Ningyuan Zheng
3D-Aware Encoding for Style-based Neural Radiance Fields
Nov 12, 2022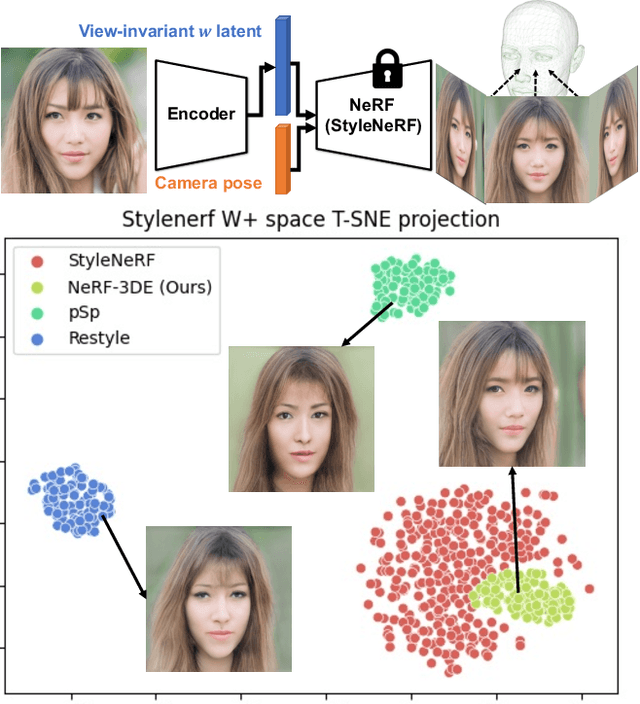
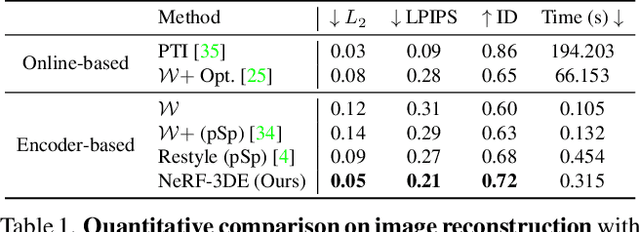
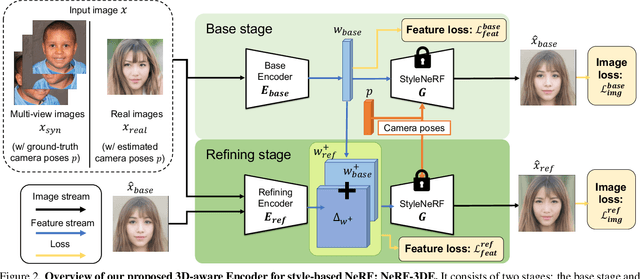
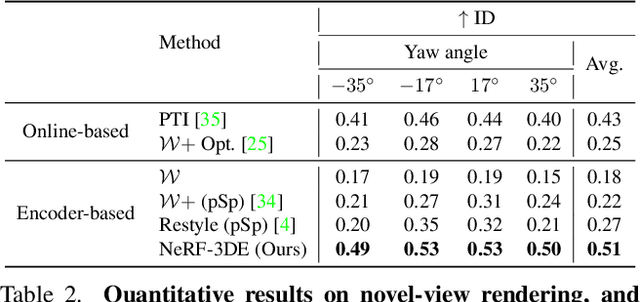
Abstract:We tackle the task of NeRF inversion for style-based neural radiance fields, (e.g., StyleNeRF). In the task, we aim to learn an inversion function to project an input image to the latent space of a NeRF generator and then synthesize novel views of the original image based on the latent code. Compared with GAN inversion for 2D generative models, NeRF inversion not only needs to 1) preserve the identity of the input image, but also 2) ensure 3D consistency in generated novel views. This requires the latent code obtained from the single-view image to be invariant across multiple views. To address this new challenge, we propose a two-stage encoder for style-based NeRF inversion. In the first stage, we introduce a base encoder that converts the input image to a latent code. To ensure the latent code is view-invariant and is able to synthesize 3D consistent novel view images, we utilize identity contrastive learning to train the base encoder. Second, to better preserve the identity of the input image, we introduce a refining encoder to refine the latent code and add finer details to the output image. Importantly note that the novelty of this model lies in the design of its first-stage encoder which produces the closest latent code lying on the latent manifold and thus the refinement in the second stage would be close to the NeRF manifold. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed two-stage encoder qualitatively and quantitatively exhibits superiority over the existing encoders for inversion in both image reconstruction and novel-view rendering.
Multiface: A Dataset for Neural Face Rendering
Jul 22, 2022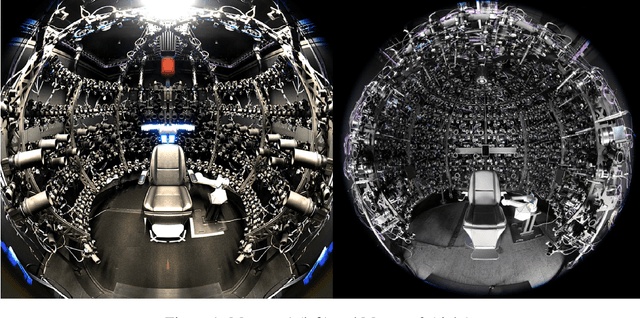



Abstract:Photorealistic avatars of human faces have come a long way in recent years, yet research along this area is limited by a lack of publicly available, high-quality datasets covering both, dense multi-view camera captures, and rich facial expressions of the captured subjects. In this work, we present Multiface, a new multi-view, high-resolution human face dataset collected from 13 identities at Reality Labs Research for neural face rendering. We introduce Mugsy, a large scale multi-camera apparatus to capture high-resolution synchronized videos of a facial performance. The goal of Multiface is to close the gap in accessibility to high quality data in the academic community and to enable research in VR telepresence. Along with the release of the dataset, we conduct ablation studies on the influence of different model architectures toward the model's interpolation capacity of novel viewpoint and expressions. With a conditional VAE model serving as our baseline, we found that adding spatial bias, texture warp field, and residual connections improves performance on novel view synthesis. Our code and data is available at: https://github.com/facebookresearch/multiface
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge