Siyu Liu
School of Computer and Information Engineering, Xiamen University of Technology, Xiamen, China
ReWeaver: Towards Simulation-Ready and Topology-Accurate Garment Reconstruction
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:High-quality 3D garment reconstruction plays a crucial role in mitigating the sim-to-real gap in applications such as digital avatars, virtual try-on and robotic manipulation. However, existing garment reconstruction methods typically rely on unstructured representations, such as 3D Gaussian Splats, struggling to provide accurate reconstructions of garment topology and sewing structures. As a result, the reconstructed outputs are often unsuitable for high-fidelity physical simulation. We propose ReWeaver, a novel framework for topology-accurate 3D garment and sewing pattern reconstruction from sparse multi-view RGB images. Given as few as four input views, ReWeaver predicts seams and panels as well as their connectivities in both the 2D UV space and the 3D space. The predicted seams and panels align precisely with the multi-view images, yielding structured 2D--3D garment representations suitable for 3D perception, high-fidelity physical simulation, and robotic manipulation. To enable effective training, we construct a large-scale dataset GCD-TS, comprising multi-view RGB images, 3D garment geometries, textured human body meshes and annotated sewing patterns. The dataset contains over 100,000 synthetic samples covering a wide range of complex geometries and topologies. Extensive experiments show that ReWeaver consistently outperforms existing methods in terms of topology accuracy, geometry alignment and seam-panel consistency.
PerTouch: VLM-Driven Agent for Personalized and Semantic Image Retouching
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Image retouching aims to enhance visual quality while aligning with users' personalized aesthetic preferences. To address the challenge of balancing controllability and subjectivity, we propose a unified diffusion-based image retouching framework called PerTouch. Our method supports semantic-level image retouching while maintaining global aesthetics. Using parameter maps containing attribute values in specific semantic regions as input, PerTouch constructs an explicit parameter-to-image mapping for fine-grained image retouching. To improve semantic boundary perception, we introduce semantic replacement and parameter perturbation mechanisms in the training process. To connect natural language instructions with visual control, we develop a VLM-driven agent that can handle both strong and weak user instructions. Equipped with mechanisms of feedback-driven rethinking and scene-aware memory, PerTouch better aligns with user intent and captures long-term preferences. Extensive experiments demonstrate each component's effectiveness and the superior performance of PerTouch in personalized image retouching. Code is available at: https://github.com/Auroral703/PerTouch.
MatTools: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Materials Science Tools
May 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to materials science questions, including literature comprehension, property prediction, materials discovery and alloy design. At the same time, a wide range of physics-based computational approaches have been developed in which materials properties can be calculated. Here, we propose a benchmark application to evaluate the proficiency of LLMs to answer materials science questions through the generation and safe execution of codes based on such physics-based computational materials science packages. MatTools is built on two complementary components: a materials simulation tool question-answer (QA) benchmark and a real-world tool-usage benchmark. We designed an automated methodology to efficiently collect real-world materials science tool-use examples. The QA benchmark, derived from the pymatgen (Python Materials Genomics) codebase and documentation, comprises 69,225 QA pairs that assess the ability of an LLM to understand materials science tools. The real-world benchmark contains 49 tasks (138 subtasks) requiring the generation of functional Python code for materials property calculations. Our evaluation of diverse LLMs yields three key insights: (1)Generalists outshine specialists;(2)AI knows AI; and (3)Simpler is better. MatTools provides a standardized framework for assessing and improving LLM capabilities for materials science tool applications, facilitating the development of more effective AI systems for materials science and general scientific research.
A Diffusion-Based Framework for Occluded Object Movement
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Seamlessly moving objects within a scene is a common requirement for image editing, but it is still a challenge for existing editing methods. Especially for real-world images, the occlusion situation further increases the difficulty. The main difficulty is that the occluded portion needs to be completed before movement can proceed. To leverage the real-world knowledge embedded in the pre-trained diffusion models, we propose a Diffusion-based framework specifically designed for Occluded Object Movement, named DiffOOM. The proposed DiffOOM consists of two parallel branches that perform object de-occlusion and movement simultaneously. The de-occlusion branch utilizes a background color-fill strategy and a continuously updated object mask to focus the diffusion process on completing the obscured portion of the target object. Concurrently, the movement branch employs latent optimization to place the completed object in the target location and adopts local text-conditioned guidance to integrate the object into new surroundings appropriately. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of our method, which is further validated by a comprehensive user study.
Iterative Predictor-Critic Code Decoding for Real-World Image Dehazing
Mar 17, 2025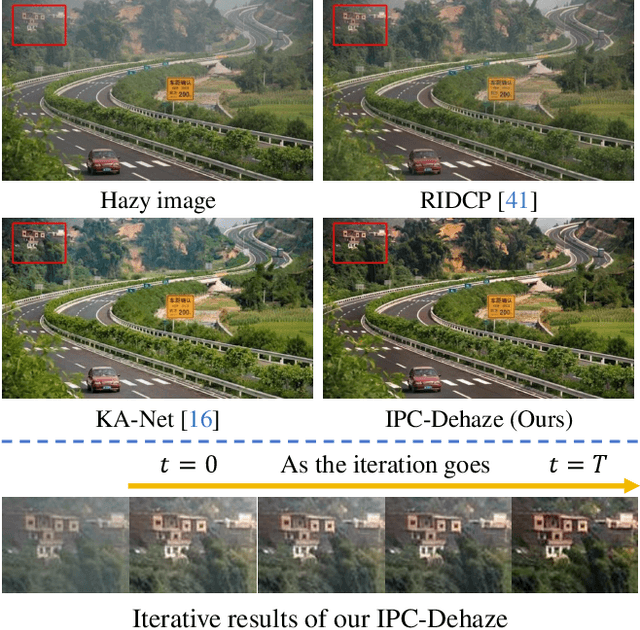
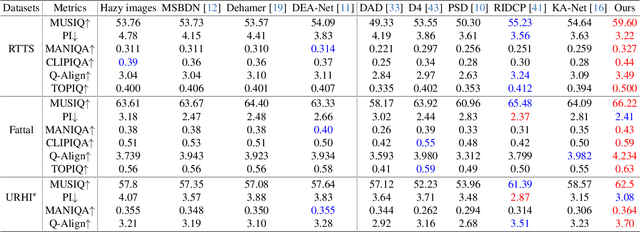
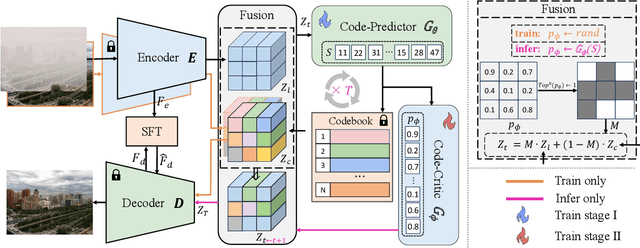
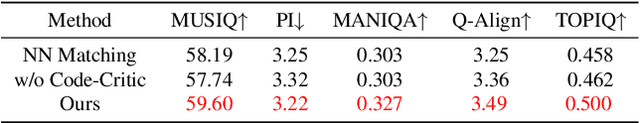
Abstract:We propose a novel Iterative Predictor-Critic Code Decoding framework for real-world image dehazing, abbreviated as IPC-Dehaze, which leverages the high-quality codebook prior encapsulated in a pre-trained VQGAN. Apart from previous codebook-based methods that rely on one-shot decoding, our method utilizes high-quality codes obtained in the previous iteration to guide the prediction of the Code-Predictor in the subsequent iteration, improving code prediction accuracy and ensuring stable dehazing performance. Our idea stems from the observations that 1) the degradation of hazy images varies with haze density and scene depth, and 2) clear regions play crucial cues in restoring dense haze regions. However, it is non-trivial to progressively refine the obtained codes in subsequent iterations, owing to the difficulty in determining which codes should be retained or replaced at each iteration. Another key insight of our study is to propose Code-Critic to capture interrelations among codes. The Code-Critic is used to evaluate code correlations and then resample a set of codes with the highest mask scores, i.e., a higher score indicates that the code is more likely to be rejected, which helps retain more accurate codes and predict difficult ones. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art methods in real-world dehazing.
Active Learning for Conditional Inverse Design with Crystal Generation and Foundation Atomic Models
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming materials science, enabling both theoretical advancements and accelerated materials discovery. Recent progress in crystal generation models, which design crystal structures for targeted properties, and foundation atomic models (FAMs), which capture interatomic interactions across the periodic table, has significantly improved inverse materials design. However, an efficient integration of these two approaches remains an open challenge. Here, we present an active learning framework that combines crystal generation models and foundation atomic models to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of inverse design. As a case study, we employ Con-CDVAE to generate candidate crystal structures and MACE-MP-0 FAM as one of the high-throughput screeners for bulk modulus evaluation. Through iterative active learning, we demonstrate that Con-CDVAE progressively improves its accuracy in generating crystals with target properties, highlighting the effectiveness of a property-driven fine-tuning process. Our framework is general to accommodate different crystal generation and foundation atomic models, and establishes a scalable approach for AI-driven materials discovery. By bridging generative modeling with atomic-scale simulations, this work paves the way for more accurate and efficient inverse materials design.
FaceMe: Robust Blind Face Restoration with Personal Identification
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:Blind face restoration is a highly ill-posed problem due to the lack of necessary context. Although existing methods produce high-quality outputs, they often fail to faithfully preserve the individual's identity. In this paper, we propose a personalized face restoration method, FaceMe, based on a diffusion model. Given a single or a few reference images, we use an identity encoder to extract identity-related features, which serve as prompts to guide the diffusion model in restoring high-quality and identity-consistent facial images. By simply combining identity-related features, we effectively minimize the impact of identity-irrelevant features during training and support any number of reference image inputs during inference. Additionally, thanks to the robustness of the identity encoder, synthesized images can be used as reference images during training, and identity changing during inference does not require fine-tuning the model. We also propose a pipeline for constructing a reference image training pool that simulates the poses and expressions that may appear in real-world scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that our FaceMe can restore high-quality facial images while maintaining identity consistency, achieving excellent performance and robustness.
CovidLLM: A Robust Large Language Model with Missing Value Adaptation and Multi-Objective Learning Strategy for Predicting Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), which emerged in 2019, has caused millions of deaths worldwide. Although effective vaccines have been developed to mitigate severe symptoms, certain populations, particularly the elderly and those with comorbidities, remain at high risk for severe outcomes and increased mortality. Consequently, early identification of the severity and clinical outcomes of the disease in these patients is vital to prevent adverse prognoses. Although traditional machine learning and deep learning models have been widely employed in this area, the potential of large language models (LLMs) remains largely unexplored. Our research focuses primarily on constructing specialized prompts and adopting multi-objective learning strategies. We started by selecting serological indicators that significantly correlate with clinical outcomes and disease severity to serve as input data for the model. Blood test samples often contain numerous missing values, and traditional models generally rely on imputation to handle these gaps in the data. In contrast, LLMs offer the advantage of robust semantic understanding. By setting prompts, we can explicitly inform the model when a feature's value is missing, without the need for imputation. For the multi-objective learning strategy, the model is designed to first predict disease severity and then predict clinical outcomes. Given that LLMs utilize both the input text and the generated tokens as input for generating the next token, the predicted severity is used as a basis for generating the clinical outcome. During the fine-tuning of the LLM, the two objectives influence and improve each other. Our experiments were implemented based on the ChatGLM model. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of LLMs in this task, suggesting promising potential for further development.
SMILE-UHURA Challenge -- Small Vessel Segmentation at Mesoscopic Scale from Ultra-High Resolution 7T Magnetic Resonance Angiograms
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:The human brain receives nutrients and oxygen through an intricate network of blood vessels. Pathology affecting small vessels, at the mesoscopic scale, represents a critical vulnerability within the cerebral blood supply and can lead to severe conditions, such as Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases. The advent of 7 Tesla MRI systems has enabled the acquisition of higher spatial resolution images, making it possible to visualise such vessels in the brain. However, the lack of publicly available annotated datasets has impeded the development of robust, machine learning-driven segmentation algorithms. To address this, the SMILE-UHURA challenge was organised. This challenge, held in conjunction with the ISBI 2023, in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, aimed to provide a platform for researchers working on related topics. The SMILE-UHURA challenge addresses the gap in publicly available annotated datasets by providing an annotated dataset of Time-of-Flight angiography acquired with 7T MRI. This dataset was created through a combination of automated pre-segmentation and extensive manual refinement. In this manuscript, sixteen submitted methods and two baseline methods are compared both quantitatively and qualitatively on two different datasets: held-out test MRAs from the same dataset as the training data (with labels kept secret) and a separate 7T ToF MRA dataset where both input volumes and labels are kept secret. The results demonstrate that most of the submitted deep learning methods, trained on the provided training dataset, achieved reliable segmentation performance. Dice scores reached up to 0.838 $\pm$ 0.066 and 0.716 $\pm$ 0.125 on the respective datasets, with an average performance of up to 0.804 $\pm$ 0.15.
IterSelectTune: An Iterative Training Framework for Efficient Instruction-Tuning Data Selection
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) continue to advance, instruction tuning has become critical for improving their ability to generate accurate and contextually appropriate responses. Although numerous instruction-tuning datasets have been developed to enhance LLM performance, selecting high-quality instruction data from large source datasets typically demands significant human effort. In this work, we introduce $\textbf{IterSelectTune}$, an efficient, cost-effective iterative training policy for selecting high-quality instruction data with no human involvement and limited reliance on GPT-4. By fine-tuning on approximately 20\% of the source data, our method consistently outperforms models fine-tuned on the full dataset across multiple benchmarks and public test datasets. These results highlight the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing LLM performance while reducing the computational resources required for instruction tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge