Qinquan Gao
NTIRE 2025 Image Shadow Removal Challenge Report
Jun 18, 2025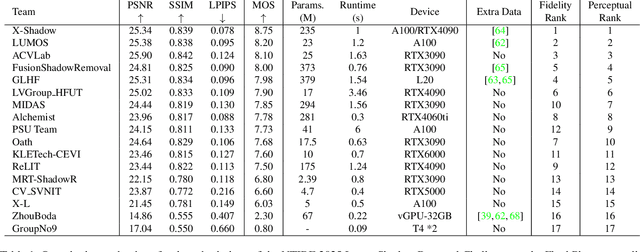

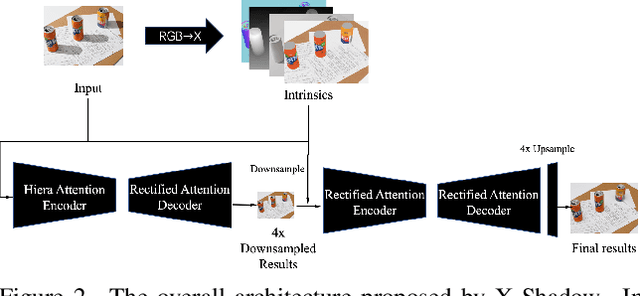
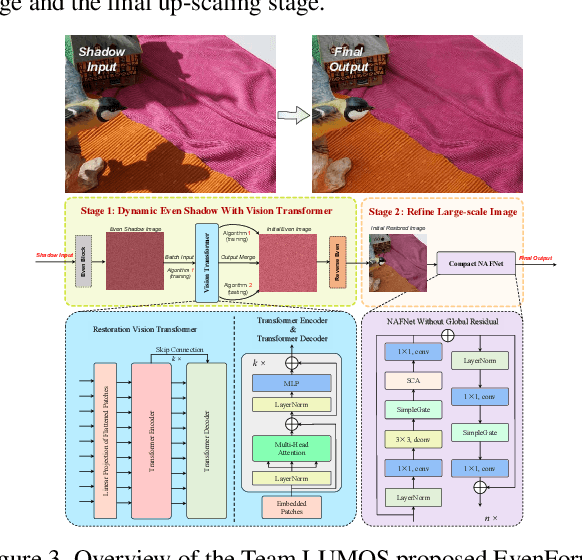
Abstract:This work examines the findings of the NTIRE 2025 Shadow Removal Challenge. A total of 306 participants have registered, with 17 teams successfully submitting their solutions during the final evaluation phase. Following the last two editions, this challenge had two evaluation tracks: one focusing on reconstruction fidelity and the other on visual perception through a user study. Both tracks were evaluated with images from the WSRD+ dataset, simulating interactions between self- and cast-shadows with a large number of diverse objects, textures, and materials.
DIffSteISR: Harnessing Diffusion Prior for Superior Real-world Stereo Image Super-Resolution
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:We introduce DiffSteISR, a pioneering framework for reconstructing real-world stereo images. DiffSteISR utilizes the powerful prior knowledge embedded in pre-trained text-to-image model to efficiently recover the lost texture details in low-resolution stereo images. Specifically, DiffSteISR implements a time-aware stereo cross attention with temperature adapter (TASCATA) to guide the diffusion process, ensuring that the generated left and right views exhibit high texture consistency thereby reducing disparity error between the super-resolved images and the ground truth (GT) images. Additionally, a stereo omni attention control network (SOA ControlNet) is proposed to enhance the consistency of super-resolved images with GT images in the pixel, perceptual, and distribution space. Finally, DiffSteISR incorporates a stereo semantic extractor (SSE) to capture unique viewpoint soft semantic information and shared hard tag semantic information, thereby effectively improving the semantic accuracy and consistency of the generated left and right images. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that DiffSteISR accurately reconstructs natural and precise textures from low-resolution stereo images while maintaining a high consistency of semantic and texture between the left and right views.
ASteISR: Adapting Single Image Super-resolution Pre-trained Model for Efficient Stereo Image Super-resolution
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Despite advances in the paradigm of pre-training then fine-tuning in low-level vision tasks, significant challenges persist particularly regarding the increased size of pre-trained models such as memory usage and training time. Another concern often encountered is the unsatisfying results yielded when directly applying pre-trained single-image models to multi-image domain. In this paper, we propose a efficient method for transferring a pre-trained single-image super-resolution (SISR) transformer network to the domain of stereo image super-resolution (SteISR) through a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) method. Specifically, we introduce the concept of stereo adapters and spatial adapters which are incorporated into the pre-trained SISR transformer network. Subsequently, the pre-trained SISR model is frozen, enabling us to fine-tune the adapters using stereo datasets along. By adopting this training method, we enhance the ability of the SISR model to accurately infer stereo images by 0.79dB on the Flickr1024 dataset. This method allows us to train only 4.8% of the original model parameters, achieving state-of-the-art performance on four commonly used SteISR benchmarks. Compared to the more complicated full fine-tuning approach, our method reduces training time and memory consumption by 57% and 15%, respectively.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Low Light Image Enhancement: Methods and Results
Apr 22, 2024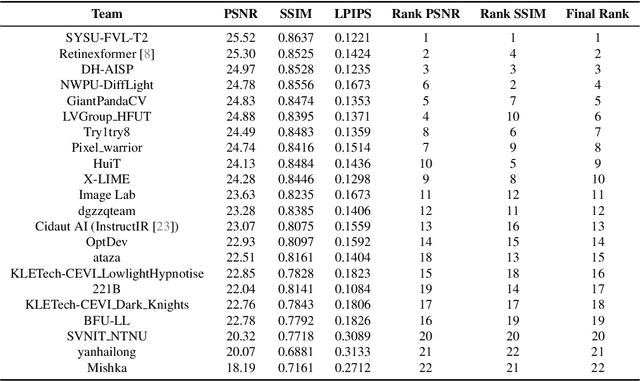

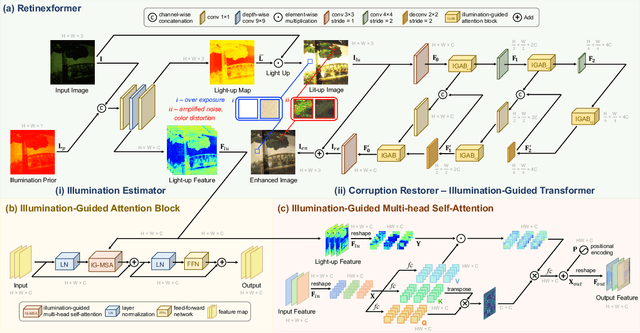

Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 low light image enhancement challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and results. The aim of this challenge is to discover an effective network design or solution capable of generating brighter, clearer, and visually appealing results when dealing with a variety of conditions, including ultra-high resolution (4K and beyond), non-uniform illumination, backlighting, extreme darkness, and night scenes. A notable total of 428 participants registered for the challenge, with 22 teams ultimately making valid submissions. This paper meticulously evaluates the state-of-the-art advancements in enhancing low-light images, reflecting the significant progress and creativity in this field.
Innovative Quantitative Analysis for Disease Progression Assessment in Familial Cerebral Cavernous Malformations
Mar 23, 2024Abstract:Familial cerebral cavernous malformation (FCCM) is a hereditary disorder characterized by abnormal vascular structures within the central nervous system. The FCCM lesions are often numerous and intricate, making quantitative analysis of the lesions a labor-intensive task. Consequently, clinicians face challenges in quantitatively assessing the severity of lesions and determining whether lesions have progressed. To alleviate this problem, we propose a quantitative statistical framework for FCCM, comprising an efficient annotation module, an FCCM lesion segmentation module, and an FCCM lesion quantitative statistics module. Our framework demonstrates precise segmentation of the FCCM lesion based on efficient data annotation, achieving a Dice coefficient of 93.22\%. More importantly, we focus on quantitative statistics of lesions, which is combined with image registration to realize the quantitative comparison of lesions between different examinations of patients, and a visualization framework has been established for doctors to comprehensively compare and analyze lesions. The experimental results have demonstrated that our proposed framework not only obtains objective, accurate, and comprehensive quantitative statistical information, which provides a quantitative assessment method for disease progression and drug efficacy study, but also considerably reduces the manual measurement and statistical workload of lesions, assisting clinical decision-making for FCCM and accelerating progress in FCCM clinical research. This highlights the potential of practical application of the framework in FCCM clinical research and clinical decision-making. The codes are available at https://github.com/6zrg/Quantitative-Statistics-of-FCCM.
Distance Guided Generative Adversarial Network for Explainable Binary Classifications
Dec 29, 2023Abstract:Despite the potential benefits of data augmentation for mitigating the data insufficiency, traditional augmentation methods primarily rely on the prior intra-domain knowledge. On the other hand, advanced generative adversarial networks (GANs) generate inter-domain samples with limited variety. These previous methods make limited contributions to describing the decision boundaries for binary classification. In this paper, we propose a distance guided GAN (DisGAN) which controls the variation degrees of generated samples in the hyperplane space. Specifically, we instantiate the idea of DisGAN by combining two ways. The first way is vertical distance GAN (VerDisGAN) where the inter-domain generation is conditioned on the vertical distances. The second way is horizontal distance GAN (HorDisGAN) where the intra-domain generation is conditioned on the horizontal distances. Furthermore, VerDisGAN can produce the class-specific regions by mapping the source images to the hyperplane. Experimental results show that DisGAN consistently outperforms the GAN-based augmentation methods with explainable binary classification. The proposed method can apply to different classification architectures and has potential to extend to multi-class classification.
Toward Real World Stereo Image Super-Resolution via Hybrid Degradation Model and Discriminator for Implied Stereo Image Information
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:Real-world stereo image super-resolution has a significant influence on enhancing the performance of computer vision systems. Although existing methods for single-image super-resolution can be applied to improve stereo images, these methods often introduce notable modifications to the inherent disparity, resulting in a loss in the consistency of disparity between the original and the enhanced stereo images. To overcome this limitation, this paper proposes a novel approach that integrates a implicit stereo information discriminator and a hybrid degradation model. This combination ensures effective enhancement while preserving disparity consistency. The proposed method bridges the gap between the complex degradations in real-world stereo domain and the simpler degradations in real-world single-image super-resolution domain. Our results demonstrate impressive performance on synthetic and real datasets, enhancing visual perception while maintaining disparity consistency. The complete code is available at the following \href{https://github.com/fzuzyb/SCGLANet}{link}.
A Parameterized Generative Adversarial Network Using Cyclic Projection for Explainable Medical Image Classification
Dec 07, 2023
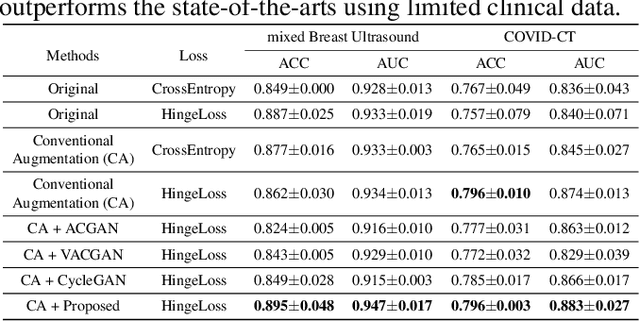

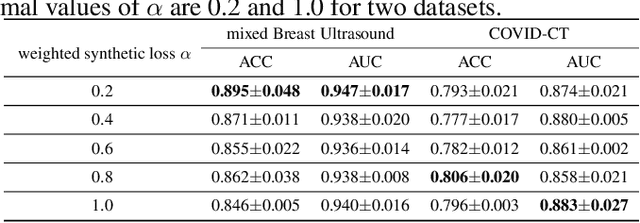
Abstract:Although current data augmentation methods are successful to alleviate the data insufficiency, conventional augmentation are primarily intra-domain while advanced generative adversarial networks (GANs) generate images remaining uncertain, particularly in small-scale datasets. In this paper, we propose a parameterized GAN (ParaGAN) that effectively controls the changes of synthetic samples among domains and highlights the attention regions for downstream classification. Specifically, ParaGAN incorporates projection distance parameters in cyclic projection and projects the source images to the decision boundary to obtain the class-difference maps. Our experiments show that ParaGAN can consistently outperform the existing augmentation methods with explainable classification on two small-scale medical datasets.
Pseudo Label-Guided Data Fusion and Output Consistency for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:Supervised learning algorithms based on Convolutional Neural Networks have become the benchmark for medical image segmentation tasks, but their effectiveness heavily relies on a large amount of labeled data. However, annotating medical image datasets is a laborious and time-consuming process. Inspired by semi-supervised algorithms that use both labeled and unlabeled data for training, we propose the PLGDF framework, which builds upon the mean teacher network for segmenting medical images with less annotation. We propose a novel pseudo-label utilization scheme, which combines labeled and unlabeled data to augment the dataset effectively. Additionally, we enforce the consistency between different scales in the decoder module of the segmentation network and propose a loss function suitable for evaluating the consistency. Moreover, we incorporate a sharpening operation on the predicted results, further enhancing the accuracy of the segmentation. Extensive experiments on three publicly available datasets demonstrate that the PLGDF framework can largely improve performance by incorporating the unlabeled data. Meanwhile, our framework yields superior performance compared to six state-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods. The codes of this study are available at https://github.com/ortonwang/PLGDF.
PCDAL: A Perturbation Consistency-Driven Active Learning Approach for Medical Image Segmentation and Classification
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, deep learning has become a breakthrough technique in assisting medical image diagnosis. Supervised learning using convolutional neural networks (CNN) provides state-of-the-art performance and has served as a benchmark for various medical image segmentation and classification. However, supervised learning deeply relies on large-scale annotated data, which is expensive, time-consuming, and even impractical to acquire in medical imaging applications. Active Learning (AL) methods have been widely applied in natural image classification tasks to reduce annotation costs by selecting more valuable examples from the unlabeled data pool. However, their application in medical image segmentation tasks is limited, and there is currently no effective and universal AL-based method specifically designed for 3D medical image segmentation. To address this limitation, we propose an AL-based method that can be simultaneously applied to 2D medical image classification, segmentation, and 3D medical image segmentation tasks. We extensively validated our proposed active learning method on three publicly available and challenging medical image datasets, Kvasir Dataset, COVID-19 Infection Segmentation Dataset, and BraTS2019 Dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that our PCDAL can achieve significantly improved performance with fewer annotations in 2D classification and segmentation and 3D segmentation tasks. The codes of this study are available at https://github.com/ortonwang/PCDAL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge