Lin Yen-Chen
Scalable Policy Evaluation with Video World Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Training generalist policies for robotic manipulation has shown great promise, as they enable language-conditioned, multi-task behaviors across diverse scenarios. However, evaluating these policies remains difficult because real-world testing is expensive, time-consuming, and labor-intensive. It also requires frequent environment resets and carries safety risks when deploying unproven policies on physical robots. Manually creating and populating simulation environments with assets for robotic manipulation has not addressed these issues, primarily due to the significant engineering effort required and the often substantial sim-to-real gap, both in terms of physics and rendering. In this paper, we explore the use of action-conditional video generation models as a scalable way to learn world models for policy evaluation. We demonstrate how to incorporate action conditioning into existing pre-trained video generation models. This allows leveraging internet-scale in-the-wild online videos during the pre-training stage, and alleviates the need for a large dataset of paired video-action data, which is expensive to collect for robotic manipulation. Our paper examines the effect of dataset diversity, pre-trained weight and common failure cases for the proposed evaluation pipeline. Our experiments demonstrate that, across various metrics, including policy ranking and the correlation between actual policy values and predicted policy values, these models offer a promising approach for evaluating policies without requiring real-world interactions.
Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform for Physical AI
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Physical AI needs to be trained digitally first. It needs a digital twin of itself, the policy model, and a digital twin of the world, the world model. In this paper, we present the Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform to help developers build customized world models for their Physical AI setups. We position a world foundation model as a general-purpose world model that can be fine-tuned into customized world models for downstream applications. Our platform covers a video curation pipeline, pre-trained world foundation models, examples of post-training of pre-trained world foundation models, and video tokenizers. To help Physical AI builders solve the most critical problems of our society, we make our platform open-source and our models open-weight with permissive licenses available via https://github.com/NVIDIA/Cosmos.
Shelving, Stacking, Hanging: Relational Pose Diffusion for Multi-modal Rearrangement
Jul 10, 2023


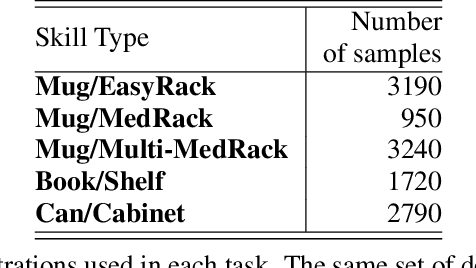
Abstract:We propose a system for rearranging objects in a scene to achieve a desired object-scene placing relationship, such as a book inserted in an open slot of a bookshelf. The pipeline generalizes to novel geometries, poses, and layouts of both scenes and objects, and is trained from demonstrations to operate directly on 3D point clouds. Our system overcomes challenges associated with the existence of many geometrically-similar rearrangement solutions for a given scene. By leveraging an iterative pose de-noising training procedure, we can fit multi-modal demonstration data and produce multi-modal outputs while remaining precise and accurate. We also show the advantages of conditioning on relevant local geometric features while ignoring irrelevant global structure that harms both generalization and precision. We demonstrate our approach on three distinct rearrangement tasks that require handling multi-modality and generalization over object shape and pose in both simulation and the real world. Project website, code, and videos: https://anthonysimeonov.github.io/rpdiff-multi-modal/
MIRA: Mental Imagery for Robotic Affordances
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:Humans form mental images of 3D scenes to support counterfactual imagination, planning, and motor control. Our abilities to predict the appearance and affordance of the scene from previously unobserved viewpoints aid us in performing manipulation tasks (e.g., 6-DoF kitting) with a level of ease that is currently out of reach for existing robot learning frameworks. In this work, we aim to build artificial systems that can analogously plan actions on top of imagined images. To this end, we introduce Mental Imagery for Robotic Affordances (MIRA), an action reasoning framework that optimizes actions with novel-view synthesis and affordance prediction in the loop. Given a set of 2D RGB images, MIRA builds a consistent 3D scene representation, through which we synthesize novel orthographic views amenable to pixel-wise affordances prediction for action optimization. We illustrate how this optimization process enables us to generalize to unseen out-of-plane rotations for 6-DoF robotic manipulation tasks given a limited number of demonstrations, paving the way toward machines that autonomously learn to understand the world around them for planning actions.
SE(3)-Equivariant Relational Rearrangement with Neural Descriptor Fields
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:We present a method for performing tasks involving spatial relations between novel object instances initialized in arbitrary poses directly from point cloud observations. Our framework provides a scalable way for specifying new tasks using only 5-10 demonstrations. Object rearrangement is formalized as the question of finding actions that configure task-relevant parts of the object in a desired alignment. This formalism is implemented in three steps: assigning a consistent local coordinate frame to the task-relevant object parts, determining the location and orientation of this coordinate frame on unseen object instances, and executing an action that brings these frames into the desired alignment. We overcome the key technical challenge of determining task-relevant local coordinate frames from a few demonstrations by developing an optimization method based on Neural Descriptor Fields (NDFs) and a single annotated 3D keypoint. An energy-based learning scheme to model the joint configuration of the objects that satisfies a desired relational task further improves performance. The method is tested on three multi-object rearrangement tasks in simulation and on a real robot. Project website, videos, and code: https://anthonysimeonov.github.io/r-ndf/
Vision Transformer for NeRF-Based View Synthesis from a Single Input Image
Jul 12, 2022
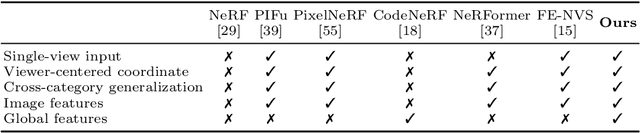
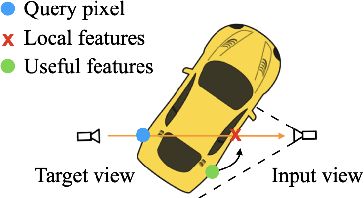
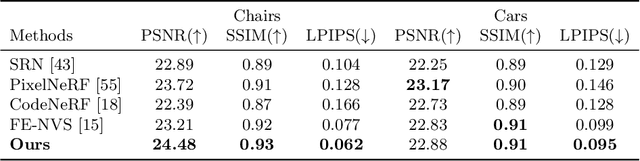
Abstract:Although neural radiance fields (NeRF) have shown impressive advances for novel view synthesis, most methods typically require multiple input images of the same scene with accurate camera poses. In this work, we seek to substantially reduce the inputs to a single unposed image. Existing approaches condition on local image features to reconstruct a 3D object, but often render blurry predictions at viewpoints that are far away from the source view. To address this issue, we propose to leverage both the global and local features to form an expressive 3D representation. The global features are learned from a vision transformer, while the local features are extracted from a 2D convolutional network. To synthesize a novel view, we train a multilayer perceptron (MLP) network conditioned on the learned 3D representation to perform volume rendering. This novel 3D representation allows the network to reconstruct unseen regions without enforcing constraints like symmetry or canonical coordinate systems. Our method can render novel views from only a single input image and generalize across multiple object categories using a single model. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance and renders richer details than existing approaches.
NeRF-Supervision: Learning Dense Object Descriptors from Neural Radiance Fields
Mar 03, 2022



Abstract:Thin, reflective objects such as forks and whisks are common in our daily lives, but they are particularly challenging for robot perception because it is hard to reconstruct them using commodity RGB-D cameras or multi-view stereo techniques. While traditional pipelines struggle with objects like these, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have recently been shown to be remarkably effective for performing view synthesis on objects with thin structures or reflective materials. In this paper we explore the use of NeRF as a new source of supervision for robust robot vision systems. In particular, we demonstrate that a NeRF representation of a scene can be used to train dense object descriptors. We use an optimized NeRF to extract dense correspondences between multiple views of an object, and then use these correspondences as training data for learning a view-invariant representation of the object. NeRF's usage of a density field allows us to reformulate the correspondence problem with a novel distribution-of-depths formulation, as opposed to the conventional approach of using a depth map. Dense correspondence models supervised with our method significantly outperform off-the-shelf learned descriptors by 106% (PCK@3px metric, more than doubling performance) and outperform our baseline supervised with multi-view stereo by 29%. Furthermore, we demonstrate the learned dense descriptors enable robots to perform accurate 6-degree of freedom (6-DoF) pick and place of thin and reflective objects.
Learning to See before Learning to Act: Visual Pre-training for Manipulation
Jul 01, 2021



Abstract:Does having visual priors (e.g. the ability to detect objects) facilitate learning to perform vision-based manipulation (e.g. picking up objects)? We study this problem under the framework of transfer learning, where the model is first trained on a passive vision task, and adapted to perform an active manipulation task. We find that pre-training on vision tasks significantly improves generalization and sample efficiency for learning to manipulate objects. However, realizing these gains requires careful selection of which parts of the model to transfer. Our key insight is that outputs of standard vision models highly correlate with affordance maps commonly used in manipulation. Therefore, we explore directly transferring model parameters from vision networks to affordance prediction networks, and show that this can result in successful zero-shot adaptation, where a robot can pick up certain objects with zero robotic experience. With just a small amount of robotic experience, we can further fine-tune the affordance model to achieve better results. With just 10 minutes of suction experience or 1 hour of grasping experience, our method achieves ~80% success rate at picking up novel objects.
Neural Volume Rendering: NeRF And Beyond
Jan 14, 2021Abstract:Besides the COVID-19 pandemic and political upheaval in the US, 2020 was also the year in which neural volume rendering exploded onto the scene, triggered by the impressive NeRF paper by Mildenhall et al. (2020). Both of us have tried to capture this excitement, Frank on a blog post (Dellaert, 2020) and Yen-Chen in a Github collection (Yen-Chen, 2020). This note is an annotated bibliography of the relevant papers, and we posted the associated bibtex file on the repository.
iNeRF: Inverting Neural Radiance Fields for Pose Estimation
Dec 10, 2020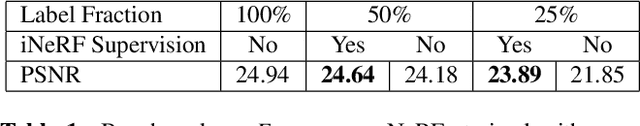
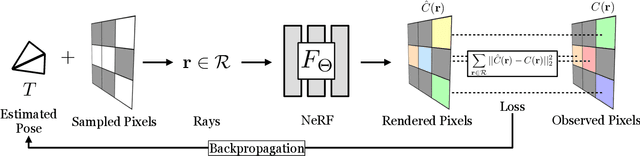
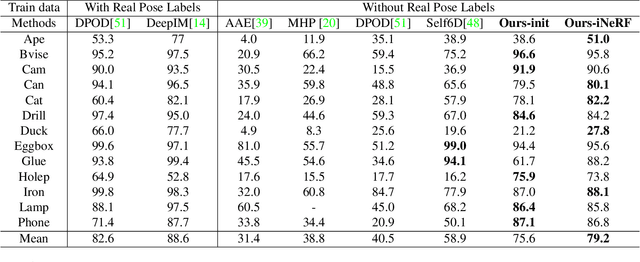
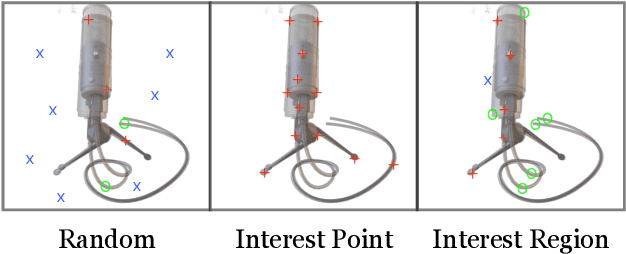
Abstract:We present iNeRF, a framework that performs pose estimation by "inverting" a trained Neural Radiance Field (NeRF). NeRFs have been shown to be remarkably effective for the task of view synthesis - synthesizing photorealistic novel views of real-world scenes or objects. In this work, we investigate whether we can apply analysis-by-synthesis with NeRF for 6DoF pose estimation - given an image, find the translation and rotation of a camera relative to a 3D model. Starting from an initial pose estimate, we use gradient descent to minimize the residual between pixels rendered from an already-trained NeRF and pixels in an observed image. In our experiments, we first study 1) how to sample rays during pose refinement for iNeRF to collect informative gradients and 2) how different batch sizes of rays affect iNeRF on a synthetic dataset. We then show that for complex real-world scenes from the LLFF dataset, iNeRF can improve NeRF by estimating the camera poses of novel images and using these images as additional training data for NeRF. Finally, we show iNeRF can be combined with feature-based pose initialization. The approach outperforms all other RGB-based methods relying on synthetic data on LineMOD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge