Prasun C. Tripathi
Multimodal Variational Autoencoder for Low-cost Cardiac Hemodynamics Instability Detection
Mar 20, 2024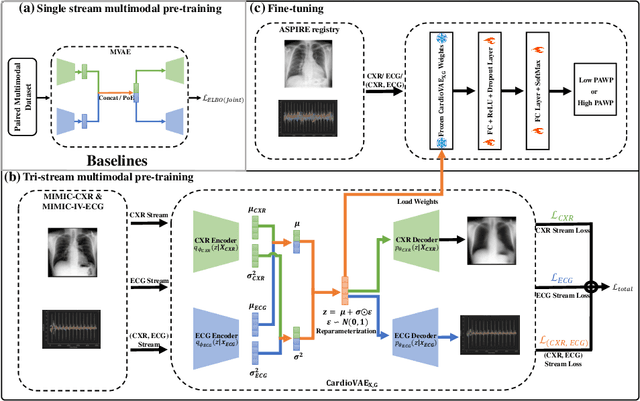
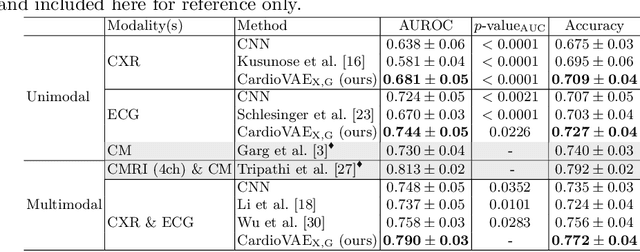
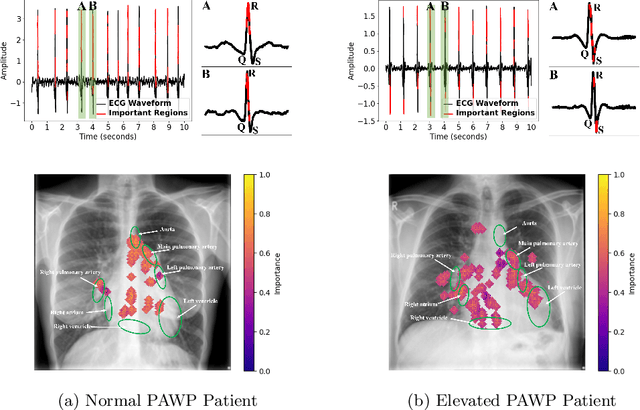
Abstract:Recent advancements in non-invasive detection of cardiac hemodynamic instability (CHDI) primarily focus on applying machine learning techniques to a single data modality, e.g. cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Despite their potential, these approaches often fall short especially when the size of labeled patient data is limited, a common challenge in the medical domain. Furthermore, only a few studies have explored multimodal methods to study CHDI, which mostly rely on costly modalities such as cardiac MRI and echocardiogram. In response to these limitations, we propose a novel multimodal variational autoencoder ($\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$) to integrate low-cost chest X-ray (CXR) and electrocardiogram (ECG) modalities with pre-training on a large unlabeled dataset. Specifically, $\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$ introduces a novel tri-stream pre-training strategy to learn both shared and modality-specific features, thus enabling fine-tuning with both unimodal and multimodal datasets. We pre-train $\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$ on a large, unlabeled dataset of $50,982$ subjects from a subset of MIMIC database and then fine-tune the pre-trained model on a labeled dataset of $795$ subjects from the ASPIRE registry. Comprehensive evaluations against existing methods show that $\text{CardioVAE}_\text{X,G}$ offers promising performance (AUROC $=0.79$ and Accuracy $=0.77$), representing a significant step forward in non-invasive prediction of CHDI. Our model also excels in producing fine interpretations of predictions directly associated with clinical features, thereby supporting clinical decision-making.
Tensor-based Multimodal Learning for Prediction of Pulmonary Arterial Wedge Pressure from Cardiac MRI
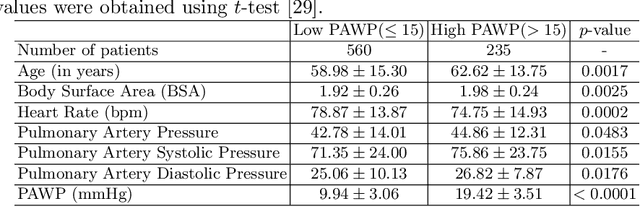
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Heart failure is a serious and life-threatening condition that can lead to elevated pressure in the left ventricle. Pulmonary Arterial Wedge Pressure (PAWP) is an important surrogate marker indicating high pressure in the left ventricle. PAWP is determined by Right Heart Catheterization (RHC) but it is an invasive procedure. A non-invasive method is useful in quickly identifying high-risk patients from a large population. In this work, we develop a tensor learning-based pipeline for identifying PAWP from multimodal cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). This pipeline extracts spatial and temporal features from high-dimensional scans. For quality control, we incorporate an epistemic uncertainty-based binning strategy to identify poor-quality training samples. To improve the performance, we learn complementary information by integrating features from multimodal data: cardiac MRI with short-axis and four-chamber views, and Electronic Health Records. The experimental analysis on a large cohort of $1346$ subjects who underwent the RHC procedure for PAWP estimation indicates that the proposed pipeline has a diagnostic value and can produce promising performance with significant improvement over the baseline in clinical practice (i.e., $\Delta$AUC $=0.10$, $\Delta$Accuracy $=0.06$, and $\Delta$MCC $=0.39$). The decision curve analysis further confirms the clinical utility of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge