Dean Barratt
Understanding the Transfer Limits of Vision Foundation Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Foundation models leverage large-scale pretraining to capture extensive knowledge, demonstrating generalization in a wide range of language tasks. By comparison, vision foundation models (VFMs) often exhibit uneven improvements across downstream tasks, despite substantial computational investment. We postulate that this limitation arises from a mismatch between pretraining objectives and the demands of downstream vision-and-imaging tasks. Pretraining strategies like masked image reconstruction or contrastive learning shape representations for tasks such as recovery of generic visual patterns or global semantic structures, which may not align with the task-specific requirements of downstream applications including segmentation, classification, or image synthesis. To investigate this in a concrete real-world clinical area, we assess two VFMs, a reconstruction-focused MAE-based model (ProFound) and a contrastive-learning-based model (ProViCNet), on five prostate multiparametric MR imaging tasks, examining how such task alignment influences transfer performance, i.e., from pretraining to fine-tuning. Our findings indicate that better alignment between pretraining and downstream tasks, measured by simple divergence metrics such as maximum-mean-discrepancy (MMD) between the same features before and after fine-tuning, correlates with greater performance improvements and faster convergence, emphasizing the importance of designing and analyzing pretraining objectives with downstream applicability in mind.
Tell2Reg: Establishing spatial correspondence between images by the same language prompts
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Spatial correspondence can be represented by pairs of segmented regions, such that the image registration networks aim to segment corresponding regions rather than predicting displacement fields or transformation parameters. In this work, we show that such a corresponding region pair can be predicted by the same language prompt on two different images using the pre-trained large multimodal models based on GroundingDINO and SAM. This enables a fully automated and training-free registration algorithm, potentially generalisable to a wide range of image registration tasks. In this paper, we present experimental results using one of the challenging tasks, registering inter-subject prostate MR images, which involves both highly variable intensity and morphology between patients. Tell2Reg is training-free, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming data curation and labelling that was previously required for this registration task. This approach outperforms unsupervised learning-based registration methods tested, and has a performance comparable to weakly-supervised methods. Additional qualitative results are also presented to suggest that, for the first time, there is a potential correlation between language semantics and spatial correspondence, including the spatial invariance in language-prompted regions and the difference in language prompts between the obtained local and global correspondences. Code is available at https://github.com/yanwenCi/Tell2Reg.git.
SAMReg: SAM-enabled Image Registration with ROI-based Correspondence
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:This paper describes a new spatial correspondence representation based on paired regions-of-interest (ROIs), for medical image registration. The distinct properties of the proposed ROI-based correspondence are discussed, in the context of potential benefits in clinical applications following image registration, compared with alternative correspondence-representing approaches, such as those based on sampled displacements and spatial transformation functions. These benefits include a clear connection between learning-based image registration and segmentation, which in turn motivates two cases of image registration approaches using (pre-)trained segmentation networks. Based on the segment anything model (SAM), a vision foundation model for segmentation, we develop a new registration algorithm SAMReg, which does not require any training (or training data), gradient-based fine-tuning or prompt engineering. The proposed SAMReg models are evaluated across five real-world applications, including intra-subject registration tasks with cardiac MR and lung CT, challenging inter-subject registration scenarios with prostate MR and retinal imaging, and an additional evaluation with a non-clinical example with aerial image registration. The proposed methods outperform both intensity-based iterative algorithms and DDF-predicting learning-based networks across tested metrics including Dice and target registration errors on anatomical structures, and further demonstrates competitive performance compared to weakly-supervised registration approaches that rely on fully-segmented training data. Open source code and examples are available at: https://github.com/sqhuang0103/SAMReg.git.
Poisson Ordinal Network for Gleason Group Estimation Using Bi-Parametric MRI
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:The Gleason groups serve as the primary histological grading system for prostate cancer, providing crucial insights into the cancer's potential for growth and metastasis. In clinical practice, pathologists determine the Gleason groups based on specimens obtained from ultrasound-guided biopsies. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of directly estimating the Gleason groups from MRI scans to reduce otherwise required biopsies. We identify two characteristics of this task, ordinality and the resulting dependent yet unknown variances between Gleason groups. In addition to the inter- / intra- observer variability in a multi-step Gleason scoring process based on the interpretation of Gleason patterns, our MR-based prediction is also subject to specimen sampling variance and, to a lesser degree, varying MR imaging protocols. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Poisson ordinal network (PON). PONs model the prediction using a Poisson distribution and leverages Poisson encoding and Poisson focal loss to capture a learnable dependency between ordinal classes (here, Gleason groups), rather than relying solely on the numerical ground-truth (e.g. Gleason Groups 1-5 or Gleason Scores 6-10). To improve this modelling efficacy, PONs also employ contrastive learning with a memory bank to regularise intra-class variance, decoupling the memory requirement of contrast learning from the batch size. Experimental results based on the images labelled by saturation biopsies from 265 prior-biopsy-blind patients, across two tasks demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of our proposed method.
One registration is worth two segmentations
May 17, 2024



Abstract:The goal of image registration is to establish spatial correspondence between two or more images, traditionally through dense displacement fields (DDFs) or parametric transformations (e.g., rigid, affine, and splines). Rethinking the existing paradigms of achieving alignment via spatial transformations, we uncover an alternative but more intuitive correspondence representation: a set of corresponding regions-of-interest (ROI) pairs, which we demonstrate to have sufficient representational capability as other correspondence representation methods.Further, it is neither necessary nor sufficient for these ROIs to hold specific anatomical or semantic significance. In turn, we formulate image registration as searching for the same set of corresponding ROIs from both moving and fixed images - in other words, two multi-class segmentation tasks on a pair of images. For a general-purpose and practical implementation, we integrate the segment anything model (SAM) into our proposed algorithms, resulting in a SAM-enabled registration (SAMReg) that does not require any training data, gradient-based fine-tuning or engineered prompts. We experimentally show that the proposed SAMReg is capable of segmenting and matching multiple ROI pairs, which establish sufficiently accurate correspondences, in three clinical applications of registering prostate MR, cardiac MR and abdominal CT images. Based on metrics including Dice and target registration errors on anatomical structures, the proposed registration outperforms both intensity-based iterative algorithms and DDF-predicting learning-based networks, even yielding competitive performance with weakly-supervised registration which requires fully-segmented training data.
Meta-Learning Initializations for Interactive Medical Image Registration
Oct 27, 2022



Abstract:We present a meta-learning framework for interactive medical image registration. Our proposed framework comprises three components: a learning-based medical image registration algorithm, a form of user interaction that refines registration at inference, and a meta-learning protocol that learns a rapidly adaptable network initialization. This paper describes a specific algorithm that implements the registration, interaction and meta-learning protocol for our exemplar clinical application: registration of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging to interactively acquired, sparsely-sampled transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) images. Our approach obtains comparable registration error (4.26 mm) to the best-performing non-interactive learning-based 3D-to-3D method (3.97 mm) while requiring only a fraction of the data, and occurring in real-time during acquisition. Applying sparsely sampled data to non-interactive methods yields higher registration errors (6.26 mm), demonstrating the effectiveness of interactive MR-TRUS registration, which may be applied intraoperatively given the real-time nature of the adaptation process.
Prototypical few-shot segmentation for cross-institution male pelvic structures with spatial registration
Sep 13, 2022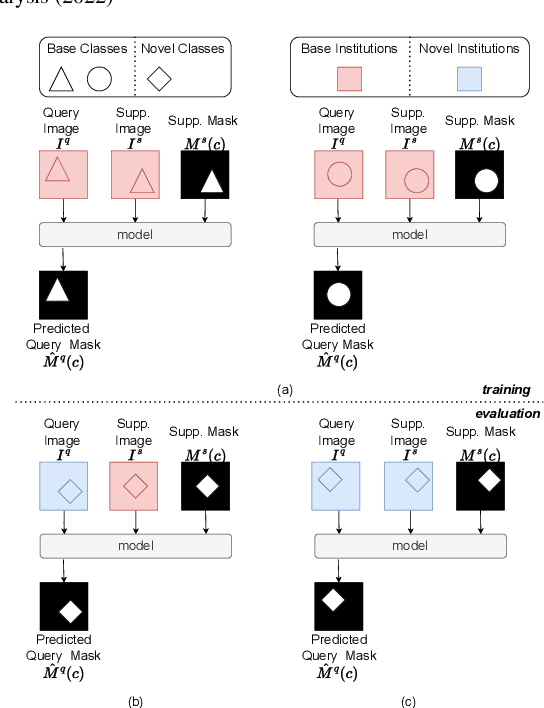

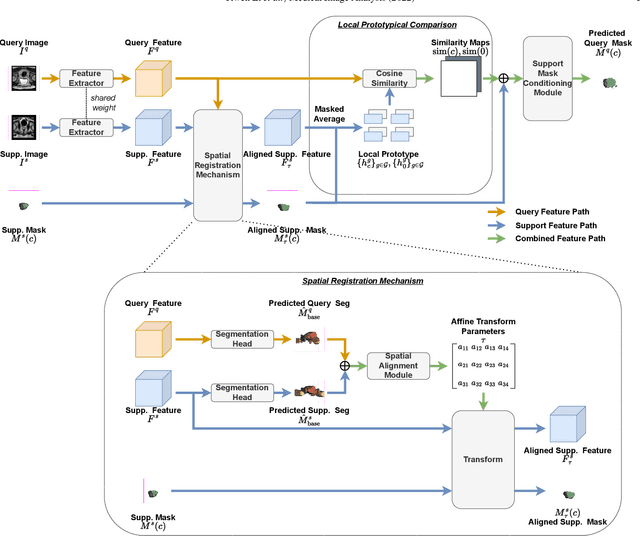
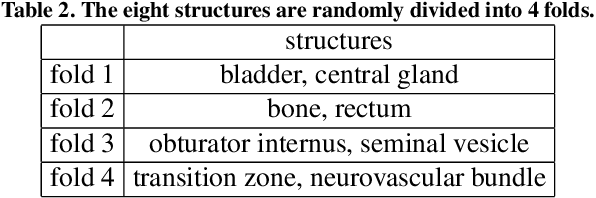
Abstract:The prowess that makes few-shot learning desirable in medical image analysis is the efficient use of the support image data, which are labelled to classify or segment new classes, a task that otherwise requires substantially more training images and expert annotations. This work describes a fully 3D prototypical few-shot segmentation algorithm, such that the trained networks can be effectively adapted to clinically interesting structures that are absent in training, using only a few labelled images from a different institute. First, to compensate for the widely recognised spatial variability between institutions in episodic adaptation of novel classes, a novel spatial registration mechanism is integrated into prototypical learning, consisting of a segmentation head and an spatial alignment module. Second, to assist the training with observed imperfect alignment, support mask conditioning module is proposed to further utilise the annotation available from the support images. Extensive experiments are presented in an application of segmenting eight anatomical structures important for interventional planning, using a data set of 589 pelvic T2-weighted MR images, acquired at seven institutes. The results demonstrate the efficacy in each of the 3D formulation, the spatial registration, and the support mask conditioning, all of which made positive contributions independently or collectively. Compared with the previously proposed 2D alternatives, the few-shot segmentation performance was improved with statistical significance, regardless whether the support data come from the same or different institutes.
Collaborative Quantization Embeddings for Intra-Subject Prostate MR Image Registration
Jul 14, 2022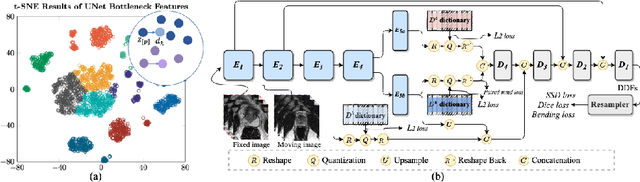
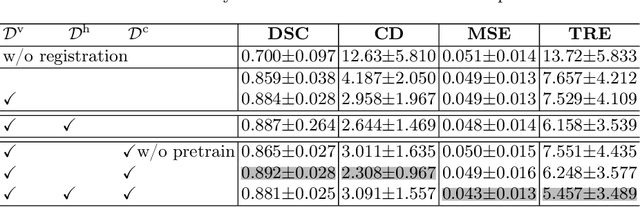
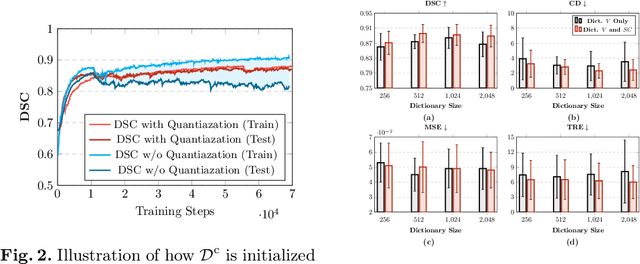
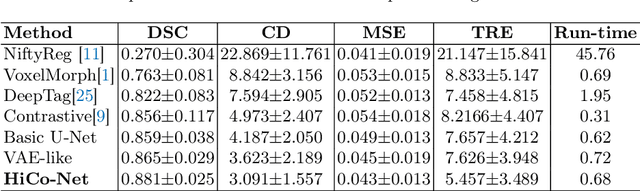
Abstract:Image registration is useful for quantifying morphological changes in longitudinal MR images from prostate cancer patients. This paper describes a development in improving the learning-based registration algorithms, for this challenging clinical application often with highly variable yet limited training data. First, we report that the latent space can be clustered into a much lower dimensional space than that commonly found as bottleneck features at the deep layer of a trained registration network. Based on this observation, we propose a hierarchical quantization method, discretizing the learned feature vectors using a jointly-trained dictionary with a constrained size, in order to improve the generalisation of the registration networks. Furthermore, a novel collaborative dictionary is independently optimised to incorporate additional prior information, such as the segmentation of the gland or other regions of interest, in the latent quantized space. Based on 216 real clinical images from 86 prostate cancer patients, we show the efficacy of both the designed components. Improved registration accuracy was obtained with statistical significance, in terms of both Dice on gland and target registration error on corresponding landmarks, the latter of which achieved 5.46 mm, an improvement of 28.7\% from the baseline without quantization. Experimental results also show that the difference in performance was indeed minimised between training and testing data.
Few-shot image segmentation for cross-institution male pelvic organs using registration-assisted prototypical learning
Jan 17, 2022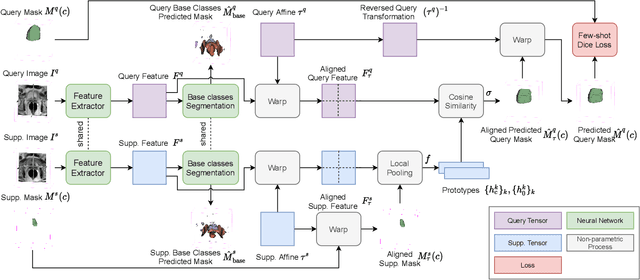
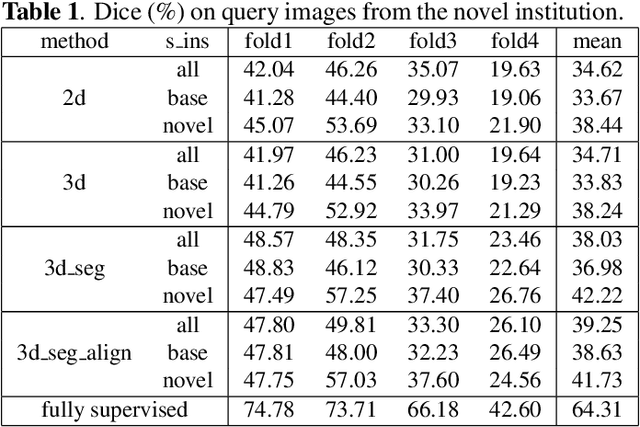
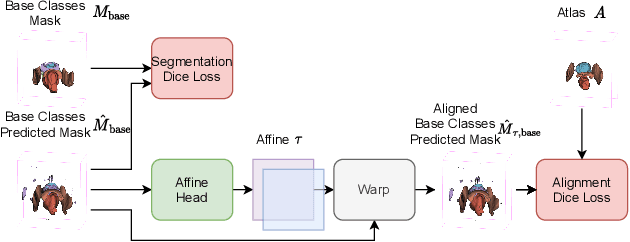
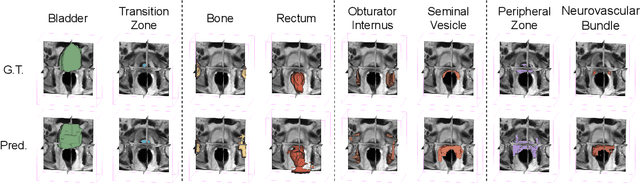
Abstract:The ability to adapt medical image segmentation networks for a novel class such as an unseen anatomical or pathological structure, when only a few labelled examples of this class are available from local healthcare providers, is sought-after. This potentially addresses two widely recognised limitations in deploying modern deep learning models to clinical practice, expertise-and-labour-intensive labelling and cross-institution generalisation. This work presents the first 3D few-shot interclass segmentation network for medical images, using a labelled multi-institution dataset from prostate cancer patients with eight regions of interest. We propose an image alignment module registering the predicted segmentation of both query and support data, in a standard prototypical learning algorithm, to a reference atlas space. The built-in registration mechanism can effectively utilise the prior knowledge of consistent anatomy between subjects, regardless whether they are from the same institution or not. Experimental results demonstrated that the proposed registration-assisted prototypical learning significantly improved segmentation accuracy (p-values<0.01) on query data from a holdout institution, with varying availability of support data from multiple institutions. We also report the additional benefits of the proposed 3D networks with 75% fewer parameters and an arguably simpler implementation, compared with existing 2D few-shot approaches that segment 2D slices of volumetric medical images.
Controlling False Positive/Negative Rates for Deep-Learning-Based Prostate Cancer Detection on Multiparametric MR images
Jun 04, 2021



Abstract:Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the leading causes of death for men worldwide. Multi-parametric magnetic resonance (mpMR) imaging has emerged as a non-invasive diagnostic tool for detecting and localising prostate tumours by specialised radiologists. These radiological examinations, for example, for differentiating malignant lesions from benign prostatic hyperplasia in transition zones and for defining the boundaries of clinically significant cancer, remain challenging and highly skill-and-experience-dependent. We first investigate experimental results in developing object detection neural networks that are trained to predict the radiological assessment, using these high-variance labels. We further argue that such a computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) system needs to have the ability to control the false-positive rate (FPR) or false-negative rate (FNR), in order to be usefully deployed in a clinical workflow, informing clinical decisions without further human intervention. This work proposes a novel PCa detection network that incorporates a lesion-level cost-sensitive loss and an additional slice-level loss based on a lesion-to-slice mapping function, to manage the lesion- and slice-level costs, respectively. Our experiments based on 290 clinical patients concludes that 1) The lesion-level FNR was effectively reduced from 0.19 to 0.10 and the lesion-level FPR was reduced from 1.03 to 0.66 by changing the lesion-level cost; 2) The slice-level FNR was reduced from 0.19 to 0.00 by taking into account the slice-level cost; (3) Both lesion-level and slice-level FNRs were reduced with lower FP/FPR by changing the lesion-level or slice-level costs, compared with post-training threshold adjustment using networks without the proposed cost-aware training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge