Shonit Punwani
Understanding the Transfer Limits of Vision Foundation Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Foundation models leverage large-scale pretraining to capture extensive knowledge, demonstrating generalization in a wide range of language tasks. By comparison, vision foundation models (VFMs) often exhibit uneven improvements across downstream tasks, despite substantial computational investment. We postulate that this limitation arises from a mismatch between pretraining objectives and the demands of downstream vision-and-imaging tasks. Pretraining strategies like masked image reconstruction or contrastive learning shape representations for tasks such as recovery of generic visual patterns or global semantic structures, which may not align with the task-specific requirements of downstream applications including segmentation, classification, or image synthesis. To investigate this in a concrete real-world clinical area, we assess two VFMs, a reconstruction-focused MAE-based model (ProFound) and a contrastive-learning-based model (ProViCNet), on five prostate multiparametric MR imaging tasks, examining how such task alignment influences transfer performance, i.e., from pretraining to fine-tuning. Our findings indicate that better alignment between pretraining and downstream tasks, measured by simple divergence metrics such as maximum-mean-discrepancy (MMD) between the same features before and after fine-tuning, correlates with greater performance improvements and faster convergence, emphasizing the importance of designing and analyzing pretraining objectives with downstream applicability in mind.
Dual Deep Learning Approach for Non-invasive Renal Tumour Subtyping with VERDICT-MRI
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:This work aims to characterise renal tumour microstructure using diffusion MRI (dMRI); via the Vascular, Extracellular and Restricted Diffusion for Cytometry in Tumours (VERDICT)-MRI framework with self-supervised learning. Comprehensive datasets were acquired from 14 patients with 15 biopsy-confirmed renal tumours, with nine b-values in the range b=[0,2500]s/mm2. A three-compartment VERDICT model for renal tumours was fitted to the dMRI data using a self-supervised deep neural network, and ROIs were drawn by an experienced uroradiologist. An economical acquisition protocol for future studies with larger patient cohorts was optimised using a recursive feature selection approach. The VERDICT model described the diffusion data in renal tumours more accurately than IVIM or ADC. Combined with self-supervised deep learning, VERDICT identified significant differences in the intracellular volume fraction between cancerous and normal tissue, and in the vascular volume fraction between vascular and non-vascular. The feature selector yields a 4 b-value acquisition of b = [70,150,1000,2000], with a duration of 14 minutes.
Tell2Reg: Establishing spatial correspondence between images by the same language prompts
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Spatial correspondence can be represented by pairs of segmented regions, such that the image registration networks aim to segment corresponding regions rather than predicting displacement fields or transformation parameters. In this work, we show that such a corresponding region pair can be predicted by the same language prompt on two different images using the pre-trained large multimodal models based on GroundingDINO and SAM. This enables a fully automated and training-free registration algorithm, potentially generalisable to a wide range of image registration tasks. In this paper, we present experimental results using one of the challenging tasks, registering inter-subject prostate MR images, which involves both highly variable intensity and morphology between patients. Tell2Reg is training-free, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming data curation and labelling that was previously required for this registration task. This approach outperforms unsupervised learning-based registration methods tested, and has a performance comparable to weakly-supervised methods. Additional qualitative results are also presented to suggest that, for the first time, there is a potential correlation between language semantics and spatial correspondence, including the spatial invariance in language-prompted regions and the difference in language prompts between the obtained local and global correspondences. Code is available at https://github.com/yanwenCi/Tell2Reg.git.
T2-Only Prostate Cancer Prediction by Meta-Learning from Bi-Parametric MR Imaging
Nov 11, 2024


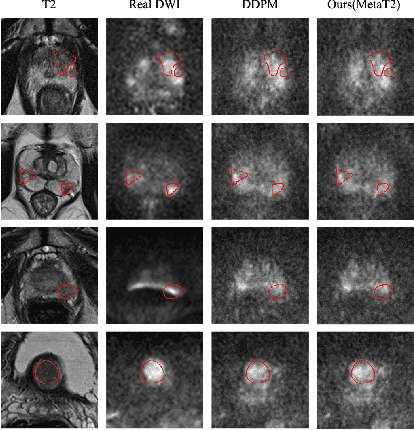
Abstract:Current imaging-based prostate cancer diagnosis requires both MR T2-weighted (T2w) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences, with additional sequences for potentially greater accuracy improvement. However, measuring diffusion patterns in DWI sequences can be time-consuming, prone to artifacts and sensitive to imaging parameters. While machine learning (ML) models have demonstrated radiologist-level accuracy in detecting prostate cancer from these two sequences, this study investigates the potential of ML-enabled methods using only the T2w sequence as input during inference time. We first discuss the technical feasibility of such a T2-only approach, and then propose a novel ML formulation, where DWI sequences - readily available for training purposes - are only used to train a meta-learning model, which subsequently only uses T2w sequences at inference. Using multiple datasets from more than 3,000 prostate cancer patients, we report superior or comparable performance in localising radiologist-identified prostate cancer using our proposed T2-only models, compared with alternative models using T2-only or both sequences as input. Real patient cases are presented and discussed to demonstrate, for the first time, the exclusively true-positive cases from models with different input sequences.
AI-assisted prostate cancer detection and localisation on biparametric MR by classifying radiologist-positives
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Prostate cancer diagnosis through MR imaging have currently relied on radiologists' interpretation, whilst modern AI-based methods have been developed to detect clinically significant cancers independent of radiologists. In this study, we propose to develop deep learning models that improve the overall cancer diagnostic accuracy, by classifying radiologist-identified patients or lesions (i.e. radiologist-positives), as opposed to the existing models that are trained to discriminate over all patients. We develop a single voxel-level classification model, with a simple percentage threshold to determine positive cases, at levels of lesions, Barzell-zones and patients. Based on the presented experiments from two clinical data sets, consisting of histopathology-labelled MR images from more than 800 and 500 patients in the respective UCLA and UCL PROMIS studies, we show that the proposed strategy can improve the diagnostic accuracy, by augmenting the radiologist reading of the MR imaging. Among varying definition of clinical significance, the proposed strategy, for example, achieved a specificity of 44.1% (with AI assistance) from 36.3% (by radiologists alone), at a controlled sensitivity of 80.0% on the publicly available UCLA data set. This provides measurable clinical values in a range of applications such as reducing unnecessary biopsies, lowering cost in cancer screening and quantifying risk in therapies.
Poisson Ordinal Network for Gleason Group Estimation Using Bi-Parametric MRI
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:The Gleason groups serve as the primary histological grading system for prostate cancer, providing crucial insights into the cancer's potential for growth and metastasis. In clinical practice, pathologists determine the Gleason groups based on specimens obtained from ultrasound-guided biopsies. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of directly estimating the Gleason groups from MRI scans to reduce otherwise required biopsies. We identify two characteristics of this task, ordinality and the resulting dependent yet unknown variances between Gleason groups. In addition to the inter- / intra- observer variability in a multi-step Gleason scoring process based on the interpretation of Gleason patterns, our MR-based prediction is also subject to specimen sampling variance and, to a lesser degree, varying MR imaging protocols. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Poisson ordinal network (PON). PONs model the prediction using a Poisson distribution and leverages Poisson encoding and Poisson focal loss to capture a learnable dependency between ordinal classes (here, Gleason groups), rather than relying solely on the numerical ground-truth (e.g. Gleason Groups 1-5 or Gleason Scores 6-10). To improve this modelling efficacy, PONs also employ contrastive learning with a memory bank to regularise intra-class variance, decoupling the memory requirement of contrast learning from the batch size. Experimental results based on the images labelled by saturation biopsies from 265 prior-biopsy-blind patients, across two tasks demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of our proposed method.
ssVERDICT: Self-Supervised VERDICT-MRI for Enhanced Prostate Tumour Characterisation
Sep 27, 2023
Abstract:Purpose: Demonstrating and assessing self-supervised machine learning fitting of the VERDICT (Vascular, Extracellular and Restricted DIffusion for Cytometry in Tumours) model for prostate. Methods: We derive a self-supervised neural network for fitting VERDICT (ssVERDICT) that estimates parameter maps without training data. We compare the performance of ssVERDICT to two established baseline methods for fitting diffusion MRI models: conventional nonlinear least squares (NLLS) and supervised deep learning. We do this quantitatively on simulated data, by comparing the Pearson's correlation coefficient, mean-squared error (MSE), bias, and variance with respect to the simulated ground truth. We also calculate in vivo parameter maps on a cohort of 20 prostate cancer patients and compare the methods' performance in discriminating benign from cancerous tissue via Wilcoxon's signed-rank test. Results: In simulations, ssVERDICT outperforms the baseline methods (NLLS and supervised DL) in estimating all the parameters from the VERDICT prostate model in terms of Pearson's correlation coefficient, bias, and MSE. In vivo, ssVERDICT shows stronger lesion conspicuity across all parameter maps, and improves discrimination between benign and cancerous tissue over the baseline methods. Conclusion: ssVERDICT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods for VERDICT model fitting, and shows for the first time, fitting of a complex three-compartment biophysical model with machine learning without the requirement of explicit training labels.
Combiner and HyperCombiner Networks: Rules to Combine Multimodality MR Images for Prostate Cancer Localisation
Jul 17, 2023



Abstract:One of the distinct characteristics in radiologists' reading of multiparametric prostate MR scans, using reporting systems such as PI-RADS v2.1, is to score individual types of MR modalities, T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted, and dynamic contrast-enhanced, and then combine these image-modality-specific scores using standardised decision rules to predict the likelihood of clinically significant cancer. This work aims to demonstrate that it is feasible for low-dimensional parametric models to model such decision rules in the proposed Combiner networks, without compromising the accuracy of predicting radiologic labels: First, it is shown that either a linear mixture model or a nonlinear stacking model is sufficient to model PI-RADS decision rules for localising prostate cancer. Second, parameters of these (generalised) linear models are proposed as hyperparameters, to weigh multiple networks that independently represent individual image modalities in the Combiner network training, as opposed to end-to-end modality ensemble. A HyperCombiner network is developed to train a single image segmentation network that can be conditioned on these hyperparameters during inference, for much improved efficiency. Experimental results based on data from 850 patients, for the application of automating radiologist labelling multi-parametric MR, compare the proposed combiner networks with other commonly-adopted end-to-end networks. Using the added advantages of obtaining and interpreting the modality combining rules, in terms of the linear weights or odds-ratios on individual image modalities, three clinical applications are presented for prostate cancer segmentation, including modality availability assessment, importance quantification and rule discovery.
Bi-parametric prostate MR image synthesis using pathology and sequence-conditioned stable diffusion
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:We propose an image synthesis mechanism for multi-sequence prostate MR images conditioned on text, to control lesion presence and sequence, as well as to generate paired bi-parametric images conditioned on images e.g. for generating diffusion-weighted MR from T2-weighted MR for paired data, which are two challenging tasks in pathological image synthesis. Our proposed mechanism utilises and builds upon the recent stable diffusion model by proposing image-based conditioning for paired data generation. We validate our method using 2D image slices from real suspected prostate cancer patients. The realism of the synthesised images is validated by means of a blind expert evaluation for identifying real versus fake images, where a radiologist with 4 years experience reading urological MR only achieves 59.4% accuracy across all tested sequences (where chance is 50%). For the first time, we evaluate the realism of the generated pathology by blind expert identification of the presence of suspected lesions, where we find that the clinician performs similarly for both real and synthesised images, with a 2.9 percentage point difference in lesion identification accuracy between real and synthesised images, demonstrating the potentials in radiological training purposes. Furthermore, we also show that a machine learning model, trained for lesion identification, shows better performance (76.2% vs 70.4%, statistically significant improvement) when trained with real data augmented by synthesised data as opposed to training with only real images, demonstrating usefulness for model training.
Cross-Modality Image Registration using a Training-Time Privileged Third Modality
Jul 26, 2022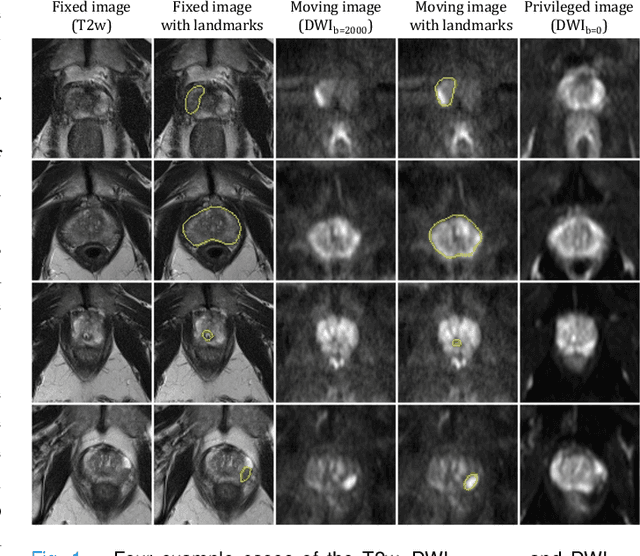
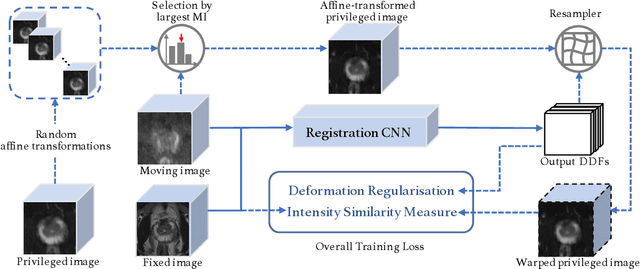
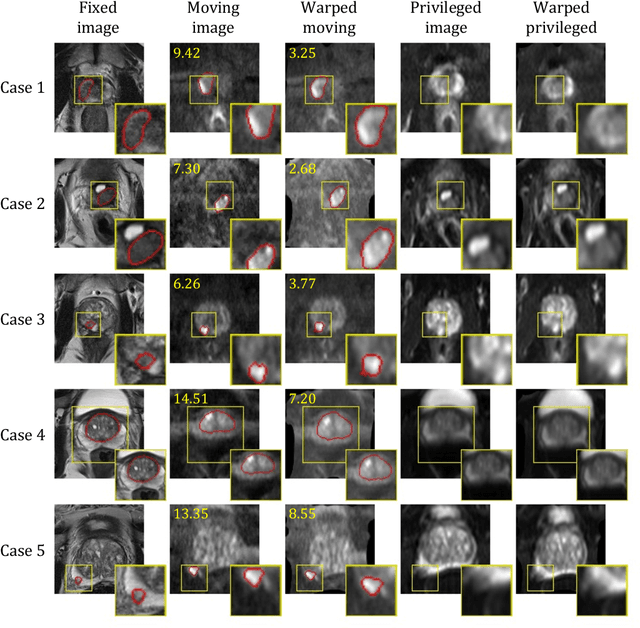
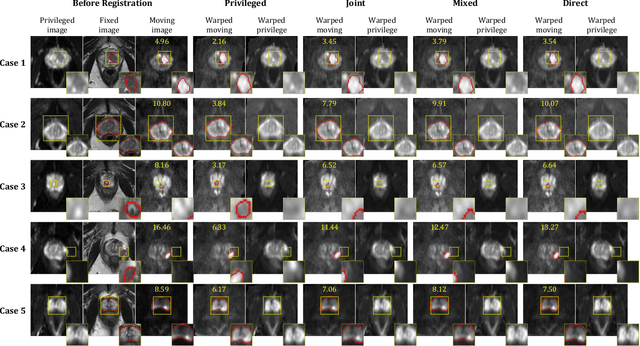
Abstract:In this work, we consider the task of pairwise cross-modality image registration, which may benefit from exploiting additional images available only at training time from an additional modality that is different to those being registered. As an example, we focus on aligning intra-subject multiparametric Magnetic Resonance (mpMR) images, between T2-weighted (T2w) scans and diffusion-weighted scans with high b-value (DWI$_{high-b}$). For the application of localising tumours in mpMR images, diffusion scans with zero b-value (DWI$_{b=0}$) are considered easier to register to T2w due to the availability of corresponding features. We propose a learning from privileged modality algorithm, using a training-only imaging modality DWI$_{b=0}$, to support the challenging multi-modality registration problems. We present experimental results based on 369 sets of 3D multiparametric MRI images from 356 prostate cancer patients and report, with statistical significance, a lowered median target registration error of 4.34 mm, when registering the holdout DWI$_{high-b}$ and T2w image pairs, compared with that of 7.96 mm before registration. Results also show that the proposed learning-based registration networks enabled efficient registration with comparable or better accuracy, compared with a classical iterative algorithm and other tested learning-based methods with/without the additional modality. These compared algorithms also failed to produce any significantly improved alignment between DWI$_{high-b}$ and T2w in this challenging application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge