Songsong Wu
Source-free domain adaptation based on label reliability for cross-domain bearing fault diagnosis
Mar 11, 2025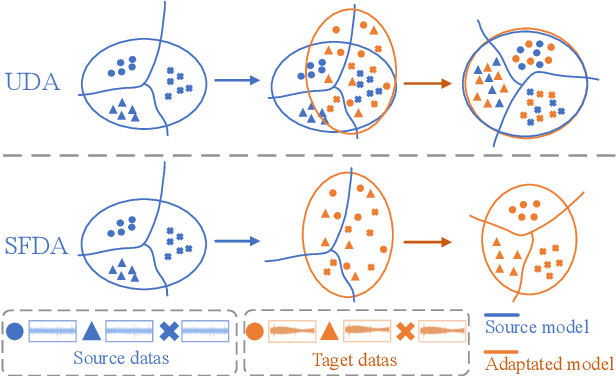
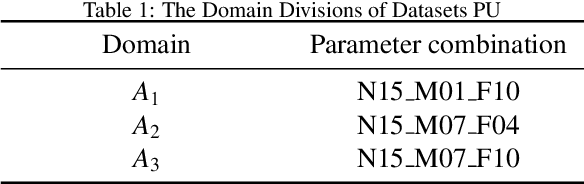
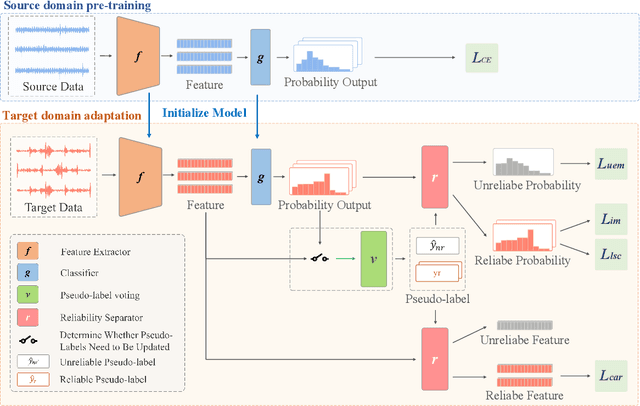
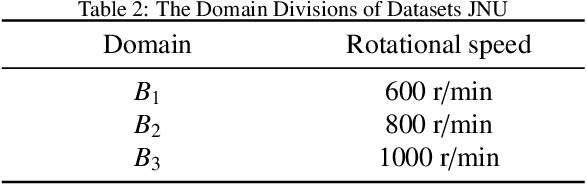
Abstract:Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) has been exploited for cross-domain bearing fault diagnosis without access to source data. Current methods select partial target samples with reliable pseudo-labels for model adaptation, which is sub-optimal due to the ignored target samples. We argue that every target sample can contribute to model adaptation, and accordingly propose in this paper a novel SFDA-based approach for bearing fault diagnosis that exploits both reliable and unreliable pseudo-labels. We develop a data-augmentation-based label voting strategy to divide the target samples into reliable and unreliable ones. We propose to explore the underlying relation between feature space and label space by using the reliable pseudo-labels as ground-truth labels, meanwhile, alleviating negative transfer by maximizing the entropy of the unreliable pseudo-labels. The proposed method achieves well-balance between discriminability and diversity by taking advantage of reliable and unreliable pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments are conducted on two bearing fault benchmarks, demonstrating that our approach achieves significant performance improvements against existing SFDA-based bearing fault diagnosis methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/BdLab405/SDALR.
Deep Unsupervised Key Frame Extraction for Efficient Video Classification
Nov 12, 2022Abstract:Video processing and analysis have become an urgent task since a huge amount of videos (e.g., Youtube, Hulu) are uploaded online every day. The extraction of representative key frames from videos is very important in video processing and analysis since it greatly reduces computing resources and time. Although great progress has been made recently, large-scale video classification remains an open problem, as the existing methods have not well balanced the performance and efficiency simultaneously. To tackle this problem, this work presents an unsupervised method to retrieve the key frames, which combines Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Temporal Segment Density Peaks Clustering (TSDPC). The proposed TSDPC is a generic and powerful framework and it has two advantages compared with previous works, one is that it can calculate the number of key frames automatically. The other is that it can preserve the temporal information of the video. Thus it improves the efficiency of video classification. Furthermore, a Long Short-Term Memory network (LSTM) is added on the top of the CNN to further elevate the performance of classification. Moreover, a weight fusion strategy of different input networks is presented to boost the performance. By optimizing both video classification and key frame extraction simultaneously, we achieve better classification performance and higher efficiency. We evaluate our method on two popular datasets (i.e., HMDB51 and UCF101) and the experimental results consistently demonstrate that our strategy achieves competitive performance and efficiency compared with the state-of-the-art approaches.
Cross-View Panorama Image Synthesis
Mar 22, 2022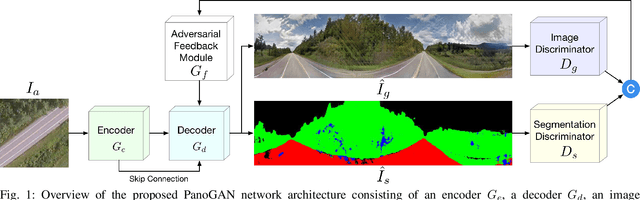
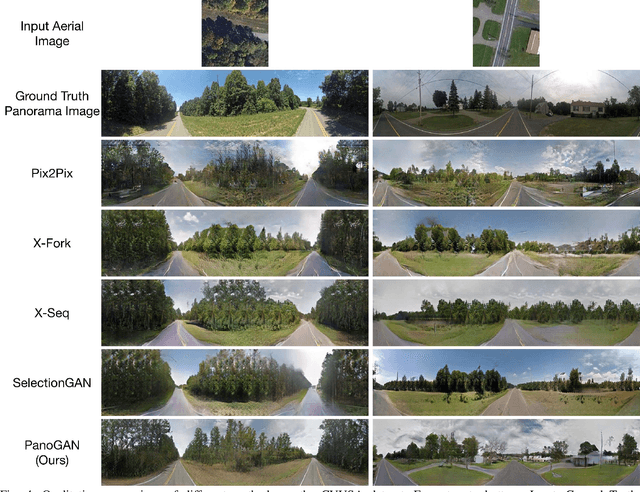
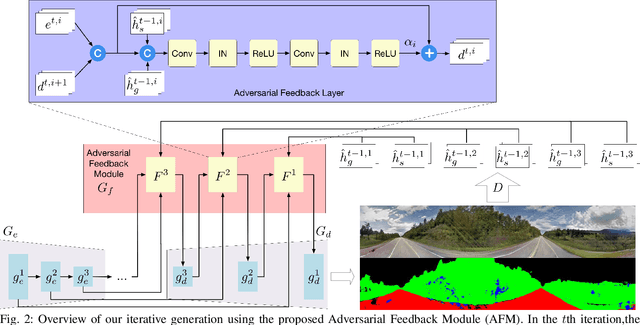
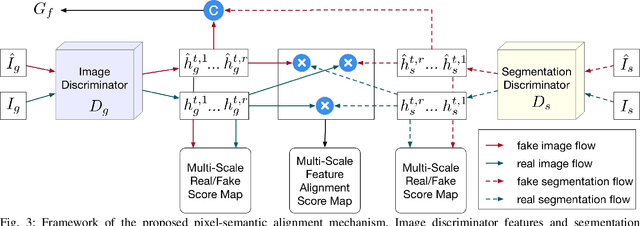

Abstract:In this paper, we tackle the problem of synthesizing a ground-view panorama image conditioned on a top-view aerial image, which is a challenging problem due to the large gap between the two image domains with different view-points. Instead of learning cross-view mapping in a feedforward pass, we propose a novel adversarial feedback GAN framework named PanoGAN with two key components: an adversarial feedback module and a dual branch discrimination strategy. First, the aerial image is fed into the generator to produce a target panorama image and its associated segmentation map in favor of model training with layout semantics. Second, the feature responses of the discriminator encoded by our adversarial feedback module are fed back to the generator to refine the intermediate representations, so that the generation performance is continually improved through an iterative generation process. Third, to pursue high-fidelity and semantic consistency of the generated panorama image, we propose a pixel-segmentation alignment mechanism under the dual branch discrimiantion strategy to facilitate cooperation between the generator and the discriminator. Extensive experimental results on two challenging cross-view image datasets show that PanoGAN enables high-quality panorama image generation with more convincing details than state-of-the-art approaches. The source code and trained models are available at \url{https://github.com/sswuai/PanoGAN}.
DF-GAN: Deep Fusion Generative Adversarial Networks for Text-to-Image Synthesis
Aug 13, 2020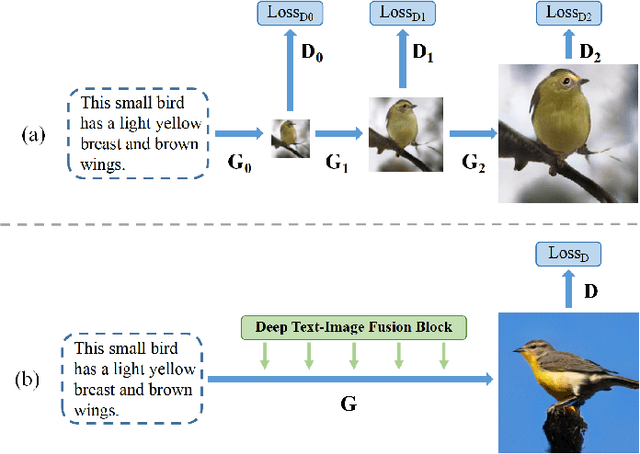

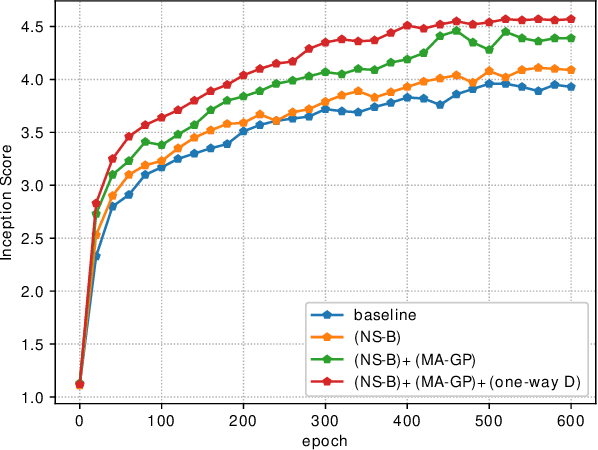
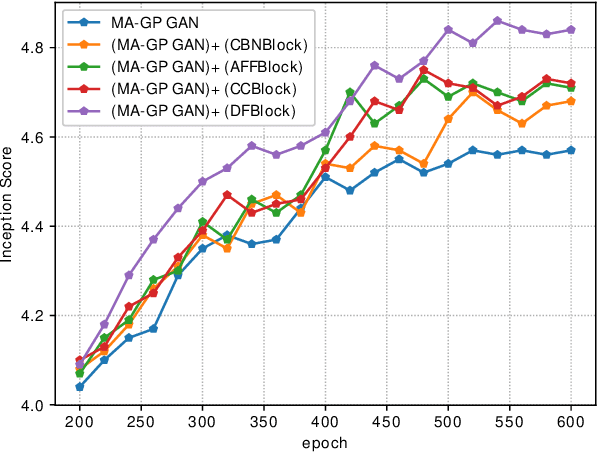
Abstract:Synthesizing high-resolution realistic images from text descriptions is a challenging task. Almost all existing text-to-image methods employ stacked generative adversarial networks as the backbone, utilize cross-modal attention mechanisms to fuse text and image features, and use extra networks to ensure text-image semantic consistency. The existing text-to-image models have three problems: 1) For the backbone, there are multiple generators and discriminators stacked for generating different scales of images making the training process slow and inefficient. 2) For semantic consistency, the existing models employ extra networks to ensure the semantic consistency increasing the training complexity and bringing an additional computational cost. 3) For the text-image feature fusion method, cross-modal attention is only applied a few times during the generation process due to its computational cost impeding fusing the text and image features deeply. To solve these limitations, we propose 1) a novel simplified text-to-image backbone which is able to synthesize high-quality images directly by one pair of generator and discriminator, 2) a novel regularization method called Matching-Aware zero-centered Gradient Penalty which promotes the generator to synthesize more realistic and text-image semantic consistent images without introducing extra networks, 3) a novel fusion module called Deep Text-Image Fusion Block which can exploit the semantics of text descriptions effectively and fuse text and image features deeply during the generation process. Compared with the previous text-to-image models, our DF-GAN is simpler and more efficient and achieves better performance. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on both Caltech-UCSD Birds 200 and COCO datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model in comparison to state-of-the-art models.
Cross-View Image Synthesis with Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism
Jul 20, 2020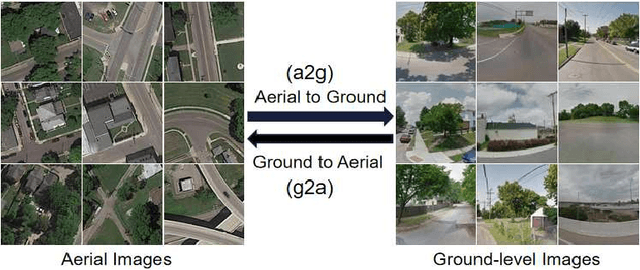
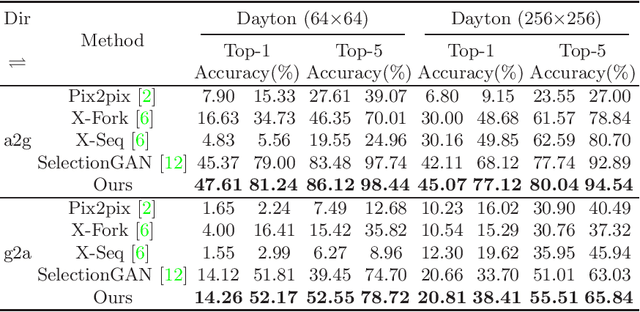
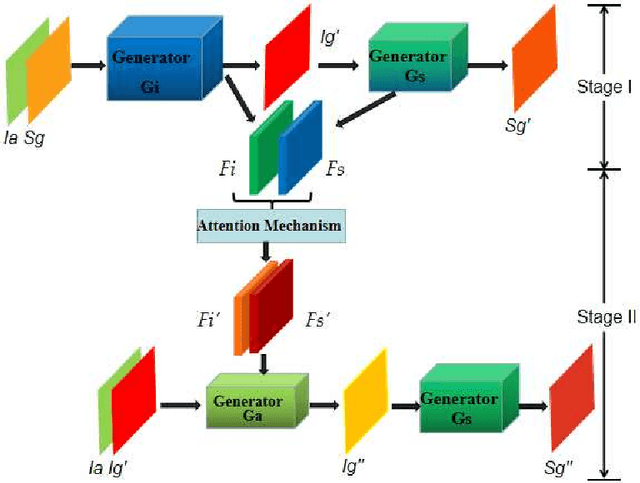
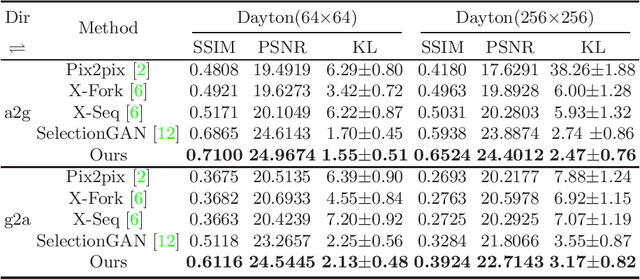
Abstract:Learning to generate natural scenes has always been a daunting task in computer vision. This is even more laborious when generating images with very different views. When the views are very different, the view fields have little overlap or objects are occluded, leading the task very challenging. In this paper, we propose to use Generative Adversarial Networks(GANs) based on a deformable convolution and attention mechanism to solve the problem of cross-view image synthesis (see Fig.1). It is difficult to understand and transform scenes appearance and semantic information from another view, thus we use deformed convolution in the U-net network to improve the network's ability to extract features of objects at different scales. Moreover, to better learn the correspondence between images from different views, we apply an attention mechanism to refine the intermediate feature map thus generating more realistic images. A large number of experiments on different size images on the Dayton dataset[1] show that our model can produce better results than state-of-the-art methods.
SiENet: Siamese Expansion Network for Image Extrapolation
Jul 08, 2020
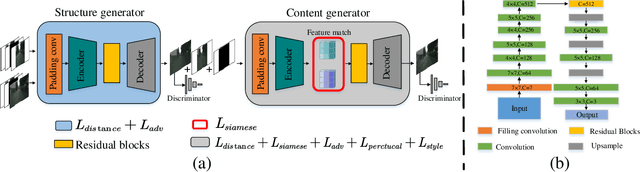
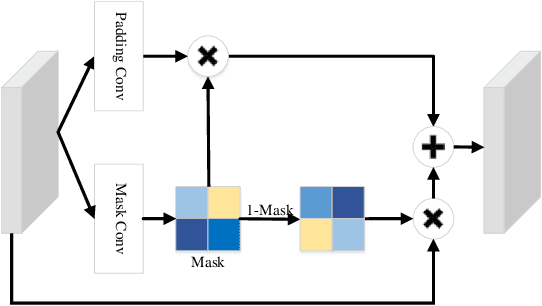

Abstract:Different from image inpainting, image outpainting has relative less context in the image center to capture and more content at the image border to predict. Therefore, classical encoder-decoder pipeline of existing methods may not predict the outstretched unknown content perfectly. In this paper, a novel two-stage siamese adversarial model for image extrapolation, named Siamese Expansion Network (SiENet) is proposed. In two stages, a novel border sensitive convolution named adaptive filling convolution is designed for allowing encoder to predict the unknown content, alleviating the burden of decoder. Besides, to introduce prior knowledge to network and reinforce the inferring ability of encoder, siamese adversarial mechanism is designed to enable our network to model the distribution of covered long range feature for that of uncovered image feature. The results on four datasets has demonstrated that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-arts and could produce realistic results.
Expression Conditional GAN for Facial Expression-to-Expression Translation
May 14, 2019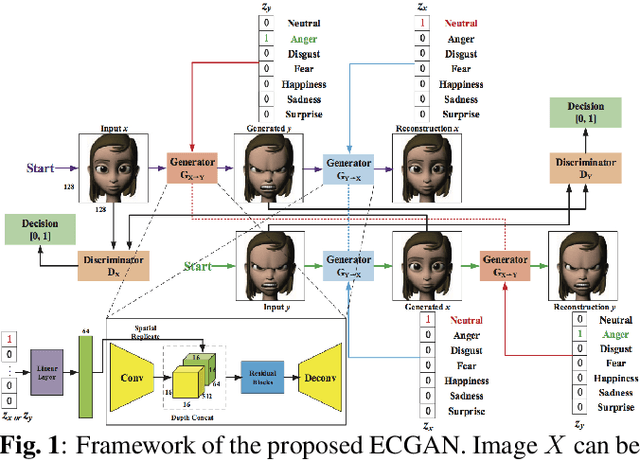

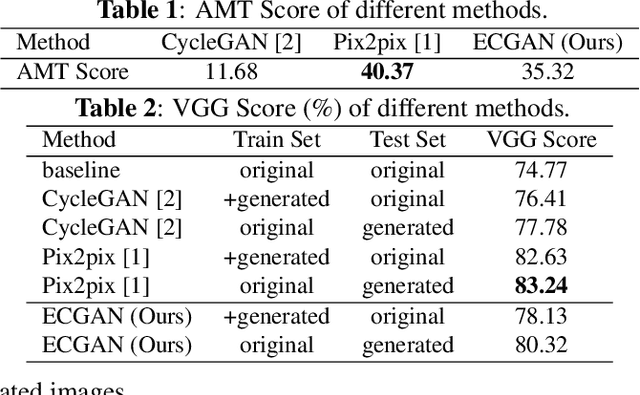

Abstract:In this paper, we focus on the facial expression translation task and propose a novel Expression Conditional GAN (ECGAN) which can learn the mapping from one image domain to another one based on an additional expression attribute. The proposed ECGAN is a generic framework and is applicable to different expression generation tasks where specific facial expression can be easily controlled by the conditional attribute label. Besides, we introduce a novel face mask loss to reduce the influence of background changing. Moreover, we propose an entire framework for facial expression generation and recognition in the wild, which consists of two modules, i.e., generation and recognition. Finally, we evaluate our framework on several public face datasets in which the subjects have different races, illumination, occlusion, pose, color, content and background conditions. Even though these datasets are very diverse, both the qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our approach is able to generate facial expressions accurately and robustly.
Joint Learning of Self-Representation and Indicator for Multi-View Image Clustering
May 11, 2019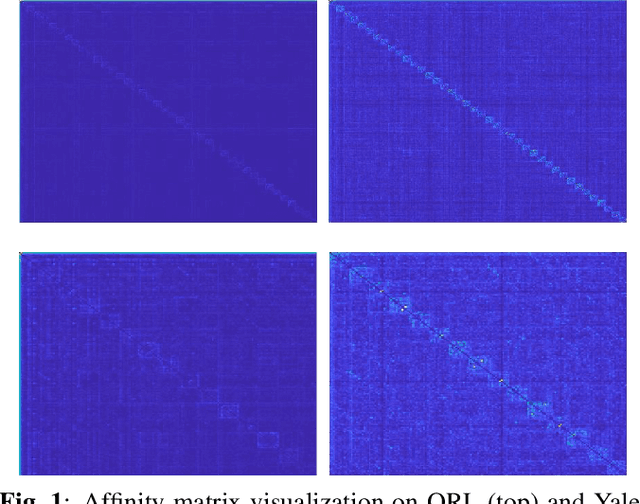
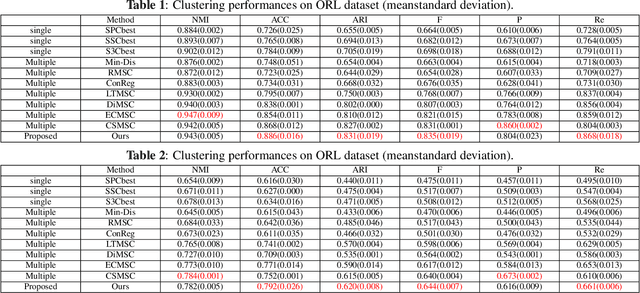
Abstract:Multi-view subspace clustering aims to divide a set of multisource data into several groups according to their underlying subspace structure. Although the spectral clustering based methods achieve promotion in multi-view clustering, their utility is limited by the separate learning manner in which affinity matrix construction and cluster indicator estimation are isolated. In this paper, we propose to jointly learn the self-representation, continue and discrete cluster indicators in an unified model. Our model can explore the subspace structure of each view and fusion them to facilitate clustering simultaneously. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms other existing competitive multi-view clustering methods.
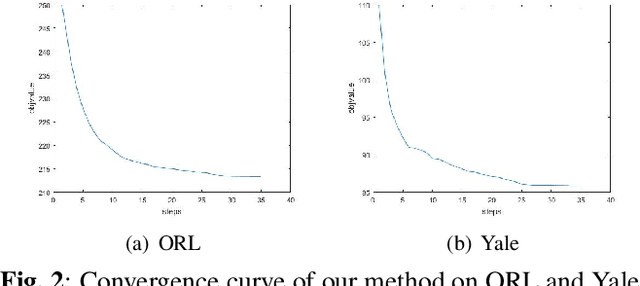
Structured Discriminative Tensor Dictionary Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
May 11, 2019
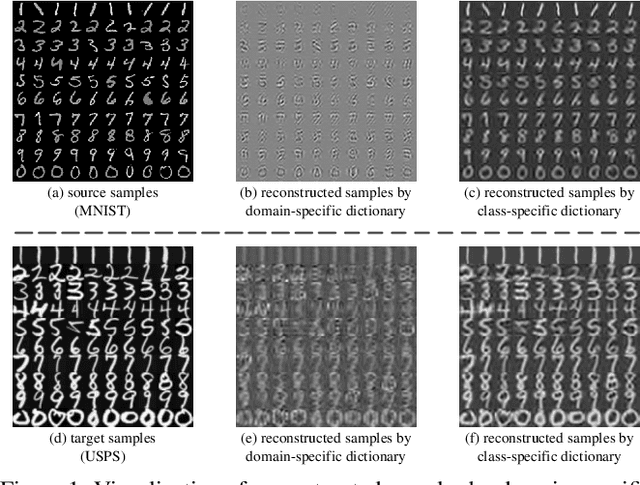
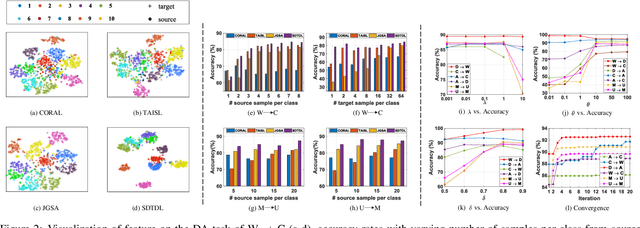
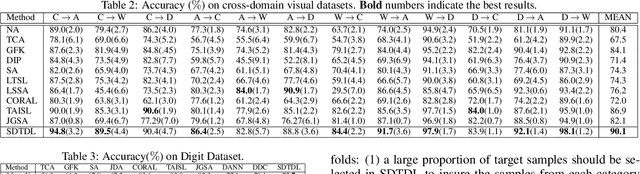
Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) addresses the problem of performance degradation due to domain shift between training and testing sets, which is common in computer vision applications. Most existing UDA approaches are based on vector-form data although the typical format of data or features in visual applications is multi-dimensional tensor. Besides, current methods, including the deep network approaches, assume that abundant labeled source samples are provided for training. However, the number of labeled source samples are always limited due to expensive annotation cost in practice, making sub-optimal performance been observed. In this paper, we propose to seek discriminative representation for multi-dimensional data by learning a structured dictionary in tensor space. The dictionary separates domain-specific information and class-specific information to guarantee the representation robust to domains. In addition, a pseudo-label estimation scheme is developed to combine with discriminant analysis in the algorithm iteration for avoiding the external classifier design. We perform extensive results on different datasets with limited source samples. Experimental results demonstrates that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge