Shrikanth S. Narayanan
ModalityMirror: Improving Audio Classification in Modality Heterogeneity Federated Learning with Multimodal Distillation
Aug 28, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Federated Learning frequently encounters challenges of client modality heterogeneity, leading to undesired performances for secondary modality in multimodal learning. It is particularly prevalent in audiovisual learning, with audio is often assumed to be the weaker modality in recognition tasks. To address this challenge, we introduce ModalityMirror to improve audio model performance by leveraging knowledge distillation from an audiovisual federated learning model. ModalityMirror involves two phases: a modality-wise FL stage to aggregate uni-modal encoders; and a federated knowledge distillation stage on multi-modality clients to train an unimodal student model. Our results demonstrate that ModalityMirror significantly improves the audio classification compared to the state-of-the-art FL methods such as Harmony, particularly in audiovisual FL facing video missing. Our approach unlocks the potential for exploiting the diverse modality spectrum inherent in multi-modal FL.
Creating a Lens of Chinese Culture: A Multimodal Dataset for Chinese Pun Rebus Art Understanding
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable abilities in understanding everyday content. However, their performance in the domain of art, particularly culturally rich art forms, remains less explored. As a pearl of human wisdom and creativity, art encapsulates complex cultural narratives and symbolism. In this paper, we offer the Pun Rebus Art Dataset, a multimodal dataset for art understanding deeply rooted in traditional Chinese culture. We focus on three primary tasks: identifying salient visual elements, matching elements with their symbolic meanings, and explanations for the conveyed messages. Our evaluation reveals that state-of-the-art VLMs struggle with these tasks, often providing biased and hallucinated explanations and showing limited improvement through in-context learning. By releasing the Pun Rebus Art Dataset, we aim to facilitate the development of VLMs that can better understand and interpret culturally specific content, promoting greater inclusiveness beyond English-based corpora.
TI-ASU: Toward Robust Automatic Speech Understanding through Text-to-speech Imputation Against Missing Speech Modality
Apr 27, 2024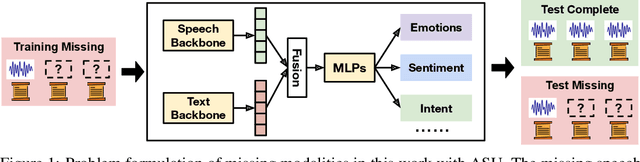
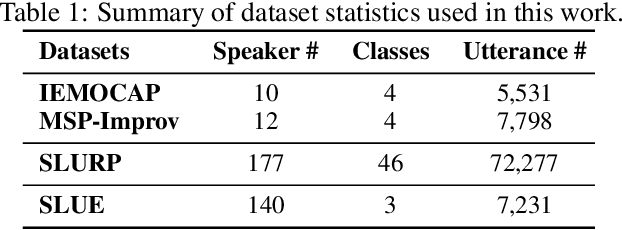
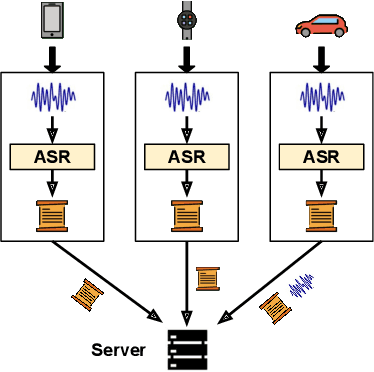

Abstract:Automatic Speech Understanding (ASU) aims at human-like speech interpretation, providing nuanced intent, emotion, sentiment, and content understanding from speech and language (text) content conveyed in speech. Typically, training a robust ASU model relies heavily on acquiring large-scale, high-quality speech and associated transcriptions. However, it is often challenging to collect or use speech data for training ASU due to concerns such as privacy. To approach this setting of enabling ASU when speech (audio) modality is missing, we propose TI-ASU, using a pre-trained text-to-speech model to impute the missing speech. We report extensive experiments evaluating TI-ASU on various missing scales, both multi- and single-modality settings, and the use of LLMs. Our findings show that TI-ASU yields substantial benefits to improve ASU in scenarios where even up to 95% of training speech is missing. Moreover, we show that TI-ASU is adaptive to dropout training, improving model robustness in addressing missing speech during inference.
The NeurIPS 2023 Machine Learning for Audio Workshop: Affective Audio Benchmarks and Novel Data
Mar 21, 2024
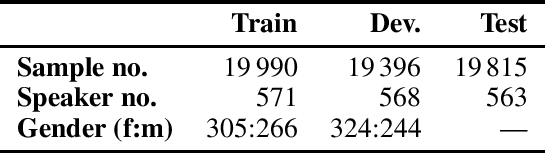
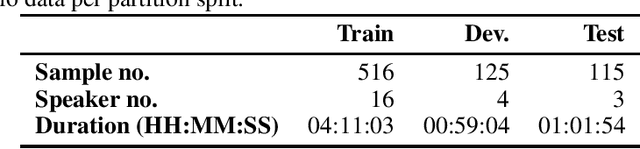
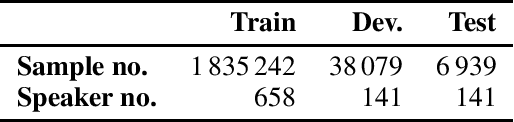
Abstract:The NeurIPS 2023 Machine Learning for Audio Workshop brings together machine learning (ML) experts from various audio domains. There are several valuable audio-driven ML tasks, from speech emotion recognition to audio event detection, but the community is sparse compared to other ML areas, e.g., computer vision or natural language processing. A major limitation with audio is the available data; with audio being a time-dependent modality, high-quality data collection is time-consuming and costly, making it challenging for academic groups to apply their often state-of-the-art strategies to a larger, more generalizable dataset. In this short white paper, to encourage researchers with limited access to large-datasets, the organizers first outline several open-source datasets that are available to the community, and for the duration of the workshop are making several propriety datasets available. Namely, three vocal datasets, Hume-Prosody, Hume-VocalBurst, an acted emotional speech dataset Modulate-Sonata, and an in-game streamer dataset Modulate-Stream. We outline the current baselines on these datasets but encourage researchers from across audio to utilize them outside of the initial baseline tasks.
FedAIoT: A Federated Learning Benchmark for Artificial Intelligence of Things
Sep 29, 2023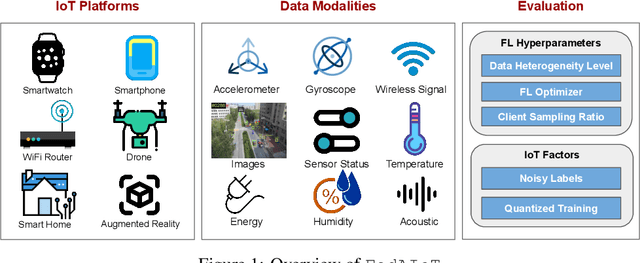
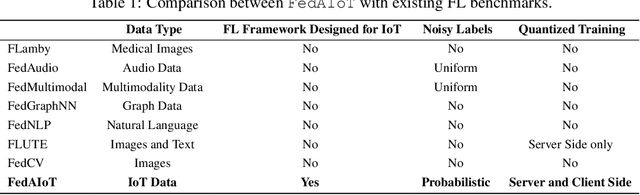
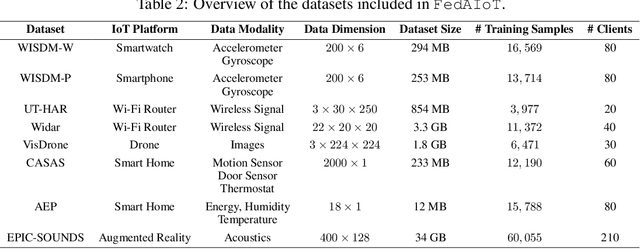
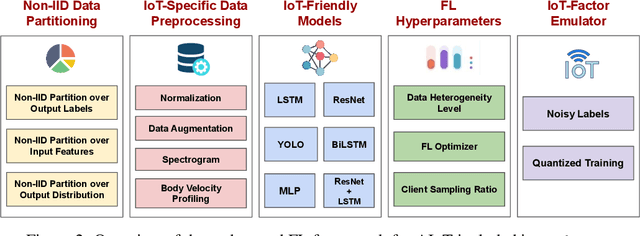
Abstract:There is a significant relevance of federated learning (FL) in the realm of Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT). However, most existing FL works are not conducted on datasets collected from authentic IoT devices that capture unique modalities and inherent challenges of IoT data. In this work, we introduce FedAIoT, an FL benchmark for AIoT to fill this critical gap. FedAIoT includes eight datatsets collected from a wide range of IoT devices. These datasets cover unique IoT modalities and target representative applications of AIoT. FedAIoT also includes a unified end-to-end FL framework for AIoT that simplifies benchmarking the performance of the datasets. Our benchmark results shed light on the opportunities and challenges of FL for AIoT. We hope FedAIoT could serve as an invaluable resource to foster advancements in the important field of FL for AIoT. The repository of FedAIoT is maintained at https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/FedAIoT.
GPT-FL: Generative Pre-trained Model-Assisted Federated Learning
Jun 03, 2023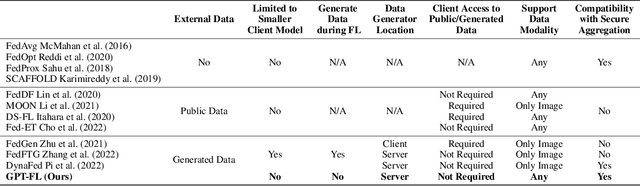
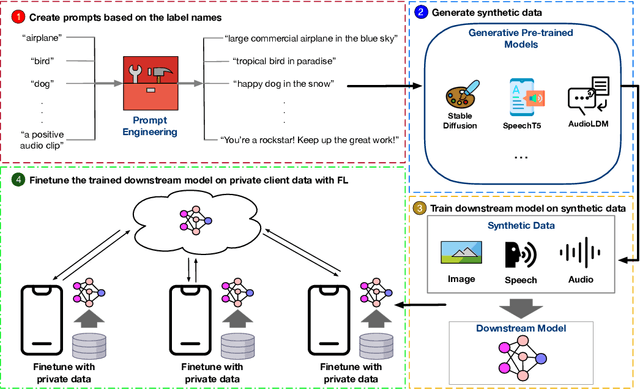
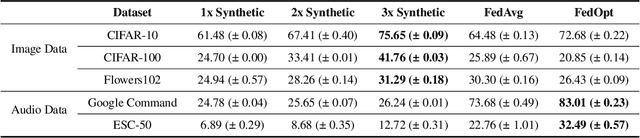
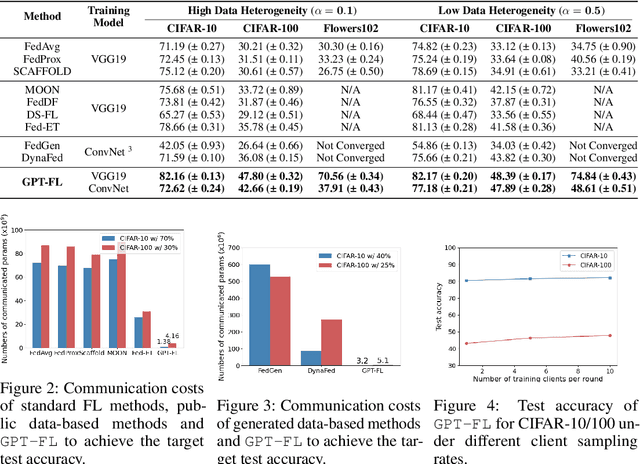
Abstract:In this work, we propose GPT-FL, a generative pre-trained model-assisted federated learning (FL) framework. At its core, GPT-FL leverages generative pre-trained models to generate diversified synthetic data. These generated data are used to train a downstream model on the server, which is then fine-tuned with private client data under the standard FL framework. We show that GPT-FL consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FL methods in terms of model test accuracy, communication efficiency, and client sampling efficiency. Through comprehensive ablation analysis, we discover that the downstream model generated by synthetic data plays a crucial role in controlling the direction of gradient diversity during FL training, which enhances convergence speed and contributes to the notable accuracy boost observed with GPT-FL. Also, regardless of whether the target data falls within or outside the domain of the pre-trained generative model, GPT-FL consistently achieves significant performance gains, surpassing the results obtained by models trained solely with FL or synthetic data.
FedAudio: A Federated Learning Benchmark for Audio Tasks
Nov 18, 2022



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has gained substantial attention in recent years due to the data privacy concerns related to the pervasiveness of consumer devices that continuously collect data from users. While a number of FL benchmarks have been developed to facilitate FL research, none of them include audio data and audio-related tasks. In this paper, we fill this critical gap by introducing a new FL benchmark for audio tasks which we refer to as FedAudio. FedAudio includes four representative and commonly used audio datasets from three important audio tasks that are well aligned with FL use cases. In particular, a unique contribution of FedAudio is the introduction of data noises and label errors to the datasets to emulate challenges when deploying FL systems in real-world settings. FedAudio also includes the benchmark results of the datasets and a PyTorch library with the objective of facilitating researchers to fairly compare their algorithms. We hope FedAudio could act as a catalyst to inspire new FL research for audio tasks and thus benefit the acoustic and speech research community. The datasets and benchmark results can be accessed at https://github.com/zhang-tuo-pdf/FedAudio.
Attribute Inference Attack of Speech Emotion Recognition in Federated Learning Settings
Dec 26, 2021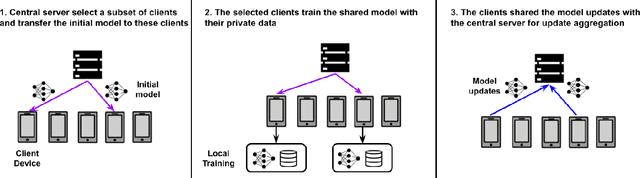
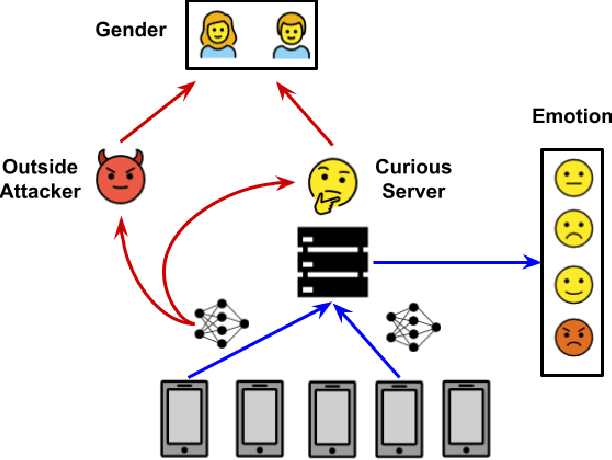
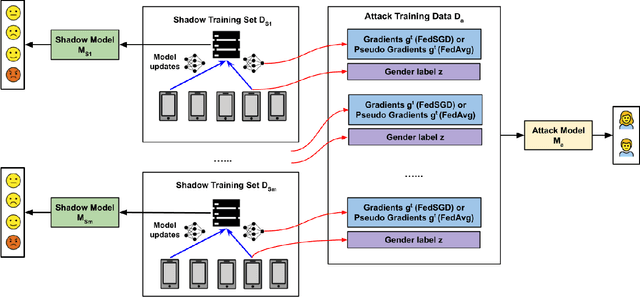
Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) processes speech signals to detect and characterize expressed perceived emotions. Many SER application systems often acquire and transmit speech data collected at the client-side to remote cloud platforms for inference and decision making. However, speech data carry rich information not only about emotions conveyed in vocal expressions, but also other sensitive demographic traits such as gender, age and language background. Consequently, it is desirable for SER systems to have the ability to classify emotion constructs while preventing unintended/improper inferences of sensitive and demographic information. Federated learning (FL) is a distributed machine learning paradigm that coordinates clients to train a model collaboratively without sharing their local data. This training approach appears secure and can improve privacy for SER. However, recent works have demonstrated that FL approaches are still vulnerable to various privacy attacks like reconstruction attacks and membership inference attacks. Although most of these have focused on computer vision applications, such information leakages exist in the SER systems trained using the FL technique. To assess the information leakage of SER systems trained using FL, we propose an attribute inference attack framework that infers sensitive attribute information of the clients from shared gradients or model parameters, corresponding to the FedSGD and the FedAvg training algorithms, respectively. As a use case, we empirically evaluate our approach for predicting the client's gender information using three SER benchmark datasets: IEMOCAP, CREMA-D, and MSP-Improv. We show that the attribute inference attack is achievable for SER systems trained using FL. We further identify that most information leakage possibly comes from the first layer in the SER model.
A multispeaker dataset of raw and reconstructed speech production real-time MRI video and 3D volumetric images
Feb 16, 2021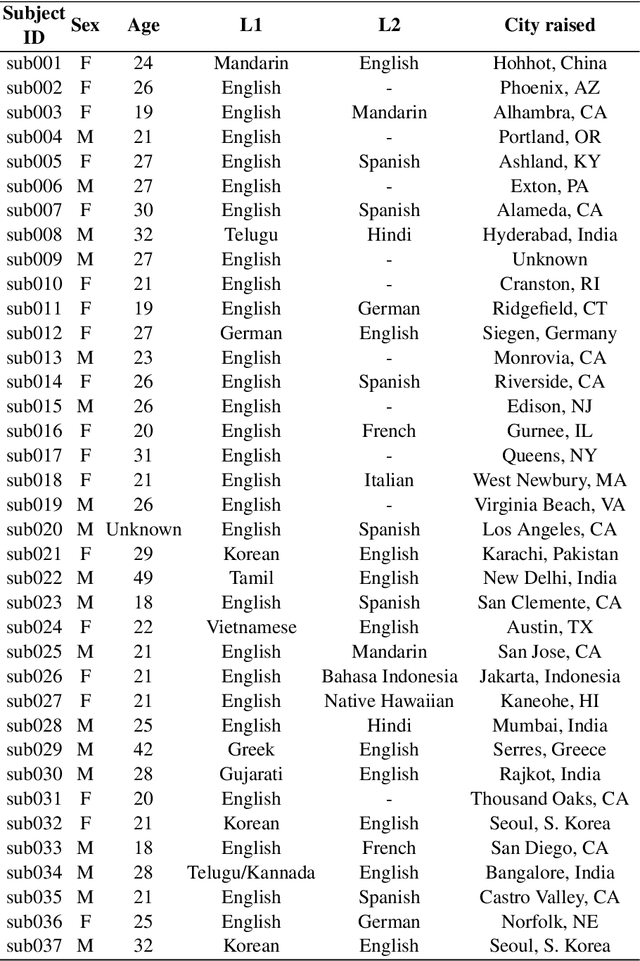
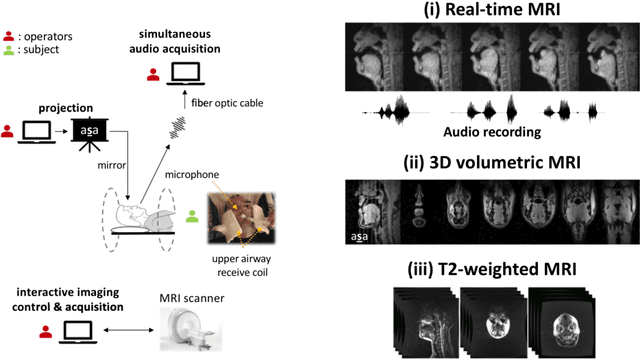
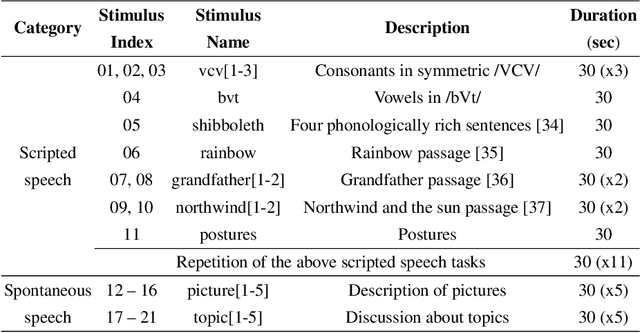
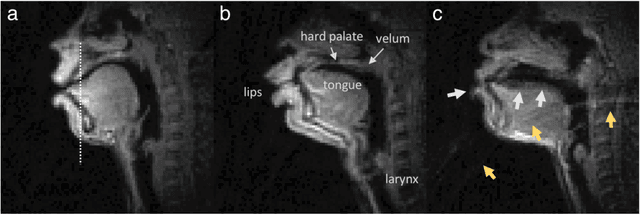
Abstract:Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (RT-MRI) of human speech production is enabling significant advances in speech science, linguistics, bio-inspired speech technology development, and clinical applications. Easy access to RT-MRI is however limited, and comprehensive datasets with broad access are needed to catalyze research across numerous domains. The imaging of the rapidly moving articulators and dynamic airway shaping during speech demands high spatio-temporal resolution and robust reconstruction methods. Further, while reconstructed images have been published, to-date there is no open dataset providing raw multi-coil RT-MRI data from an optimized speech production experimental setup. Such datasets could enable new and improved methods for dynamic image reconstruction, artifact correction, feature extraction, and direct extraction of linguistically-relevant biomarkers. The present dataset offers a unique corpus of 2D sagittal-view RT-MRI videos along with synchronized audio for 75 subjects performing linguistically motivated speech tasks, alongside the corresponding first-ever public domain raw RT-MRI data. The dataset also includes 3D volumetric vocal tract MRI during sustained speech sounds and high-resolution static anatomical T2-weighted upper airway MRI for each subject.
Attention-gated convolutional neural networks for off-resonance correction of spiral real-time MRI
Feb 14, 2021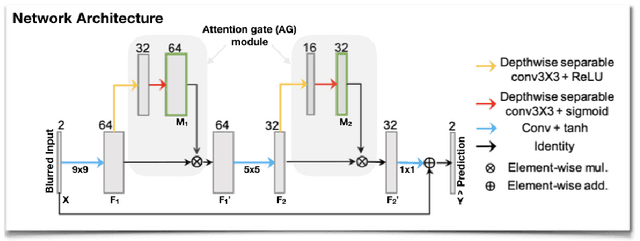
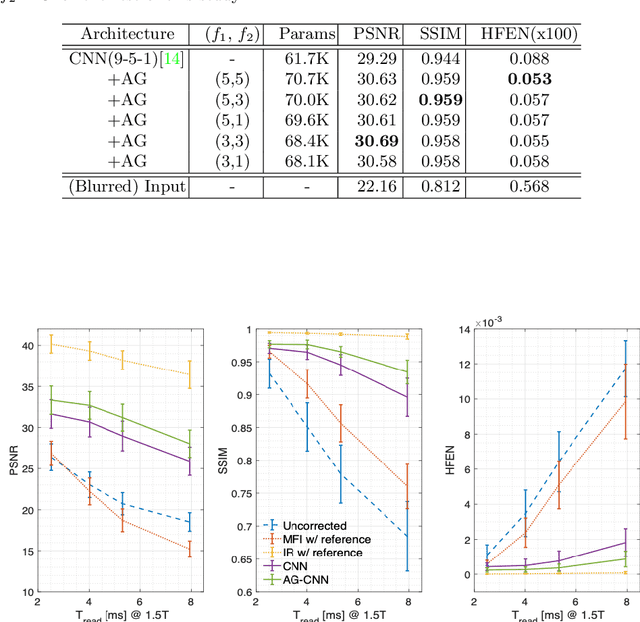

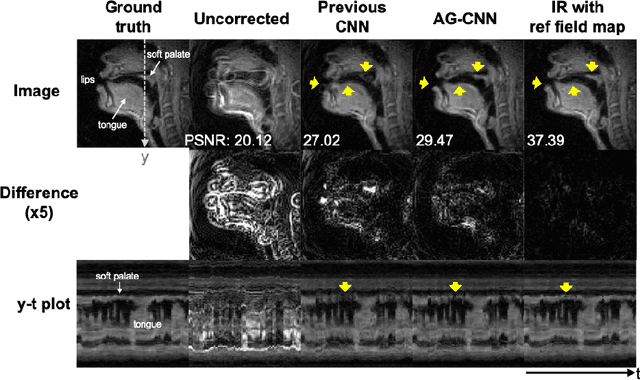
Abstract:Spiral acquisitions are preferred in real-time MRI because of their efficiency, which has made it possible to capture vocal tract dynamics during natural speech. A fundamental limitation of spirals is blurring and signal loss due to off-resonance, which degrades image quality at air-tissue boundaries. Here, we present a new CNN-based off-resonance correction method that incorporates an attention-gate mechanism. This leverages spatial and channel relationships of filtered outputs and improves the expressiveness of the networks. We demonstrate improved performance with the attention-gate, on 1.5 Tesla spiral speech RT-MRI, compared to existing off-resonance correction methods.
* 8 pages, 4 figures, 1 table
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge