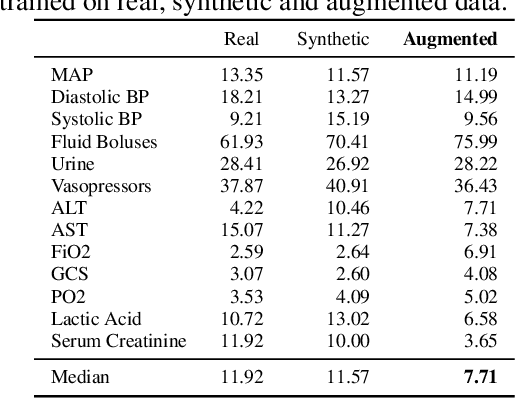
Abstract:Several approaches have been developed to mitigate algorithmic bias stemming from health data poverty, where minority groups are underrepresented in training datasets. Augmenting the minority class using resampling (such as SMOTE) is a widely used approach due to the simplicity of the algorithms. However, these algorithms decrease data variability and may introduce correlations between samples, giving rise to the use of generative approaches based on GAN. Generation of high-dimensional, time-series, authentic data that provides a wide distribution coverage of the real data, remains a challenging task for both resampling and GAN-based approaches. In this work we propose CA-GAN architecture that addresses some of the shortcomings of the current approaches, where we provide a detailed comparison with both SMOTE and WGAN-GP*, using a high-dimensional, time-series, real dataset of 3343 hypotensive Caucasian and Black patients. We show that our approach is better at both generating authentic data of the minority class and remaining within the original distribution of the real data.
Prediction of Blood Lactate Values in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Multi-center Cohort Study
Jul 07, 2021
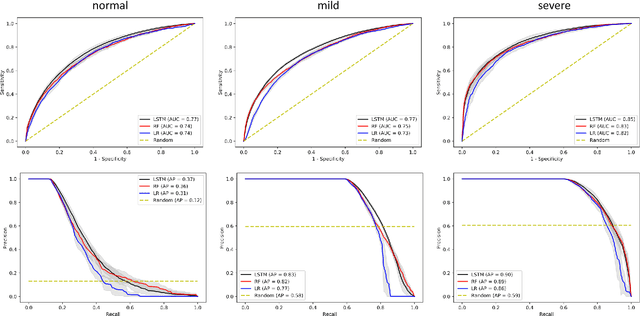
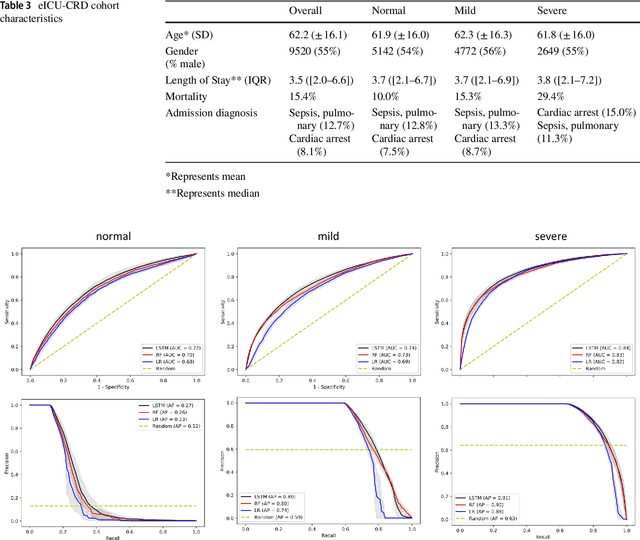
Abstract:Purpose. Elevations in initially obtained serum lactate levels are strong predictors of mortality in critically ill patients. Identifying patients whose serum lactate levels are more likely to increase can alert physicians to intensify care and guide them in the frequency of tending the blood test. We investigate whether machine learning models can predict subsequent serum lactate changes. Methods. We investigated serum lactate change prediction using the MIMIC-III and eICU-CRD datasets in internal as well as external validation of the eICU cohort on the MIMIC-III cohort. Three subgroups were defined based on the initial lactate levels: i) normal group (<2 mmol/L), ii) mild group (2-4 mmol/L), and iii) severe group (>4 mmol/L). Outcomes were defined based on increase or decrease of serum lactate levels between the groups. We also performed sensitivity analysis by defining the outcome as lactate change of >10% and furthermore investigated the influence of the time interval between subsequent lactate measurements on predictive performance. Results. The LSTM models were able to predict deterioration of serum lactate values of MIMIC-III patients with an AUC of 0.77 (95% CI 0.762-0.771) for the normal group, 0.77 (95% CI 0.768-0.772) for the mild group, and 0.85 (95% CI 0.840-0.851) for the severe group, with a slightly lower performance in the external validation. Conclusion. The LSTM demonstrated good discrimination of patients who had deterioration in serum lactate levels. Clinical studies are needed to evaluate whether utilization of a clinical decision support tool based on these results could positively impact decision-making and patient outcomes.
* 15 pages, 6 Appendices
Deep ROC Analysis and AUC as Balanced Average Accuracy to Improve Model Selection, Understanding and Interpretation
Mar 21, 2021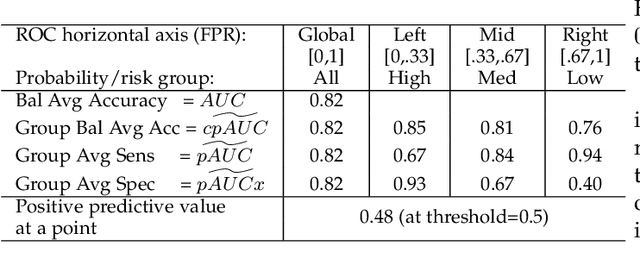
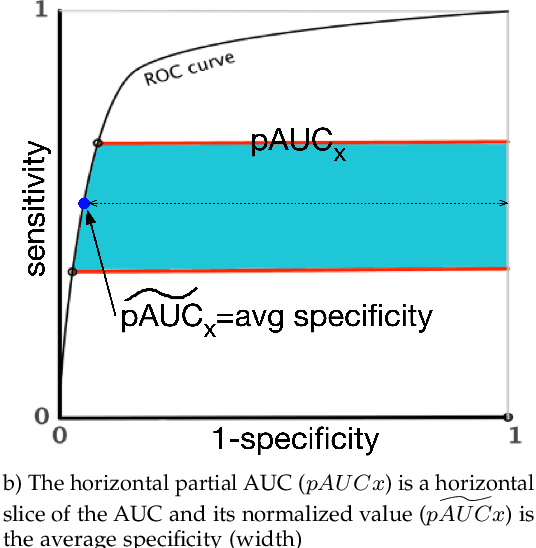
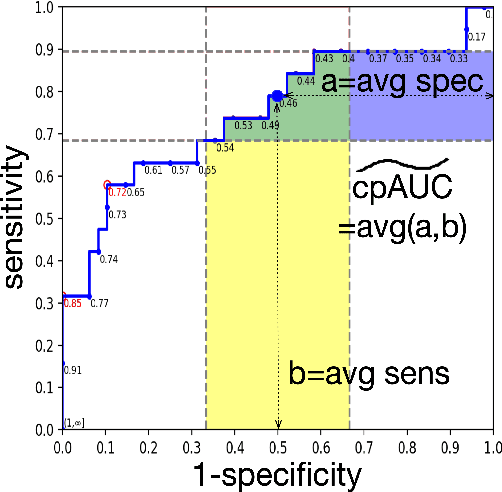
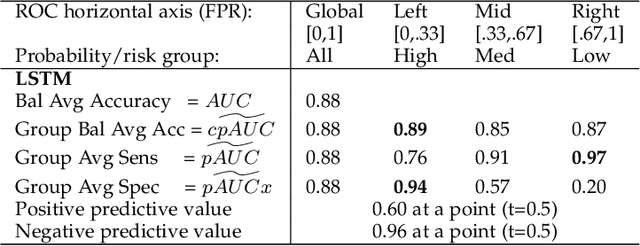
Abstract:Optimal performance is critical for decision-making tasks from medicine to autonomous driving, however common performance measures may be too general or too specific. For binary classifiers, diagnostic tests or prognosis at a timepoint, measures such as the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, or the area under the precision recall curve, are too general because they include unrealistic decision thresholds. On the other hand, measures such as accuracy, sensitivity or the F1 score are measures at a single threshold that reflect an individual single probability or predicted risk, rather than a range of individuals or risk. We propose a method in between, deep ROC analysis, that examines groups of probabilities or predicted risks for more insightful analysis. We translate esoteric measures into familiar terms: AUC and the normalized concordant partial AUC are balanced average accuracy (a new finding); the normalized partial AUC is average sensitivity; and the normalized horizontal partial AUC is average specificity. Along with post-test measures, we provide a method that can improve model selection in some cases and provide interpretation and assurance for patients in each risk group. We demonstrate deep ROC analysis in two case studies and provide a toolkit in Python.
Blood lactate concentration prediction in critical care patients: handling missing values
Oct 03, 2019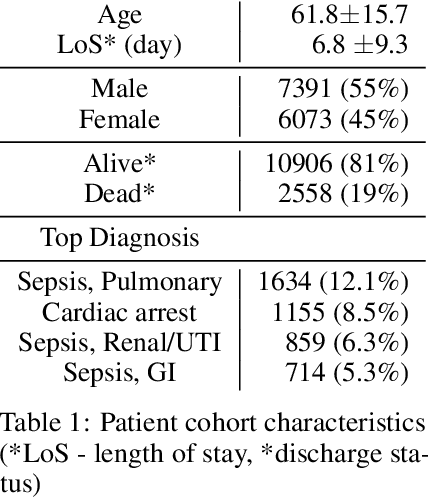
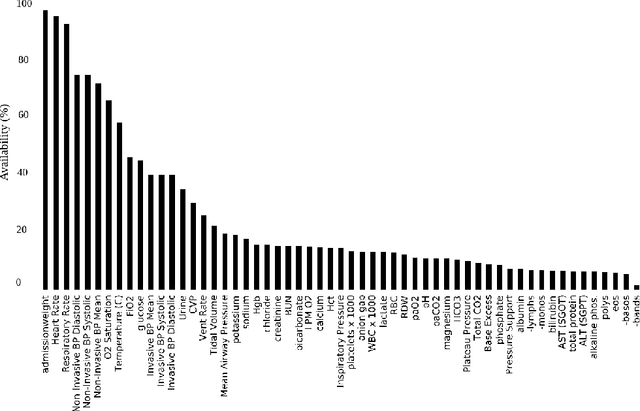
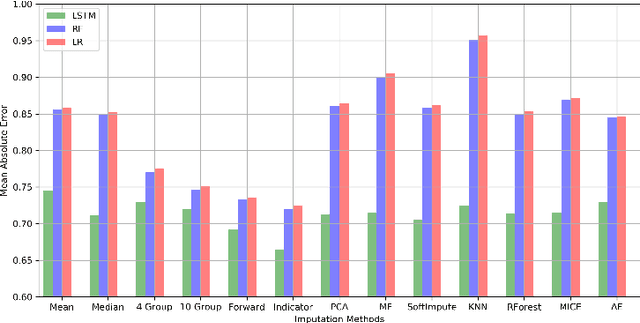
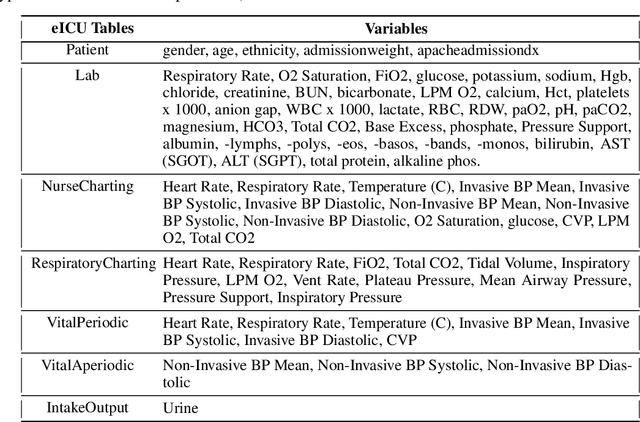
Abstract:Blood lactate concentration is a strong indicator of mortality risk in critically ill patients. While frequent lactate measurements are necessary to assess patient's health state, the measurement is an invasive procedure that can increase risk of hospital-acquired infections. For this reason we formally define the problem of lactate prediction as a clinically relevant benchmark problem for machine learning community so as to assist clinical decision making in blood lactate testing. Accordingly, we demonstrate the relevant challenges of the problem and its data in addition to the adopted solutions. Also, we evaluate the performance of different prediction algorithms on a large dataset of ICU patients from the multi-centre eICU database. More specifically, we focus on investigating the impact of missing value imputation methods in lactate prediction for each algorithm. The experimental analysis shows promising prediction results that encourages further investigation of this problem.
Benchmarking machine learning models on eICU critical care dataset
Oct 02, 2019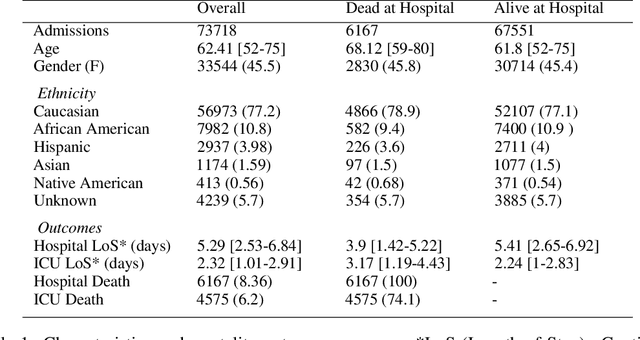
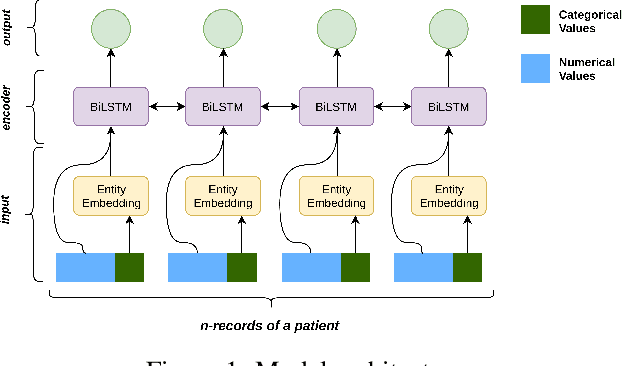

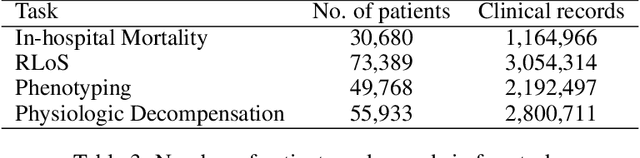
Abstract:Progress of machine learning in critical care has been difficult to track, in part due to absence of public benchmarks. Other fields of research (such as vision and NLP) have already established various competitions and benchmarks, whereas only recent availability of large clinical datasets has enabled the possibility of public benchmarks. Taking advantage of this opportunity, we propose a public benchmark suite to address four areas of critical care, namely mortality prediction, estimation of length of stay, patient phenotyping and risk of decompensation. We define each task and compare the performance of both clinical models as well as baseline and deep models using eICU critical care dataset of around 73,000 patients. Furthermore, we investigate the impact of numerical variables as well as handling of categorical variables for each of the defined tasks.
Natural Language Processing of Clinical Notes on Chronic Diseases: Systematic Review
Aug 15, 2019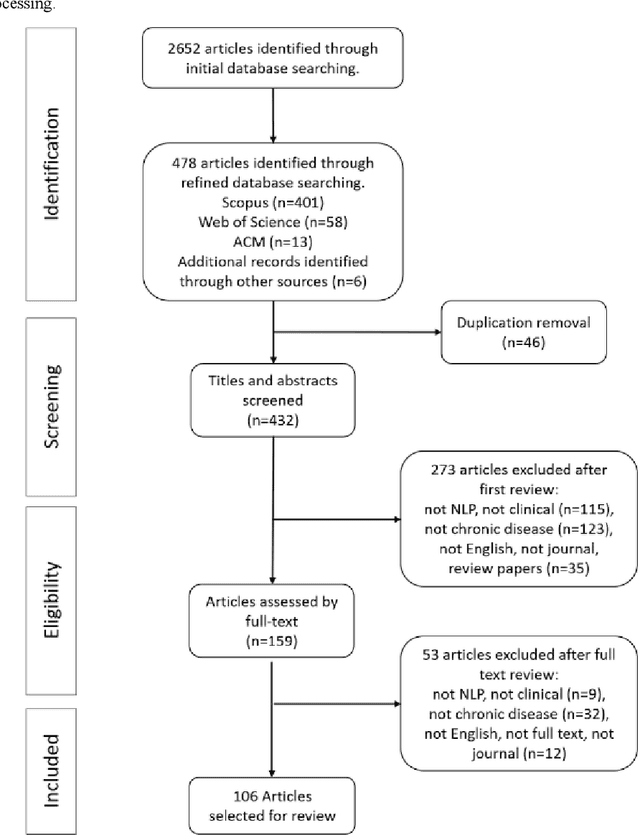

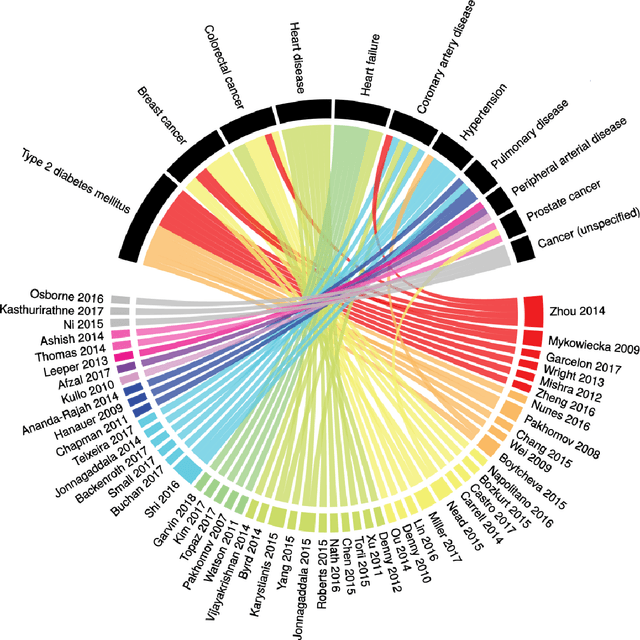

Abstract:Of the 2652 articles considered, 106 met the inclusion criteria. Review of the included papers resulted in identification of 43 chronic diseases, which were then further classified into 10 disease categories using ICD-10. The majority of studies focused on diseases of the circulatory system (n=38) while endocrine and metabolic diseases were fewest (n=14). This was due to the structure of clinical records related to metabolic diseases, which typically contain much more structured data, compared with medical records for diseases of the circulatory system, which focus more on unstructured data and consequently have seen a stronger focus of NLP. The review has shown that there is a significant increase in the use of machine learning methods compared to rule-based approaches; however, deep learning methods remain emergent (n=3). Consequently, the majority of works focus on classification of disease phenotype with only a handful of papers addressing extraction of comorbidities from the free text or integration of clinical notes with structured data. There is a notable use of relatively simple methods, such as shallow classifiers (or combination with rule-based methods), due to the interpretability of predictions, which still represents a significant issue for more complex methods. Finally, scarcity of publicly available data may also have contributed to insufficient development of more advanced methods, such as extraction of word embeddings from clinical notes. Further efforts are still required to improve (1) progression of clinical NLP methods from extraction toward understanding; (2) recognition of relations among entities rather than entities in isolation; (3) temporal extraction to understand past, current, and future clinical events; (4) exploitation of alternative sources of clinical knowledge; and (5) availability of large-scale, de-identified clinical corpora.
* Supplementary material detailing articles reviewed, classification of diseases and associated algorithms, can be found at: http://venetosmani.com/research/publications.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge