Oshri Halimi
PhysGraph: Physics-Based Integration Using Graph Neural Networks
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:Physics-based simulation of mesh based domains remains a challenging task. State-of-the-art techniques can produce realistic results but require expert knowledge. A major bottleneck in many approaches is the step of integrating a potential energy in order to compute velocities or displacements. Recently, learning based method for physics-based simulation have sparked interest with graph based approaches being a promising research direction. One of the challenges for these methods is to generate models that are mesh independent and generalize to different material properties. Moreover, the model should also be able to react to unforeseen external forces like ubiquitous collisions. Our contribution is based on a simple observation: evaluating forces is computationally relatively cheap for traditional simulation methods and can be computed in parallel in contrast to their integration. If we learn how a system reacts to forces in general, irrespective of their origin, we can learn an integrator that can predict state changes due to the total forces with high generalization power. We effectively factor out the physical model behind resulting forces by relying on an opaque force module. We demonstrate that this idea leads to a learnable module that can be trained on basic internal forces of small mesh patches and generalizes to different mesh typologies, resolutions, material parameters and unseen forces like collisions at inference time. Our proposed paradigm is general and can be used to model a variety of physical phenomena. We focus our exposition on the detail enhancement of coarse clothing geometry which has many applications including computer games, virtual reality and virtual try-on.
FETA: Towards Specializing Foundation Models for Expert Task Applications
Sep 08, 2022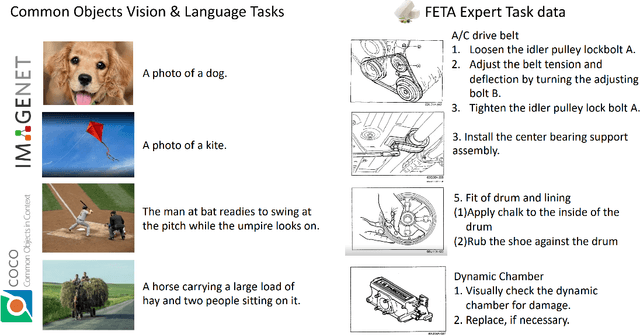
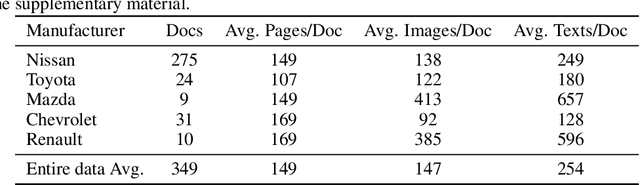
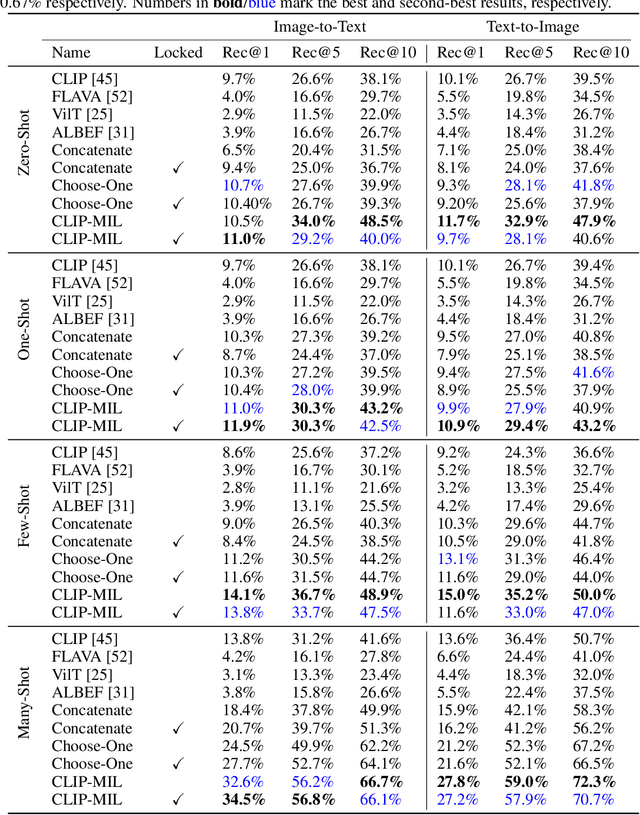
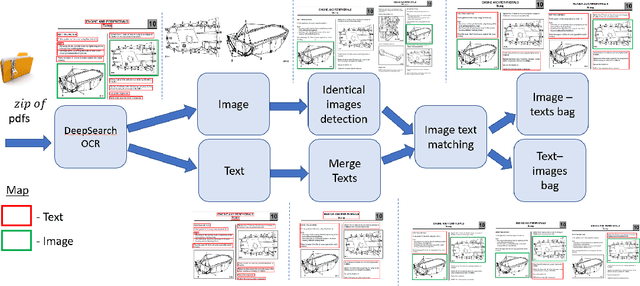
Abstract:Foundation Models (FMs) have demonstrated unprecedented capabilities including zero-shot learning, high fidelity data synthesis, and out of domain generalization. However, as we show in this paper, FMs still have poor out-of-the-box performance on expert tasks (e.g. retrieval of car manuals technical illustrations from language queries), data for which is either unseen or belonging to a long-tail part of the data distribution of the huge datasets used for FM pre-training. This underlines the necessity to explicitly evaluate and finetune FMs on such expert tasks, arguably ones that appear the most in practical real-world applications. In this paper, we propose a first of its kind FETA benchmark built around the task of teaching FMs to understand technical documentation, via learning to match their graphical illustrations to corresponding language descriptions. Our FETA benchmark focuses on text-to-image and image-to-text retrieval in public car manuals and sales catalogue brochures. FETA is equipped with a procedure for completely automatic annotation extraction (code would be released upon acceptance), allowing easy extension of FETA to more documentation types and application domains in the future. Our automatic annotation leads to an automated performance metric shown to be consistent with metrics computed on human-curated annotations (also released). We provide multiple baselines and analysis of popular FMs on FETA leading to several interesting findings that we believe would be very valuable to the FM community, paving the way towards real-world application of FMs for practical expert tasks currently 'overlooked' by standard benchmarks focusing on common objects.
Garment Avatars: Realistic Cloth Driving using Pattern Registration
Jun 07, 2022
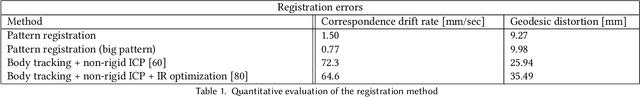
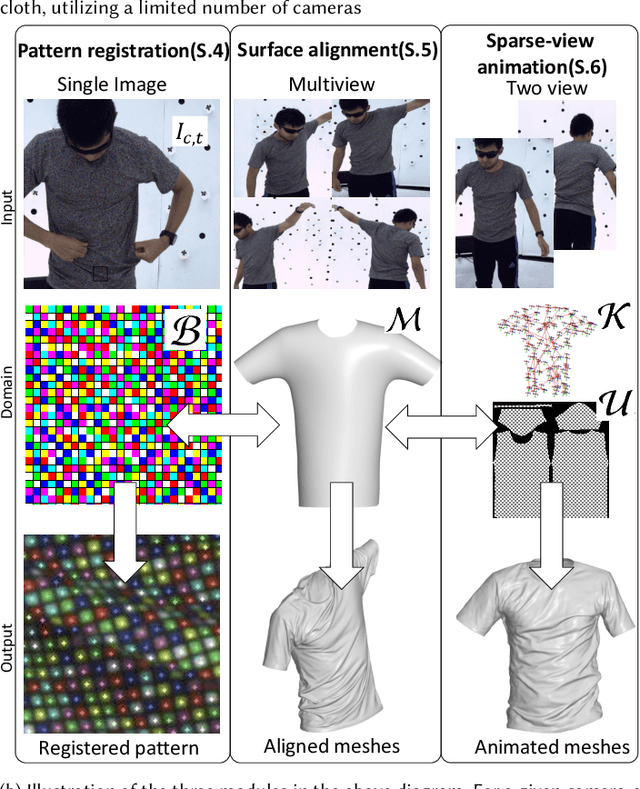

Abstract:Virtual telepresence is the future of online communication. Clothing is an essential part of a person's identity and self-expression. Yet, ground truth data of registered clothes is currently unavailable in the required resolution and accuracy for training telepresence models for realistic cloth animation. Here, we propose an end-to-end pipeline for building drivable representations for clothing. The core of our approach is a multi-view patterned cloth tracking algorithm capable of capturing deformations with high accuracy. We further rely on the high-quality data produced by our tracking method to build a Garment Avatar: an expressive and fully-drivable geometry model for a piece of clothing. The resulting model can be animated using a sparse set of views and produces highly realistic reconstructions which are faithful to the driving signals. We demonstrate the efficacy of our pipeline on a realistic virtual telepresence application, where a garment is being reconstructed from two views, and a user can pick and swap garment design as they wish. In addition, we show a challenging scenario when driven exclusively with body pose, our drivable garment avatar is capable of producing realistic cloth geometry of significantly higher quality than the state-of-the-art.
LIMP: Learning Latent Shape Representations with Metric Preservation Priors
Mar 27, 2020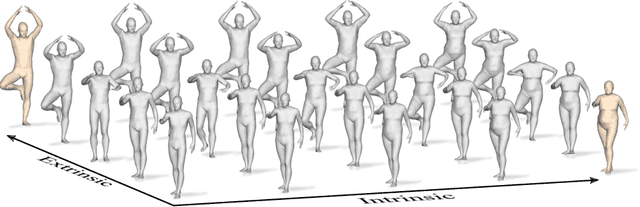
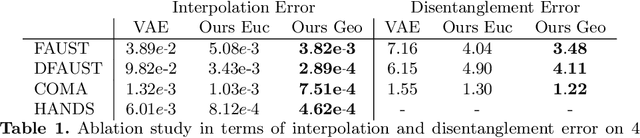
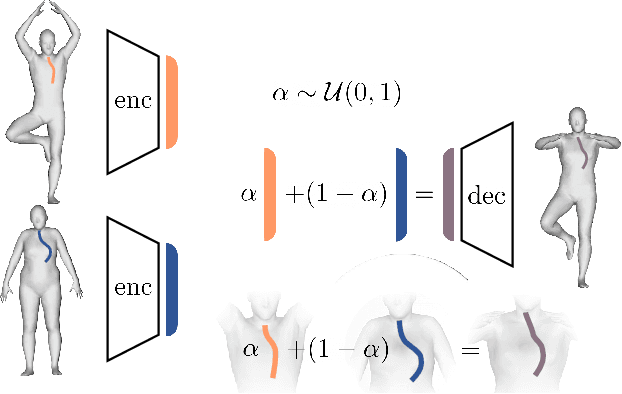
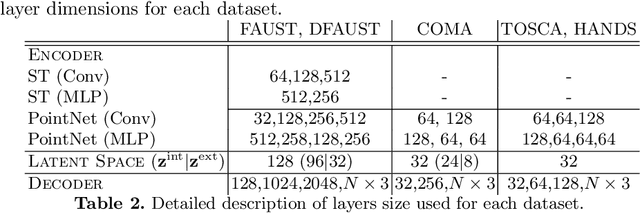
Abstract:In this paper, we advocate the adoption of metric preservation as a powerful prior for learning latent representations of deformable 3D shapes. Key to our construction is the introduction of a geometric distortion criterion, defined directly on the decoded shapes, translating the preservation of the metric on the decoding to the formation of linear paths in the underlying latent space. Our rationale lies in the observation that training samples alone are often insufficient to endow generative models with high fidelity, motivating the need for large training datasets. In contrast, metric preservation provides a rigorous way to control the amount of geometric distortion incurring in the construction of the latent space, leading in turn to synthetic samples of higher quality. We further demonstrate, for the first time, the adoption of differentiable intrinsic distances in the backpropagation of a geodesic loss. Our geometric priors are particularly relevant in the presence of scarce training data, where learning any meaningful latent structure can be especially challenging. The effectiveness and potential of our generative model is showcased in applications of style transfer, content generation, and shape completion.
The Whole Is Greater Than the Sum of Its Nonrigid Parts
Jan 27, 2020



Abstract:According to Aristotle, a philosopher in Ancient Greece, "the whole is greater than the sum of its parts". This observation was adopted to explain human perception by the Gestalt psychology school of thought in the twentieth century. Here, we claim that observing part of an object which was previously acquired as a whole, one could deal with both partial matching and shape completion in a holistic manner. More specifically, given the geometry of a full, articulated object in a given pose, as well as a partial scan of the same object in a different pose, we address the problem of matching the part to the whole while simultaneously reconstructing the new pose from its partial observation. Our approach is data-driven, and takes the form of a Siamese autoencoder without the requirement of a consistent vertex labeling at inference time; as such, it can be used on unorganized point clouds as well as on triangle meshes. We demonstrate the practical effectiveness of our model in the applications of single-view deformable shape completion and dense shape correspondence, both on synthetic and real-world geometric data, where we outperform prior work on these tasks by a large margin.
Self-supervised Learning of Dense Shape Correspondence
Dec 06, 2018



Abstract:We introduce the first completely unsupervised correspondence learning approach for deformable 3D shapes. Key to our model is the understanding that natural deformations (such as changes in pose) approximately preserve the metric structure of the surface, yielding a natural criterion to drive the learning process toward distortion-minimizing predictions. On this basis, we overcome the need for annotated data and replace it by a purely geometric criterion. The resulting learning model is class-agnostic, and is able to leverage any type of deformable geometric data for the training phase. In contrast to existing supervised approaches which specialize on the class seen at training time, we demonstrate stronger generalization as well as applicability to a variety of challenging settings. We showcase our method on a wide selection of correspondence benchmarks, where we outperform other methods in terms of accuracy, generalization, and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge