Neil Zeghidour
PSL, FAIR, LSCP
Streaming Sequence-to-Sequence Learning with Delayed Streams Modeling
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce Delayed Streams Modeling (DSM), a flexible formulation for streaming, multimodal sequence-to-sequence learning. Sequence-to-sequence generation is often cast in an offline manner, where the model consumes the complete input sequence before generating the first output timestep. Alternatively, streaming sequence-to-sequence rely on learning a policy for choosing when to advance on the input stream, or write to the output stream. DSM instead models already time-aligned streams with a decoder-only language model. By moving the alignment to a pre-processing step,and introducing appropriate delays between streams, DSM provides streaming inference of arbitrary output sequences, from any input combination, making it applicable to many sequence-to-sequence problems. In particular, given text and audio streams, automatic speech recognition (ASR) corresponds to the text stream being delayed, while the opposite gives a text-to-speech (TTS) model. We perform extensive experiments for these two major sequence-to-sequence tasks, showing that DSM provides state-of-the-art performance and latency while supporting arbitrary long sequences, being even competitive with offline baselines. Code, samples and demos are available at https://github.com/kyutai-labs/delayed-streams-modeling
Continuous Audio Language Models
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Audio Language Models (ALM) have emerged as the dominant paradigm for speech and music generation by representing audio as sequences of discrete tokens. Yet, unlike text tokens, which are invertible, audio tokens are extracted from lossy codecs with a limited bitrate. As a consequence, increasing audio quality requires generating more tokens, which imposes a trade-off between fidelity and computational cost. We address this issue by studying Continuous Audio Language Models (CALM). These models instantiate a large Transformer backbone that produces a contextual embedding at every timestep. This sequential information then conditions an MLP that generates the next continuous frame of an audio VAE through consistency modeling. By avoiding lossy compression, CALM achieves higher quality at lower computational cost than their discrete counterpart. Experiments on speech and music demonstrate improved efficiency and fidelity over state-of-the-art discrete audio language models, facilitating lightweight, high-quality audio generation. Samples are available at hf.co/spaces/kyutai/calm-samples
Aligning Spoken Dialogue Models from User Interactions
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel preference alignment framework for improving spoken dialogue models on real-time conversations from user interactions. Current preference learning methods primarily focus on text-based language models, and are not directly suited to the complexities of real-time speech interactions, with richer dynamics (e.g. interruption, interjection) and no explicit segmentation between speaker turns.We create a large-scale dataset of more than 150,000 preference pairs from raw multi-turn speech conversations, annotated with AI feedback, to cover preferences over both linguistic content and temporal context variations. We leverage offline alignment methods to finetune a full-duplex autoregressive speech-to-speech model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that feedback on generic conversations can be consistently effective in improving spoken dialogue models to produce more factual, safer and more contextually aligned interactions. We deploy the finetuned model and conduct holistic human evaluations to assess the impact beyond single-turn conversations. Our findings shed light on the importance of a well-calibrated balance among various dynamics, crucial for natural real-time speech dialogue systems.
CaReAQA: A Cardiac and Respiratory Audio Question Answering Model for Open-Ended Diagnostic Reasoning
May 02, 2025Abstract:Medical audio signals, such as heart and lung sounds, play a crucial role in clinical diagnosis. However, analyzing these signals remains challenging: traditional methods rely on handcrafted features or supervised deep learning models that demand extensive labeled datasets, limiting their scalability and applicability. To address these issues, we propose CaReAQA, an audio-language model that integrates a foundation audio model with the reasoning capabilities of large language models, enabling clinically relevant, open-ended diagnostic responses. Alongside CaReAQA, we introduce CaReSound, a benchmark dataset of annotated medical audio recordings enriched with metadata and paired question-answer examples, intended to drive progress in diagnostic reasoning research. Evaluation results show that CaReAQA achieves 86.2% accuracy on open-ended diagnostic reasoning tasks, outperforming baseline models. It also generalizes well to closed-ended classification tasks, achieving an average accuracy of 56.9% on unseen datasets. Our findings show how audio-language integration and reasoning advances medical diagnostics, enabling efficient AI systems for clinical decision support.
Vision-Speech Models: Teaching Speech Models to Converse about Images
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:The recent successes of Vision-Language models raise the question of how to equivalently imbue a pretrained speech model with vision understanding, an important milestone towards building a multimodal speech model able to freely converse about images. Building such a conversational Vision-Speech model brings its unique challenges: (i) paired image-speech datasets are much scarcer than their image-text counterparts, (ii) ensuring real-time latency at inference is crucial thus bringing compute and memory constraints, and (iii) the model should preserve prosodic features (e.g., speaker tone) which cannot be inferred from text alone. In this work, we introduce MoshiVis, augmenting a recent dialogue speech LLM, Moshi, with visual inputs through lightweight adaptation modules. An additional dynamic gating mechanism enables the model to more easily switch between the visual inputs and unrelated conversation topics. To reduce training costs, we design a simple one-stage, parameter-efficient fine-tuning pipeline in which we leverage a mixture of image-text (i.e., "speechless") and image-speech samples. We evaluate the model on downstream visual understanding tasks with both audio and text prompts, and report qualitative samples of interactions with MoshiVis. Our inference code will be made available, as well as the image-speech data used for audio evaluation.
High-Fidelity Simultaneous Speech-To-Speech Translation
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Hibiki, a decoder-only model for simultaneous speech translation. Hibiki leverages a multistream language model to synchronously process source and target speech, and jointly produces text and audio tokens to perform speech-to-text and speech-to-speech translation. We furthermore address the fundamental challenge of simultaneous interpretation, which unlike its consecutive counterpart, where one waits for the end of the source utterance to start translating, adapts its flow to accumulate just enough context to produce a correct translation in real-time, chunk by chunk. To do so, we introduce a weakly-supervised method that leverages the perplexity of an off-the-shelf text translation system to identify optimal delays on a per-word basis and create aligned synthetic data. After supervised training, Hibiki performs adaptive, simultaneous speech translation with vanilla temperature sampling. On a French-English simultaneous speech translation task, Hibiki demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in translation quality, speaker fidelity and naturalness. Moreover, the simplicity of its inference process makes it compatible with batched translation and even real-time on-device deployment. We provide examples as well as models and inference code.
MAD Speech: Measures of Acoustic Diversity of Speech
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Generative spoken language models produce speech in a wide range of voices, prosody, and recording conditions, seemingly approaching the diversity of natural speech. However, the extent to which generated speech is acoustically diverse remains unclear due to a lack of appropriate metrics. We address this gap by developing lightweight metrics of acoustic diversity, which we collectively refer to as MAD Speech. We focus on measuring five facets of acoustic diversity: voice, gender, emotion, accent, and background noise. We construct the metrics as a composition of specialized, per-facet embedding models and an aggregation function that measures diversity within the embedding space. Next, we build a series of datasets with a priori known diversity preferences for each facet. Using these datasets, we demonstrate that our proposed metrics achieve a stronger agreement with the ground-truth diversity than baselines. Finally, we showcase the applicability of our proposed metrics across several real-life evaluation scenarios. MAD Speech will be made publicly accessible.
MusicRL: Aligning Music Generation to Human Preferences
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:We propose MusicRL, the first music generation system finetuned from human feedback. Appreciation of text-to-music models is particularly subjective since the concept of musicality as well as the specific intention behind a caption are user-dependent (e.g. a caption such as "upbeat work-out music" can map to a retro guitar solo or a techno pop beat). Not only this makes supervised training of such models challenging, but it also calls for integrating continuous human feedback in their post-deployment finetuning. MusicRL is a pretrained autoregressive MusicLM (Agostinelli et al., 2023) model of discrete audio tokens finetuned with reinforcement learning to maximise sequence-level rewards. We design reward functions related specifically to text-adherence and audio quality with the help from selected raters, and use those to finetune MusicLM into MusicRL-R. We deploy MusicLM to users and collect a substantial dataset comprising 300,000 pairwise preferences. Using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), we train MusicRL-U, the first text-to-music model that incorporates human feedback at scale. Human evaluations show that both MusicRL-R and MusicRL-U are preferred to the baseline. Ultimately, MusicRL-RU combines the two approaches and results in the best model according to human raters. Ablation studies shed light on the musical attributes influencing human preferences, indicating that text adherence and quality only account for a part of it. This underscores the prevalence of subjectivity in musical appreciation and calls for further involvement of human listeners in the finetuning of music generation models.
TokenSplit: Using Discrete Speech Representations for Direct, Refined, and Transcript-Conditioned Speech Separation and Recognition
Aug 21, 2023


Abstract:We present TokenSplit, a speech separation model that acts on discrete token sequences. The model is trained on multiple tasks simultaneously: separate and transcribe each speech source, and generate speech from text. The model operates on transcripts and audio token sequences and achieves multiple tasks through masking of inputs. The model is a sequence-to-sequence encoder-decoder model that uses the Transformer architecture. We also present a "refinement" version of the model that predicts enhanced audio tokens from the audio tokens of speech separated by a conventional separation model. Using both objective metrics and subjective MUSHRA listening tests, we show that our model achieves excellent performance in terms of separation, both with or without transcript conditioning. We also measure the automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance and provide audio samples of speech synthesis to demonstrate the additional utility of our model.
AudioPaLM: A Large Language Model That Can Speak and Listen
Jun 22, 2023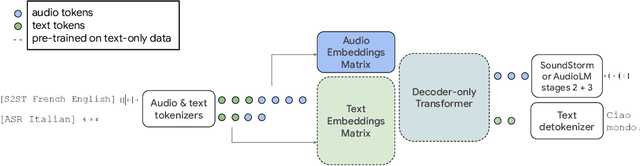



Abstract:We introduce AudioPaLM, a large language model for speech understanding and generation. AudioPaLM fuses text-based and speech-based language models, PaLM-2 [Anil et al., 2023] and AudioLM [Borsos et al., 2022], into a unified multimodal architecture that can process and generate text and speech with applications including speech recognition and speech-to-speech translation. AudioPaLM inherits the capability to preserve paralinguistic information such as speaker identity and intonation from AudioLM and the linguistic knowledge present only in text large language models such as PaLM-2. We demonstrate that initializing AudioPaLM with the weights of a text-only large language model improves speech processing, successfully leveraging the larger quantity of text training data used in pretraining to assist with the speech tasks. The resulting model significantly outperforms existing systems for speech translation tasks and has the ability to perform zero-shot speech-to-text translation for many languages for which input/target language combinations were not seen in training. AudioPaLM also demonstrates features of audio language models, such as transferring a voice across languages based on a short spoken prompt. We release examples of our method at https://google-research.github.io/seanet/audiopalm/examples
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge