Youngkyung Seo
Mi:dm 2.0 Korea-centric Bilingual Language Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We introduce Mi:dm 2.0, a bilingual large language model (LLM) specifically engineered to advance Korea-centric AI. This model goes beyond Korean text processing by integrating the values, reasoning patterns, and commonsense knowledge inherent to Korean society, enabling nuanced understanding of cultural contexts, emotional subtleties, and real-world scenarios to generate reliable and culturally appropriate responses. To address limitations of existing LLMs, often caused by insufficient or low-quality Korean data and lack of cultural alignment, Mi:dm 2.0 emphasizes robust data quality through a comprehensive pipeline that includes proprietary data cleansing, high-quality synthetic data generation, strategic data mixing with curriculum learning, and a custom Korean-optimized tokenizer to improve efficiency and coverage. To realize this vision, we offer two complementary configurations: Mi:dm 2.0 Base (11.5B parameters), built with a depth-up scaling strategy for general-purpose use, and Mi:dm 2.0 Mini (2.3B parameters), optimized for resource-constrained environments and specialized tasks. Mi:dm 2.0 achieves state-of-the-art performance on Korean-specific benchmarks, with top-tier zero-shot results on KMMLU and strong internal evaluation results across language, humanities, and social science tasks. The Mi:dm 2.0 lineup is released under the MIT license to support extensive research and commercial use. By offering accessible and high-performance Korea-centric LLMs, KT aims to accelerate AI adoption across Korean industries, public services, and education, strengthen the Korean AI developer community, and lay the groundwork for the broader vision of K-intelligence. Our models are available at https://huggingface.co/K-intelligence. For technical inquiries, please contact midm-llm@kt.com.
Efficient and Accurate Memorable Conversation Model using DPO based on sLLM
Jul 09, 2024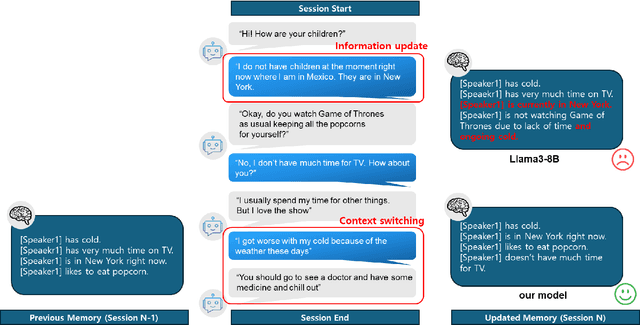

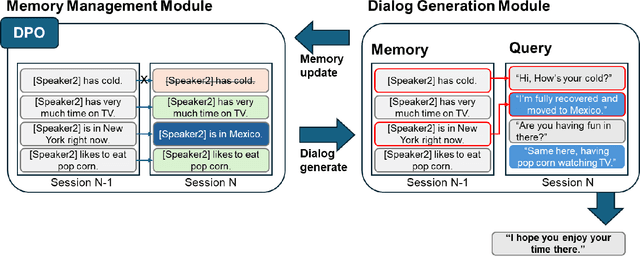
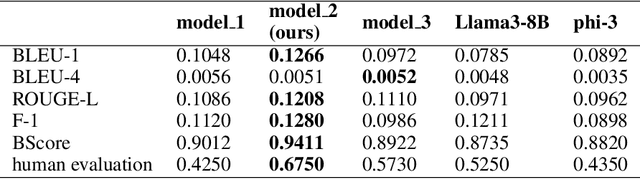
Abstract:In multi-session dialog system, it is essential to continuously update the memory as the session progresses. Simply accumulating memory can make it difficult to focus on the content of the conversation for inference due to the limited input sentence size. Therefore, efficient and accurate conversation model that is capable of managing memory to reflect the conversation history continuously is necessary. This paper presents a conversation model that efficiently manages memory as sessions progress and incorporates this into the model to reflect the conversation history accurately with 3 methodologies: SFT, DPO and DPO with SFT model. Our model using DPO algorithm shows an improvement about 0.0591 of BERTScore in memory accuracy, and the rate of responses reflecting the memory increased as well. Also, response generation performance enhanced about 4.292 in fluency, 3.935 in coherence, and 2.896 in consistency. This paper describes a training method that yields better performance than models with more than twice the parameter size, even when the model size is smaller. Thus, our model demonstrates efficiency not only in terms of accuracy but also in resource utilization.
How Do Large Language Models Acquire Factual Knowledge During Pretraining?
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Despite the recent observation that large language models (LLMs) can store substantial factual knowledge, there is a limited understanding of the mechanisms of how they acquire factual knowledge through pretraining. This work addresses this gap by studying how LLMs acquire factual knowledge during pretraining. The findings reveal several important insights into the dynamics of factual knowledge acquisition during pretraining. First, counterintuitively, we observe that pretraining on more data shows no significant improvement in the model's capability to acquire and maintain factual knowledge. Next, there is a power-law relationship between training steps and forgetting of memorization and generalization of factual knowledge, and LLMs trained with duplicated training data exhibit faster forgetting. Third, training LLMs with larger batch sizes can enhance the models' robustness to forgetting. Overall, our observations suggest that factual knowledge acquisition in LLM pretraining occurs by progressively increasing the probability of factual knowledge presented in the pretraining data at each step. However, this increase is diluted by subsequent forgetting. Based on this interpretation, we demonstrate that we can provide plausible explanations for recently observed behaviors of LLMs, such as the poor performance of LLMs on long-tail knowledge and the benefits of deduplicating the pretraining corpus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge