Min Zhao
Causal Forcing: Autoregressive Diffusion Distillation Done Right for High-Quality Real-Time Interactive Video Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:To achieve real-time interactive video generation, current methods distill pretrained bidirectional video diffusion models into few-step autoregressive (AR) models, facing an architectural gap when full attention is replaced by causal attention. However, existing approaches do not bridge this gap theoretically. They initialize the AR student via ODE distillation, which requires frame-level injectivity, where each noisy frame must map to a unique clean frame under the PF-ODE of an AR teacher. Distilling an AR student from a bidirectional teacher violates this condition, preventing recovery of the teacher's flow map and instead inducing a conditional-expectation solution, which degrades performance. To address this issue, we propose Causal Forcing that uses an AR teacher for ODE initialization, thereby bridging the architectural gap. Empirical results show that our method outperforms all baselines across all metrics, surpassing the SOTA Self Forcing by 19.3\% in Dynamic Degree, 8.7\% in VisionReward, and 16.7\% in Instruction Following. Project page and the code: \href{https://thu-ml.github.io/CausalForcing.github.io/}{https://thu-ml.github.io/CausalForcing.github.io/}
FlexWorld: Progressively Expanding 3D Scenes for Flexiable-View Synthesis
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Generating flexible-view 3D scenes, including 360{\deg} rotation and zooming, from single images is challenging due to a lack of 3D data. To this end, we introduce FlexWorld, a novel framework consisting of two key components: (1) a strong video-to-video (V2V) diffusion model to generate high-quality novel view images from incomplete input rendered from a coarse scene, and (2) a progressive expansion process to construct a complete 3D scene. In particular, leveraging an advanced pre-trained video model and accurate depth-estimated training pairs, our V2V model can generate novel views under large camera pose variations. Building upon it, FlexWorld progressively generates new 3D content and integrates it into the global scene through geometry-aware scene fusion. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of FlexWorld in generating high-quality novel view videos and flexible-view 3D scenes from single images, achieving superior visual quality under multiple popular metrics and datasets compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. Qualitatively, we highlight that FlexWorld can generate high-fidelity scenes with flexible views like 360{\deg} rotations and zooming. Project page: https://ml-gsai.github.io/FlexWorld.
FedDA-TSformer: Federated Domain Adaptation with Vision TimeSformer for Left Ventricle Segmentation on Gated Myocardial Perfusion SPECT Image
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Background and Purpose: Functional assessment of the left ventricle using gated myocardial perfusion (MPS) single-photon emission computed tomography relies on the precise extraction of the left ventricular contours while simultaneously ensuring the security of patient data. Methods: In this paper, we introduce the integration of Federated Domain Adaptation with TimeSformer, named 'FedDA-TSformer' for left ventricle segmentation using MPS. FedDA-TSformer captures spatial and temporal features in gated MPS images, leveraging spatial attention, temporal attention, and federated learning for improved domain adaptation while ensuring patient data security. In detail, we employed Divide-Space-Time-Attention mechanism to extract spatio-temporal correlations from the multi-centered MPS datasets, ensuring that predictions are spatio-temporally consistent. To achieve domain adaptation, we align the model output on MPS from three different centers using local maximum mean discrepancy (LMMD) loss. This approach effectively addresses the dual requirements of federated learning and domain adaptation, enhancing the model's performance during training with multi-site datasets while ensuring the protection of data from different hospitals. Results: Our FedDA-TSformer was trained and evaluated using MPS datasets collected from three hospitals, comprising a total of 150 subjects. Each subject's cardiac cycle was divided into eight gates. The model achieved Dice Similarity Coefficients (DSC) of 0.842 and 0.907 for left ventricular (LV) endocardium and epicardium segmentation, respectively. Conclusion: Our proposed FedDA-TSformer model addresses the challenge of multi-center generalization, ensures patient data privacy protection, and demonstrates effectiveness in left ventricular (LV) segmentation.
RIFLEx: A Free Lunch for Length Extrapolation in Video Diffusion Transformers
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in video generation have enabled models to synthesize high-quality, minute-long videos. However, generating even longer videos with temporal coherence remains a major challenge, and existing length extrapolation methods lead to temporal repetition or motion deceleration. In this work, we systematically analyze the role of frequency components in positional embeddings and identify an intrinsic frequency that primarily governs extrapolation behavior. Based on this insight, we propose RIFLEx, a minimal yet effective approach that reduces the intrinsic frequency to suppress repetition while preserving motion consistency, without requiring any additional modifications. RIFLEx offers a true free lunch--achieving high-quality $2\times$ extrapolation on state-of-the-art video diffusion transformers in a completely training-free manner. Moreover, it enhances quality and enables $3\times$ extrapolation by minimal fine-tuning without long videos. Project page and codes: \href{https://riflex-video.github.io/}{https://riflex-video.github.io/.}
Unrolling Plug-and-Play Network for Hyperspectral Unmixing
Sep 07, 2024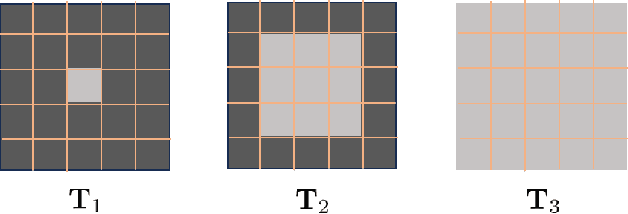
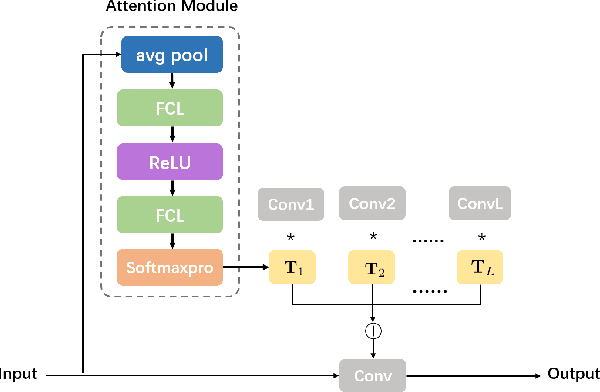
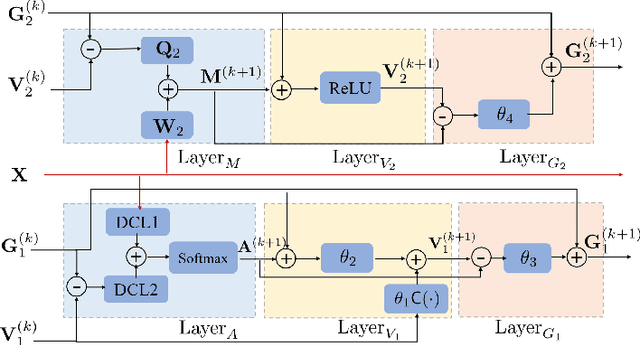
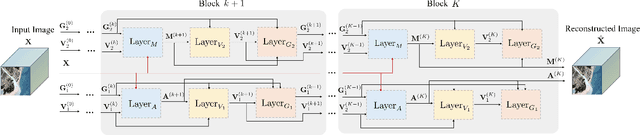
Abstract:Deep learning based unmixing methods have received great attention in recent years and achieve remarkable performance. These methods employ a data-driven approach to extract structure features from hyperspectral image, however, they tend to be less physical interpretable. Conventional unmixing methods are with much more interpretability, whereas they require manually designing regularization and choosing penalty parameters. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel unmixing method by unrolling the plug-and-play unmixing algorithm to conduct the deep architecture. Our method integrates both inner and outer priors. The carefully designed unfolding deep architecture is used to learn the spectral and spatial information from the hyperspectral image, which we refer to as inner priors. Additionally, our approach incorporates deep denoisers that have been pretrained on a large volume of image data to leverage the outer priors. Secondly, we design a dynamic convolution to model the multiscale information. Different scales are fused using an attention module. Experimental results of both synthetic and real datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms compared methods.
Identifying and Solving Conditional Image Leakage in Image-to-Video Diffusion Model
Jun 22, 2024
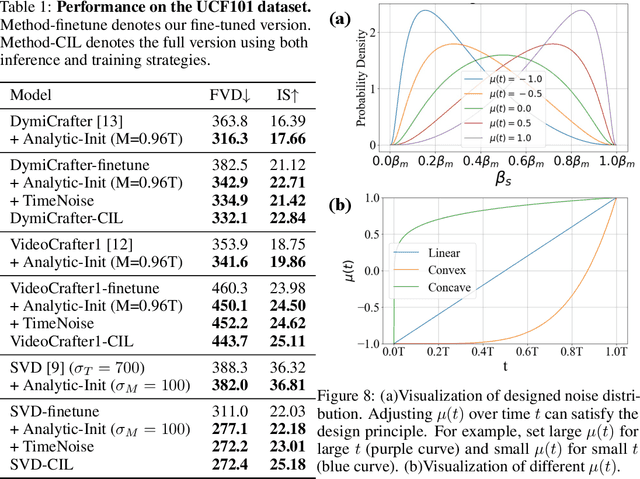


Abstract:Diffusion models have obtained substantial progress in image-to-video (I2V) generation. However, such models are not fully understood. In this paper, we report a significant but previously overlooked issue in I2V diffusion models (I2V-DMs), namely, conditional image leakage. I2V-DMs tend to over-rely on the conditional image at large time steps, neglecting the crucial task of predicting the clean video from noisy inputs, which results in videos lacking dynamic and vivid motion. We further address this challenge from both inference and training aspects by presenting plug-and-play strategies accordingly. First, we introduce a training-free inference strategy that starts the generation process from an earlier time step to avoid the unreliable late-time steps of I2V-DMs, as well as an initial noise distribution with optimal analytic expressions (Analytic-Init) by minimizing the KL divergence between it and the actual marginal distribution to effectively bridge the training-inference gap. Second, to mitigate conditional image leakage during training, we design a time-dependent noise distribution for the conditional image, which favors high noise levels at large time steps to sufficiently interfere with the conditional image. We validate these strategies on various I2V-DMs using our collected open-domain image benchmark and the UCF101 dataset. Extensive results demonstrate that our methods outperform baselines by producing videos with more dynamic and natural motion without compromising image alignment and temporal consistency. The project page: \url{https://cond-image-leak.github.io/}.
PoseCrafter: One-Shot Personalized Video Synthesis Following Flexible Poses
May 23, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce PoseCrafter, a one-shot method for personalized video generation following the control of flexible poses. Built upon Stable Diffusion and ControlNet, we carefully design an inference process to produce high-quality videos without the corresponding ground-truth frames. First, we select an appropriate reference frame from the training video and invert it to initialize all latent variables for generation. Then, we insert the corresponding training pose into the target pose sequences to enhance faithfulness through a trained temporal attention module. Furthermore, to alleviate the face and hand degradation resulting from discrepancies between poses of training videos and inference poses, we implement simple latent editing through an affine transformation matrix involving facial and hand landmarks. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrate that PoseCrafter achieves superior results to baselines pre-trained on a vast collection of videos under 8 commonly used metrics. Besides, PoseCrafter can follow poses from different individuals or artificial edits and simultaneously retain the human identity in an open-domain training video.
Vidu: a Highly Consistent, Dynamic and Skilled Text-to-Video Generator with Diffusion Models
May 07, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Vidu, a high-performance text-to-video generator that is capable of producing 1080p videos up to 16 seconds in a single generation. Vidu is a diffusion model with U-ViT as its backbone, which unlocks the scalability and the capability for handling long videos. Vidu exhibits strong coherence and dynamism, and is capable of generating both realistic and imaginative videos, as well as understanding some professional photography techniques, on par with Sora -- the most powerful reported text-to-video generator. Finally, we perform initial experiments on other controllable video generation, including canny-to-video generation, video prediction and subject-driven generation, which demonstrate promising results.
AE-RED: A Hyperspectral Unmixing Framework Powered by Deep Autoencoder and Regularization by Denoising
Jul 01, 2023



Abstract:Spectral unmixing has been extensively studied with a variety of methods and used in many applications. Recently, data-driven techniques with deep learning methods have obtained great attention to spectral unmixing for its superior learning ability to automatically learn the structure information. In particular, autoencoder based architectures are elaborately designed to solve blind unmixing and model complex nonlinear mixtures. Nevertheless, these methods perform unmixing task as blackboxes and lack of interpretability. On the other hand, conventional unmixing methods carefully design the regularizer to add explicit information, in which algorithms such as plug-and-play (PnP) strategies utilize off-the-shelf denoisers to plug powerful priors. In this paper, we propose a generic unmixing framework to integrate the autoencoder network with regularization by denoising (RED), named AE-RED. More specially, we decompose the unmixing optimized problem into two subproblems. The first one is solved using deep autoencoders to implicitly regularize the estimates and model the mixture mechanism. The second one leverages the denoiser to bring in the explicit information. In this way, both the characteristics of the deep autoencoder based unmixing methods and priors provided by denoisers are merged into our well-designed framework to enhance the unmixing performance. Experiment results on both synthetic and real data sets show the superiority of our proposed framework compared with state-of-the-art unmixing approaches.
Guided Deep Generative Model-based Spatial Regularization for Multiband Imaging Inverse Problems
Jun 29, 2023

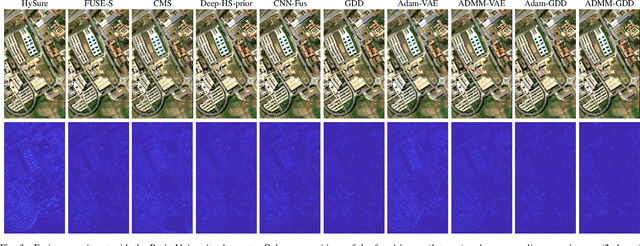

Abstract:When adopting a model-based formulation, solving inverse problems encountered in multiband imaging requires to define spatial and spectral regularizations. In most of the works of the literature, spectral information is extracted from the observations directly to derive data-driven spectral priors. Conversely, the choice of the spatial regularization often boils down to the use of conventional penalizations (e.g., total variation) promoting expected features of the reconstructed image (e.g., piecewise constant). In this work, we propose a generic framework able to capitalize on an auxiliary acquisition of high spatial resolution to derive tailored data-driven spatial regularizations. This approach leverages on the ability of deep learning to extract high level features. More precisely, the regularization is conceived as a deep generative network able to encode spatial semantic features contained in this auxiliary image of high spatial resolution. To illustrate the versatility of this approach, it is instantiated to conduct two particular tasks, namely multiband image fusion and multiband image inpainting. Experimental results obtained on these two tasks demonstrate the benefit of this class of informed regularizations when compared to more conventional ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge