Hoyeon Chang
Dynamics Reveals Structure: Challenging the Linear Propagation Assumption
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Neural networks adapt through first-order parameter updates, yet it remains unclear whether such updates preserve logical coherence. We investigate the geometric limits of the Linear Propagation Assumption (LPA), the premise that local updates coherently propagate to logical consequences. To formalize this, we adopt relation algebra and study three core operations on relations: negation flips truth values, converse swaps argument order, and composition chains relations. For negation and converse, we prove that guaranteeing direction-agnostic first-order propagation necessitates a tensor factorization separating entity-pair context from relation content. However, for composition, we identify a fundamental obstruction. We show that composition reduces to conjunction, and prove that any conjunction well-defined on linear features must be bilinear. Since bilinearity is incompatible with negation, this forces the feature map to collapse. These results suggest that failures in knowledge editing, the reversal curse, and multi-hop reasoning may stem from common structural limitations inherent to the LPA.
Dynamic VLM-Guided Negative Prompting for Diffusion Models
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel approach for dynamic negative prompting in diffusion models that leverages Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to adaptively generate negative prompts during the denoising process. Unlike traditional Negative Prompting methods that use fixed negative prompts, our method generates intermediate image predictions at specific denoising steps and queries a VLM to produce contextually appropriate negative prompts. We evaluate our approach on various benchmark datasets and demonstrate the trade-offs between negative guidance strength and text-image alignment.
Let's Predict Sentence by Sentence
May 28, 2025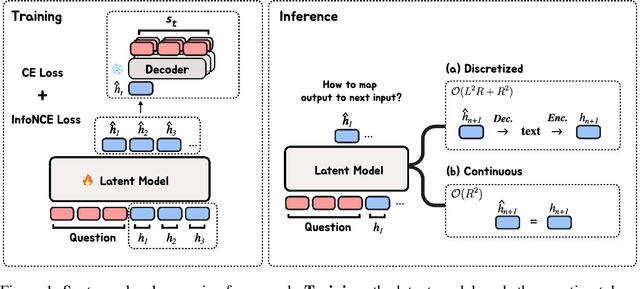
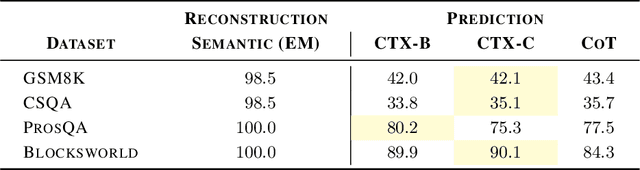
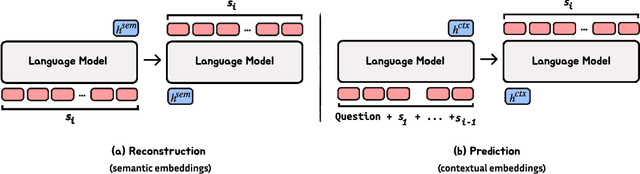
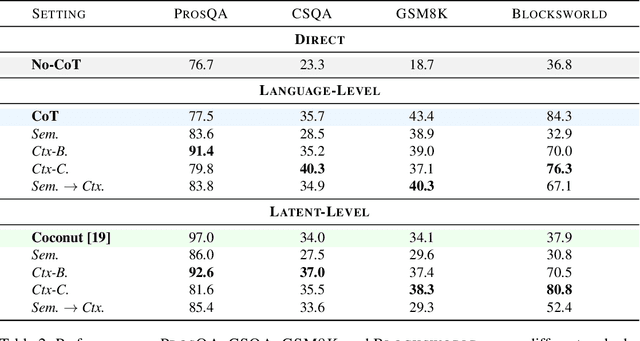
Abstract:Autoregressive language models (LMs) generate one token at a time, yet human reasoning operates over higher-level abstractions - sentences, propositions, and concepts. This contrast raises a central question- Can LMs likewise learn to reason over structured semantic units rather than raw token sequences? In this work, we investigate whether pretrained LMs can be lifted into such abstract reasoning spaces by building on their learned representations. We present a framework that adapts a pretrained token-level LM to operate in sentence space by autoregressively predicting continuous embeddings of next sentences. We explore two embedding paradigms inspired by classical representation learning: 1) semantic embeddings, learned via autoencoding to preserve surface meaning; and 2) contextual embeddings, trained via next-sentence prediction to encode anticipatory structure. We evaluate both under two inference regimes: Discretized, which decodes each predicted embedding into text before re-encoding; and Continuous, which reasons entirely in embedding space for improved efficiency. Across four domains - mathematics, logic, commonsense, and planning - contextual embeddings under continuous inference show competitive performance with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) while reducing inference-time FLOPs on average by half. We also present early signs of scalability and modular adaptation. Finally, to visualize latent trajectories, we introduce SentenceLens, a diagnostic tool that decodes intermediate model states into interpretable sentences. Together, our results indicate that pretrained LMs can effectively transition to abstract, structured reasoning within latent embedding spaces.
The Coverage Principle: A Framework for Understanding Compositional Generalization
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models excel at pattern matching, yet often fall short in systematic compositional generalization. We propose the coverage principle: a data-centric framework showing that models relying primarily on pattern matching for compositional tasks cannot reliably generalize beyond substituting fragments that yield identical results when used in the same contexts. We demonstrate that this framework has a strong predictive power for the generalization capabilities of Transformers. First, we derive and empirically confirm that the training data required for two-hop generalization grows at least quadratically with the token set size, and the training data efficiency does not improve with 20x parameter scaling. Second, for compositional tasks with path ambiguity where one variable affects the output through multiple computational paths, we show that Transformers learn context-dependent state representations that undermine both performance and interoperability. Third, Chain-of-Thought supervision improves training data efficiency for multi-hop tasks but still struggles with path ambiguity. Finally, we outline a \emph{mechanism-based} taxonomy that distinguishes three ways neural networks can generalize: structure-based (bounded by coverage), property-based (leveraging algebraic invariances), and shared-operator (through function reuse). This conceptual lens contextualizes our results and highlights where new architectural ideas are needed to achieve systematic compositionally. Overall, the coverage principle provides a unified lens for understanding compositional reasoning, and underscores the need for fundamental architectural or training innovations to achieve truly systematic compositionality.
How Does Vision-Language Adaptation Impact the Safety of Vision Language Models?
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Vision-Language adaptation (VL adaptation) transforms Large Language Models (LLMs) into Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) for multimodal tasks, but this process often compromises the inherent safety capabilities embedded in the original LLMs. Despite potential harmfulness due to weakened safety measures, in-depth analysis on the effects of VL adaptation on safety remains under-explored. This study examines how VL adaptation influences safety and evaluates the impact of safety fine-tuning methods. Our analysis reveals that safety degradation occurs during VL adaptation, even when the training data is safe. While safety tuning techniques like supervised fine-tuning with safety datasets or reinforcement learning from human feedback mitigate some risks, they still lead to safety degradation and a reduction in helpfulness due to over-rejection issues. Further analysis of internal model weights suggests that VL adaptation may impact certain safety-related layers, potentially lowering overall safety levels. Additionally, our findings demonstrate that the objectives of VL adaptation and safety tuning are divergent, which often results in their simultaneous application being suboptimal. To address this, we suggest the weight merging approach as an optimal solution effectively reducing safety degradation while maintaining helpfulness. These insights help guide the development of more reliable and secure LVLMs for real-world applications.
How Do Large Language Models Acquire Factual Knowledge During Pretraining?
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Despite the recent observation that large language models (LLMs) can store substantial factual knowledge, there is a limited understanding of the mechanisms of how they acquire factual knowledge through pretraining. This work addresses this gap by studying how LLMs acquire factual knowledge during pretraining. The findings reveal several important insights into the dynamics of factual knowledge acquisition during pretraining. First, counterintuitively, we observe that pretraining on more data shows no significant improvement in the model's capability to acquire and maintain factual knowledge. Next, there is a power-law relationship between training steps and forgetting of memorization and generalization of factual knowledge, and LLMs trained with duplicated training data exhibit faster forgetting. Third, training LLMs with larger batch sizes can enhance the models' robustness to forgetting. Overall, our observations suggest that factual knowledge acquisition in LLM pretraining occurs by progressively increasing the probability of factual knowledge presented in the pretraining data at each step. However, this increase is diluted by subsequent forgetting. Based on this interpretation, we demonstrate that we can provide plausible explanations for recently observed behaviors of LLMs, such as the poor performance of LLMs on long-tail knowledge and the benefits of deduplicating the pretraining corpus.
Contextualized Generative Retrieval
Oct 07, 2022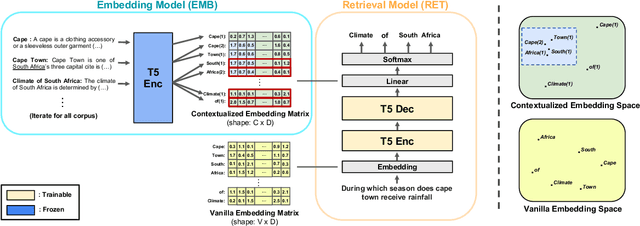
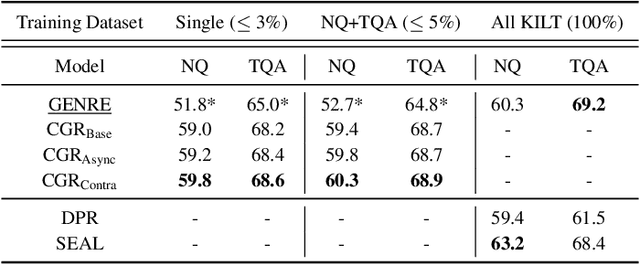
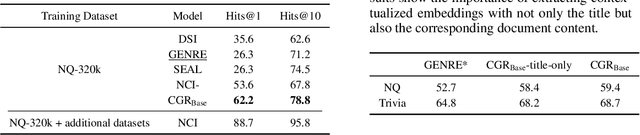

Abstract:The text retrieval task is mainly performed in two ways: the bi-encoder approach and the generative approach. The bi-encoder approach maps the document and query embeddings to common vector space and performs a nearest neighbor search. It stably shows high performance and efficiency across different domains but has an embedding space bottleneck as it interacts in L2 or inner product space. The generative retrieval model retrieves by generating a target sequence and overcomes the embedding space bottleneck by interacting in the parametric space. However, it fails to retrieve the information it has not seen during the training process as it depends solely on the information encoded in its own model parameters. To leverage the advantages of both approaches, we propose Contextualized Generative Retrieval model, which uses contextualized embeddings (output embeddings of a language model encoder) as vocab embeddings at the decoding step of generative retrieval. The model uses information encoded in both the non-parametric space of contextualized token embeddings and the parametric space of the generative retrieval model. Our approach of generative retrieval with contextualized vocab embeddings shows higher performance than generative retrieval with only vanilla vocab embeddings in the document retrieval task, an average of 6% higher performance in KILT (NQ, TQA) and 2X higher in NQ-320k, suggesting the benefits of using contextualized embedding in generative retrieval models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge