Srishti Yadav
Who Evaluates AI's Social Impacts? Mapping Coverage and Gaps in First and Third Party Evaluations
Nov 06, 2025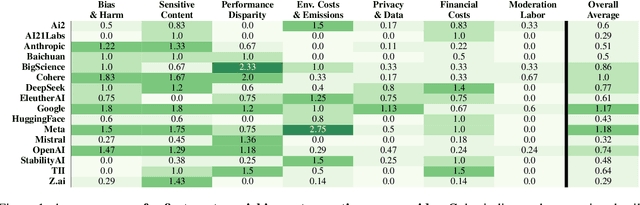
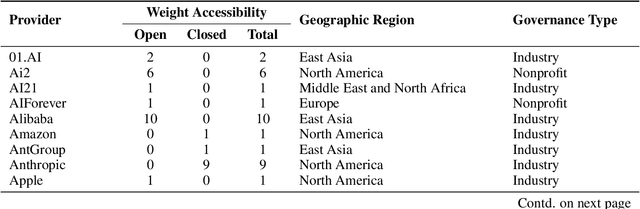
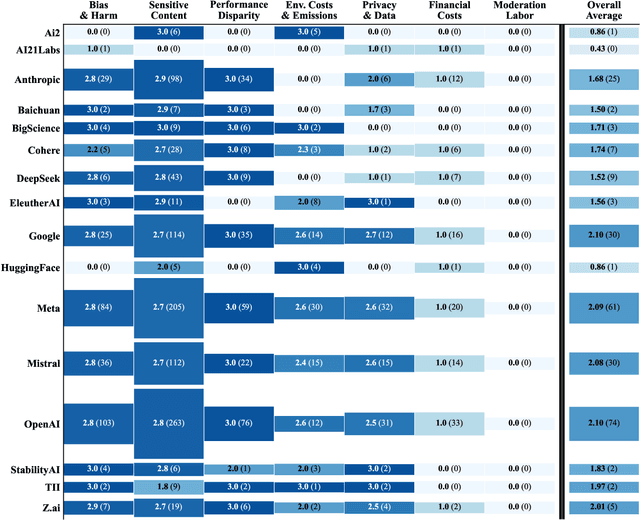
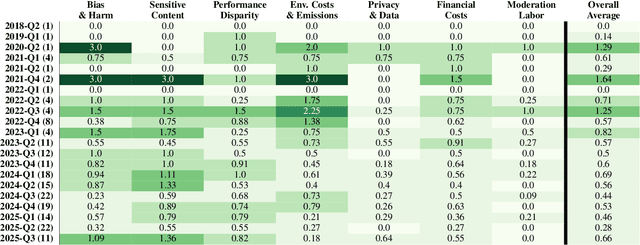
Abstract:Foundation models are increasingly central to high-stakes AI systems, and governance frameworks now depend on evaluations to assess their risks and capabilities. Although general capability evaluations are widespread, social impact assessments covering bias, fairness, privacy, environmental costs, and labor practices remain uneven across the AI ecosystem. To characterize this landscape, we conduct the first comprehensive analysis of both first-party and third-party social impact evaluation reporting across a wide range of model developers. Our study examines 186 first-party release reports and 183 post-release evaluation sources, and complements this quantitative analysis with interviews of model developers. We find a clear division of evaluation labor: first-party reporting is sparse, often superficial, and has declined over time in key areas such as environmental impact and bias, while third-party evaluators including academic researchers, nonprofits, and independent organizations provide broader and more rigorous coverage of bias, harmful content, and performance disparities. However, this complementarity has limits. Only model developers can authoritatively report on data provenance, content moderation labor, financial costs, and training infrastructure, yet interviews reveal that these disclosures are often deprioritized unless tied to product adoption or regulatory compliance. Our findings indicate that current evaluation practices leave major gaps in assessing AI's societal impacts, highlighting the urgent need for policies that promote developer transparency, strengthen independent evaluation ecosystems, and create shared infrastructure to aggregate and compare third-party evaluations in a consistent and accessible way.
Cultural Evaluations of Vision-Language Models Have a Lot to Learn from Cultural Theory
May 28, 2025Abstract:Modern vision-language models (VLMs) often fail at cultural competency evaluations and benchmarks. Given the diversity of applications built upon VLMs, there is renewed interest in understanding how they encode cultural nuances. While individual aspects of this problem have been studied, we still lack a comprehensive framework for systematically identifying and annotating the nuanced cultural dimensions present in images for VLMs. This position paper argues that foundational methodologies from visual culture studies (cultural studies, semiotics, and visual studies) are necessary for cultural analysis of images. Building upon this review, we propose a set of five frameworks, corresponding to cultural dimensions, that must be considered for a more complete analysis of the cultural competencies of VLMs.
Uncovering Cultural Representation Disparities in Vision-Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across a range of tasks, yet concerns about their potential biases exist. This work investigates the extent to which prominent VLMs exhibit cultural biases by evaluating their performance on an image-based country identification task at a country level. Utilizing the geographically diverse Country211 dataset, we probe several large vision language models (VLMs) under various prompting strategies: open-ended questions, multiple-choice questions (MCQs) including challenging setups like multilingual and adversarial settings. Our analysis aims to uncover disparities in model accuracy across different countries and question formats, providing insights into how training data distribution and evaluation methodologies might influence cultural biases in VLMs. The findings highlight significant variations in performance, suggesting that while VLMs possess considerable visual understanding, they inherit biases from their pre-training data and scale that impact their ability to generalize uniformly across diverse global contexts.
Multi-Modal Framing Analysis of News
Mar 26, 2025



Abstract:Automated frame analysis of political communication is a popular task in computational social science that is used to study how authors select aspects of a topic to frame its reception. So far, such studies have been narrow, in that they use a fixed set of pre-defined frames and focus only on the text, ignoring the visual contexts in which those texts appear. Especially for framing in the news, this leaves out valuable information about editorial choices, which include not just the written article but also accompanying photographs. To overcome such limitations, we present a method for conducting multi-modal, multi-label framing analysis at scale using large (vision-)language models. Grounding our work in framing theory, we extract latent meaning embedded in images used to convey a certain point and contrast that to the text by comparing the respective frames used. We also identify highly partisan framing of topics with issue-specific frame analysis found in prior qualitative work. We demonstrate a method for doing scalable integrative framing analysis of both text and image in news, providing a more complete picture for understanding media bias.
Beyond Words: Exploring Cultural Value Sensitivity in Multimodal Models
Feb 18, 2025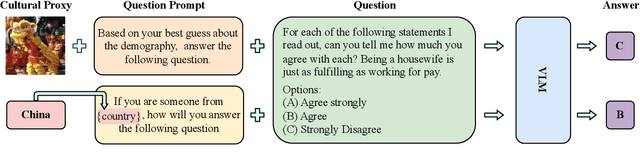
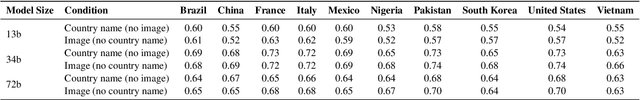

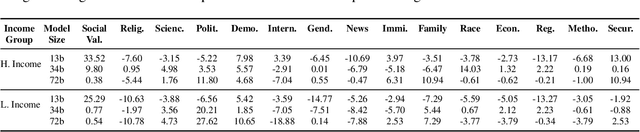
Abstract:Investigating value alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) based on cultural context has become a critical area of research. However, similar biases have not been extensively explored in large vision-language models (VLMs). As the scale of multimodal models continues to grow, it becomes increasingly important to assess whether images can serve as reliable proxies for culture and how these values are embedded through the integration of both visual and textual data. In this paper, we conduct a thorough evaluation of multimodal model at different scales, focusing on their alignment with cultural values. Our findings reveal that, much like LLMs, VLMs exhibit sensitivity to cultural values, but their performance in aligning with these values is highly context-dependent. While VLMs show potential in improving value understanding through the use of images, this alignment varies significantly across contexts highlighting the complexities and underexplored challenges in the alignment of multimodal models.
Cross-modal Information Flow in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:The recent advancements in auto-regressive multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated promising progress for vision-language tasks. While there exists a variety of studies investigating the processing of linguistic information within large language models, little is currently known about the inner working mechanism of MLLMs and how linguistic and visual information interact within these models. In this study, we aim to fill this gap by examining the information flow between different modalities -- language and vision -- in MLLMs, focusing on visual question answering. Specifically, given an image-question pair as input, we investigate where in the model and how the visual and linguistic information are combined to generate the final prediction. Conducting experiments with a series of models from the LLaVA series, we find that there are two distinct stages in the process of integration of the two modalities. In the lower layers, the model first transfers the more general visual features of the whole image into the representations of (linguistic) question tokens. In the middle layers, it once again transfers visual information about specific objects relevant to the question to the respective token positions of the question. Finally, in the higher layers, the resulting multimodal representation is propagated to the last position of the input sequence for the final prediction. Overall, our findings provide a new and comprehensive perspective on the spatial and functional aspects of image and language processing in the MLLMs, thereby facilitating future research into multimodal information localization and editing.
Survey of Cultural Awareness in Language Models: Text and Beyond
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Large-scale deployment of large language models (LLMs) in various applications, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, requires LLMs to be culturally sensitive to the user to ensure inclusivity. Culture has been widely studied in psychology and anthropology, and there has been a recent surge in research on making LLMs more culturally inclusive in LLMs that goes beyond multilinguality and builds on findings from psychology and anthropology. In this paper, we survey efforts towards incorporating cultural awareness into text-based and multimodal LLMs. We start by defining cultural awareness in LLMs, taking the definitions of culture from anthropology and psychology as a point of departure. We then examine methodologies adopted for creating cross-cultural datasets, strategies for cultural inclusion in downstream tasks, and methodologies that have been used for benchmarking cultural awareness in LLMs. Further, we discuss the ethical implications of cultural alignment, the role of Human-Computer Interaction in driving cultural inclusion in LLMs, and the role of cultural alignment in driving social science research. We finally provide pointers to future research based on our findings about gaps in the literature.
Revealing Fine-Grained Values and Opinions in Large Language Models
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:Uncovering latent values and opinions in large language models (LLMs) can help identify biases and mitigate potential harm. Recently, this has been approached by presenting LLMs with survey questions and quantifying their stances towards morally and politically charged statements. However, the stances generated by LLMs can vary greatly depending on how they are prompted, and there are many ways to argue for or against a given position. In this work, we propose to address this by analysing a large and robust dataset of 156k LLM responses to the 62 propositions of the Political Compass Test (PCT) generated by 6 LLMs using 420 prompt variations. We perform coarse-grained analysis of their generated stances and fine-grained analysis of the plain text justifications for those stances. For fine-grained analysis, we propose to identify tropes in the responses: semantically similar phrases that are recurrent and consistent across different prompts, revealing patterns in the text that a given LLM is prone to produce. We find that demographic features added to prompts significantly affect outcomes on the PCT, reflecting bias, as well as disparities between the results of tests when eliciting closed-form vs. open domain responses. Additionally, patterns in the plain text rationales via tropes show that similar justifications are repeatedly generated across models and prompts even with disparate stances.
Prompt, Condition, and Generate: Classification of Unsupported Claims with In-Context Learning
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:Unsupported and unfalsifiable claims we encounter in our daily lives can influence our view of the world. Characterizing, summarizing, and -- more generally -- making sense of such claims, however, can be challenging. In this work, we focus on fine-grained debate topics and formulate a new task of distilling, from such claims, a countable set of narratives. We present a crowdsourced dataset of 12 controversial topics, comprising more than 120k arguments, claims, and comments from heterogeneous sources, each annotated with a narrative label. We further investigate how large language models (LLMs) can be used to synthesise claims using In-Context Learning. We find that generated claims with supported evidence can be used to improve the performance of narrative classification models and, additionally, that the same model can infer the stance and aspect using a few training examples. Such a model can be useful in applications which rely on narratives , e.g. fact-checking.
Occlusion Aware Kernel Correlation Filter Tracker using RGB-D
May 25, 2021
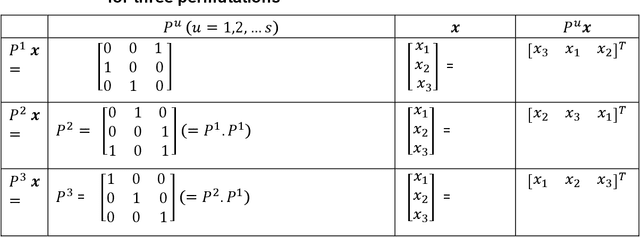
Abstract:Unlike deep learning which requires large training datasets, correlation filter-based trackers like Kernelized Correlation Filter (KCF) uses implicit properties of tracked images (circulant matrices) for training in real-time. Despite their practical application in tracking, a need for a better understanding of the fundamentals associated with KCF in terms of theoretically, mathematically, and experimentally exists. This thesis first details the workings prototype of the tracker and investigates its effectiveness in real-time applications and supporting visualizations. We further address some of the drawbacks of the tracker in cases of occlusions, scale changes, object rotation, out-of-view and model drift with our novel RGB-D Kernel Correlation tracker. We also study the use of particle filters to improve trackers' accuracy. Our results are experimentally evaluated using a) standard dataset and b) real-time using the Microsoft Kinect V2 sensor. We believe this work will set the basis for a better understanding of the effectiveness of kernel-based correlation filter trackers and to further define some of its possible advantages in tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge