Nasser Zalmout
Hephaestus: Improving Fundamental Agent Capabilities of Large Language Models through Continual Pre-Training
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Due to the scarcity of agent-oriented pre-training data, LLM-based autonomous agents typically rely on complex prompting or extensive fine-tuning, which often fails to introduce new capabilities while preserving strong generalizability. We introduce Hephaestus-Forge, the first large-scale pre-training corpus designed to enhance the fundamental capabilities of LLM agents in API function calling, intrinsic reasoning and planning, and adapting to environmental feedback. Hephaestus-Forge comprises 103B agent-specific data encompassing 76,537 APIs, including both tool documentation to introduce knowledge of API functions and function calling trajectories to strengthen intrinsic reasoning. To explore effective training protocols, we investigate scaling laws to identify the optimal recipe in data mixing ratios. By continual pre-training on Hephaestus-Forge, Hephaestus outperforms small- to medium-scale open-source LLMs and rivals commercial LLMs on three agent benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of our pre-training corpus in enhancing fundamental agentic capabilities and generalization of LLMs to new tasks or environments.
PV2TEA: Patching Visual Modality to Textual-Established Information Extraction
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:Information extraction, e.g., attribute value extraction, has been extensively studied and formulated based only on text. However, many attributes can benefit from image-based extraction, like color, shape, pattern, among others. The visual modality has long been underutilized, mainly due to multimodal annotation difficulty. In this paper, we aim to patch the visual modality to the textual-established attribute information extractor. The cross-modality integration faces several unique challenges: (C1) images and textual descriptions are loosely paired intra-sample and inter-samples; (C2) images usually contain rich backgrounds that can mislead the prediction; (C3) weakly supervised labels from textual-established extractors are biased for multimodal training. We present PV2TEA, an encoder-decoder architecture equipped with three bias reduction schemes: (S1) Augmented label-smoothed contrast to improve the cross-modality alignment for loosely-paired image and text; (S2) Attention-pruning that adaptively distinguishes the visual foreground; (S3) Two-level neighborhood regularization that mitigates the label textual bias via reliability estimation. Empirical results on real-world e-Commerce datasets demonstrate up to 11.74% absolute (20.97% relatively) F1 increase over unimodal baselines.
End-to-End Conversational Search for Online Shopping with Utterance Transfer
Sep 12, 2021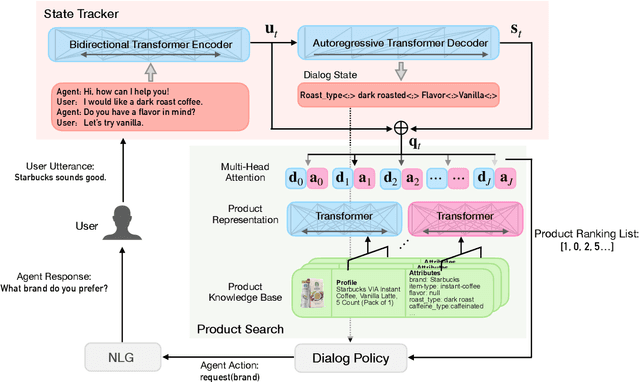
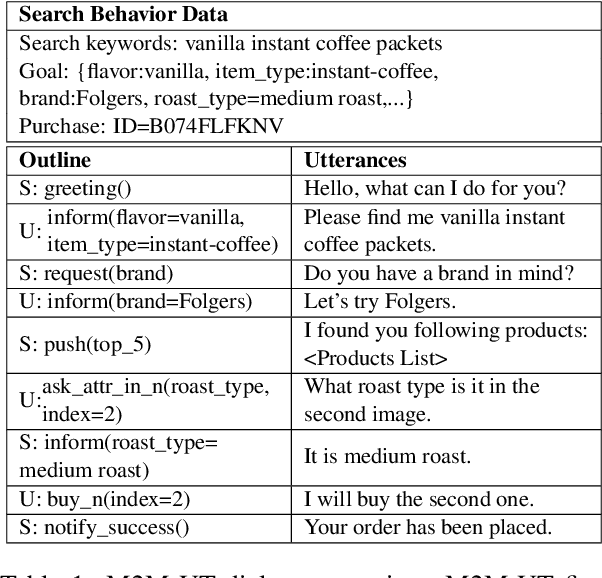
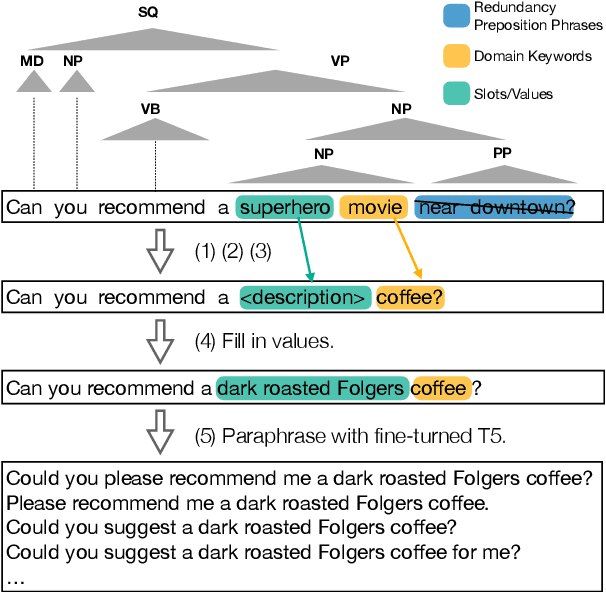

Abstract:Successful conversational search systems can present natural, adaptive and interactive shopping experience for online shopping customers. However, building such systems from scratch faces real word challenges from both imperfect product schema/knowledge and lack of training dialog data.In this work we first propose ConvSearch, an end-to-end conversational search system that deeply combines the dialog system with search. It leverages the text profile to retrieve products, which is more robust against imperfect product schema/knowledge compared with using product attributes alone. We then address the lack of data challenges by proposing an utterance transfer approach that generates dialogue utterances by using existing dialog from other domains, and leveraging the search behavior data from e-commerce retailer. With utterance transfer, we introduce a new conversational search dataset for online shopping. Experiments show that our utterance transfer method can significantly improve the availability of training dialogue data without crowd-sourcing, and the conversational search system significantly outperformed the best tested baseline.
PAM: Understanding Product Images in Cross Product Category Attribute Extraction
Jun 08, 2021



Abstract:Understanding product attributes plays an important role in improving online shopping experience for customers and serves as an integral part for constructing a product knowledge graph. Most existing methods focus on attribute extraction from text description or utilize visual information from product images such as shape and color. Compared to the inputs considered in prior works, a product image in fact contains more information, represented by a rich mixture of words and visual clues with a layout carefully designed to impress customers. This work proposes a more inclusive framework that fully utilizes these different modalities for attribute extraction. Inspired by recent works in visual question answering, we use a transformer based sequence to sequence model to fuse representations of product text, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) tokens and visual objects detected in the product image. The framework is further extended with the capability to extract attribute value across multiple product categories with a single model, by training the decoder to predict both product category and attribute value and conditioning its output on product category. The model provides a unified attribute extraction solution desirable at an e-commerce platform that offers numerous product categories with a diverse body of product attributes. We evaluated the model on two product attributes, one with many possible values and one with a small set of possible values, over 14 product categories and found the model could achieve 15% gain on the Recall and 10% gain on the F1 score compared to existing methods using text-only features.
AdaTag: Multi-Attribute Value Extraction from Product Profiles with Adaptive Decoding
Jun 04, 2021
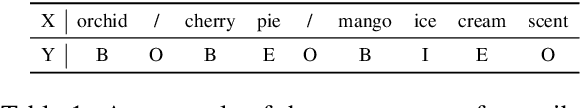
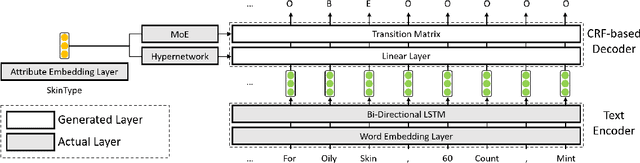
Abstract:Automatic extraction of product attribute values is an important enabling technology in e-Commerce platforms. This task is usually modeled using sequence labeling architectures, with several extensions to handle multi-attribute extraction. One line of previous work constructs attribute-specific models, through separate decoders or entirely separate models. However, this approach constrains knowledge sharing across different attributes. Other contributions use a single multi-attribute model, with different techniques to embed attribute information. But sharing the entire network parameters across all attributes can limit the model's capacity to capture attribute-specific characteristics. In this paper we present AdaTag, which uses adaptive decoding to handle extraction. We parameterize the decoder with pretrained attribute embeddings, through a hypernetwork and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) module. This allows for separate, but semantically correlated, decoders to be generated on the fly for different attributes. This approach facilitates knowledge sharing, while maintaining the specificity of each attribute. Our experiments on a real-world e-Commerce dataset show marked improvements over previous methods.
Adversarial Multitask Learning for Joint Multi-Feature and Multi-Dialect Morphological Modeling
Oct 28, 2019



Abstract:Morphological tagging is challenging for morphologically rich languages due to the large target space and the need for more training data to minimize model sparsity. Dialectal variants of morphologically rich languages suffer more as they tend to be more noisy and have less resources. In this paper we explore the use of multitask learning and adversarial training to address morphological richness and dialectal variations in the context of full morphological tagging. We use multitask learning for joint morphological modeling for the features within two dialects, and as a knowledge-transfer scheme for cross-dialectal modeling. We use adversarial training to learn dialect invariant features that can help the knowledge-transfer scheme from the high to low-resource variants. We work with two dialectal variants: Modern Standard Arabic (high-resource "dialect") and Egyptian Arabic (low-resource dialect) as a case study. Our models achieve state-of-the-art results for both. Furthermore, adversarial training provides more significant improvement when using smaller training datasets in particular.
Joint Diacritization, Lemmatization, Normalization, and Fine-Grained Morphological Tagging
Oct 05, 2019



Abstract:Semitic languages can be highly ambiguous, having several interpretations of the same surface forms, and morphologically rich, having many morphemes that realize several morphological features. This is further exacerbated for dialectal content, which is more prone to noise and lacks a standard orthography. The morphological features can be lexicalized, like lemmas and diacritized forms, or non-lexicalized, like gender, number, and part-of-speech tags, among others. Joint modeling of the lexicalized and non-lexicalized features can identify more intricate morphological patterns, which provide better context modeling, and further disambiguate ambiguous lexical choices. However, the different modeling granularity can make joint modeling more difficult. Our approach models the different features jointly, whether lexicalized (on the character-level), where we also model surface form normalization, or non-lexicalized (on the word-level). We use Arabic as a test case, and achieve state-of-the-art results for Modern Standard Arabic, with 20% relative error reduction, and Egyptian Arabic (a dialectal variant of Arabic), with 11% reduction.
Utilizing Character and Word Embeddings for Text Normalization with Sequence-to-Sequence Models
Sep 05, 2018



Abstract:Text normalization is an important enabling technology for several NLP tasks. Recently, neural-network-based approaches have outperformed well-established models in this task. However, in languages other than English, there has been little exploration in this direction. Both the scarcity of annotated data and the complexity of the language increase the difficulty of the problem. To address these challenges, we use a sequence-to-sequence model with character-based attention, which in addition to its self-learned character embeddings, uses word embeddings pre-trained with an approach that also models subword information. This provides the neural model with access to more linguistic information especially suitable for text normalization, without large parallel corpora. We show that providing the model with word-level features bridges the gap for the neural network approach to achieve a state-of-the-art F1 score on a standard Arabic language correction shared task dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge