Takaaki Shiratori
CHOICE: Coordinated Human-Object Interaction in Cluttered Environments for Pick-and-Place Actions
Dec 09, 2024
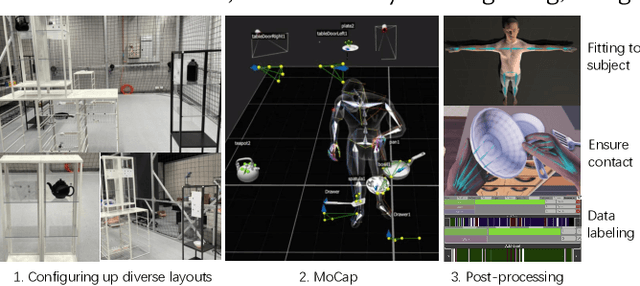
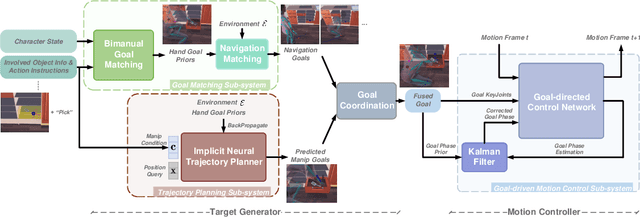
Abstract:Animating human-scene interactions such as pick-and-place tasks in cluttered, complex layouts is a challenging task, with objects of a wide variation of geometries and articulation under scenarios with various obstacles. The main difficulty lies in the sparsity of the motion data compared to the wide variation of the objects and environments as well as the poor availability of transition motions between different tasks, increasing the complexity of the generalization to arbitrary conditions. To cope with this issue, we develop a system that tackles the interaction synthesis problem as a hierarchical goal-driven task. Firstly, we develop a bimanual scheduler that plans a set of keyframes for simultaneously controlling the two hands to efficiently achieve the pick-and-place task from an abstract goal signal such as the target object selected by the user. Next, we develop a neural implicit planner that generates guidance hand trajectories under diverse object shape/types and obstacle layouts. Finally, we propose a linear dynamic model for our DeepPhase controller that incorporates a Kalman filter to enable smooth transitions in the frequency domain, resulting in a more realistic and effective multi-objective control of the character.Our system can produce a wide range of natural pick-and-place movements with respect to the geometry of objects, the articulation of containers and the layout of the objects in the scene.
Expressive Whole-Body 3D Gaussian Avatar
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Facial expression and hand motions are necessary to express our emotions and interact with the world. Nevertheless, most of the 3D human avatars modeled from a casually captured video only support body motions without facial expressions and hand motions.In this work, we present ExAvatar, an expressive whole-body 3D human avatar learned from a short monocular video. We design ExAvatar as a combination of the whole-body parametric mesh model (SMPL-X) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). The main challenges are 1) a limited diversity of facial expressions and poses in the video and 2) the absence of 3D observations, such as 3D scans and RGBD images. The limited diversity in the video makes animations with novel facial expressions and poses non-trivial. In addition, the absence of 3D observations could cause significant ambiguity in human parts that are not observed in the video, which can result in noticeable artifacts under novel motions. To address them, we introduce our hybrid representation of the mesh and 3D Gaussians. Our hybrid representation treats each 3D Gaussian as a vertex on the surface with pre-defined connectivity information (i.e., triangle faces) between them following the mesh topology of SMPL-X. It makes our ExAvatar animatable with novel facial expressions by driven by the facial expression space of SMPL-X. In addition, by using connectivity-based regularizers, we significantly reduce artifacts in novel facial expressions and poses.
Authentic Hand Avatar from a Phone Scan via Universal Hand Model
May 13, 2024

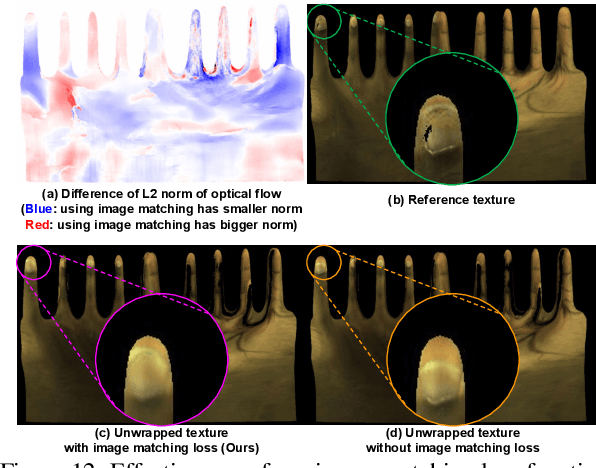
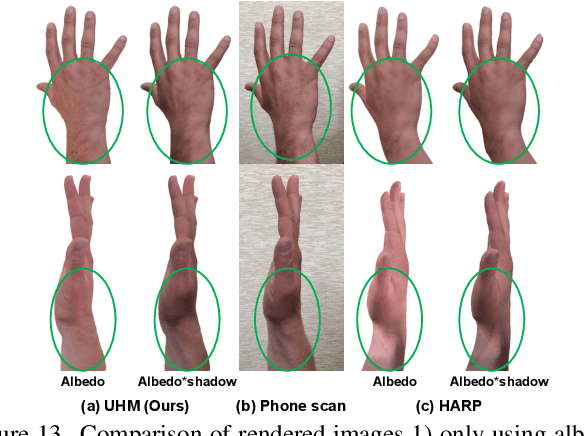
Abstract:The authentic 3D hand avatar with every identifiable information, such as hand shapes and textures, is necessary for immersive experiences in AR/VR. In this paper, we present a universal hand model (UHM), which 1) can universally represent high-fidelity 3D hand meshes of arbitrary identities (IDs) and 2) can be adapted to each person with a short phone scan for the authentic hand avatar. For effective universal hand modeling, we perform tracking and modeling at the same time, while previous 3D hand models perform them separately. The conventional separate pipeline suffers from the accumulated errors from the tracking stage, which cannot be recovered in the modeling stage. On the other hand, ours does not suffer from the accumulated errors while having a much more concise overall pipeline. We additionally introduce a novel image matching loss function to address a skin sliding during the tracking and modeling, while existing works have not focused on it much. Finally, using learned priors from our UHM, we effectively adapt our UHM to each person's short phone scan for the authentic hand avatar.
Diffusion Shape Prior for Wrinkle-Accurate Cloth Registration
Nov 10, 2023



Abstract:Registering clothes from 4D scans with vertex-accurate correspondence is challenging, yet important for dynamic appearance modeling and physics parameter estimation from real-world data. However, previous methods either rely on texture information, which is not always reliable, or achieve only coarse-level alignment. In this work, we present a novel approach to enabling accurate surface registration of texture-less clothes with large deformation. Our key idea is to effectively leverage a shape prior learned from pre-captured clothing using diffusion models. We also propose a multi-stage guidance scheme based on learned functional maps, which stabilizes registration for large-scale deformation even when they vary significantly from training data. Using high-fidelity real captured clothes, our experiments show that the proposed approach based on diffusion models generalizes better than surface registration with VAE or PCA-based priors, outperforming both optimization-based and learning-based non-rigid registration methods for both interpolation and extrapolation tests.
A Dataset of Relighted 3D Interacting Hands
Oct 26, 2023



Abstract:The two-hand interaction is one of the most challenging signals to analyze due to the self-similarity, complicated articulations, and occlusions of hands. Although several datasets have been proposed for the two-hand interaction analysis, all of them do not achieve 1) diverse and realistic image appearances and 2) diverse and large-scale groundtruth (GT) 3D poses at the same time. In this work, we propose Re:InterHand, a dataset of relighted 3D interacting hands that achieve the two goals. To this end, we employ a state-of-the-art hand relighting network with our accurately tracked two-hand 3D poses. We compare our Re:InterHand with existing 3D interacting hands datasets and show the benefit of it. Our Re:InterHand is available in https://mks0601.github.io/ReInterHand/.
RelightableHands: Efficient Neural Relighting of Articulated Hand Models
Feb 09, 2023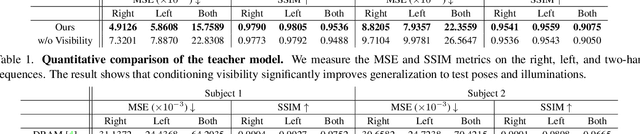
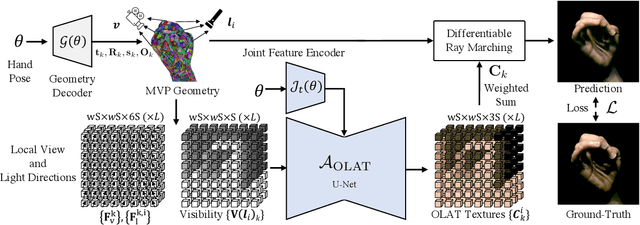
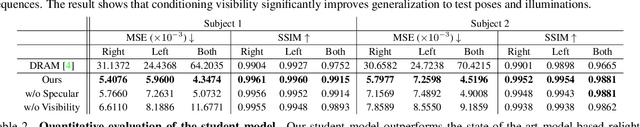
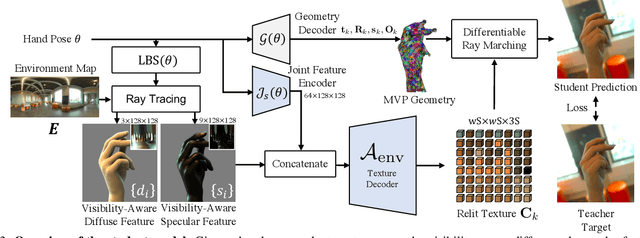
Abstract:We present the first neural relighting approach for rendering high-fidelity personalized hands that can be animated in real-time under novel illumination. Our approach adopts a teacher-student framework, where the teacher learns appearance under a single point light from images captured in a light-stage, allowing us to synthesize hands in arbitrary illuminations but with heavy compute. Using images rendered by the teacher model as training data, an efficient student model directly predicts appearance under natural illuminations in real-time. To achieve generalization, we condition the student model with physics-inspired illumination features such as visibility, diffuse shading, and specular reflections computed on a coarse proxy geometry, maintaining a small computational overhead. Our key insight is that these features have strong correlation with subsequent global light transport effects, which proves sufficient as conditioning data for the neural relighting network. Moreover, in contrast to bottleneck illumination conditioning, these features are spatially aligned based on underlying geometry, leading to better generalization to unseen illuminations and poses. In our experiments, we demonstrate the efficacy of our illumination feature representations, outperforming baseline approaches. We also show that our approach can photorealistically relight two interacting hands at real-time speeds. https://sh8.io/#/relightable_hands
Multiface: A Dataset for Neural Face Rendering
Jul 22, 2022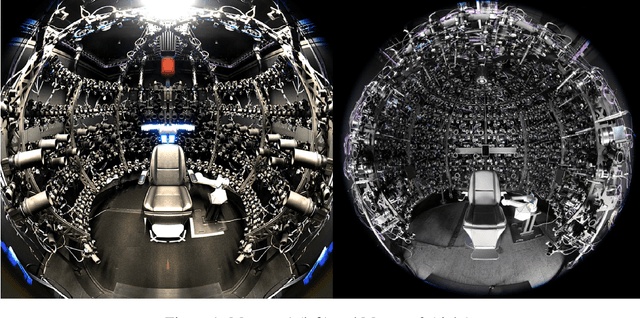



Abstract:Photorealistic avatars of human faces have come a long way in recent years, yet research along this area is limited by a lack of publicly available, high-quality datasets covering both, dense multi-view camera captures, and rich facial expressions of the captured subjects. In this work, we present Multiface, a new multi-view, high-resolution human face dataset collected from 13 identities at Reality Labs Research for neural face rendering. We introduce Mugsy, a large scale multi-camera apparatus to capture high-resolution synchronized videos of a facial performance. The goal of Multiface is to close the gap in accessibility to high quality data in the academic community and to enable research in VR telepresence. Along with the release of the dataset, we conduct ablation studies on the influence of different model architectures toward the model's interpolation capacity of novel viewpoint and expressions. With a conditional VAE model serving as our baseline, we found that adding spatial bias, texture warp field, and residual connections improves performance on novel view synthesis. Our code and data is available at: https://github.com/facebookresearch/multiface
3D Clothed Human Reconstruction in the Wild
Jul 20, 2022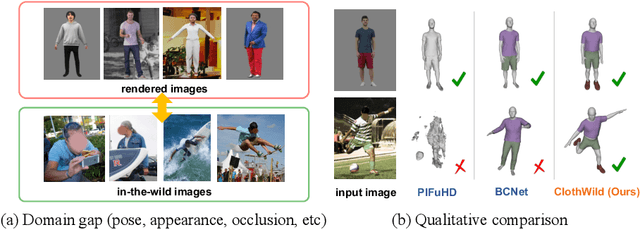
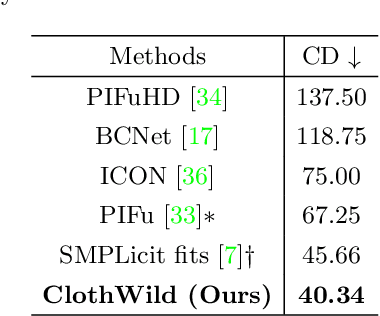
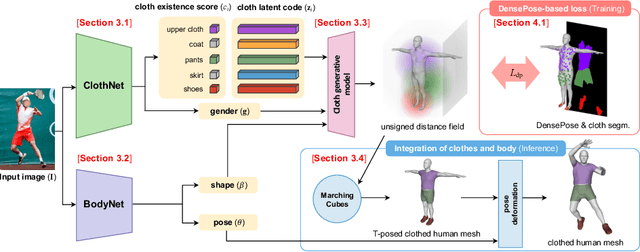
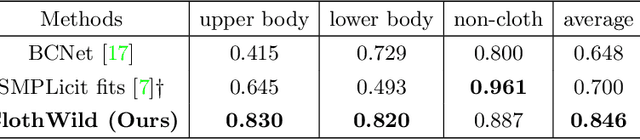
Abstract:Although much progress has been made in 3D clothed human reconstruction, most of the existing methods fail to produce robust results from in-the-wild images, which contain diverse human poses and appearances. This is mainly due to the large domain gap between training datasets and in-the-wild datasets. The training datasets are usually synthetic ones, which contain rendered images from GT 3D scans. However, such datasets contain simple human poses and less natural image appearances compared to those of real in-the-wild datasets, which makes generalization of it to in-the-wild images extremely challenging. To resolve this issue, in this work, we propose ClothWild, a 3D clothed human reconstruction framework that firstly addresses the robustness on in-thewild images. First, for the robustness to the domain gap, we propose a weakly supervised pipeline that is trainable with 2D supervision targets of in-the-wild datasets. Second, we design a DensePose-based loss function to reduce ambiguities of the weak supervision. Extensive empirical tests on several public in-the-wild datasets demonstrate that our proposed ClothWild produces much more accurate and robust results than the state-of-the-art methods. The codes are available in here: https://github.com/hygenie1228/ClothWild_RELEASE.
Dressing Avatars: Deep Photorealistic Appearance for Physically Simulated Clothing
Jun 30, 2022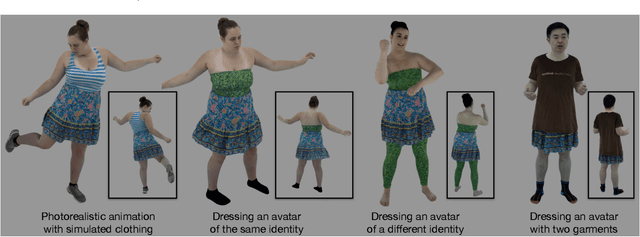
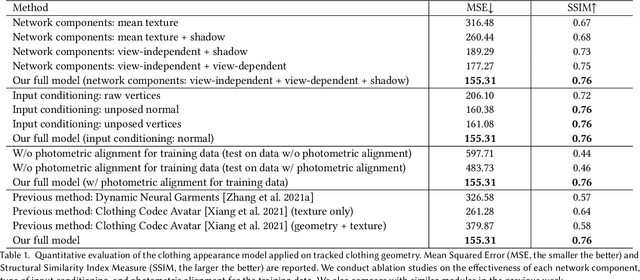
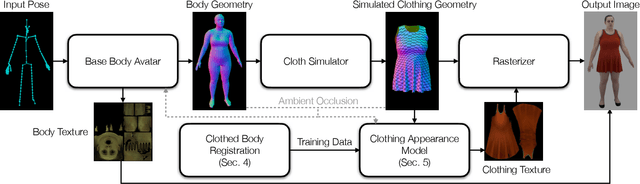
Abstract:Despite recent progress in developing animatable full-body avatars, realistic modeling of clothing - one of the core aspects of human self-expression - remains an open challenge. State-of-the-art physical simulation methods can generate realistically behaving clothing geometry at interactive rate. Modeling photorealistic appearance, however, usually requires physically-based rendering which is too expensive for interactive applications. On the other hand, data-driven deep appearance models are capable of efficiently producing realistic appearance, but struggle at synthesizing geometry of highly dynamic clothing and handling challenging body-clothing configurations. To this end, we introduce pose-driven avatars with explicit modeling of clothing that exhibit both realistic clothing dynamics and photorealistic appearance learned from real-world data. The key idea is to introduce a neural clothing appearance model that operates on top of explicit geometry: at train time we use high-fidelity tracking, whereas at animation time we rely on physically simulated geometry. Our key contribution is a physically-inspired appearance network, capable of generating photorealistic appearance with view-dependent and dynamic shadowing effects even for unseen body-clothing configurations. We conduct a thorough evaluation of our model and demonstrate diverse animation results on several subjects and different types of clothing. Unlike previous work on photorealistic full-body avatars, our approach can produce much richer dynamics and more realistic deformations even for loose clothing. We also demonstrate that our formulation naturally allows clothing to be used with avatars of different people while staying fully animatable, thus enabling, for the first time, photorealistic avatars with novel clothing.
Garment Avatars: Realistic Cloth Driving using Pattern Registration
Jun 07, 2022
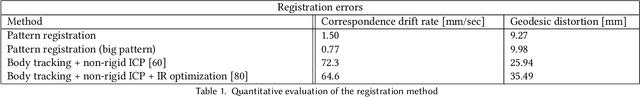
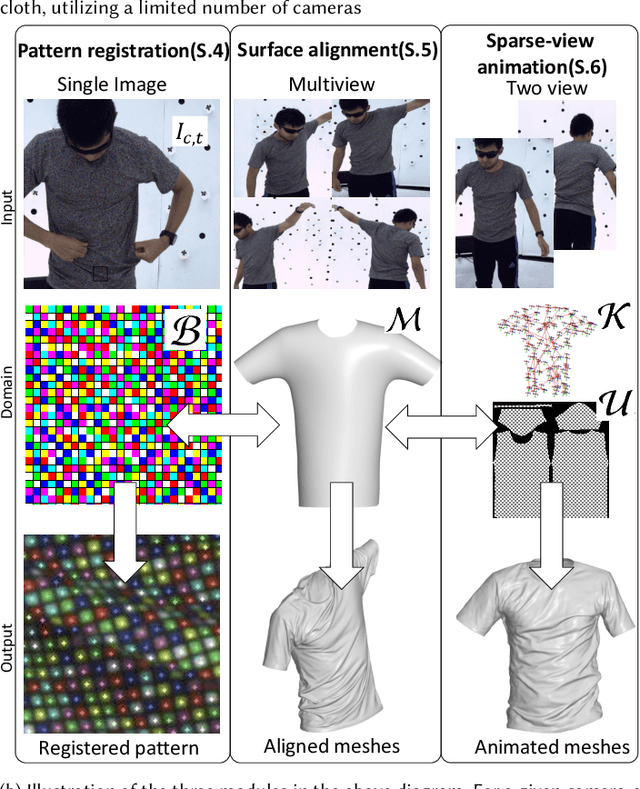

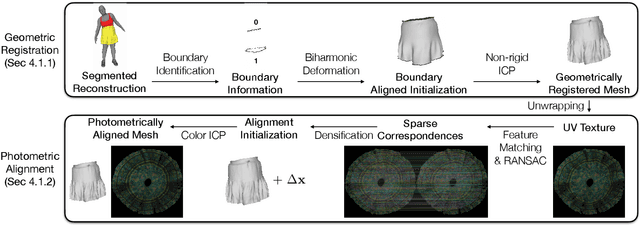
Abstract:Virtual telepresence is the future of online communication. Clothing is an essential part of a person's identity and self-expression. Yet, ground truth data of registered clothes is currently unavailable in the required resolution and accuracy for training telepresence models for realistic cloth animation. Here, we propose an end-to-end pipeline for building drivable representations for clothing. The core of our approach is a multi-view patterned cloth tracking algorithm capable of capturing deformations with high accuracy. We further rely on the high-quality data produced by our tracking method to build a Garment Avatar: an expressive and fully-drivable geometry model for a piece of clothing. The resulting model can be animated using a sparse set of views and produces highly realistic reconstructions which are faithful to the driving signals. We demonstrate the efficacy of our pipeline on a realistic virtual telepresence application, where a garment is being reconstructed from two views, and a user can pick and swap garment design as they wish. In addition, we show a challenging scenario when driven exclusively with body pose, our drivable garment avatar is capable of producing realistic cloth geometry of significantly higher quality than the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge