Siddhant Gupta
Uncovering Cultural Representation Disparities in Vision-Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across a range of tasks, yet concerns about their potential biases exist. This work investigates the extent to which prominent VLMs exhibit cultural biases by evaluating their performance on an image-based country identification task at a country level. Utilizing the geographically diverse Country211 dataset, we probe several large vision language models (VLMs) under various prompting strategies: open-ended questions, multiple-choice questions (MCQs) including challenging setups like multilingual and adversarial settings. Our analysis aims to uncover disparities in model accuracy across different countries and question formats, providing insights into how training data distribution and evaluation methodologies might influence cultural biases in VLMs. The findings highlight significant variations in performance, suggesting that while VLMs possess considerable visual understanding, they inherit biases from their pre-training data and scale that impact their ability to generalize uniformly across diverse global contexts.
Robust and Fine-Grained Detection of AI Generated Texts
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:An ideal detection system for machine generated content is supposed to work well on any generator as many more advanced LLMs come into existence day by day. Existing systems often struggle with accurately identifying AI-generated content over shorter texts. Further, not all texts might be entirely authored by a human or LLM, hence we focused more over partial cases i.e human-LLM co-authored texts. Our paper introduces a set of models built for the task of token classification which are trained on an extensive collection of human-machine co-authored texts, which performed well over texts of unseen domains, unseen generators, texts by non-native speakers and those with adversarial inputs. We also introduce a new dataset of over 2.4M such texts mostly co-authored by several popular proprietary LLMs over 23 languages. We also present findings of our models' performance over each texts of each domain and generator. Additional findings include comparison of performance against each adversarial method, length of input texts and characteristics of generated texts compared to the original human authored texts.
Improving Multilingual Capabilities with Cultural and Local Knowledge in Large Language Models While Enhancing Native Performance
Apr 13, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities, but their development has primarily focused on English and other high-resource languages, leaving many languages underserved. We present our latest Hindi-English bi-lingual LLM \textbf{Mantra-14B} with ~3\% average improvement in benchmark scores over both languages, outperforming models twice its size. Using a curated dataset composed of English and Hindi instruction data of 485K samples, we instruction tuned models such as Qwen-2.5-14B-Instruct and Phi-4 to improve performance over both English and Hindi. Our experiments encompassing seven different LLMs of varying parameter sizes and over 140 training attempts with varying English-Hindi training data ratios demonstrated that it is possible to significantly improve multilingual performance without compromising native performance. Further, our approach avoids resource-intensive techniques like vocabulary expansion or architectural modifications, thus keeping the model size small. Our results indicate that modest fine-tuning with culturally and locally informed data can bridge performance gaps without incurring significant computational overhead. We release our training code, datasets, and models under mit and apache licenses to aid further research towards under-represented and low-resource languages.
IITR-CIOL@NLU of Devanagari Script Languages 2025: Multilingual Hate Speech Detection and Target Identification in Devanagari-Scripted Languages
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:This work focuses on two subtasks related to hate speech detection and target identification in Devanagari-scripted languages, specifically Hindi, Marathi, Nepali, Bhojpuri, and Sanskrit. Subtask B involves detecting hate speech in online text, while Subtask C requires identifying the specific targets of hate speech, such as individuals, organizations, or communities. We propose the MultilingualRobertaClass model, a deep neural network built on the pretrained multilingual transformer model ia-multilingual-transliterated-roberta, optimized for classification tasks in multilingual and transliterated contexts. The model leverages contextualized embeddings to handle linguistic diversity, with a classifier head for binary classification. We received 88.40% accuracy in Subtask B and 66.11% accuracy in Subtask C, in the test set.
1-800-SHARED-TASKS at RegNLP: Lexical Reranking of Semantic Retrieval (LeSeR) for Regulatory Question Answering
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the system description of our entry for the COLING 2025 RegNLP RIRAG (Regulatory Information Retrieval and Answer Generation) challenge, focusing on leveraging advanced information retrieval and answer generation techniques in regulatory domains. We experimented with a combination of embedding models, including Stella, BGE, CDE, and Mpnet, and leveraged fine-tuning and reranking for retrieving relevant documents in top ranks. We utilized a novel approach, LeSeR, which achieved competitive results with a recall@10 of 0.8201 and map@10 of 0.6655 for retrievals. This work highlights the transformative potential of natural language processing techniques in regulatory applications, offering insights into their capabilities for implementing a retrieval augmented generation system while identifying areas for future improvement in robustness and domain adaptation.
SeQwen at the Financial Misinformation Detection Challenge Task: Sequential Learning for Claim Verification and Explanation Generation in Financial Domains
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:This paper presents the system description of our entry for the COLING 2025 FMD challenge, focusing on misinformation detection in financial domains. We experimented with a combination of large language models, including Qwen, Mistral, and Gemma-2, and leveraged pre-processing and sequential learning for not only identifying fraudulent financial content but also generating coherent, and concise explanations that clarify the rationale behind the classifications. Our approach achieved competitive results with an F1-score of 0.8283 for classification, and ROUGE-1 of 0.7253 for explanations. This work highlights the transformative potential of LLMs in financial applications, offering insights into their capabilities for combating misinformation and enhancing transparency while identifying areas for future improvement in robustness and domain adaptation.
Living off the Analyst: Harvesting Features from Yara Rules for Malware Detection
Nov 27, 2024
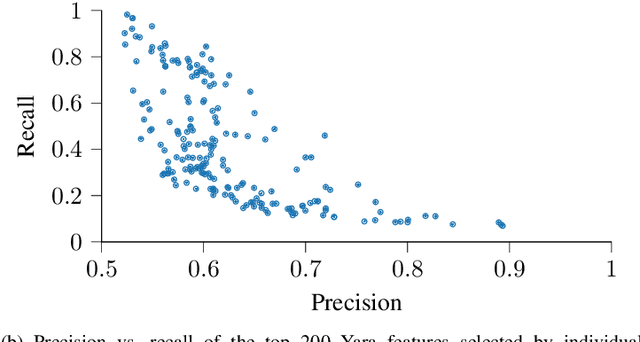
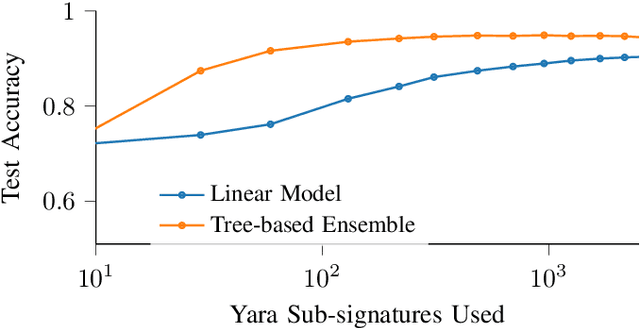
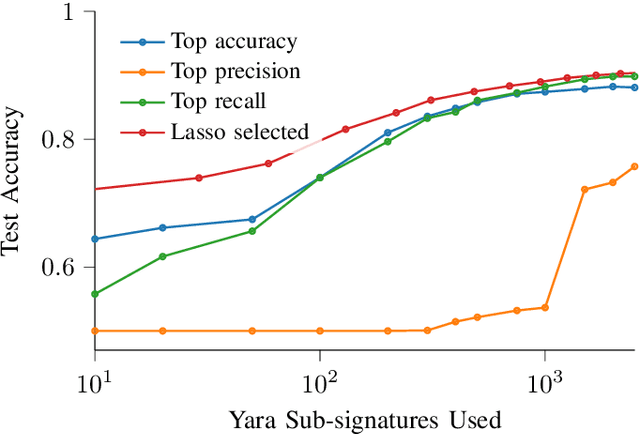
Abstract:A strategy used by malicious actors is to "live off the land," where benign systems and tools already available on a victim's systems are used and repurposed for the malicious actor's intent. In this work, we ask if there is a way for anti-virus developers to similarly re-purpose existing work to improve their malware detection capability. We show that this is plausible via YARA rules, which use human-written signatures to detect specific malware families, functionalities, or other markers of interest. By extracting sub-signatures from publicly available YARA rules, we assembled a set of features that can more effectively discriminate malicious samples from benign ones. Our experiments demonstrate that these features add value beyond traditional features on the EMBER 2018 dataset. Manual analysis of the added sub-signatures shows a power-law behavior in a combination of features that are specific and unique, as well as features that occur often. A prior expectation may be that the features would be limited in being overly specific to unique malware families. This behavior is observed, and is apparently useful in practice. In addition, we also find sub-signatures that are dual-purpose (e.g., detecting virtual machine environments) or broadly generic (e.g., DLL imports).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge