Michael P. Brenner
Accelerating Scientific Research with Gemini: Case Studies and Common Techniques
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues for accelerating scientific research. While models are increasingly capable of assisting with routine tasks, their ability to contribute to novel, expert-level mathematical discovery is less understood. We present a collection of case studies demonstrating how researchers have successfully collaborated with advanced AI models, specifically Google's Gemini-based models (in particular Gemini Deep Think and its advanced variants), to solve open problems, refute conjectures, and generate new proofs across diverse areas in theoretical computer science, as well as other areas such as economics, optimization, and physics. Based on these experiences, we extract common techniques for effective human-AI collaboration in theoretical research, such as iterative refinement, problem decomposition, and cross-disciplinary knowledge transfer. While the majority of our results stem from this interactive, conversational methodology, we also highlight specific instances that push beyond standard chat interfaces. These include deploying the model as a rigorous adversarial reviewer to detect subtle flaws in existing proofs, and embedding it within a "neuro-symbolic" loop that autonomously writes and executes code to verify complex derivations. Together, these examples highlight the potential of AI not just as a tool for automation, but as a versatile, genuine partner in the creative process of scientific discovery.
Generalizing PDE Emulation with Equation-Aware Neural Operators
Nov 12, 2025


Abstract:Solving partial differential equations (PDEs) can be prohibitively expensive using traditional numerical methods. Deep learning-based surrogate models typically specialize in a single PDE with fixed parameters. We present a framework for equation-aware emulation that generalizes to unseen PDEs, conditioning a neural model on a vector encoding representing the terms in a PDE and their coefficients. We present a baseline of four distinct modeling technqiues, trained on a family of 1D PDEs from the APEBench suite. Our approach achieves strong performance on parameter sets held out from the training distribution, with strong stability for rollout beyond the training window, and generalization to an entirely unseen PDE. This work was developed as part of a broader effort exploring AI systems that automate the creation of expert-level empirical software for scorable scientific tasks. The data and codebase are available at https://github.com/google-research/generalized-pde-emulator.
Expert Evaluation of LLM World Models: A High-$T_c$ Superconductivity Case Study
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) show great promise as a powerful tool for scientific literature exploration. However, their effectiveness in providing scientifically accurate and comprehensive answers to complex questions within specialized domains remains an active area of research. Using the field of high-temperature cuprates as an exemplar, we evaluate the ability of LLM systems to understand the literature at the level of an expert. We construct an expert-curated database of 1,726 scientific papers that covers the history of the field, and a set of 67 expert-formulated questions that probe deep understanding of the literature. We then evaluate six different LLM-based systems for answering these questions, including both commercially available closed models and a custom retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system capable of retrieving images alongside text. Experts then evaluate the answers of these systems against a rubric that assesses balanced perspectives, factual comprehensiveness, succinctness, and evidentiary support. Among the six systems two using RAG on curated literature outperformed existing closed models across key metrics, particularly in providing comprehensive and well-supported answers. We discuss promising aspects of LLM performances as well as critical short-comings of all the models. The set of expert-formulated questions and the rubric will be valuable for assessing expert level performance of LLM based reasoning systems.
Meshless solutions of PDE inverse problems on irregular geometries
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Solving inverse and optimization problems over solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations (PDEs) on complex spatial domains is a long-standing challenge. Here we introduce a method that parameterizes the solution using spectral bases on arbitrary spatiotemporal domains, whereby the basis is defined on a hyperrectangle containing the true domain. We find the coefficients of the basis expansion by solving an optimization problem whereby both the equations, the boundary conditions and any optimization targets are enforced by a loss function, building on a key idea from Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs). Since the representation of the function natively has exponential convergence, so does the solution of the optimization problem, as long as it can be solved efficiently. We find empirically that the optimization protocols developed for machine learning find solutions with exponential convergence on a wide range of equations. The method naturally allows for the incorporation of data assimilation by including additional terms in the loss function, and for the efficient solution of optimization problems over the PDE solutions.
HARDMath2: A Benchmark for Applied Mathematics Built by Students as Part of a Graduate Class
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in mathematical problem-solving, but evaluation has largely focused on problems that have exact analytical solutions or involve formal proofs, often overlooking approximation-based problems ubiquitous in applied science and engineering. To fill this gap, we build on prior work and present HARDMath2, a dataset of 211 original problems covering the core topics in an introductory graduate applied math class, including boundary-layer analysis, WKB methods, asymptotic solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations, and the asymptotics of oscillatory integrals. This dataset was designed and verified by the students and instructors of a core graduate applied mathematics course at Harvard. We build the dataset through a novel collaborative environment that challenges students to write and refine difficult problems consistent with the class syllabus, peer-validate solutions, test different models, and automatically check LLM-generated solutions against their own answers and numerical ground truths. Evaluation results show that leading frontier models still struggle with many of the problems in the dataset, highlighting a gap in the mathematical reasoning skills of current LLMs. Importantly, students identified strategies to create increasingly difficult problems by interacting with the models and exploiting common failure modes. This back-and-forth with the models not only resulted in a richer and more challenging benchmark but also led to qualitative improvements in the students' understanding of the course material, which is increasingly important as we enter an age where state-of-the-art language models can solve many challenging problems across a wide domain of fields.
FEABench: Evaluating Language Models on Multiphysics Reasoning Ability
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Building precise simulations of the real world and invoking numerical solvers to answer quantitative problems is an essential requirement in engineering and science. We present FEABench, a benchmark to evaluate the ability of large language models (LLMs) and LLM agents to simulate and solve physics, mathematics and engineering problems using finite element analysis (FEA). We introduce a comprehensive evaluation scheme to investigate the ability of LLMs to solve these problems end-to-end by reasoning over natural language problem descriptions and operating COMSOL Multiphysics$^\circledR$, an FEA software, to compute the answers. We additionally design a language model agent equipped with the ability to interact with the software through its Application Programming Interface (API), examine its outputs and use tools to improve its solutions over multiple iterations. Our best performing strategy generates executable API calls 88% of the time. LLMs that can successfully interact with and operate FEA software to solve problems such as those in our benchmark would push the frontiers of automation in engineering. Acquiring this capability would augment LLMs' reasoning skills with the precision of numerical solvers and advance the development of autonomous systems that can tackle complex problems in the real world. The code is available at https://github.com/google/feabench
Mathematical Modeling of Option Pricing with an Extended Black-Scholes Framework
Apr 04, 2025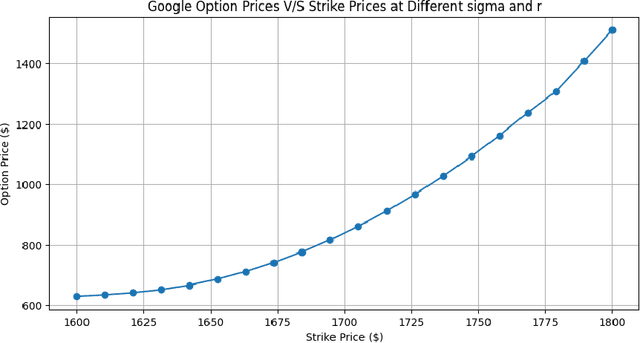
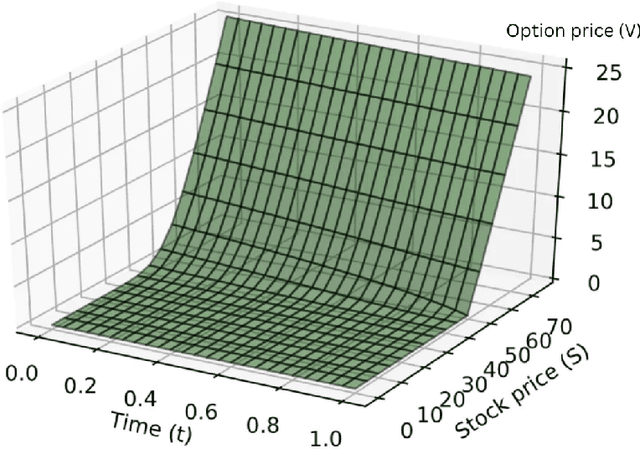
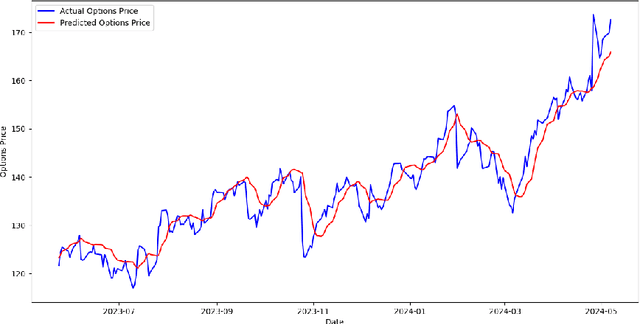
Abstract:This study investigates enhancing option pricing by extending the Black-Scholes model to include stochastic volatility and interest rate variability within the Partial Differential Equation (PDE). The PDE is solved using the finite difference method. The extended Black-Scholes model and a machine learning-based LSTM model are developed and evaluated for pricing Google stock options. Both models were backtested using historical market data. While the LSTM model exhibited higher predictive accuracy, the finite difference method demonstrated superior computational efficiency. This work provides insights into model performance under varying market conditions and emphasizes the potential of hybrid approaches for robust financial modeling.
Towards AI-assisted Academic Writing
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We present components of an AI-assisted academic writing system including citation recommendation and introduction writing. The system recommends citations by considering the user's current document context to provide relevant suggestions. It generates introductions in a structured fashion, situating the contributions of the research relative to prior work. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the components through quantitative evaluations. Finally, the paper presents qualitative research exploring how researchers incorporate citations into their writing workflows. Our findings indicate that there is demand for precise AI-assisted writing systems and simple, effective methods for meeting those needs.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
HARDMath: A Benchmark Dataset for Challenging Problems in Applied Mathematics
Oct 13, 2024



Abstract:Advanced applied mathematics problems are underrepresented in existing Large Language Model (LLM) benchmark datasets. To address this, we introduce HARDMath, a dataset inspired by a graduate course on asymptotic methods, featuring challenging applied mathematics problems that require analytical approximation techniques. These problems demand a combination of mathematical reasoning, computational tools, and subjective judgment, making them difficult for LLMs. Our framework auto-generates a large number of problems with solutions validated against numerical ground truths. We evaluate both open- and closed-source LLMs on HARDMath-mini, a sub-sampled test set of 366 problems, as well as on 40 word problems formulated in applied science contexts. Even leading closed-source models like GPT-4 achieve only 43.8% overall accuracy with few-shot Chain-of-Thought prompting, and all models demonstrate significantly lower performance compared to results on existing mathematics benchmark datasets. We additionally conduct a detailed error analysis to gain insights into the failure cases of LLMs. These results demonstrate limitations of current LLM performance on advanced graduate-level applied math problems and underscore the importance of datasets like HARDMath to advance mathematical abilities of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge