Miyoung Ko
The Coverage Principle: A Framework for Understanding Compositional Generalization
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models excel at pattern matching, yet often fall short in systematic compositional generalization. We propose the coverage principle: a data-centric framework showing that models relying primarily on pattern matching for compositional tasks cannot reliably generalize beyond substituting fragments that yield identical results when used in the same contexts. We demonstrate that this framework has a strong predictive power for the generalization capabilities of Transformers. First, we derive and empirically confirm that the training data required for two-hop generalization grows at least quadratically with the token set size, and the training data efficiency does not improve with 20x parameter scaling. Second, for compositional tasks with path ambiguity where one variable affects the output through multiple computational paths, we show that Transformers learn context-dependent state representations that undermine both performance and interoperability. Third, Chain-of-Thought supervision improves training data efficiency for multi-hop tasks but still struggles with path ambiguity. Finally, we outline a \emph{mechanism-based} taxonomy that distinguishes three ways neural networks can generalize: structure-based (bounded by coverage), property-based (leveraging algebraic invariances), and shared-operator (through function reuse). This conceptual lens contextualizes our results and highlights where new architectural ideas are needed to achieve systematic compositionally. Overall, the coverage principle provides a unified lens for understanding compositional reasoning, and underscores the need for fundamental architectural or training innovations to achieve truly systematic compositionality.
Investigating How Large Language Models Leverage Internal Knowledge to Perform Complex Reasoning
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Despite significant advancements, there is a limited understanding of how large language models (LLMs) utilize knowledge for reasoning. To address this, we propose a method that deconstructs complex real-world questions into a graph, representing each question as a node with parent nodes of background knowledge needed to solve the question. We develop the DepthQA dataset, deconstructing questions into three depths: (i) recalling conceptual knowledge, (ii) applying procedural knowledge, and (iii) analyzing strategic knowledge. Based on a hierarchical graph, we quantify forward discrepancy, discrepancies in LLMs' performance on simpler sub-problems versus complex questions. We also measure backward discrepancy, where LLMs answer complex questions but struggle with simpler ones. Our analysis shows that smaller models have more discrepancies than larger models. Additionally, guiding models from simpler to complex questions through multi-turn interactions improves performance across model sizes, highlighting the importance of structured intermediate steps in knowledge reasoning. This work enhances our understanding of LLM reasoning and suggests ways to improve their problem-solving abilities.
The BiGGen Bench: A Principled Benchmark for Fine-grained Evaluation of Language Models with Language Models
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:As language models (LMs) become capable of handling a wide range of tasks, their evaluation is becoming as challenging as their development. Most generation benchmarks currently assess LMs using abstract evaluation criteria like helpfulness and harmlessness, which often lack the flexibility and granularity of human assessment. Additionally, these benchmarks tend to focus disproportionately on specific capabilities such as instruction following, leading to coverage bias. To overcome these limitations, we introduce the BiGGen Bench, a principled generation benchmark designed to thoroughly evaluate nine distinct capabilities of LMs across 77 diverse tasks. A key feature of the BiGGen Bench is its use of instance-specific evaluation criteria, closely mirroring the nuanced discernment of human evaluation. We apply this benchmark to assess 103 frontier LMs using five evaluator LMs. Our code, data, and evaluation results are all publicly available at https://github.com/prometheus-eval/prometheus-eval/tree/main/BiGGen-Bench.
KTRL+F: Knowledge-Augmented In-Document Search
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:We introduce a new problem KTRL+F, a knowledge-augmented in-document search task that necessitates real-time identification of all semantic targets within a document with the awareness of external sources through a single natural query. This task addresses following unique challenges for in-document search: 1) utilizing knowledge outside the document for extended use of additional information about targets to bridge the semantic gap between the query and the targets, and 2) balancing between real-time applicability with the performance. We analyze various baselines in KTRL+F and find there are limitations of existing models, such as hallucinations, low latency, or difficulties in leveraging external knowledge. Therefore we propose a Knowledge-Augmented Phrase Retrieval model that shows a promising balance between speed and performance by simply augmenting external knowledge embedding in phrase embedding. Additionally, we conduct a user study to verify whether solving KTRL+F can enhance search experience of users. It demonstrates that even with our simple model users can reduce the time for searching with less queries and reduced extra visits to other sources for collecting evidence. We encourage the research community to work on KTRL+F to enhance more efficient in-document information access.
Beyond Fact Verification: Comparing and Contrasting Claims on Contentious Topics
May 24, 2022



Abstract:As the importance of identifying misinformation is increasing, many researchers focus on verifying textual claims on the web. One of the most popular tasks to achieve this is fact verification, which retrieves an evidence sentence from a large knowledge source such as Wikipedia to either verify or refute each factual claim. However, while such problem formulation is helpful for detecting false claims and fake news, it is not applicable to catching subtle differences in factually consistent claims which still might implicitly bias the readers, especially in contentious topics such as political, gender, or racial issues. In this study, we propose ClaimDiff, a novel dataset to compare the nuance between claim pairs in both a discriminative and a generative manner, with the underlying assumption that one is not necessarily more true than the other. This differs from existing fact verification datasets that verify the target sentence with respect to an absolute truth. We hope this task assists people in making more informed decisions among various sources of media.
Answering Questions on COVID-19 in Real-Time
Jun 29, 2020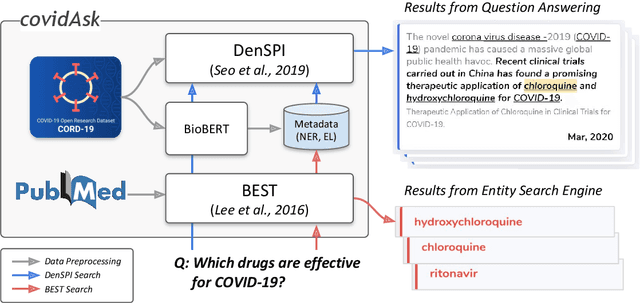
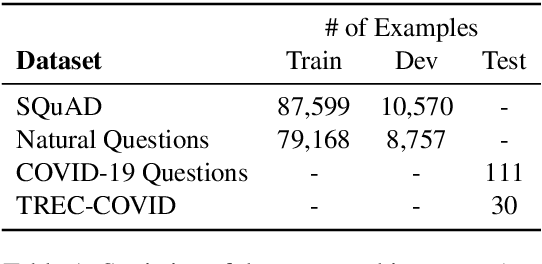
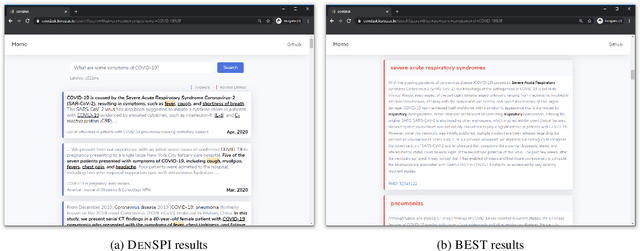

Abstract:The recent outbreak of the novel coronavirus is wreaking havoc on the world and researchers are struggling to effectively combat it. One reason why the fight is difficult is due to the lack of information and knowledge. In this work, we outline our effort to contribute to shrinking this knowledge vacuum by creating covidAsk, a question answering (QA) system that combines biomedical text mining and QA techniques to provide answers to questions in real-time. Our system leverages both supervised and unsupervised approaches to provide informative answers using DenSPI (Seo et al., 2019) and BEST (Lee et al., 2016). Evaluation of covidAsk is carried out by using a manually created dataset called COVID-19 Questions which is based on facts about COVID-19. We hope our system will be able to aid researchers in their search for knowledge and information not only for COVID-19 but for future pandemics as well.
Look at the First Sentence: Position Bias in Question Answering
Apr 30, 2020
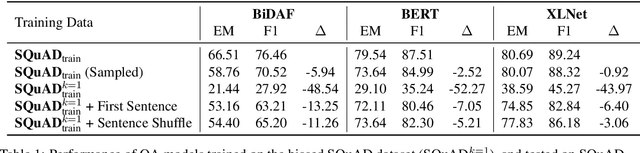
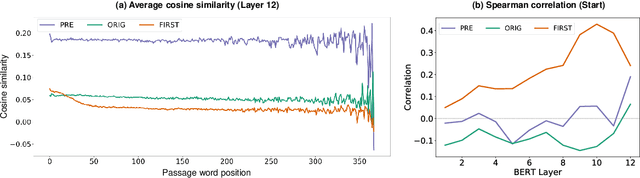
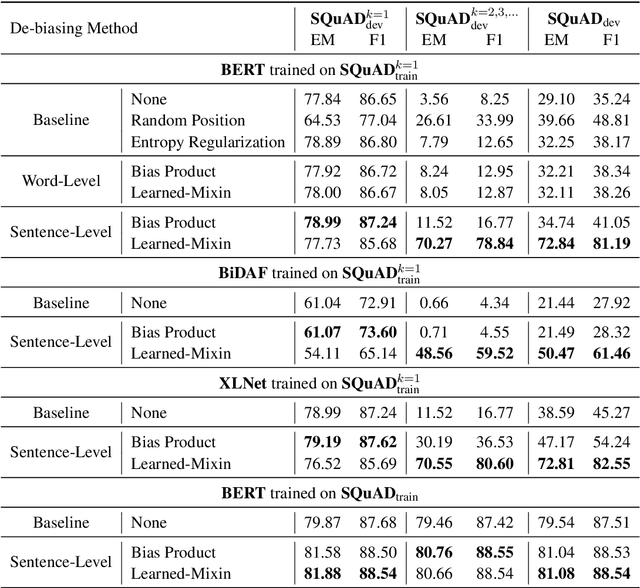
Abstract:Many extractive question answering models are trained to predict start and end positions of answers. The choice of predicting answers as positions is mainly due to its simplicity and effectiveness. In this study, we hypothesize that when the distribution of the answer positions is highly skewed in the training set (e.g., answers lie only in the k-th sentence of each passage), QA models predicting answers as positions learn spurious positional cues and fail to give answers in different positions. We first illustrate this position bias in popular extractive QA models such as BiDAF and BERT and thoroughly examine how position bias propagates through each layer of BERT. To safely deliver position information without position bias, we train models with various de-biasing methods including entropy regularization and bias ensembling. Among them, we found that using the prior distribution of answer positions as a bias model is very effective at reducing position bias recovering the performance of BERT from 35.24% to 81.17% when trained on a biased SQuAD dataset.
SAIN: Self-Attentive Integration Network for Recommendation
May 27, 2019



Abstract:With the growing importance of personalized recommendation, numerous recommendation models have been proposed recently. Among them, Matrix Factorization (MF) based models are the most widely used in the recommendation field due to their high performance. However, MF based models suffer from cold start problems where user-item interactions are sparse. To deal with this problem, content based recommendation models which use the auxiliary attributes of users and items have been proposed. Since these models use auxiliary attributes, they are effective in cold start settings. However, most of the proposed models are either unable to capture complex feature interactions or not properly designed to combine user-item feedback information with content information. In this paper, we propose Self-Attentive Integration Network (SAIN) which is a model that effectively combines user-item feedback information and auxiliary information for recommendation task. In SAIN, a self-attention mechanism is used in the feature-level interaction layer to effectively consider interactions between multiple features, while the information integration layer adaptively combines content and feedback information. The experimental results on two public datasets show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art models by 2.13%
Ranking Paragraphs for Improving Answer Recall in Open-Domain Question Answering
Oct 01, 2018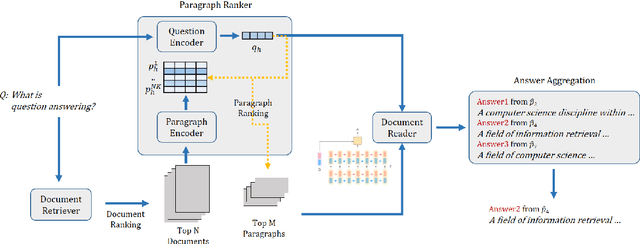
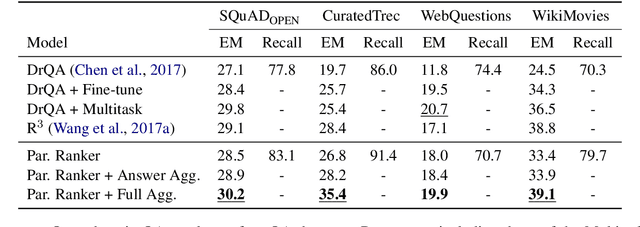
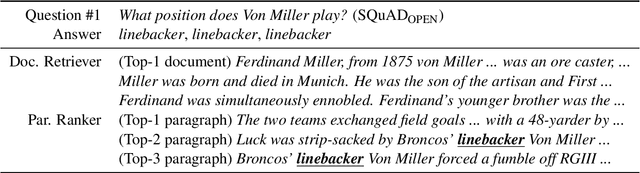
Abstract:Recently, open-domain question answering (QA) has been combined with machine comprehension models to find answers in a large knowledge source. As open-domain QA requires retrieving relevant documents from text corpora to answer questions, its performance largely depends on the performance of document retrievers. However, since traditional information retrieval systems are not effective in obtaining documents with a high probability of containing answers, they lower the performance of QA systems. Simply extracting more documents increases the number of irrelevant documents, which also degrades the performance of QA systems. In this paper, we introduce Paragraph Ranker which ranks paragraphs of retrieved documents for a higher answer recall with less noise. We show that ranking paragraphs and aggregating answers using Paragraph Ranker improves performance of open-domain QA pipeline on the four open-domain QA datasets by 7.8% on average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge