Craig H. Mermel
Predicting Prostate Cancer-Specific Mortality with A.I.-based Gleason Grading
Nov 25, 2020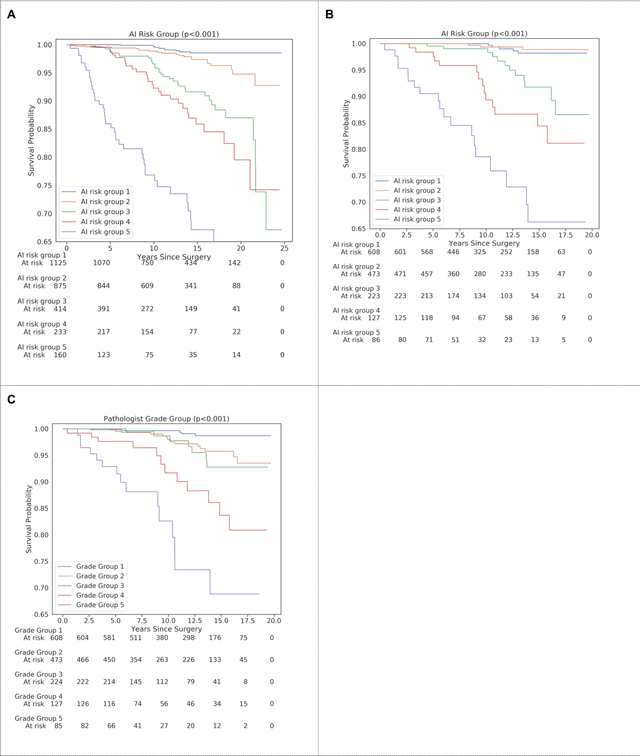
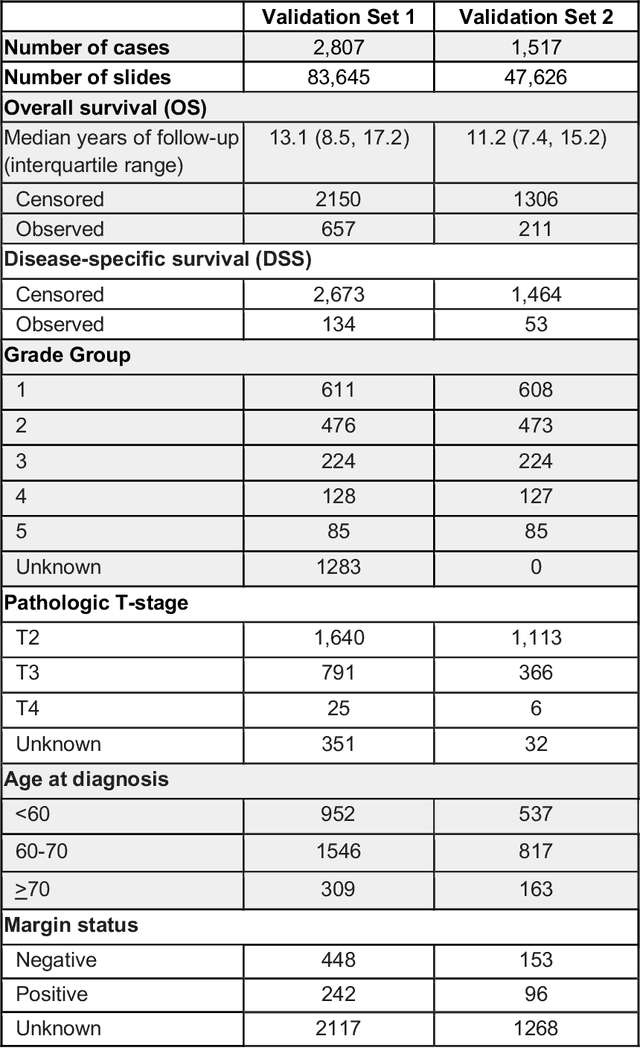
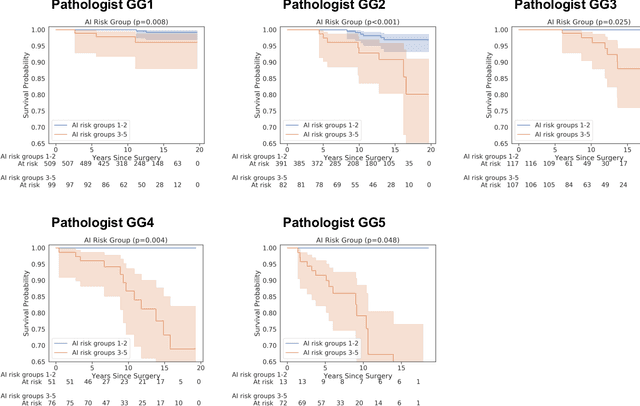
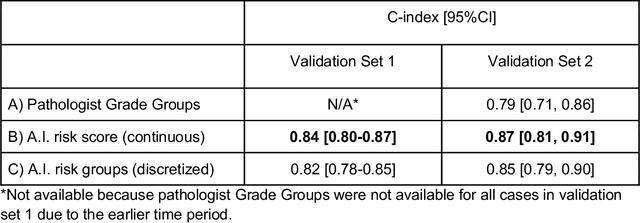
Abstract:Gleason grading of prostate cancer is an important prognostic factor but suffers from poor reproducibility, particularly among non-subspecialist pathologists. Although artificial intelligence (A.I.) tools have demonstrated Gleason grading on-par with expert pathologists, it remains an open question whether A.I. grading translates to better prognostication. In this study, we developed a system to predict prostate-cancer specific mortality via A.I.-based Gleason grading and subsequently evaluated its ability to risk-stratify patients on an independent retrospective cohort of 2,807 prostatectomy cases from a single European center with 5-25 years of follow-up (median: 13, interquartile range 9-17). The A.I.'s risk scores produced a C-index of 0.84 (95%CI 0.80-0.87) for prostate cancer-specific mortality. Upon discretizing these risk scores into risk groups analogous to pathologist Grade Groups (GG), the A.I. had a C-index of 0.82 (95%CI 0.78-0.85). On the subset of cases with a GG in the original pathology report (n=1,517), the A.I.'s C-indices were 0.87 and 0.85 for continuous and discrete grading, respectively, compared to 0.79 (95%CI 0.71-0.86) for GG obtained from the reports. These represent improvements of 0.08 (95%CI 0.01-0.15) and 0.07 (95%CI 0.00-0.14) respectively. Our results suggest that A.I.-based Gleason grading can lead to effective risk-stratification and warrants further evaluation for improving disease management.
Interpretable Survival Prediction for Colorectal Cancer using Deep Learning
Nov 17, 2020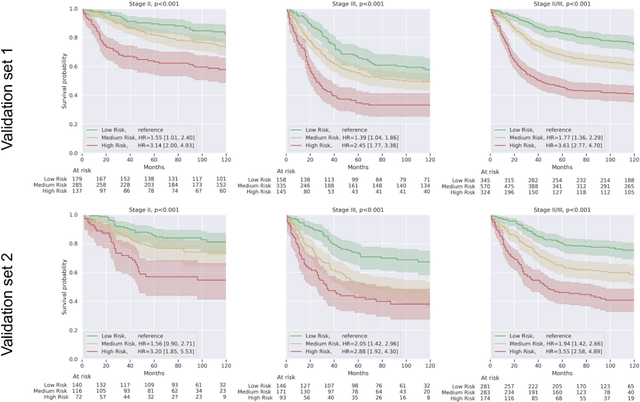
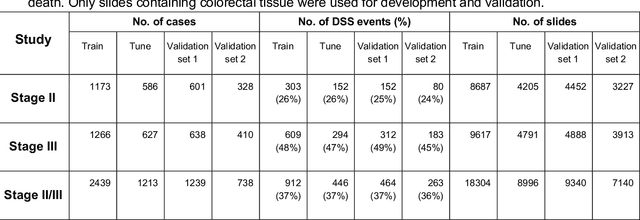
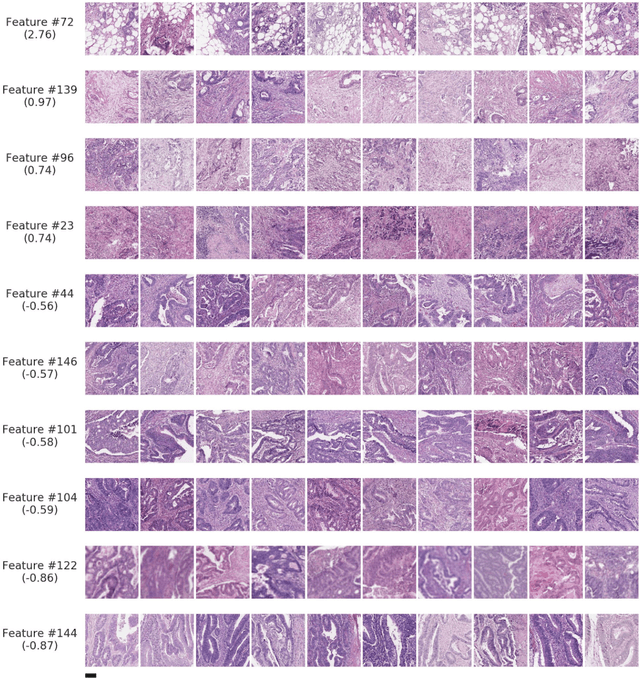
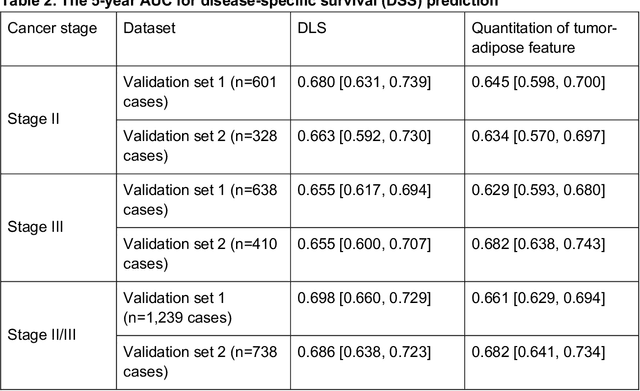
Abstract:Deriving interpretable prognostic features from deep-learning-based prognostic histopathology models remains a challenge. In this study, we developed a deep learning system (DLS) for predicting disease specific survival for stage II and III colorectal cancer using 3,652 cases (27,300 slides). When evaluated on two validation datasets containing 1,239 cases (9,340 slides) and 738 cases (7,140 slides) respectively, the DLS achieved a 5-year disease-specific survival AUC of 0.70 (95%CI 0.66-0.73) and 0.69 (95%CI 0.64-0.72), and added significant predictive value to a set of 9 clinicopathologic features. To interpret the DLS, we explored the ability of different human-interpretable features to explain the variance in DLS scores. We observed that clinicopathologic features such as T-category, N-category, and grade explained a small fraction of the variance in DLS scores (R2=18% in both validation sets). Next, we generated human-interpretable histologic features by clustering embeddings from a deep-learning based image-similarity model and showed that they explain the majority of the variance (R2 of 73% to 80%). Furthermore, the clustering-derived feature most strongly associated with high DLS scores was also highly prognostic in isolation. With a distinct visual appearance (poorly differentiated tumor cell clusters adjacent to adipose tissue), this feature was identified by annotators with 87.0-95.5% accuracy. Our approach can be used to explain predictions from a prognostic deep learning model and uncover potentially-novel prognostic features that can be reliably identified by people for future validation studies.
Deep learning-based survival prediction for multiple cancer types using histopathology images
Dec 16, 2019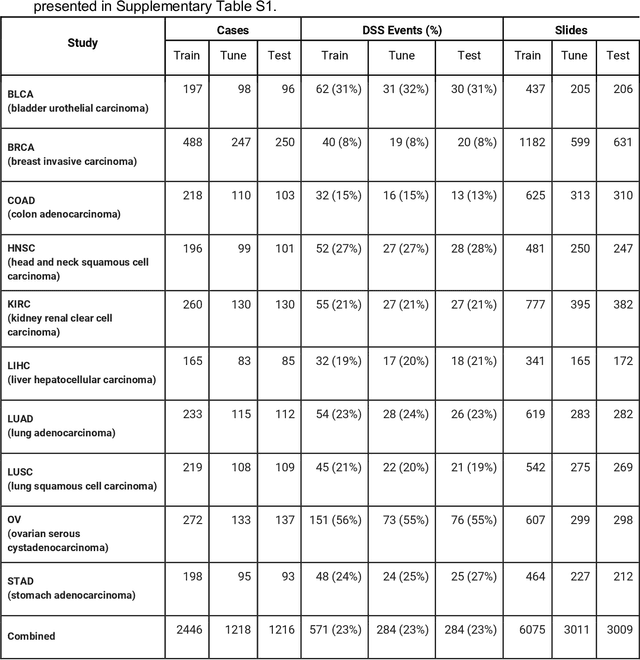
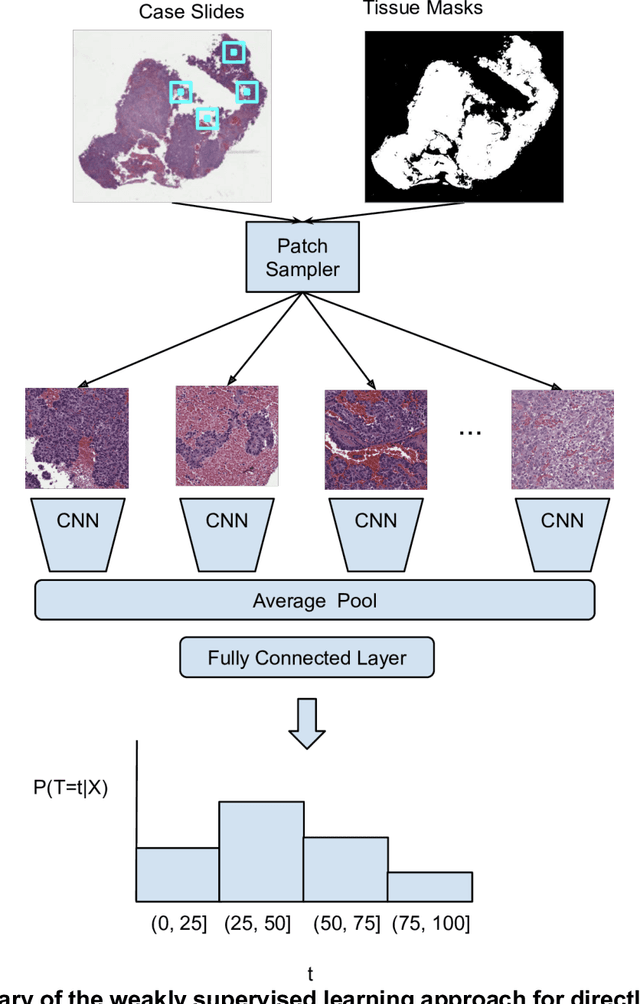
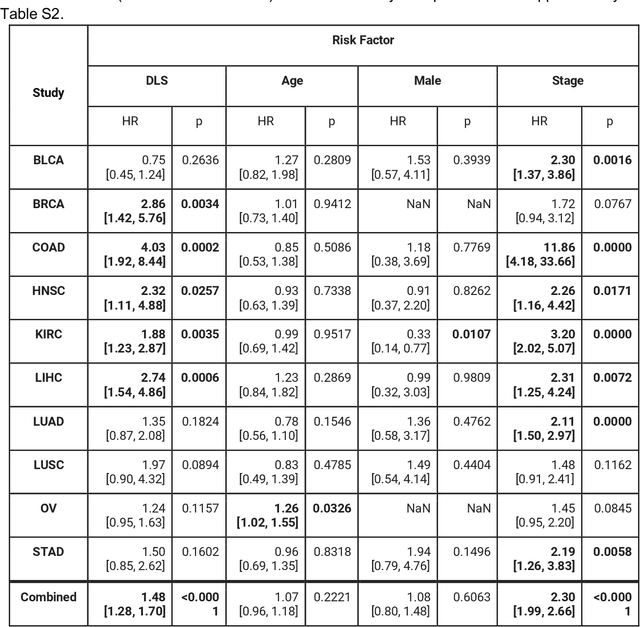
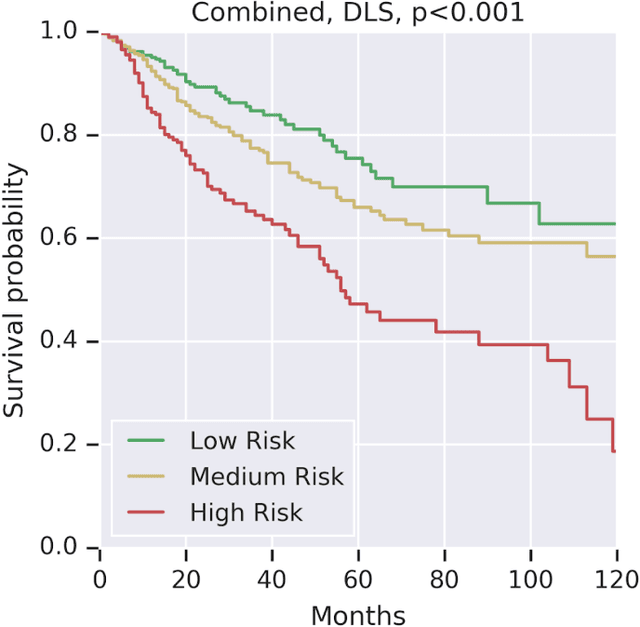
Abstract:Prognostic information at diagnosis has important implications for cancer treatment and monitoring. Although cancer staging, histopathological assessment, molecular features, and clinical variables can provide useful prognostic insights, improving risk stratification remains an active research area. We developed a deep learning system (DLS) to predict disease specific survival across 10 cancer types from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We used a weakly-supervised approach without pixel-level annotations, and tested three different survival loss functions. The DLS was developed using 9,086 slides from 3,664 cases and evaluated using 3,009 slides from 1,216 cases. In multivariable Cox regression analysis of the combined cohort including all 10 cancers, the DLS was significantly associated with disease specific survival (hazard ratio of 1.58, 95% CI 1.28-1.70, p<0.0001) after adjusting for cancer type, stage, age, and sex. In a per-cancer adjusted subanalysis, the DLS remained a significant predictor of survival in 5 of 10 cancer types. Compared to a baseline model including stage, age, and sex, the c-index of the model demonstrated an absolute 3.7% improvement (95% CI 1.0-6.5) in the combined cohort. Additionally, our models stratified patients within individual cancer stages, particularly stage II (p=0.025) and stage III (p<0.001). By developing and evaluating prognostic models across multiple cancer types, this work represents one of the most comprehensive studies exploring the direct prediction of clinical outcomes using deep learning and histopathology images. Our analysis demonstrates the potential for this approach to provide prognostic information in multiple cancer types, and even within specific pathologic stages. However, given the relatively small number of clinical events, we observed wide confidence intervals, suggesting that future work will benefit from larger datasets.
Similar Image Search for Histopathology: SMILY
Feb 06, 2019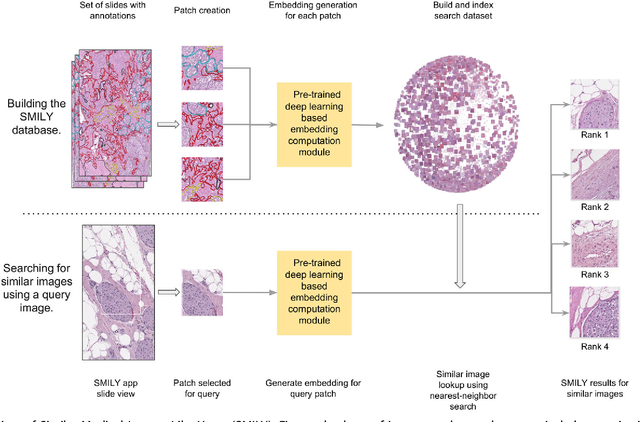
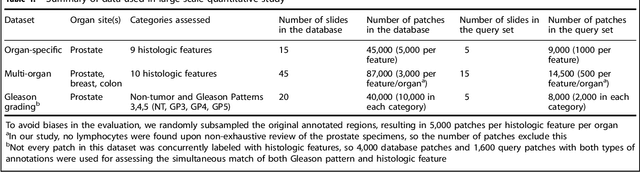
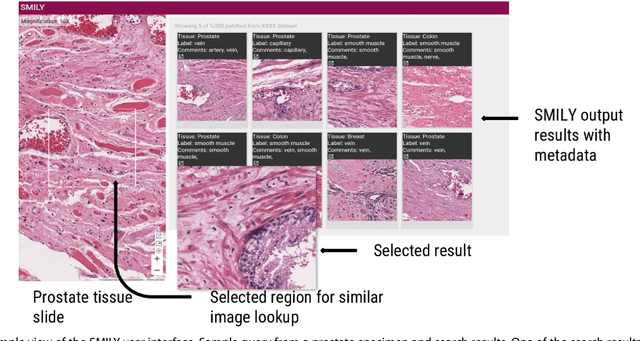
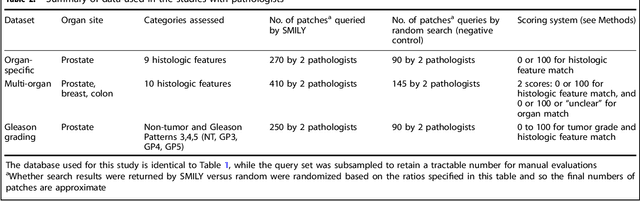
Abstract:The increasing availability of large institutional and public histopathology image datasets is enabling the searching of these datasets for diagnosis, research, and education. Though these datasets typically have associated metadata such as diagnosis or clinical notes, even carefully curated datasets rarely contain annotations of the location of regions of interest on each image. Because pathology images are extremely large (up to 100,000 pixels in each dimension), further laborious visual search of each image may be needed to find the feature of interest. In this paper, we introduce a deep learning based reverse image search tool for histopathology images: Similar Medical Images Like Yours (SMILY). We assessed SMILY's ability to retrieve search results in two ways: using pathologist-provided annotations, and via prospective studies where pathologists evaluated the quality of SMILY search results. As a negative control in the second evaluation, pathologists were blinded to whether search results were retrieved by SMILY or randomly. In both types of assessments, SMILY was able to retrieve search results with similar histologic features, organ site, and prostate cancer Gleason grade compared with the original query. SMILY may be a useful general-purpose tool in the pathologist's arsenal, to improve the efficiency of searching large archives of histopathology images, without the need to develop and implement specific tools for each application.
Whole-Slide Image Focus Quality: Automatic Assessment and Impact on AI Cancer Detection
Jan 15, 2019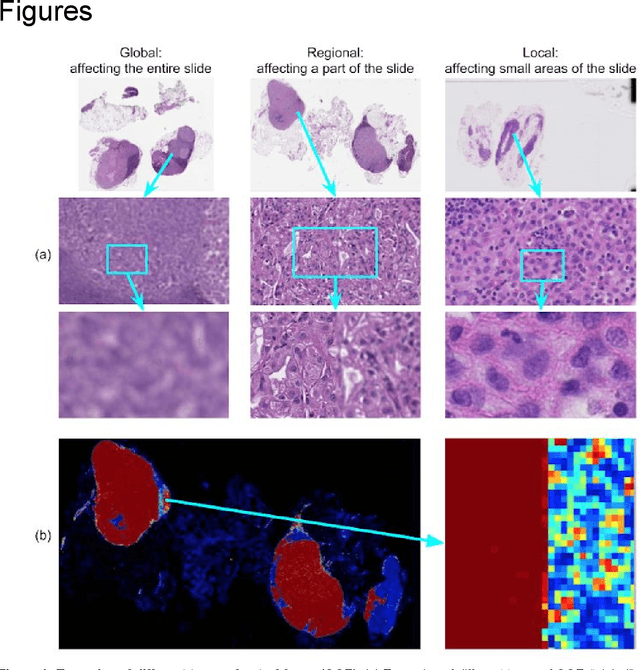
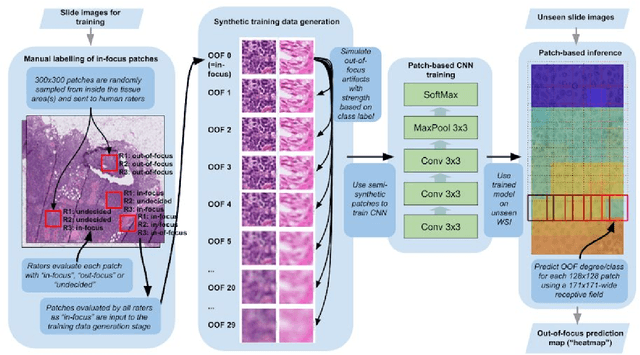

Abstract:Digital pathology enables remote access or consults and powerful image analysis algorithms. However, the slide digitization process can create artifacts such as out-of-focus (OOF). OOF is often only detected upon careful review, potentially causing rescanning and workflow delays. Although scan-time operator screening for whole-slide OOF is feasible, manual screening for OOF affecting only parts of a slide is impractical. We developed a convolutional neural network (ConvFocus) to exhaustively localize and quantify the severity of OOF regions on digitized slides. ConvFocus was developed using our refined semi-synthetic OOF data generation process, and evaluated using real whole-slide images spanning 3 different tissue types and 3 different stain types that were digitized by two different scanners. ConvFocus's predictions were compared with pathologist-annotated focus quality grades across 514 distinct regions representing 37,700 35x35{\mu}m image patches, and 21 digitized "z-stack" whole-slide images that contain known OOF patterns. When compared to pathologist-graded focus quality, ConvFocus achieved Spearman rank coefficients of 0.81 and 0.94 on two scanners, and reproduced the expected OOF patterns from z-stack scanning. We also evaluated the impact of OOF on the accuracy of a state-of-the-art metastatic breast cancer detector and saw a consistent decrease in performance with increasing OOF. Comprehensive whole-slide OOF categorization could enable rescans prior to pathologist review, potentially reducing the impact of digitization focus issues on the clinical workflow. We show that the algorithm trained on our semi-synthetic OOF data generalizes well to real OOF regions across tissue types, stains, and scanners. Finally, quantitative OOF maps can flag regions that might otherwise be misclassified by image analysis algorithms, preventing OOF-induced errors.
Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Improving Gleason Scoring of Prostate Cancer
Nov 15, 2018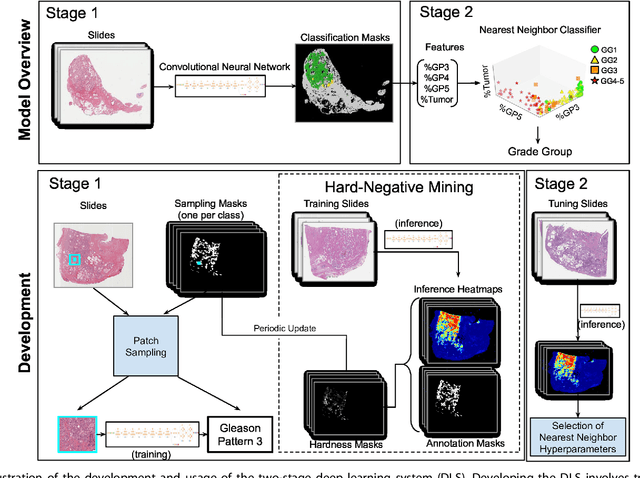
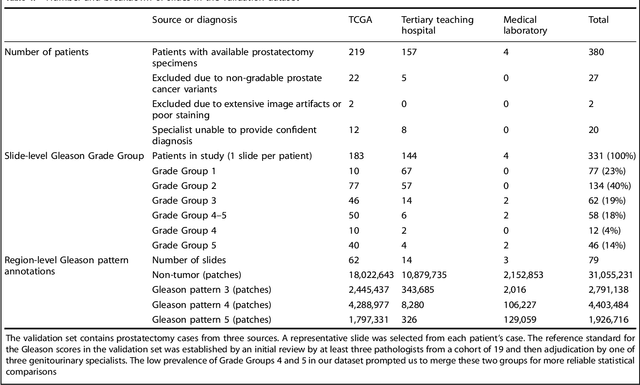
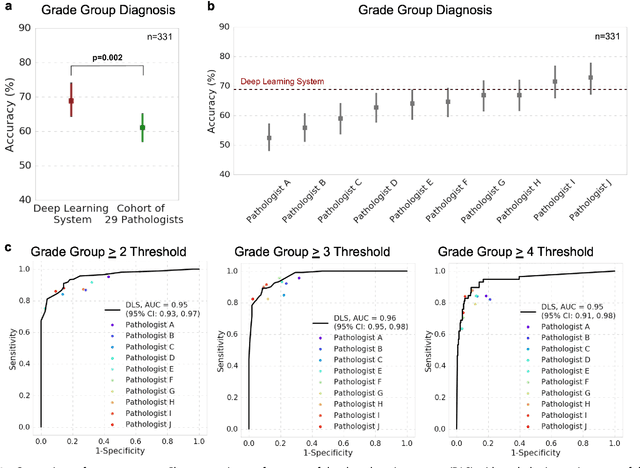
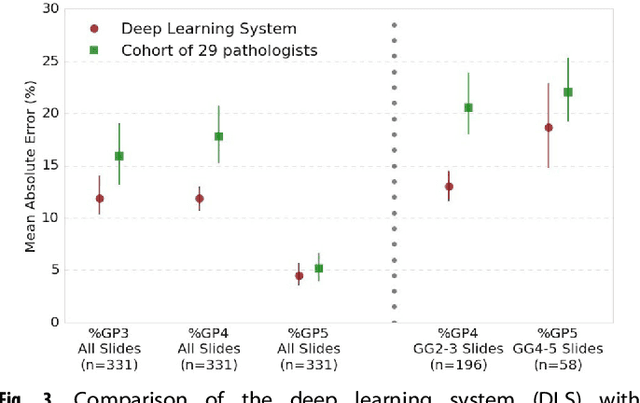
Abstract:For prostate cancer patients, the Gleason score is one of the most important prognostic factors, potentially determining treatment independent of the stage. However, Gleason scoring is based on subjective microscopic examination of tumor morphology and suffers from poor reproducibility. Here we present a deep learning system (DLS) for Gleason scoring whole-slide images of prostatectomies. Our system was developed using 112 million pathologist-annotated image patches from 1,226 slides, and evaluated on an independent validation dataset of 331 slides, where the reference standard was established by genitourinary specialist pathologists. On the validation dataset, the mean accuracy among 29 general pathologists was 0.61. The DLS achieved a significantly higher diagnostic accuracy of 0.70 (p=0.002) and trended towards better patient risk stratification in correlations to clinical follow-up data. Our approach could improve the accuracy of Gleason scoring and subsequent therapy decisions, particularly where specialist expertise is unavailable. The DLS also goes beyond the current Gleason system to more finely characterize and quantitate tumor morphology, providing opportunities for refinement of the Gleason system itself.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge