Siddhesh Pawar
Entangled in Representations: Mechanistic Investigation of Cultural Biases in Large Language Models
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:The growing deployment of large language models (LLMs) across diverse cultural contexts necessitates a better understanding of how the overgeneralization of less documented cultures within LLMs' representations impacts their cultural understanding. Prior work only performs extrinsic evaluation of LLMs' cultural competence, without accounting for how LLMs' internal mechanisms lead to cultural (mis)representation. To bridge this gap, we propose Culturescope, the first mechanistic interpretability-based method that probes the internal representations of LLMs to elicit the underlying cultural knowledge space. CultureScope utilizes a patching method to extract the cultural knowledge. We introduce a cultural flattening score as a measure of the intrinsic cultural biases. Additionally, we study how LLMs internalize Western-dominance bias and cultural flattening, which allows us to trace how cultural biases emerge within LLMs. Our experimental results reveal that LLMs encode Western-dominance bias and cultural flattening in their cultural knowledge space. We find that low-resource cultures are less susceptible to cultural biases, likely due to their limited training resources. Our work provides a foundation for future research on mitigating cultural biases and enhancing LLMs' cultural understanding. Our codes and data used for experiments are publicly available.
Presumed Cultural Identity: How Names Shape LLM Responses
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Names are deeply tied to human identity. They can serve as markers of individuality, cultural heritage, and personal history. However, using names as a core indicator of identity can lead to over-simplification of complex identities. When interacting with LLMs, user names are an important point of information for personalisation. Names can enter chatbot conversations through direct user input (requested by chatbots), as part of task contexts such as CV reviews, or as built-in memory features that store user information for personalisation. We study biases associated with names by measuring cultural presumptions in the responses generated by LLMs when presented with common suggestion-seeking queries, which might involve making assumptions about the user. Our analyses demonstrate strong assumptions about cultural identity associated with names present in LLM generations across multiple cultures. Our work has implications for designing more nuanced personalisation systems that avoid reinforcing stereotypes while maintaining meaningful customisation.
Survey of Cultural Awareness in Language Models: Text and Beyond
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Large-scale deployment of large language models (LLMs) in various applications, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, requires LLMs to be culturally sensitive to the user to ensure inclusivity. Culture has been widely studied in psychology and anthropology, and there has been a recent surge in research on making LLMs more culturally inclusive in LLMs that goes beyond multilinguality and builds on findings from psychology and anthropology. In this paper, we survey efforts towards incorporating cultural awareness into text-based and multimodal LLMs. We start by defining cultural awareness in LLMs, taking the definitions of culture from anthropology and psychology as a point of departure. We then examine methodologies adopted for creating cross-cultural datasets, strategies for cultural inclusion in downstream tasks, and methodologies that have been used for benchmarking cultural awareness in LLMs. Further, we discuss the ethical implications of cultural alignment, the role of Human-Computer Interaction in driving cultural inclusion in LLMs, and the role of cultural alignment in driving social science research. We finally provide pointers to future research based on our findings about gaps in the literature.
Agree To Disagree
Sep 24, 2023Abstract:How frequently do individuals thoroughly review terms and conditions before proceeding to register for a service, install software, or access a website? The majority of internet users do not engage in this practice. This trend is not surprising, given that terms and conditions typically consist of lengthy documents replete with intricate legal terminology and convoluted sentences. In this paper, we introduce a Machine Learning-powered approach designed to automatically parse and summarize critical information in a user-friendly manner. This technology focuses on distilling the pertinent details that users should contemplate before committing to an agreement.
Tapping BERT for Preposition Sense Disambiguation
Nov 27, 2021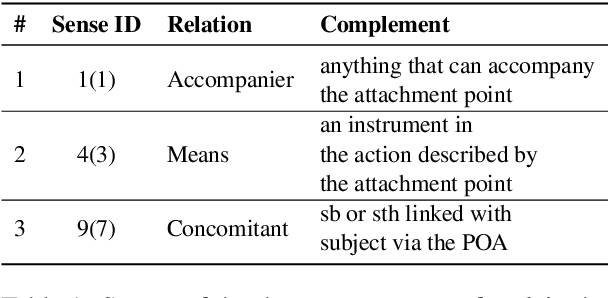
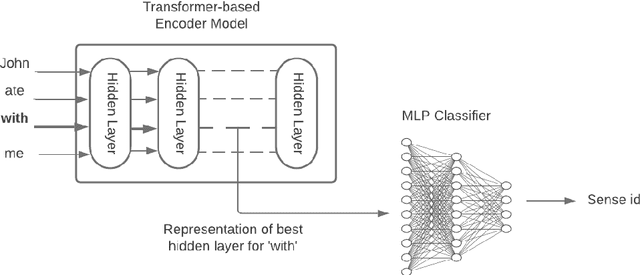

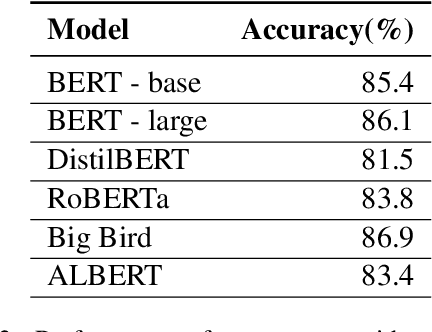
Abstract:Prepositions are frequently occurring polysemous words. Disambiguation of prepositions is crucial in tasks like semantic role labelling, question answering, text entailment, and noun compound paraphrasing. In this paper, we propose a novel methodology for preposition sense disambiguation (PSD), which does not use any linguistic tools. In a supervised setting, the machine learning model is presented with sentences wherein prepositions have been annotated with senses. These senses are IDs in what is called The Preposition Project (TPP). We use the hidden layer representations from pre-trained BERT and BERT variants. The latent representations are then classified into the correct sense ID using a Multi Layer Perceptron. The dataset used for this task is from SemEval-2007 Task-6. Our methodology gives an accuracy of 86.85% which is better than the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge