Shimin Wang
Collision-Free Bearing-Driven Formation Tracking for Euler-Lagrange Systems
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the problem of tracking formations driven by bearings for heterogeneous Euler-Lagrange systems with parametric uncertainty in the presence of multiple moving leaders. To estimate the leaders' velocities and accelerations, we first design a distributed observer for the leader system, utilizing a bearing-based localization condition in place of the conventional connectivity assumption. This observer, coupled with an adaptive mechanism, enables the synthesis of a novel distributed control law that guides the formation towards the target formation, without requiring prior knowledge of the system parameters. Furthermore, we establish a sufficient condition, dependent on the initial formation configuration, that ensures collision avoidance throughout the formation evolution. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is demonstrated through a numerical example.
Nonadaptive Output Regulation of Second-Order Nonlinear Uncertain Systems
May 28, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the robust output regulation problem of second-order nonlinear uncertain systems with an unknown exosystem. Instead of the adaptive control approach, this paper resorts to a robust control methodology to solve the problem and thus avoid the bursting phenomenon. In particular, this paper constructs generic internal models for the steady-state state and input variables of the system. By introducing a coordinate transformation, this paper converts the robust output regulation problem into a nonadaptive stabilization problem of an augmented system composed of the second-order nonlinear uncertain system and the generic internal models. Then, we design the stabilization control law and construct a strict Lyapunov function that guarantees the robustness with respect to unmodeled disturbances. The analysis shows that the output zeroing manifold of the augmented system can be made attractive by the proposed nonadaptive control law, which solves the robust output regulation problem. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed nonadaptive internal model approach by its application to the control of the Duffing system.
Optimal Output Feedback Learning Control for Discrete-Time Linear Quadratic Regulation
Mar 08, 2025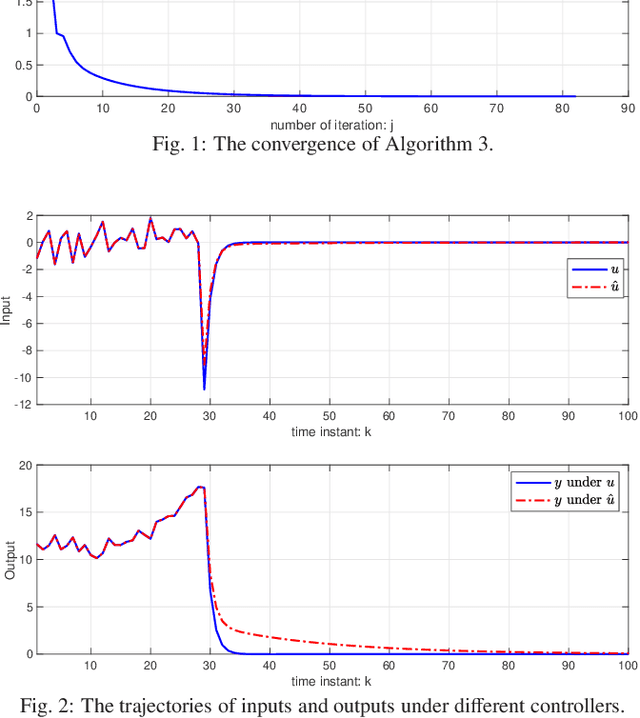
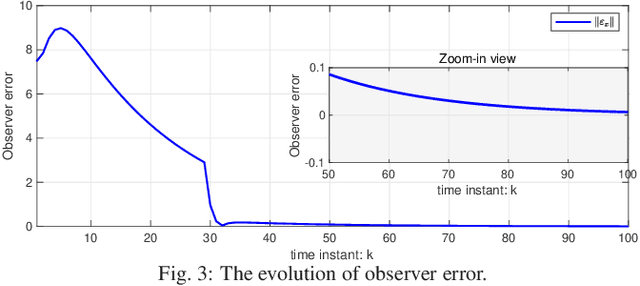
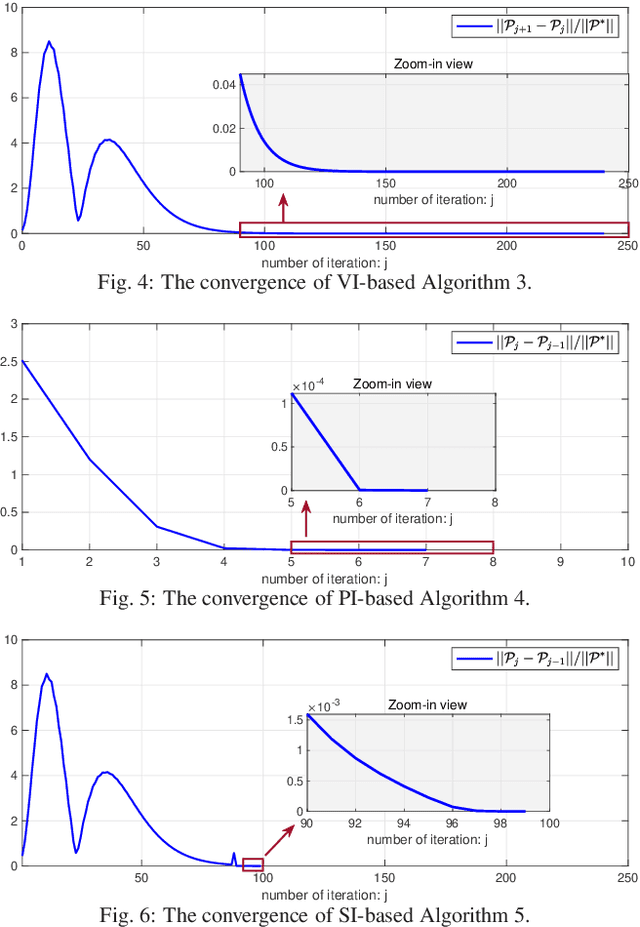
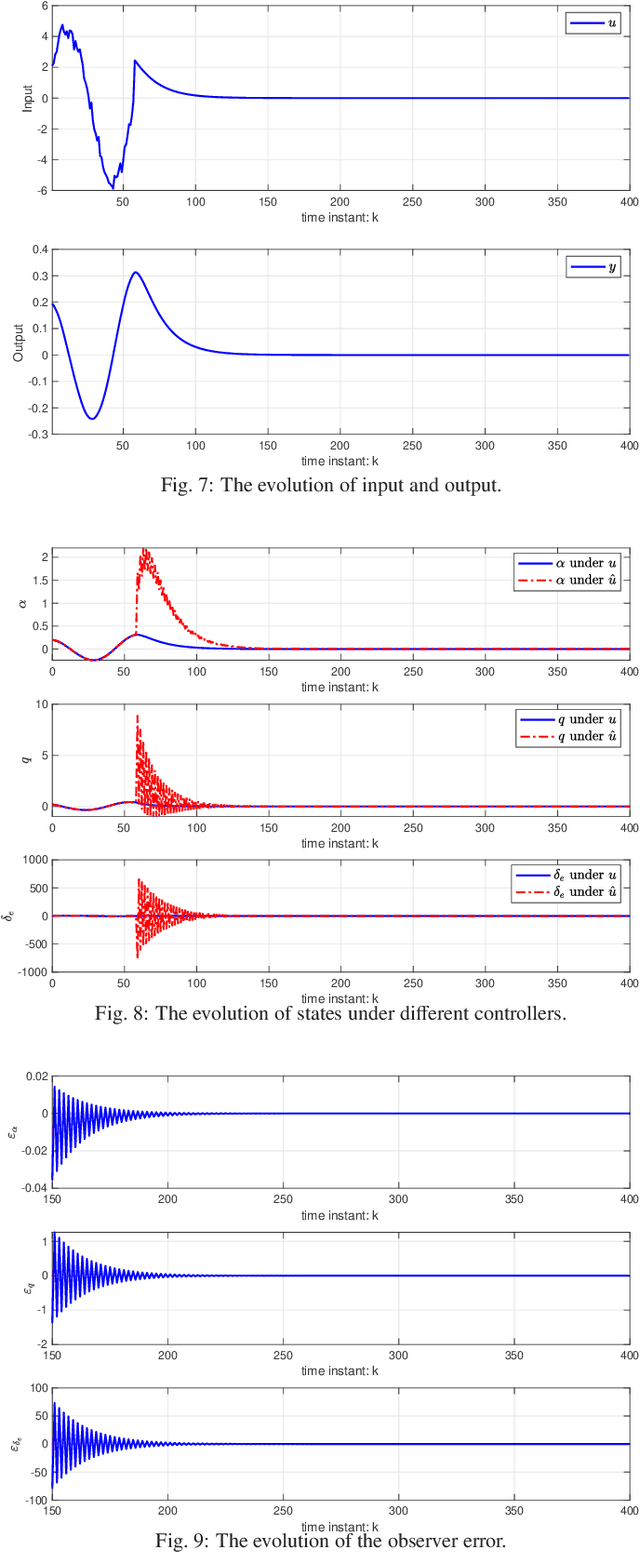
Abstract:This paper studies the linear quadratic regulation (LQR) problem of unknown discrete-time systems via dynamic output feedback learning control. In contrast to the state feedback, the optimality of the dynamic output feedback control for solving the LQR problem requires an implicit condition on the convergence of the state observer. Moreover, due to unknown system matrices and the existence of observer error, it is difficult to analyze the convergence and stability of most existing output feedback learning-based control methods. To tackle these issues, we propose a generalized dynamic output feedback learning control approach with guaranteed convergence, stability, and optimality performance for solving the LQR problem of unknown discrete-time linear systems. In particular, a dynamic output feedback controller is designed to be equivalent to a state feedback controller. This equivalence relationship is an inherent property without requiring convergence of the estimated state by the state observer, which plays a key role in establishing the off-policy learning control approaches. By value iteration and policy iteration schemes, the adaptive dynamic programming based learning control approaches are developed to estimate the optimal feedback control gain. In addition, a model-free stability criterion is provided by finding a nonsingular parameterization matrix, which contributes to establishing a switched iteration scheme. Furthermore, the convergence, stability, and optimality analyses of the proposed output feedback learning control approaches are given. Finally, the theoretical results are validated by two numerical examples.
Deficient Excitation in Parameter Learning
Mar 04, 2025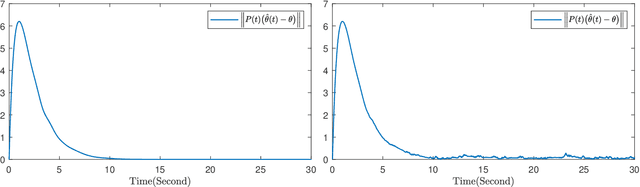
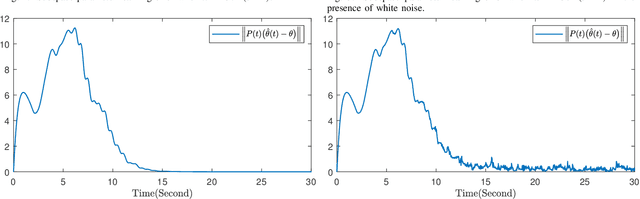
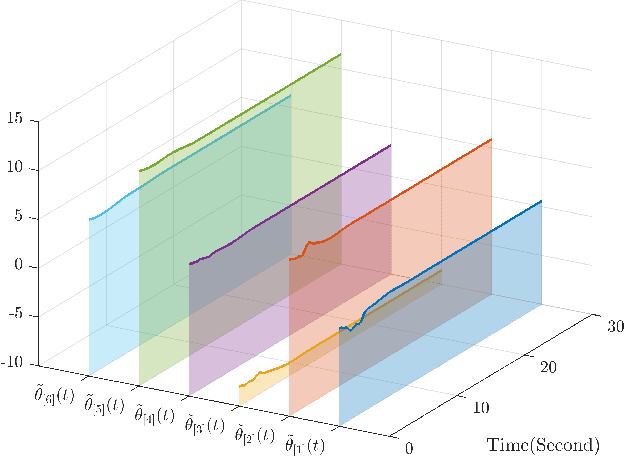
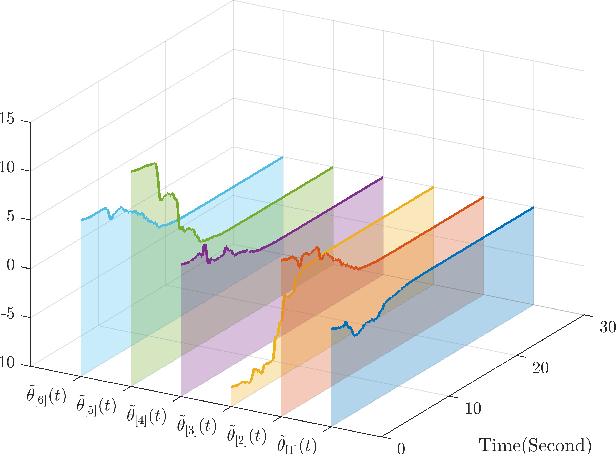
Abstract:This paper investigates parameter learning problems under deficient excitation (DE). The DE condition is a rank-deficient, and therefore, a more general evolution of the well-known persistent excitation condition. Under the DE condition, a proposed online algorithm is able to calculate the identifiable and non-identifiable subspaces, and finally give an optimal parameter estimate in the sense of least squares. In particular, the learning error within the identifiable subspace exponentially converges to zero in the noise-free case, even without persistent excitation. The DE condition also provides a new perspective for solving distributed parameter learning problems, where the challenge is posed by local regressors that are often insufficiently excited. To improve knowledge of the unknown parameters, a cooperative learning protocol is proposed for a group of estimators that collect measured information under complementary DE conditions. This protocol allows each local estimator to operate locally in its identifiable subspace, and reach a consensus with neighbours in its non-identifiable subspace. As a result, the task of estimating unknown parameters can be achieved in a distributed way using cooperative local estimators. Application examples in system identification are given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the theoretical results developed in this paper.
Learning-Enhanced Safeguard Control for High-Relative-Degree Systems: Robust Optimization under Disturbances and Faults
Jan 26, 2025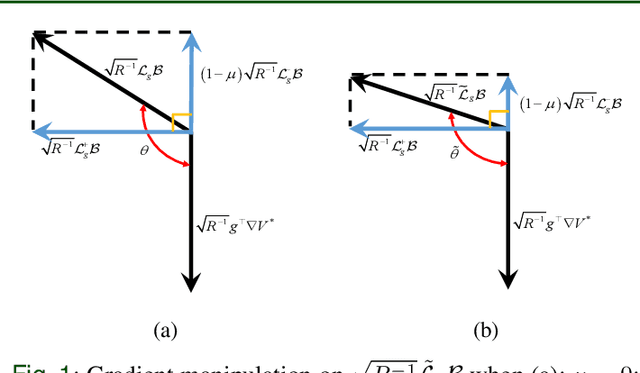
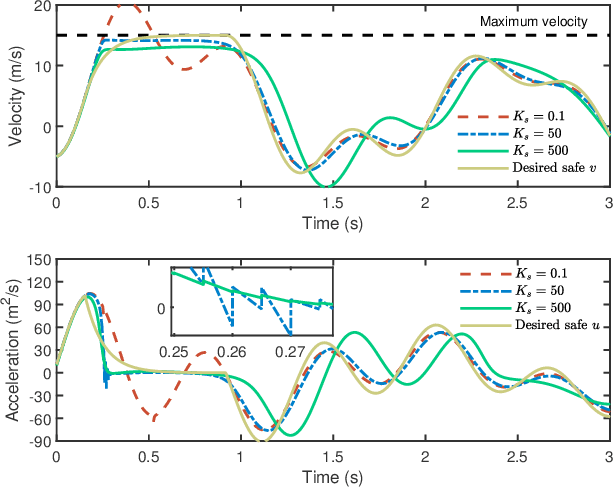
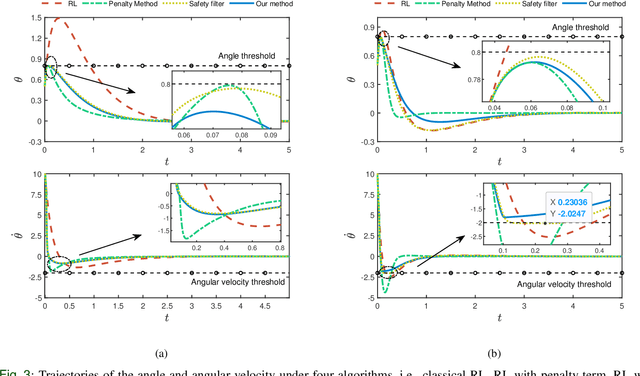
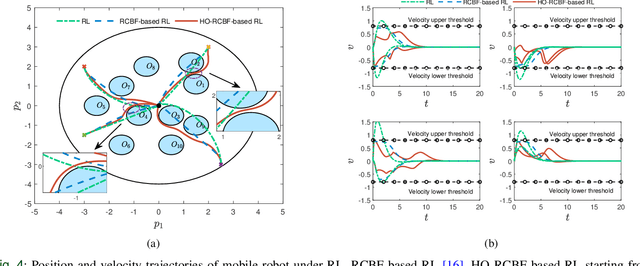
Abstract:Merely pursuing performance may adversely affect the safety, while a conservative policy for safe exploration will degrade the performance. How to balance the safety and performance in learning-based control problems is an interesting yet challenging issue. This paper aims to enhance system performance with safety guarantee in solving the reinforcement learning (RL)-based optimal control problems of nonlinear systems subject to high-relative-degree state constraints and unknown time-varying disturbance/actuator faults. First, to combine control barrier functions (CBFs) with RL, a new type of CBFs, termed high-order reciprocal control barrier function (HO-RCBF) is proposed to deal with high-relative-degree constraints during the learning process. Then, the concept of gradient similarity is proposed to quantify the relationship between the gradient of safety and the gradient of performance. Finally, gradient manipulation and adaptive mechanisms are introduced in the safe RL framework to enhance the performance with a safety guarantee. Two simulation examples illustrate that the proposed safe RL framework can address high-relative-degree constraint, enhance safety robustness and improve system performance.
Nonlinear Bipartite Output Regulation with Application to Turing Pattern
May 25, 2023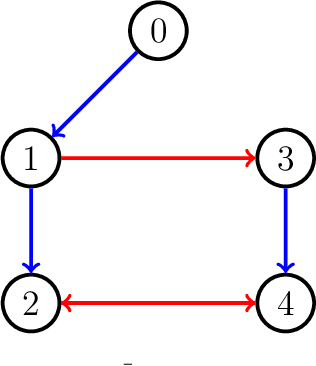
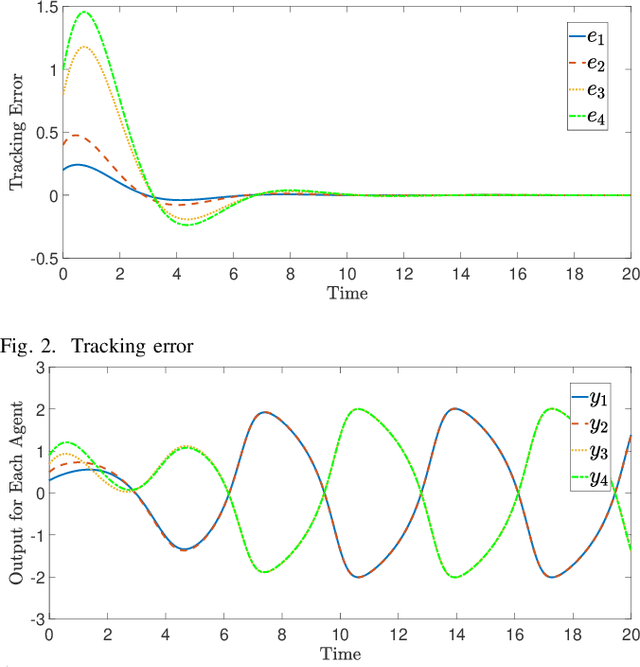
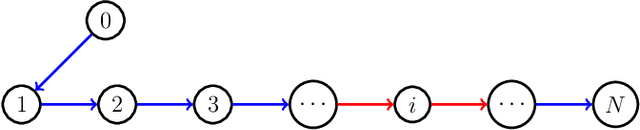

Abstract:In this paper, a bipartite output regulation problem is solved for a class of nonlinear multi-agent systems subject to static signed communication networks. A nonlinear distributed observer is proposed for a nonlinear exosystem with cooperation-competition interactions to address the problem. Sufficient conditions are provided to guarantee its existence and stability. The exponential stability of the observer is established. As a practical application, a leader-following bipartite consensus problem is solved for a class of nonlinear multi-agent systems based on the observer. Finally, a network of multiple pendulum systems is treated to support the feasibility of the proposed design. The possible application of the approach to generate specific Turing patterns is also presented.
Learning nonlinear dynamics in synchronization of knowledge-based leader-following networks
Dec 29, 2021



Abstract:Knowledge-based leader-following synchronization problem of heterogeneous nonlinear multi-agent systems is challenging since the leader's dynamic information is unknown to all follower nodes. This paper proposes a learning-based fully distributed observer for a class of nonlinear leader systems, which can simultaneously learn the leader's dynamics and states. The class of leader dynamics considered here does not require a bounded Jacobian matrix. Based on this learning-based distributed observer, we further synthesize an adaptive distributed control law for solving the leader-following synchronization problem of multiple Euler-Lagrange systems subject to an uncertain nonlinear leader system. The results are illustrated by a simulation example.
Cooperative Output Regulation with Mixed Time- and Event-triggered Observers
May 05, 2021



Abstract:Mixed time- and event-triggered cooperative output regulation for heterogeneous distributed systems is investigated in this paper. A distributed observer with time-triggered observations is proposed to estimate the state of the leader, and an auxiliary observer with event-triggered communication is designed to reduce the information exchange among followers. A necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of desirable time-triggered observers is established, and delicate relationships among sampling periods, topologies, and reference signals are revealed. An event-triggering mechanism based on local sampled data is proposed to regulate the communication among agents; and the convergence of the estimation errors under the mechanism holds for a class of positive and convergent triggering functions, which include the commonly used exponential function as a special case. The mixed time- and event-triggered system naturally excludes the existence of Zeno behavior as the system updates at discrete instants. When the triggering function is bounded by exponential functions, analytical characterization of the relationship among sampling, event triggering, and inter-event behaviour is established. Finally, several examples are provided to illustrate the effectiveness and merits of the theoretical results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge