Marios M. Polycarpou
Adaptive Monitoring of Stochastic Fire Front Processes via Information-seeking Predictive Control
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:We consider the problem of adaptively monitoring a wildfire front using a mobile agent (e.g., a drone), whose trajectory determines where sensor data is collected and thus influences the accuracy of fire propagation estimation. This is a challenging problem, as the stochastic nature of wildfire evolution requires the seamless integration of sensing, estimation, and control, often treated separately in existing methods. State-of-the-art methods either impose linear-Gaussian assumptions to establish optimality or rely on approximations and heuristics, often without providing explicit performance guarantees. To address these limitations, we formulate the fire front monitoring task as a stochastic optimal control problem that integrates sensing, estimation, and control. We derive an optimal recursive Bayesian estimator for a class of stochastic nonlinear elliptical-growth fire front models. Subsequently, we transform the resulting nonlinear stochastic control problem into a finite-horizon Markov decision process and design an information-seeking predictive control law obtained via a lower confidence bound-based adaptive search algorithm with asymptotic convergence to the optimal policy.
Adaptive event-triggered robust tracking control of soft robots
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Soft robots manufactured with flexible materials can be highly compliant and adaptive to their surroundings, which facilitates their application in areas such as dexterous manipulation and environmental exploration. This paper aims at investigating the tracking control problem for soft robots under uncertainty such as unmodeled dynamics and external disturbance. First, we establish a novel switching function and design the compensated tracking error dynamics by virtue of the command filter. Then, based on the backstepping methodology, the virtual controllers and the adaptive logic estimating the supremum of uncertainty impacts are developed for synthesizing an event-triggered control strategy. In addition, the uniformed finite-time stability certification is derived for different scenarios of the switching function. Finally, we perform a case study of a soft robot to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm.
Interpretable Event Diagnosis in Water Distribution Networks
May 12, 2025Abstract:The increasing penetration of information and communication technologies in the design, monitoring, and control of water systems enables the use of algorithms for detecting and identifying unanticipated events (such as leakages or water contamination) using sensor measurements. However, data-driven methodologies do not always give accurate results and are often not trusted by operators, who may prefer to use their engineering judgment and experience to deal with such events. In this work, we propose a framework for interpretable event diagnosis -- an approach that assists the operators in associating the results of algorithmic event diagnosis methodologies with their own intuition and experience. This is achieved by providing contrasting (i.e., counterfactual) explanations of the results provided by fault diagnosis algorithms; their aim is to improve the understanding of the algorithm's inner workings by the operators, thus enabling them to take a more informed decision by combining the results with their personal experiences. Specifically, we propose counterfactual event fingerprints, a representation of the difference between the current event diagnosis and the closest alternative explanation, which can be presented in a graphical way. The proposed methodology is applied and evaluated on a realistic use case using the L-Town benchmark.
Rolling Horizon Coverage Control with Collaborative Autonomous Agents
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:This work proposes a coverage controller that enables an aerial team of distributed autonomous agents to collaboratively generate non-myopic coverage plans over a rolling finite horizon, aiming to cover specific points on the surface area of a 3D object of interest. The collaborative coverage problem, formulated, as a distributed model predictive control problem, optimizes the agents' motion and camera control inputs, while considering inter-agent constraints aiming at reducing work redundancy. The proposed coverage controller integrates constraints based on light-path propagation techniques to predict the parts of the object's surface that are visible with regard to the agents' future anticipated states. This work also demonstrates how complex, non-linear visibility assessment constraints can be converted into logical expressions that are embedded as binary constraints into a mixed-integer optimization framework. The proposed approach has been demonstrated through simulations and practical applications for inspecting buildings with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Jointly-optimized Trajectory Generation and Camera Control for 3D Coverage Planning
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:This work proposes a jointly optimized trajectory generation and camera control approach, enabling an autonomous agent, such as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operating in 3D environments, to plan and execute coverage trajectories that maximally cover the surface area of a 3D object of interest. Specifically, the UAV's kinematic and camera control inputs are jointly optimized over a rolling planning horizon to achieve complete 3D coverage of the object. The proposed controller incorporates ray-tracing into the planning process to simulate the propagation of light rays, thereby determining the visible parts of the object through the UAV's camera. This integration enables the generation of precise look-ahead coverage trajectories. The coverage planning problem is formulated as a rolling finite-horizon optimal control problem and solved using mixed-integer programming techniques. Extensive real-world and synthetic experiments validate the performance of the proposed approach.
SiameseDuo++: Active Learning from Data Streams with Dual Augmented Siamese Networks
Apr 06, 2025



Abstract:Data stream mining, also known as stream learning, is a growing area which deals with learning from high-speed arriving data. Its relevance has surged recently due to its wide range of applicability, such as, critical infrastructure monitoring, social media analysis, and recommender systems. The design of stream learning methods faces significant research challenges; from the nonstationary nature of the data (referred to as concept drift) and the fact that data streams are typically not annotated with the ground truth, to the requirement that such methods should process large amounts of data in real-time with limited memory. This work proposes the SiameseDuo++ method, which uses active learning to automatically select instances for a human expert to label according to a budget. Specifically, it incrementally trains two siamese neural networks which operate in synergy, augmented by generated examples. Both the proposed active learning strategy and augmentation operate in the latent space. SiameseDuo++ addresses the aforementioned challenges by operating with limited memory and limited labelling budget. Simulation experiments show that the proposed method outperforms strong baselines and state-of-the-art methods in terms of learning speed and/or performance. To promote open science we publicly release our code and datasets.
Deficient Excitation in Parameter Learning
Mar 04, 2025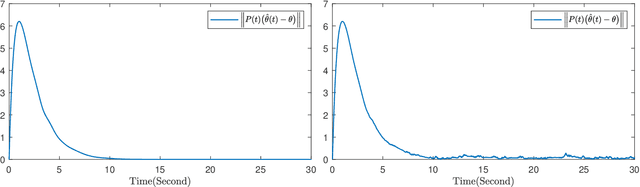
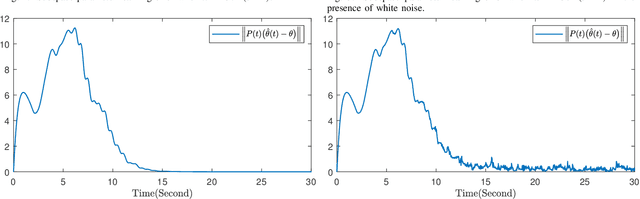
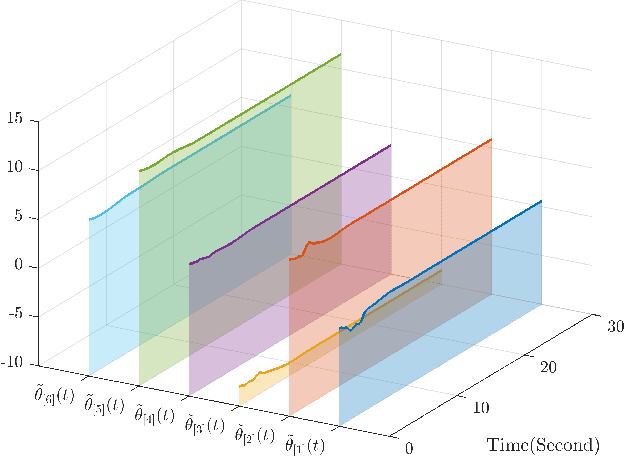
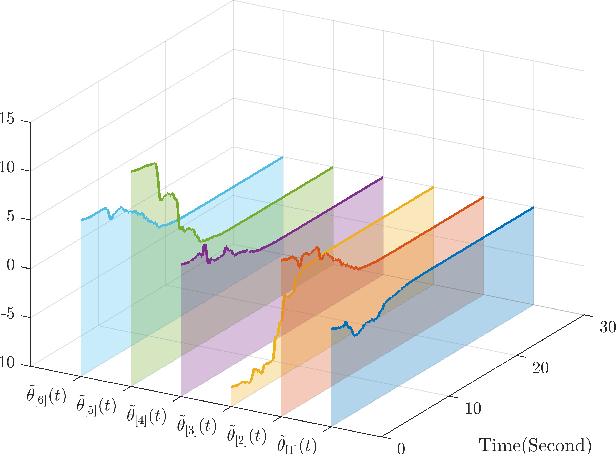
Abstract:This paper investigates parameter learning problems under deficient excitation (DE). The DE condition is a rank-deficient, and therefore, a more general evolution of the well-known persistent excitation condition. Under the DE condition, a proposed online algorithm is able to calculate the identifiable and non-identifiable subspaces, and finally give an optimal parameter estimate in the sense of least squares. In particular, the learning error within the identifiable subspace exponentially converges to zero in the noise-free case, even without persistent excitation. The DE condition also provides a new perspective for solving distributed parameter learning problems, where the challenge is posed by local regressors that are often insufficiently excited. To improve knowledge of the unknown parameters, a cooperative learning protocol is proposed for a group of estimators that collect measured information under complementary DE conditions. This protocol allows each local estimator to operate locally in its identifiable subspace, and reach a consensus with neighbours in its non-identifiable subspace. As a result, the task of estimating unknown parameters can be achieved in a distributed way using cooperative local estimators. Application examples in system identification are given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the theoretical results developed in this paper.
Transformer-based Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Localization
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:With the growing complexity of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT), the use of sensors for online monitoring generates large volume of multivariate time series (MTS) data. Consequently, the need for robust anomaly diagnosis in MTS is paramount to maintaining system reliability and safety. While significant advancements have been made in anomaly detection, localization remains a largely underexplored area, though crucial for intelligent decision-making. This paper introduces a novel transformer-based model for unsupervised anomaly diagnosis in MTS, with a focus on improving localization performance, through an in-depth analysis of the self-attention mechanism's learning behavior under both normal and anomalous conditions. We formulate the anomaly localization problem as a three-stage process: time-step, window, and segment-based. This leads to the development of the Space-Time Anomaly Score (STAS), a new metric inspired by the connection between transformer latent representations and space-time statistical models. STAS is designed to capture individual anomaly behaviors and inter-series dependencies, delivering enhanced localization performance. Additionally, the Statistical Feature Anomaly Score (SFAS) complements STAS by analyzing statistical features around anomalies, with their combination helping to reduce false alarms. Experiments on real world and synthetic datasets illustrate the model's superiority over state-of-the-art methods in both detection and localization tasks.
Cooperative Aerial Robot Inspection Challenge: A Benchmark for Heterogeneous Multi-UAV Planning and Lessons Learned
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:We propose the Cooperative Aerial Robot Inspection Challenge (CARIC), a simulation-based benchmark for motion planning algorithms in heterogeneous multi-UAV systems. CARIC features UAV teams with complementary sensors, realistic constraints, and evaluation metrics prioritizing inspection quality and efficiency. It offers a ready-to-use perception-control software stack and diverse scenarios to support the development and evaluation of task allocation and motion planning algorithms. Competitions using CARIC were held at IEEE CDC 2023 and the IROS 2024 Workshop on Multi-Robot Perception and Navigation, attracting innovative solutions from research teams worldwide. This paper examines the top three teams from CDC 2023, analyzing their exploration, inspection, and task allocation strategies while drawing insights into their performance across scenarios. The results highlight the task's complexity and suggest promising directions for future research in cooperative multi-UAV systems.
Online Detection of Water Contamination Under Concept Drift
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Water Distribution Networks (WDNs) are vital infrastructures, and contamination poses serious public health risks. Harmful substances can interact with disinfectants like chlorine, making chlorine monitoring essential for detecting contaminants. However, chlorine sensors often become unreliable and require frequent calibration. This study introduces the Dual-Threshold Anomaly and Drift Detection (AD&DD) method, an unsupervised approach combining a dual-threshold drift detection mechanism with an LSTM-based Variational Autoencoder(LSTM-VAE) for real-time contamination detection. Tested on two realistic WDNs, AD&DD effectively identifies anomalies with sensor offsets as concept drift, and outperforms other methods. A proposed decentralized architecture enables accurate contamination detection and localization by deploying AD&DD on selected nodes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge