Po-Hsuan Cameron Chen
Domain-specific optimization and diverse evaluation of self-supervised models for histopathology
Oct 20, 2023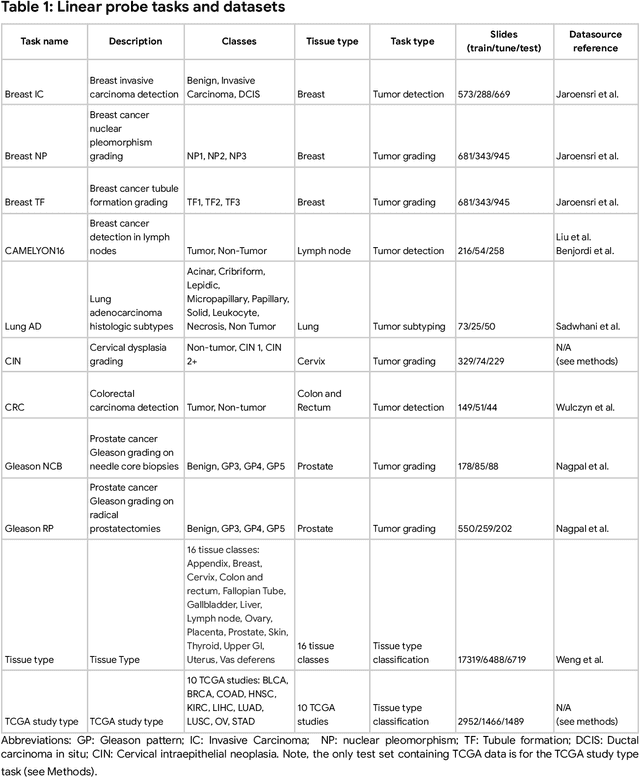
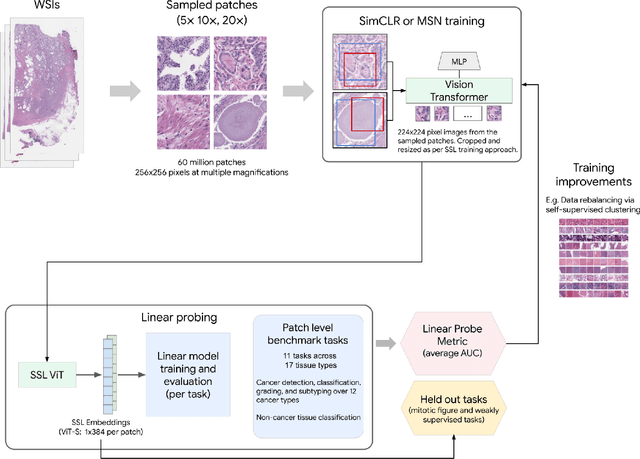
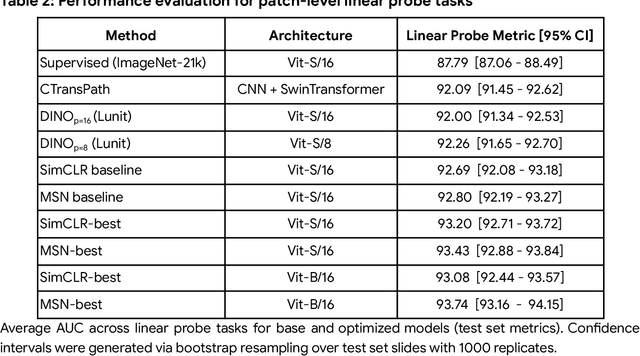
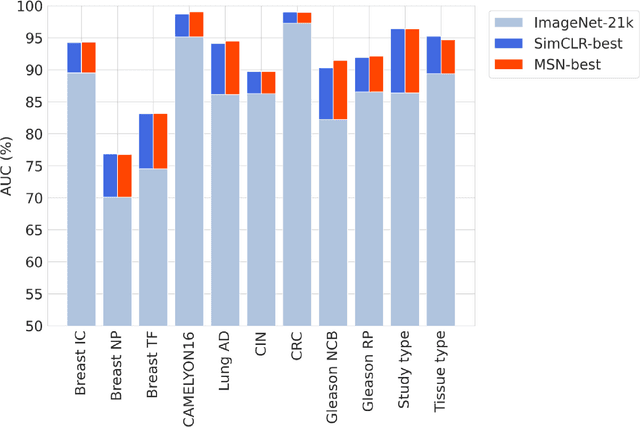
Abstract:Task-specific deep learning models in histopathology offer promising opportunities for improving diagnosis, clinical research, and precision medicine. However, development of such models is often limited by availability of high-quality data. Foundation models in histopathology that learn general representations across a wide range of tissue types, diagnoses, and magnifications offer the potential to reduce the data, compute, and technical expertise necessary to develop task-specific deep learning models with the required level of model performance. In this work, we describe the development and evaluation of foundation models for histopathology via self-supervised learning (SSL). We first establish a diverse set of benchmark tasks involving 17 unique tissue types and 12 unique cancer types and spanning different optimal magnifications and task types. Next, we use this benchmark to explore and evaluate histopathology-specific SSL methods followed by further evaluation on held out patch-level and weakly supervised tasks. We found that standard SSL methods thoughtfully applied to histopathology images are performant across our benchmark tasks and that domain-specific methodological improvements can further increase performance. Our findings reinforce the value of using domain-specific SSL methods in pathology, and establish a set of high quality foundation models to enable further research across diverse applications.
Robust and Efficient Medical Imaging with Self-Supervision
May 19, 2022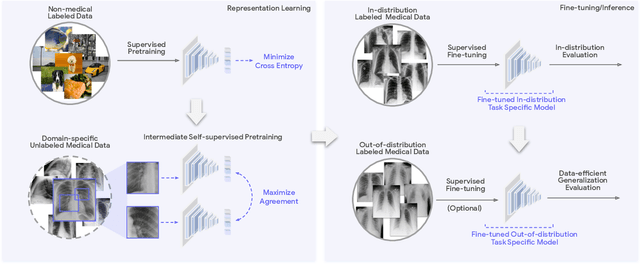
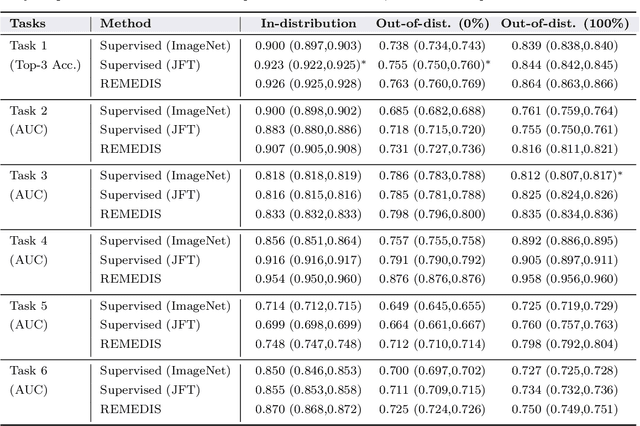
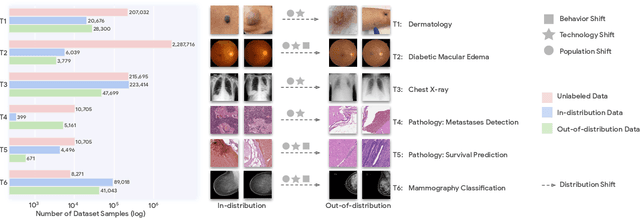
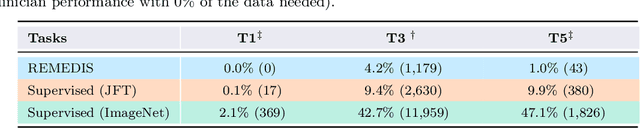
Abstract:Recent progress in Medical Artificial Intelligence (AI) has delivered systems that can reach clinical expert level performance. However, such systems tend to demonstrate sub-optimal "out-of-distribution" performance when evaluated in clinical settings different from the training environment. A common mitigation strategy is to develop separate systems for each clinical setting using site-specific data [1]. However, this quickly becomes impractical as medical data is time-consuming to acquire and expensive to annotate [2]. Thus, the problem of "data-efficient generalization" presents an ongoing difficulty for Medical AI development. Although progress in representation learning shows promise, their benefits have not been rigorously studied, specifically for out-of-distribution settings. To meet these challenges, we present REMEDIS, a unified representation learning strategy to improve robustness and data-efficiency of medical imaging AI. REMEDIS uses a generic combination of large-scale supervised transfer learning with self-supervised learning and requires little task-specific customization. We study a diverse range of medical imaging tasks and simulate three realistic application scenarios using retrospective data. REMEDIS exhibits significantly improved in-distribution performance with up to 11.5% relative improvement in diagnostic accuracy over a strong supervised baseline. More importantly, our strategy leads to strong data-efficient generalization of medical imaging AI, matching strong supervised baselines using between 1% to 33% of retraining data across tasks. These results suggest that REMEDIS can significantly accelerate the life-cycle of medical imaging AI development thereby presenting an important step forward for medical imaging AI to deliver broad impact.
Deep learning for detecting pulmonary tuberculosis via chest radiography: an international study across 10 countries
May 16, 2021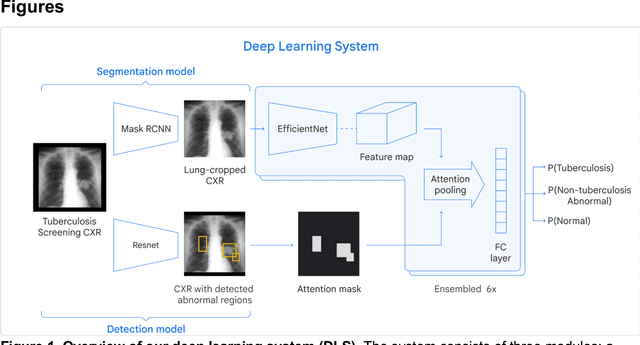
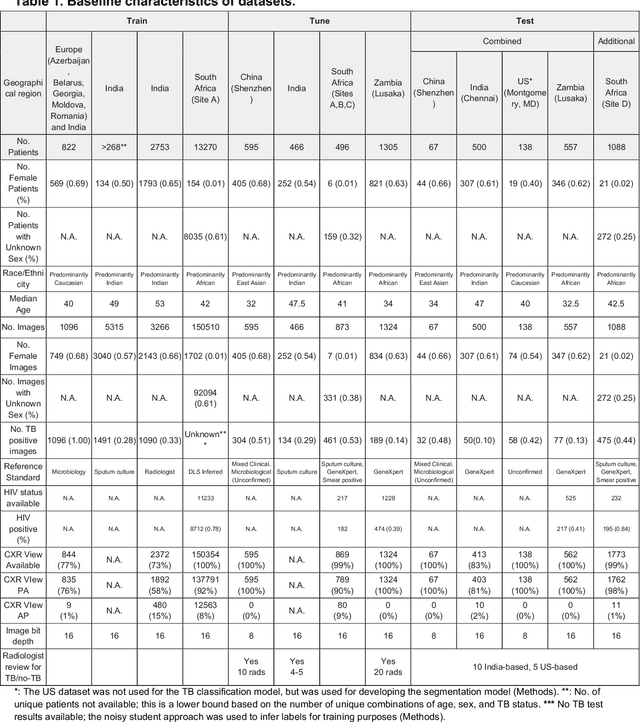
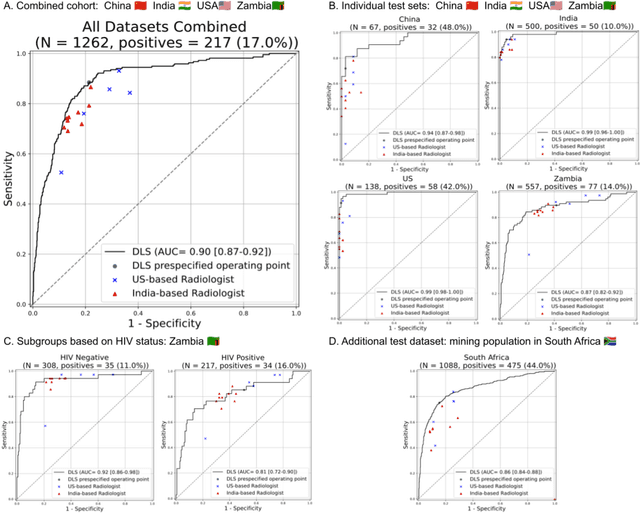
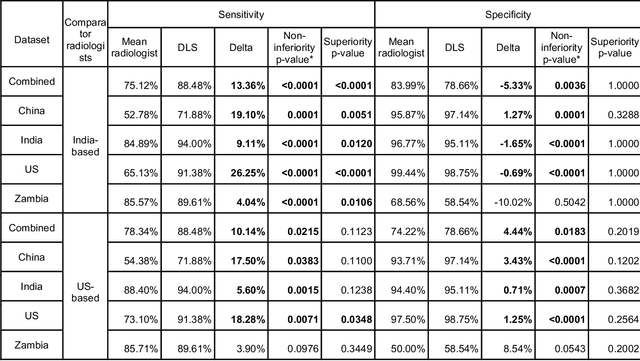
Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) is a top-10 cause of death worldwide. Though the WHO recommends chest radiographs (CXRs) for TB screening, the limited availability of CXR interpretation is a barrier. We trained a deep learning system (DLS) to detect active pulmonary TB using CXRs from 9 countries across Africa, Asia, and Europe, and utilized large-scale CXR pretraining, attention pooling, and noisy student semi-supervised learning. Evaluation was on (1) a combined test set spanning China, India, US, and Zambia, and (2) an independent mining population in South Africa. Given WHO targets of 90% sensitivity and 70% specificity, the DLS's operating point was prespecified to favor sensitivity over specificity. On the combined test set, the DLS's ROC curve was above all 9 India-based radiologists, with an AUC of 0.90 (95%CI 0.87-0.92). The DLS's sensitivity (88%) was higher than the India-based radiologists (75% mean sensitivity), p<0.001 for superiority; and its specificity (79%) was non-inferior to the radiologists (84% mean specificity), p=0.004. Similar trends were observed within HIV positive and sputum smear positive sub-groups, and in the South Africa test set. We found that 5 US-based radiologists (where TB isn't endemic) were more sensitive and less specific than the India-based radiologists (where TB is endemic). The DLS also remained non-inferior to the US-based radiologists. In simulations, using the DLS as a prioritization tool for confirmatory testing reduced the cost per positive case detected by 40-80% compared to using confirmatory testing alone. To conclude, our DLS generalized to 5 countries, and merits prospective evaluation to assist cost-effective screening efforts in radiologist-limited settings. Operating point flexibility may permit customization of the DLS to account for site-specific factors such as TB prevalence, demographics, clinical resources, and customary practice patterns.
Predicting Prostate Cancer-Specific Mortality with A.I.-based Gleason Grading
Nov 25, 2020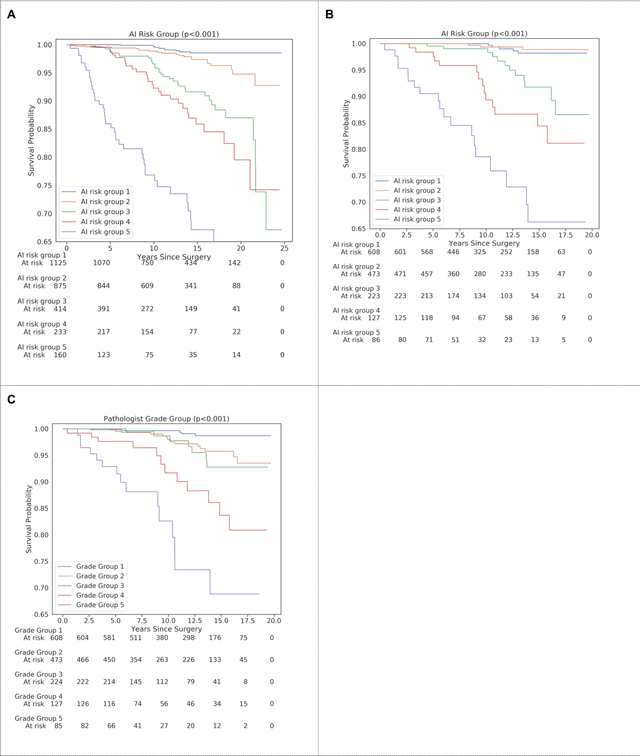
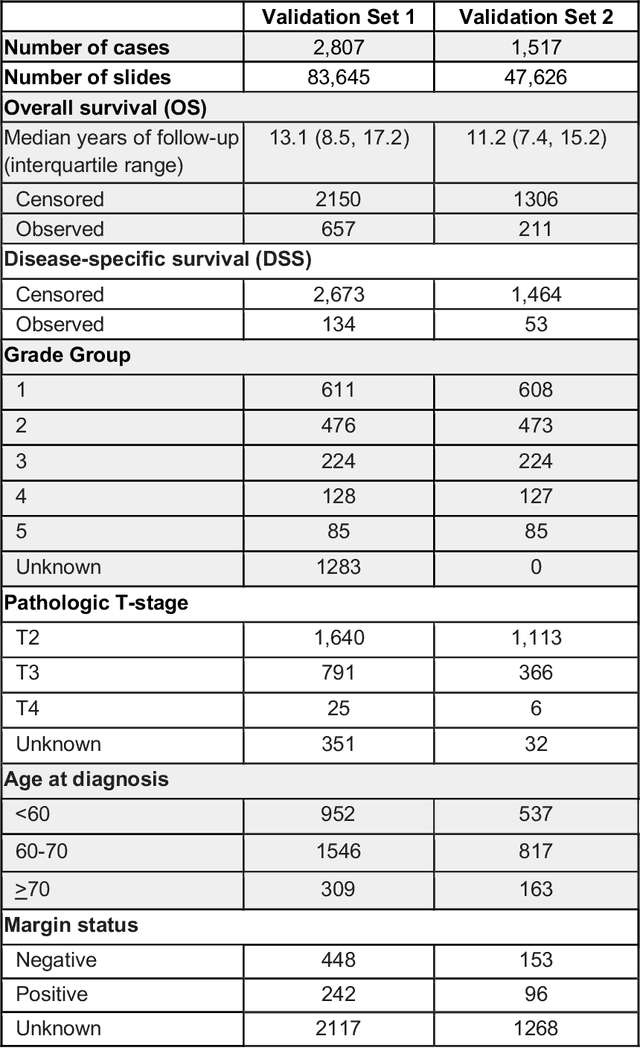
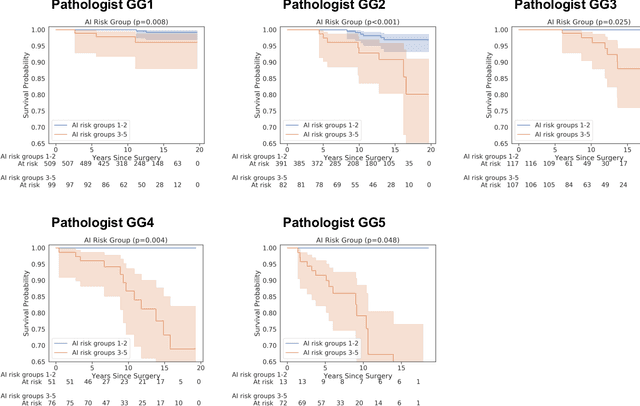
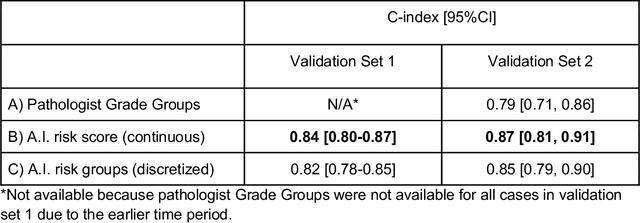
Abstract:Gleason grading of prostate cancer is an important prognostic factor but suffers from poor reproducibility, particularly among non-subspecialist pathologists. Although artificial intelligence (A.I.) tools have demonstrated Gleason grading on-par with expert pathologists, it remains an open question whether A.I. grading translates to better prognostication. In this study, we developed a system to predict prostate-cancer specific mortality via A.I.-based Gleason grading and subsequently evaluated its ability to risk-stratify patients on an independent retrospective cohort of 2,807 prostatectomy cases from a single European center with 5-25 years of follow-up (median: 13, interquartile range 9-17). The A.I.'s risk scores produced a C-index of 0.84 (95%CI 0.80-0.87) for prostate cancer-specific mortality. Upon discretizing these risk scores into risk groups analogous to pathologist Grade Groups (GG), the A.I. had a C-index of 0.82 (95%CI 0.78-0.85). On the subset of cases with a GG in the original pathology report (n=1,517), the A.I.'s C-indices were 0.87 and 0.85 for continuous and discrete grading, respectively, compared to 0.79 (95%CI 0.71-0.86) for GG obtained from the reports. These represent improvements of 0.08 (95%CI 0.01-0.15) and 0.07 (95%CI 0.00-0.14) respectively. Our results suggest that A.I.-based Gleason grading can lead to effective risk-stratification and warrants further evaluation for improving disease management.
Interpretable Survival Prediction for Colorectal Cancer using Deep Learning
Nov 17, 2020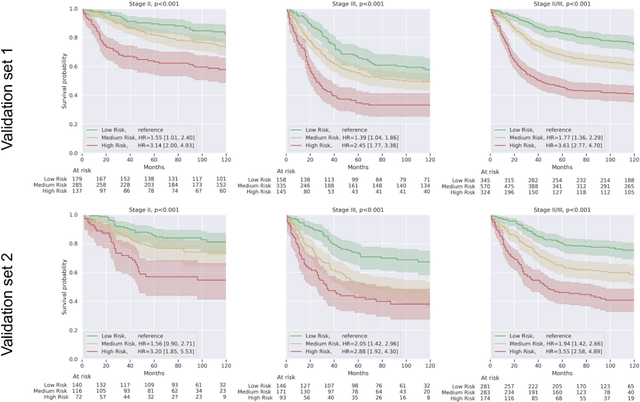
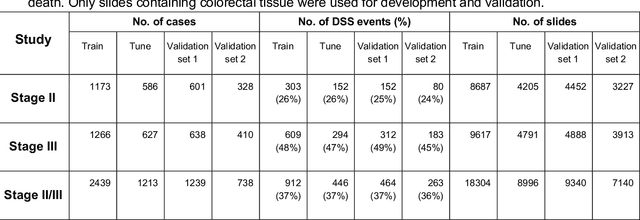
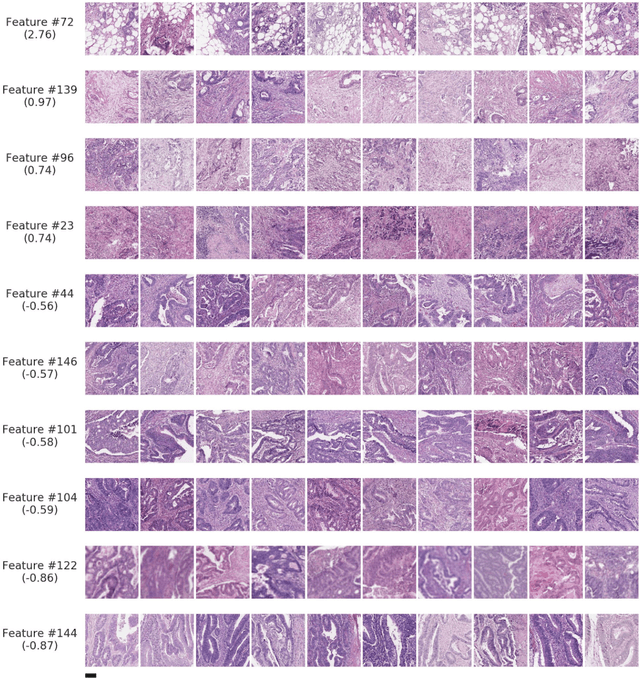
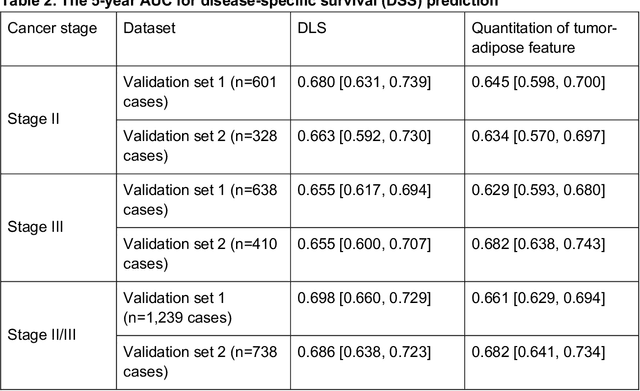
Abstract:Deriving interpretable prognostic features from deep-learning-based prognostic histopathology models remains a challenge. In this study, we developed a deep learning system (DLS) for predicting disease specific survival for stage II and III colorectal cancer using 3,652 cases (27,300 slides). When evaluated on two validation datasets containing 1,239 cases (9,340 slides) and 738 cases (7,140 slides) respectively, the DLS achieved a 5-year disease-specific survival AUC of 0.70 (95%CI 0.66-0.73) and 0.69 (95%CI 0.64-0.72), and added significant predictive value to a set of 9 clinicopathologic features. To interpret the DLS, we explored the ability of different human-interpretable features to explain the variance in DLS scores. We observed that clinicopathologic features such as T-category, N-category, and grade explained a small fraction of the variance in DLS scores (R2=18% in both validation sets). Next, we generated human-interpretable histologic features by clustering embeddings from a deep-learning based image-similarity model and showed that they explain the majority of the variance (R2 of 73% to 80%). Furthermore, the clustering-derived feature most strongly associated with high DLS scores was also highly prognostic in isolation. With a distinct visual appearance (poorly differentiated tumor cell clusters adjacent to adipose tissue), this feature was identified by annotators with 87.0-95.5% accuracy. Our approach can be used to explain predictions from a prognostic deep learning model and uncover potentially-novel prognostic features that can be reliably identified by people for future validation studies.
Deep Learning for Distinguishing Normal versus Abnormal Chest Radiographs and Generalization to Unseen Diseases
Oct 22, 2020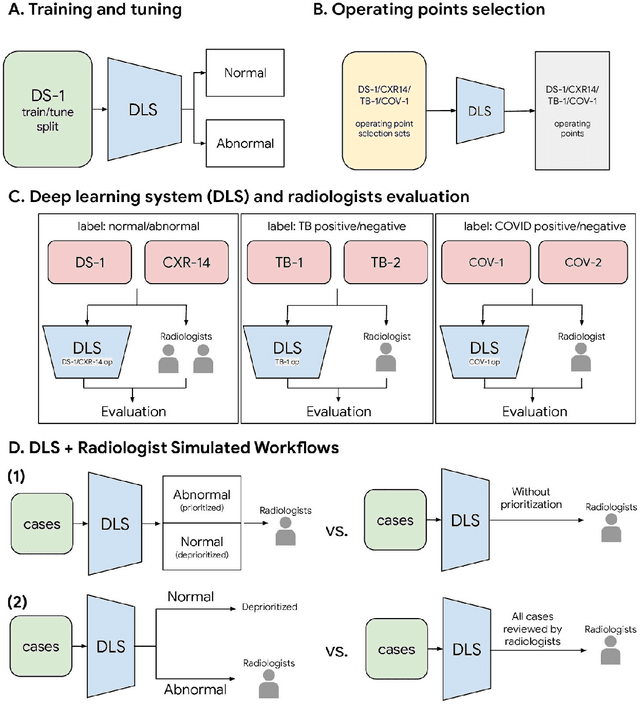
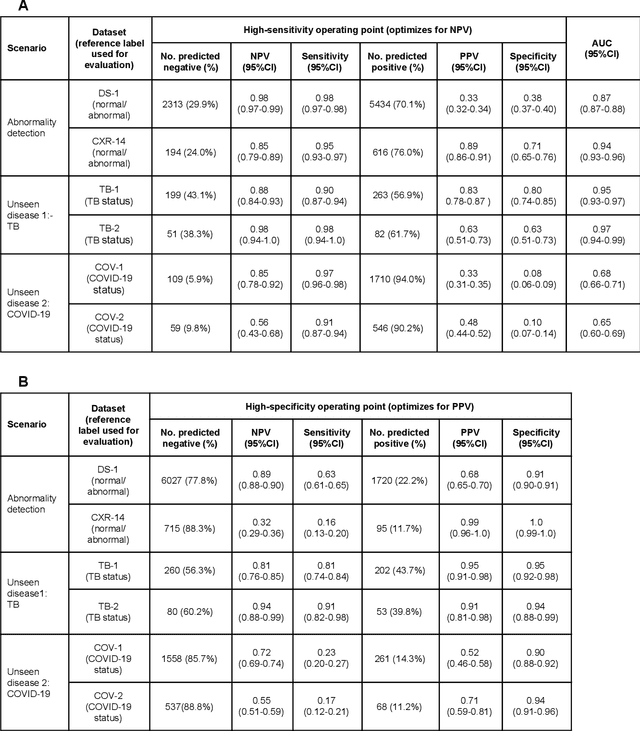
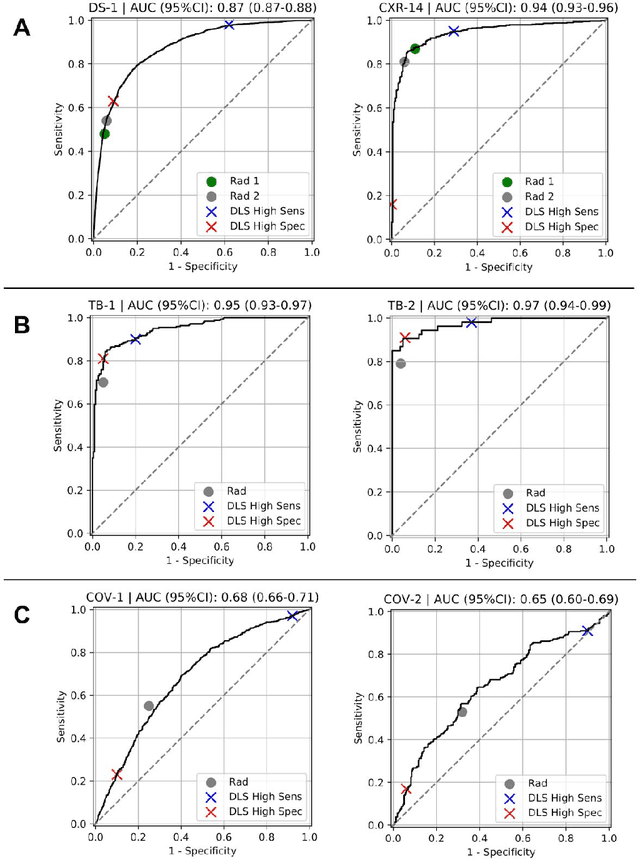
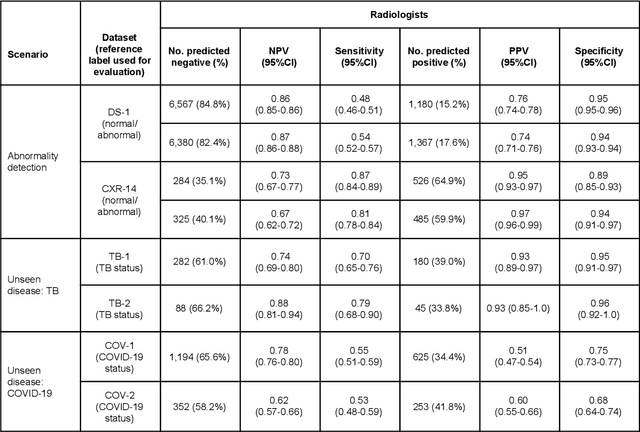
Abstract:Chest radiography (CXR) is the most widely-used thoracic clinical imaging modality and is crucial for guiding the management of cardiothoracic conditions. The detection of specific CXR findings has been the main focus of several artificial intelligence (AI) systems. However, the wide range of possible CXR abnormalities makes it impractical to build specific systems to detect every possible condition. In this work, we developed and evaluated an AI system to classify CXRs as normal or abnormal. For development, we used a de-identified dataset of 248,445 patients from a multi-city hospital network in India. To assess generalizability, we evaluated our system using 6 international datasets from India, China, and the United States. Of these datasets, 4 focused on diseases that the AI was not trained to detect: 2 datasets with tuberculosis and 2 datasets with coronavirus disease 2019. Our results suggest that the AI system generalizes to new patient populations and abnormalities. In a simulated workflow where the AI system prioritized abnormal cases, the turnaround time for abnormal cases reduced by 7-28%. These results represent an important step towards evaluating whether AI can be safely used to flag cases in a general setting where previously unseen abnormalities exist.
Deep learning-based survival prediction for multiple cancer types using histopathology images
Dec 16, 2019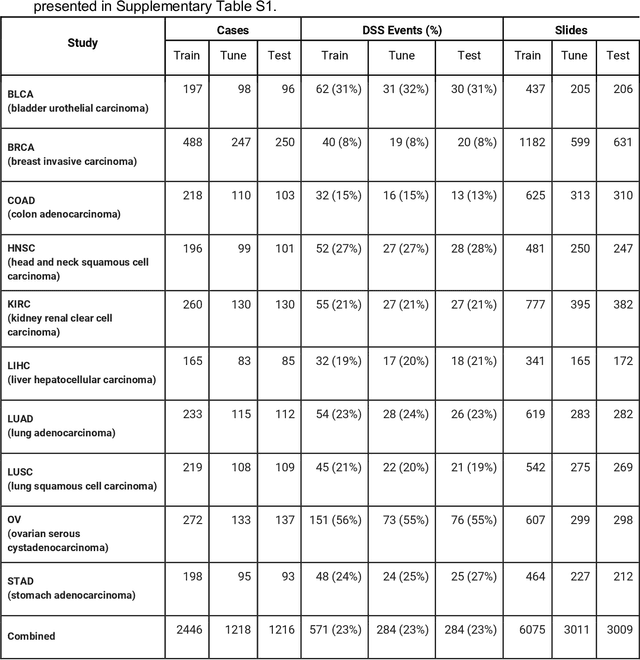
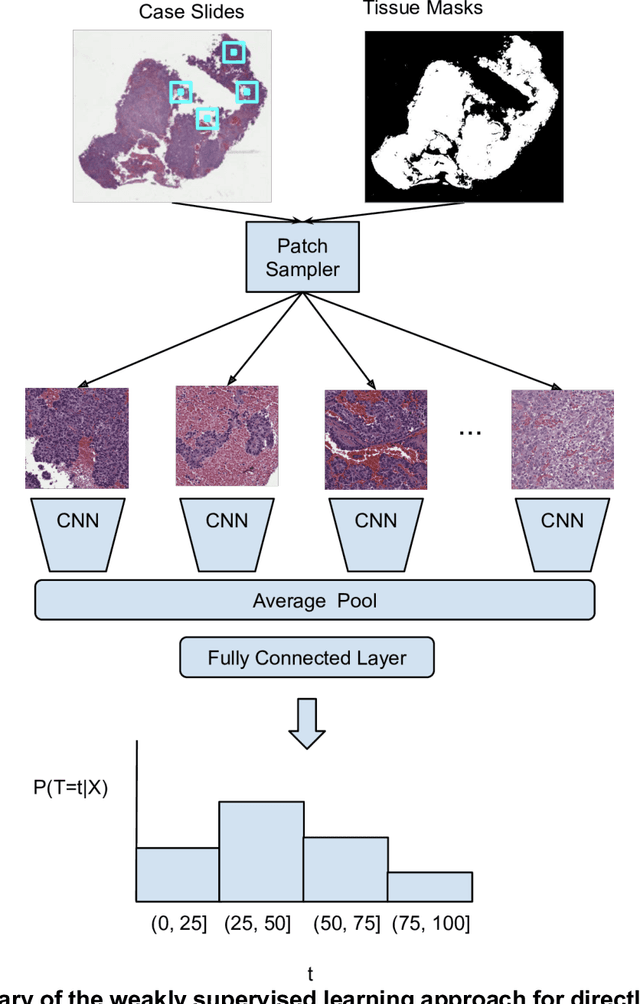
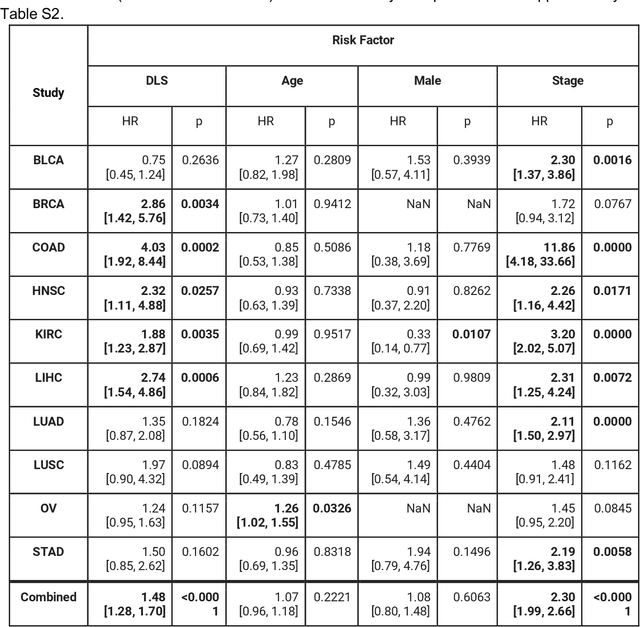
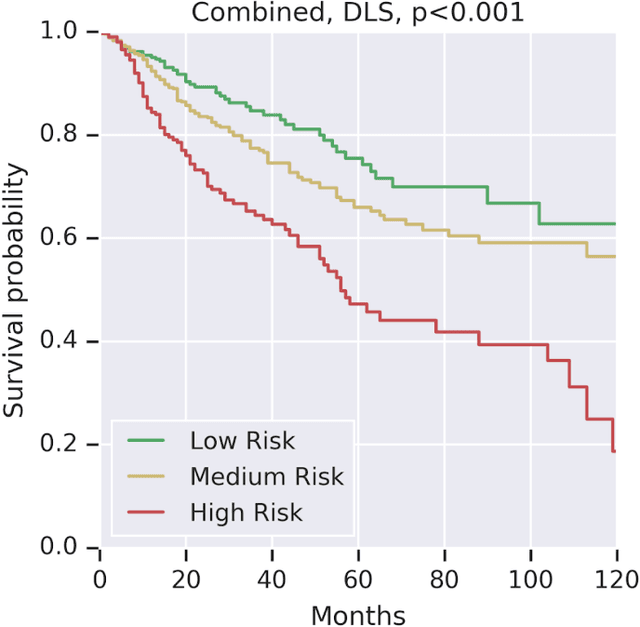
Abstract:Prognostic information at diagnosis has important implications for cancer treatment and monitoring. Although cancer staging, histopathological assessment, molecular features, and clinical variables can provide useful prognostic insights, improving risk stratification remains an active research area. We developed a deep learning system (DLS) to predict disease specific survival across 10 cancer types from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We used a weakly-supervised approach without pixel-level annotations, and tested three different survival loss functions. The DLS was developed using 9,086 slides from 3,664 cases and evaluated using 3,009 slides from 1,216 cases. In multivariable Cox regression analysis of the combined cohort including all 10 cancers, the DLS was significantly associated with disease specific survival (hazard ratio of 1.58, 95% CI 1.28-1.70, p<0.0001) after adjusting for cancer type, stage, age, and sex. In a per-cancer adjusted subanalysis, the DLS remained a significant predictor of survival in 5 of 10 cancer types. Compared to a baseline model including stage, age, and sex, the c-index of the model demonstrated an absolute 3.7% improvement (95% CI 1.0-6.5) in the combined cohort. Additionally, our models stratified patients within individual cancer stages, particularly stage II (p=0.025) and stage III (p<0.001). By developing and evaluating prognostic models across multiple cancer types, this work represents one of the most comprehensive studies exploring the direct prediction of clinical outcomes using deep learning and histopathology images. Our analysis demonstrates the potential for this approach to provide prognostic information in multiple cancer types, and even within specific pathologic stages. However, given the relatively small number of clinical events, we observed wide confidence intervals, suggesting that future work will benefit from larger datasets.
Human-centric Metric for Accelerating Pathology Reports Annotation
Nov 12, 2019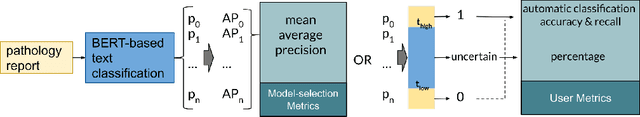
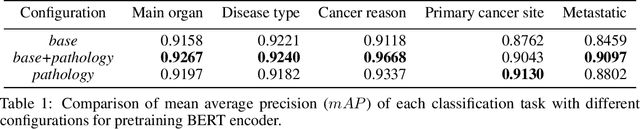
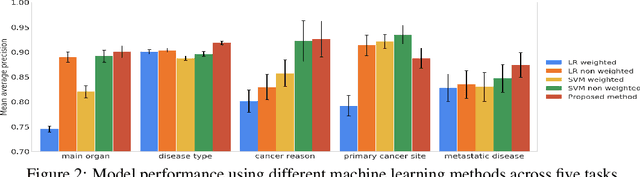
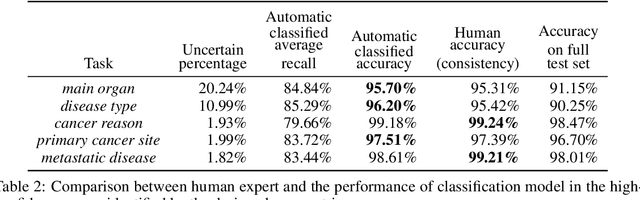
Abstract:Pathology reports contain useful information such as the main involved organ, diagnosis, etc. These information can be identified from the free text reports and used for large-scale statistical analysis or serve as annotation for other modalities such as pathology slides images. However, manual classification for a huge number of reports on multiple tasks is labor-intensive. In this paper, we have developed an automatic text classifier based on BERT and we propose a human-centric metric to evaluate the model. According to the model confidence, we identify low-confidence cases that require further expert annotation and high-confidence cases that are automatically classified. We report the percentage of low-confidence cases and the performance of automatically classified cases. On the high-confidence cases, the model achieves classification accuracy comparable to pathologists. This leads a potential of reducing 80% to 98% of the manual annotation workload.
Multimodal Multitask Representation Learning for Pathology Biobank Metadata Prediction
Sep 17, 2019



Abstract:Metadata are general characteristics of the data in a well-curated and condensed format, and have been proven to be useful for decision making, knowledge discovery, and also heterogeneous data organization of biobank. Among all data types in the biobank, pathology is the key component of the biobank and also serves as the gold standard of diagnosis. To maximize the utility of biobank and allow the rapid progress of biomedical science, it is essential to organize the data with well-populated pathology metadata. However, manual annotation of such information is tedious and time-consuming. In the study, we develop a multimodal multitask learning framework to predict four major slide-level metadata of pathology images. The framework learns generalizable representations across tissue slides, pathology reports, and case-level structured data. We demonstrate improved performance across all four tasks with the proposed method compared to a single modal single task baseline on two test sets, one external test set from a distinct data source (TCGA) and one internal held-out test set (TTH). In the test sets, the performance improvements on the averaged area under receiver operating characteristic curve across the four tasks are 16.48% and 9.05% on TCGA and TTH, respectively. Such pathology metadata prediction system may be adopted to mitigate the effort of expert annotation and ultimately accelerate the data-driven research by better utilization of the pathology biobank.
Microscope 2.0: An Augmented Reality Microscope with Real-time Artificial Intelligence Integration
Dec 04, 2018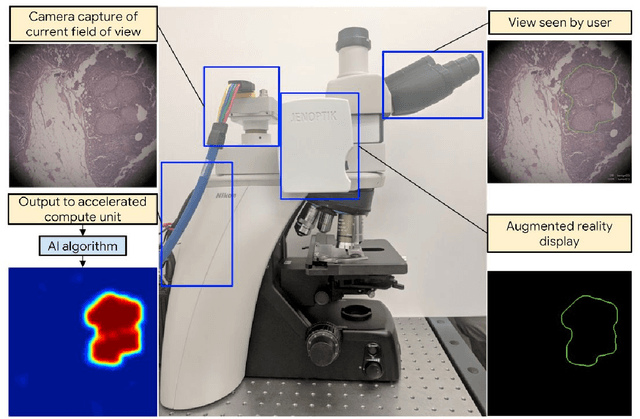
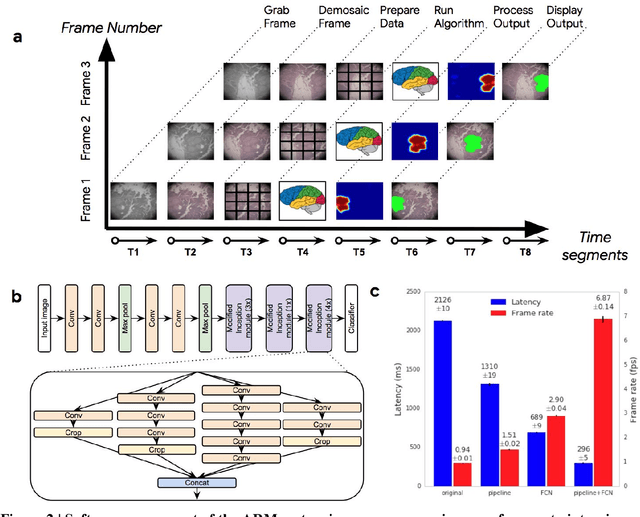
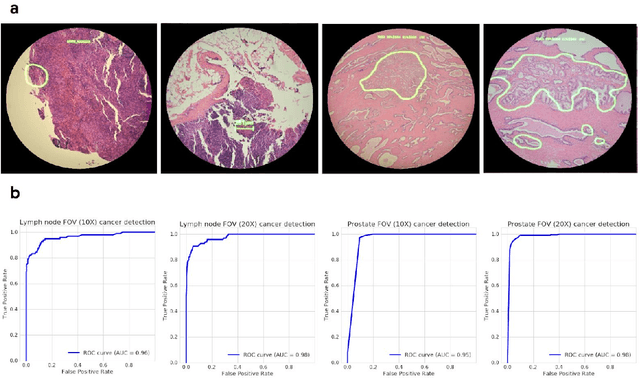
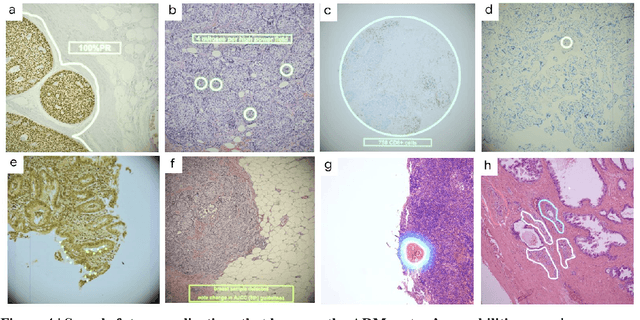
Abstract:The brightfield microscope is instrumental in the visual examination of both biological and physical samples at sub-millimeter scales. One key clinical application has been in cancer histopathology, where the microscopic assessment of the tissue samples is used for the diagnosis and staging of cancer and thus guides clinical therapy. However, the interpretation of these samples is inherently subjective, resulting in significant diagnostic variability. Moreover, in many regions of the world, access to pathologists is severely limited due to lack of trained personnel. In this regard, Artificial Intelligence (AI) based tools promise to improve the access and quality of healthcare. However, despite significant advances in AI research, integration of these tools into real-world cancer diagnosis workflows remains challenging because of the costs of image digitization and difficulties in deploying AI solutions. Here we propose a cost-effective solution to the integration of AI: the Augmented Reality Microscope (ARM). The ARM overlays AI-based information onto the current view of the sample through the optical pathway in real-time, enabling seamless integration of AI into the regular microscopy workflow. We demonstrate the utility of ARM in the detection of lymph node metastases in breast cancer and the identification of prostate cancer with a latency that supports real-time workflows. We anticipate that ARM will remove barriers towards the use of AI in microscopic analysis and thus improve the accuracy and efficiency of cancer diagnosis. This approach is applicable to other microscopy tasks and AI algorithms in the life sciences and beyond.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge