Haoqi Li
ROSAnnotator: A Web Application for ROSBag Data Analysis in Human-Robot Interaction
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Human-robot interaction (HRI) is an interdisciplinary field that utilises both quantitative and qualitative methods. While ROSBags, a file format within the Robot Operating System (ROS), offer an efficient means of collecting temporally synched multimodal data in empirical studies with real robots, there is a lack of tools specifically designed to integrate qualitative coding and analysis functions with ROSBags. To address this gap, we developed ROSAnnotator, a web-based application that incorporates a multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) to support both manual and automated annotation of ROSBag data. ROSAnnotator currently facilitates video, audio, and transcription annotations and provides an open interface for custom ROS messages and tools. By using ROSAnnotator, researchers can streamline the qualitative analysis process, create a more cohesive analysis pipeline, and quickly access statistical summaries of annotations, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of HRI data analysis. https://github.com/CHRI-Lab/ROSAnnotator
The NeurIPS 2023 Machine Learning for Audio Workshop: Affective Audio Benchmarks and Novel Data
Mar 21, 2024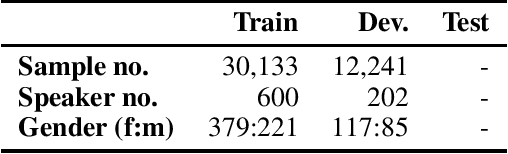
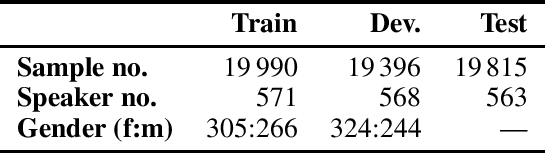
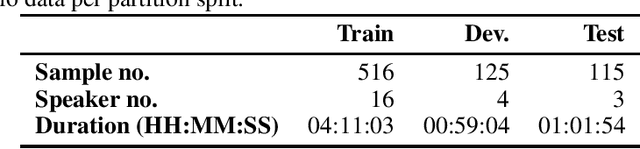
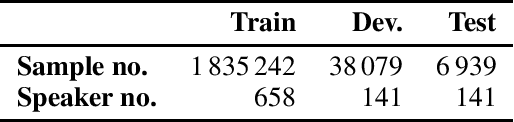
Abstract:The NeurIPS 2023 Machine Learning for Audio Workshop brings together machine learning (ML) experts from various audio domains. There are several valuable audio-driven ML tasks, from speech emotion recognition to audio event detection, but the community is sparse compared to other ML areas, e.g., computer vision or natural language processing. A major limitation with audio is the available data; with audio being a time-dependent modality, high-quality data collection is time-consuming and costly, making it challenging for academic groups to apply their often state-of-the-art strategies to a larger, more generalizable dataset. In this short white paper, to encourage researchers with limited access to large-datasets, the organizers first outline several open-source datasets that are available to the community, and for the duration of the workshop are making several propriety datasets available. Namely, three vocal datasets, Hume-Prosody, Hume-VocalBurst, an acted emotional speech dataset Modulate-Sonata, and an in-game streamer dataset Modulate-Stream. We outline the current baselines on these datasets but encourage researchers from across audio to utilize them outside of the initial baseline tasks.
Zero-Shot End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding via Cross-Modal Selective Self-Training
May 22, 2023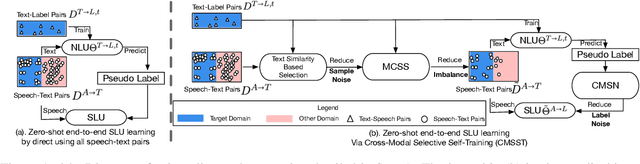
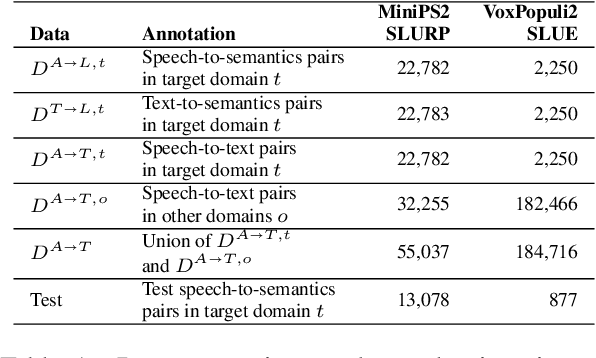
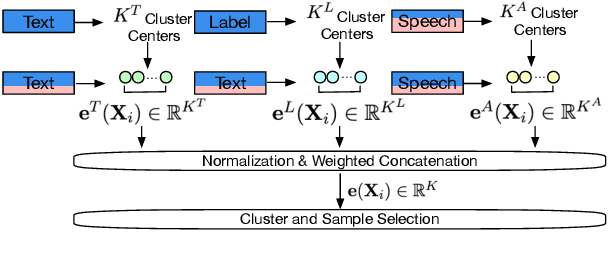
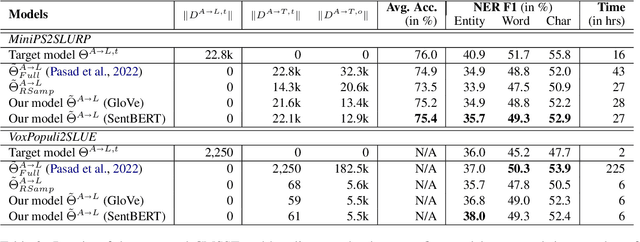
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) spoken language understanding (SLU) is constrained by the cost of collecting speech-semantics pairs, especially when label domains change. Hence, we explore \textit{zero-shot} E2E SLU, which learns E2E SLU without speech-semantics pairs, instead using only speech-text and text-semantics pairs. Previous work achieved zero-shot by pseudolabeling all speech-text transcripts with a natural language understanding (NLU) model learned on text-semantics corpora. However, this method requires the domains of speech-text and text-semantics to match, which often mismatch due to separate collections. Furthermore, using the entire speech-text corpus from any domains leads to \textit{imbalance} and \textit{noise} issues. To address these, we propose \textit{cross-modal selective self-training} (CMSST). CMSST tackles imbalance by clustering in a joint space of the three modalities (speech, text, and semantics) and handles label noise with a selection network. We also introduce two benchmarks for zero-shot E2E SLU, covering matched and found speech (mismatched) settings. Experiments show that CMSST improves performance in both two settings, with significantly reduced sample sizes and training time.
Self-Supervised Speaker Verification with Simple Siamese Network and Self-Supervised Regularization
Dec 08, 2021



Abstract:Training speaker-discriminative and robust speaker verification systems without speaker labels is still challenging and worthwhile to explore. In this study, we propose an effective self-supervised learning framework and a novel regularization strategy to facilitate self-supervised speaker representation learning. Different from contrastive learning-based self-supervised learning methods, the proposed self-supervised regularization (SSReg) focuses exclusively on the similarity between the latent representations of positive data pairs. We also explore the effectiveness of alternative online data augmentation strategies on both the time domain and frequency domain. With our strong online data augmentation strategy, the proposed SSReg shows the potential of self-supervised learning without using negative pairs and it can significantly improve the performance of self-supervised speaker representation learning with a simple Siamese network architecture. Comprehensive experiments on the VoxCeleb datasets demonstrate that our proposed self-supervised approach obtains a 23.4% relative improvement by adding the effective self-supervised regularization and outperforms other previous works.
Acted vs. Improvised: Domain Adaptation for Elicitation Approaches in Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition
Apr 05, 2021



Abstract:Key challenges in developing generalized automatic emotion recognition systems include scarcity of labeled data and lack of gold-standard references. Even for the cues that are labeled as the same emotion category, the variability of associated expressions can be high depending on the elicitation context e.g., emotion elicited during improvised conversations vs. acted sessions with predefined scripts. In this work, we regard the emotion elicitation approach as domain knowledge, and explore domain transfer learning techniques on emotional utterances collected under different emotion elicitation approaches, particularly with limited labeled target samples. Our emotion recognition model combines the gradient reversal technique with an entropy loss function as well as the softlabel loss, and the experiment results show that domain transfer learning methods can be employed to alleviate the domain mismatch between different elicitation approaches. Our work provides new insights into emotion data collection, particularly the impact of its elicitation strategies, and the importance of domain adaptation in emotion recognition aiming for generalized systems.
Unsupervised Speech Representation Learning for Behavior Modeling using Triplet Enhanced Contextualized Networks
Apr 01, 2021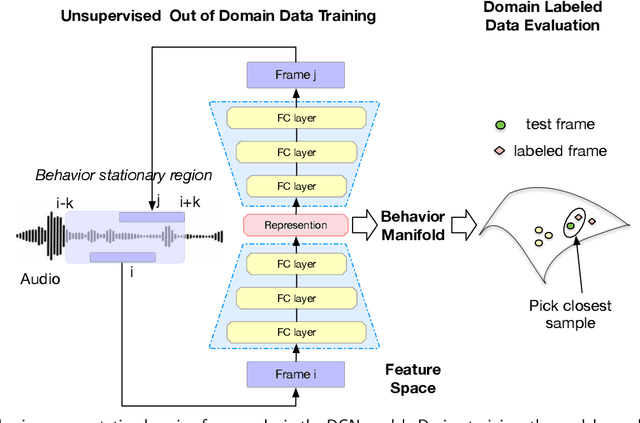

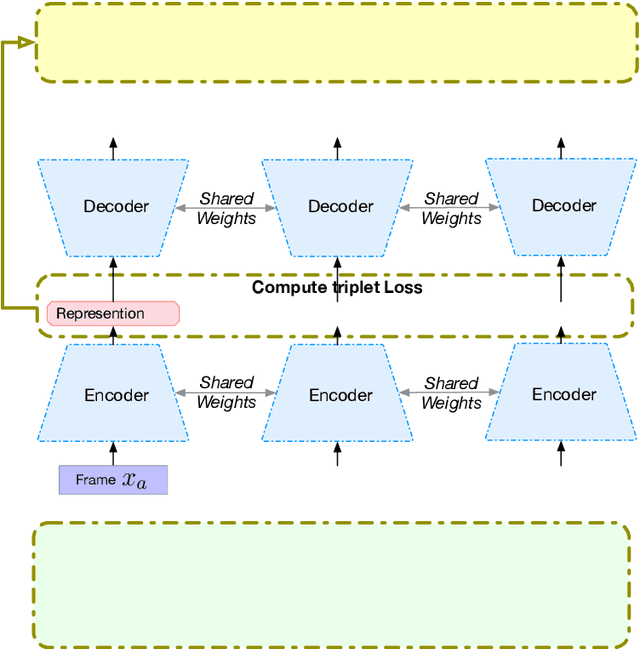
Abstract:Speech encodes a wealth of information related to human behavior and has been used in a variety of automated behavior recognition tasks. However, extracting behavioral information from speech remains challenging including due to inadequate training data resources stemming from the often low occurrence frequencies of specific behavioral patterns. Moreover, supervised behavioral modeling typically relies on domain-specific construct definitions and corresponding manually-annotated data, rendering generalizing across domains challenging. In this paper, we exploit the stationary properties of human behavior within an interaction and present a representation learning method to capture behavioral information from speech in an unsupervised way. We hypothesize that nearby segments of speech share the same behavioral context and hence map onto similar underlying behavioral representations. We present an encoder-decoder based Deep Contextualized Network (DCN) as well as a Triplet-Enhanced DCN (TE-DCN) framework to capture the behavioral context and derive a manifold representation, where speech frames with similar behaviors are closer while frames of different behaviors maintain larger distances. The models are trained on movie audio data and validated on diverse domains including on a couples therapy corpus and other publicly collected data (e.g., stand-up comedy). With encouraging results, our proposed framework shows the feasibility of unsupervised learning within cross-domain behavioral modeling.
Speaker-invariant Affective Representation Learning via Adversarial Training
Nov 04, 2019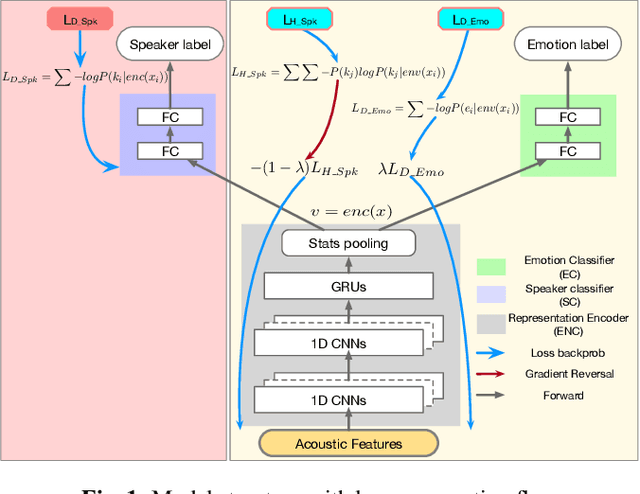
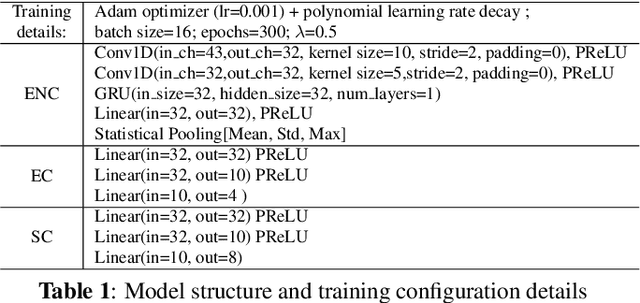
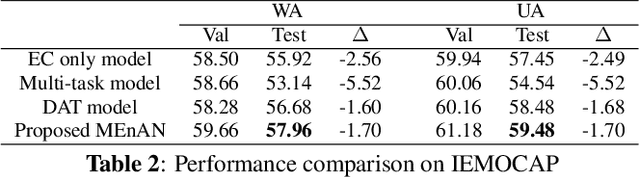
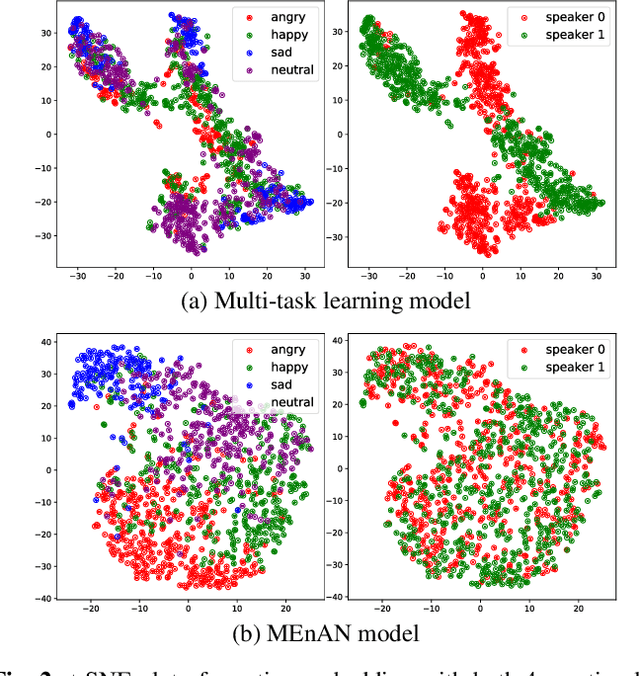
Abstract:Representation learning for speech emotion recognition is challenging due to labeled data sparsity issue and lack of gold standard references. In addition, there is much variability from input speech signals, human subjective perception of the signals and emotion label ambiguity. In this paper, we propose a machine learning framework to obtain speech emotion representations by limiting the effect of speaker variability in the speech signals. Specifically, we propose to disentangle the speaker characteristics from emotion through an adversarial training network in order to better represent emotion. Our method combines the gradient reversal technique with an entropy loss function to remove such speaker information. Our approach is evaluated on both IEMOCAP and CMU-MOSEI datasets. We show that our method improves speech emotion classification and increases generalization to unseen speakers.
Linking emotions to behaviors through deep transfer learning
Oct 08, 2019

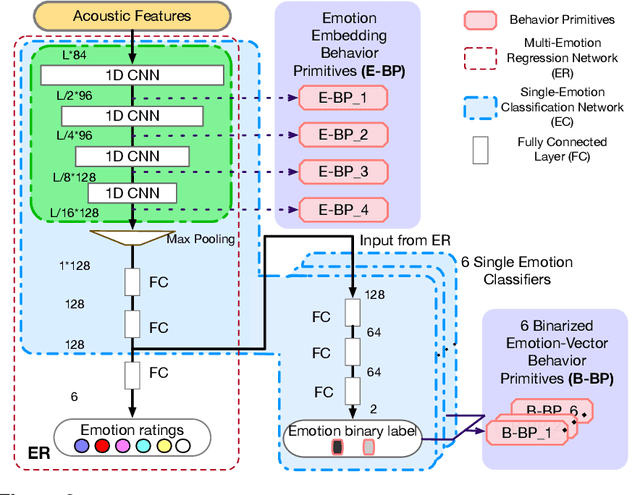
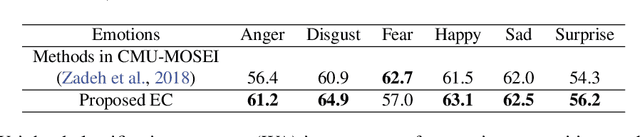
Abstract:Human behavior refers to the way humans act and interact. Understanding human behavior is a cornerstone of observational practice, especially in psychotherapy. An important cue of behavior analysis is the dynamical changes of emotions during the conversation. Domain experts integrate emotional information in a highly nonlinear manner, thus, it is challenging to explicitly quantify the relationship between emotions and behaviors. In this work, we employ deep transfer learning to analyze their inferential capacity and contextual importance. We first train a network to quantify emotions from acoustic signals and then use information from the emotion recognition network as features for behavior recognition. We treat this emotion-related information as behavioral primitives and further train higher level layers towards behavior quantification. Through our analysis, we find that emotion-related information is an important cue for behavior recognition. Further, we investigate the importance of emotional-context in the expression of behavior by constraining (or not) the neural networks' contextual view of the data. This demonstrates that the sequence of emotions is critical in behavior expression. To achieve these frameworks we employ hybrid architectures of convolutional networks and recurrent networks to extract emotion-related behavior primitives and facilitate automatic behavior recognition from speech.
Predicting Behavior in Cancer-Afflicted Patient and Spouse Interactions using Speech and Language
Aug 02, 2019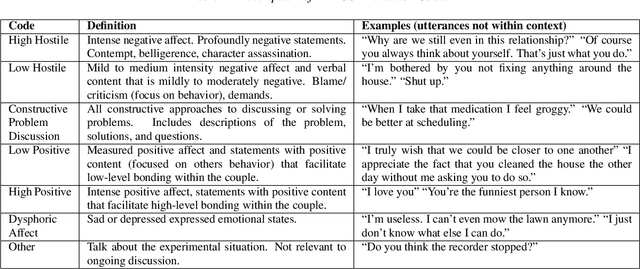
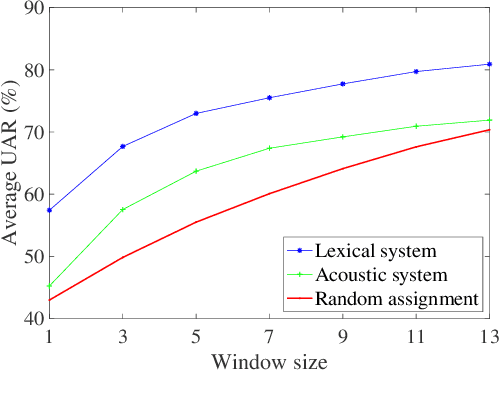
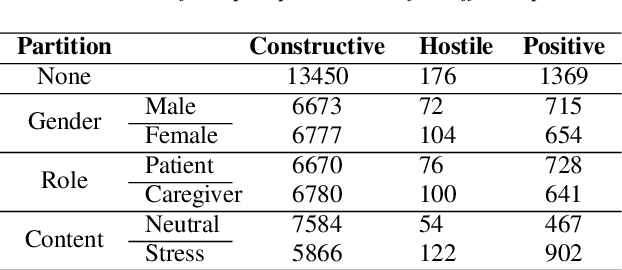
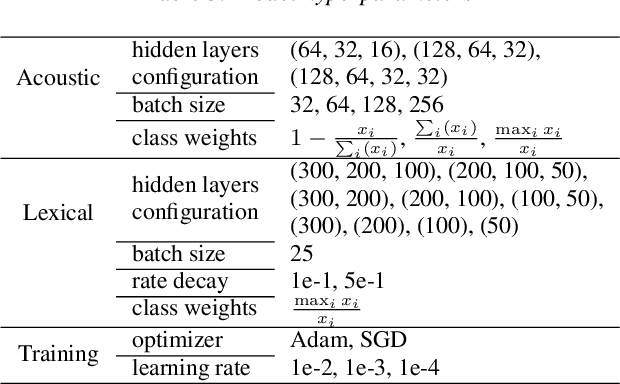
Abstract:Cancer impacts the quality of life of those diagnosed as well as their spouse caregivers, in addition to potentially influencing their day-to-day behaviors. There is evidence that effective communication between spouses can improve well-being related to cancer but it is difficult to efficiently evaluate the quality of daily life interactions using manual annotation frameworks. Automated recognition of behaviors based on the interaction cues of speakers can help analyze interactions in such couples and identify behaviors which are beneficial for effective communication. In this paper, we present and detail a dataset of dyadic interactions in 85 real-life cancer-afflicted couples and a set of observational behavior codes pertaining to interpersonal communication attributes. We describe and employ neural network-based systems for classifying these behaviors based on turn-level acoustic and lexical speech patterns. Furthermore, we investigate the effect of controlling for factors such as gender, patient/caregiver role and conversation content on behavior classification. Analysis of our preliminary results indicates the challenges in this task due to the nature of the targeted behaviors and suggests that techniques incorporating contextual processing might be better suited to tackle this problem.
Learning from Past Mistakes: Improving Automatic Speech Recognition Output via Noisy-Clean Phrase Context Modeling
Feb 07, 2018



Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems lack joint optimization during decoding over the acoustic, lexical and language models; for instance the ASR will often prune words due to acoustics using short-term context, prior to rescoring with long-term context. In this work we model the automated speech transcription process as a noisy transformation channel and propose an error correction system that can learn from the aggregate errors of all the independent modules constituting the ASR. The proposed system can exploit long-term context using a neural network language model and can better choose between existing ASR output possibilities as well as re-introduce previously pruned and unseen (out-of-vocabulary) phrases. The system provides significant corrections under poorly performing ASR conditions without degrading any accurate transcriptions. The proposed system can thus be independently optimized and post-process the output of even a highly optimized ASR. We show that the system consistently provides improvements over the baseline ASR. We also show that it performs better when used on out-of-domain and mismatched test data and under high-error ASR conditions. Finally, an extensive analysis of the type of errors corrected by our system is presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge