Lei Fu
ROSBag MCP Server: Analyzing Robot Data with LLMs for Agentic Embodied AI Applications
Nov 05, 2025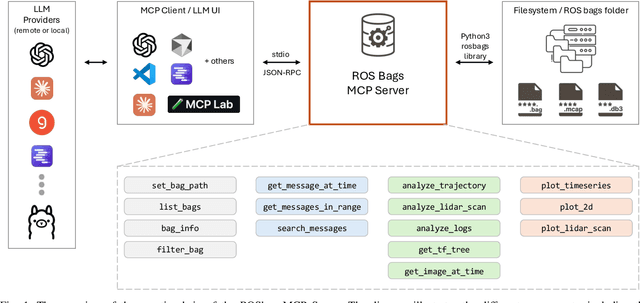
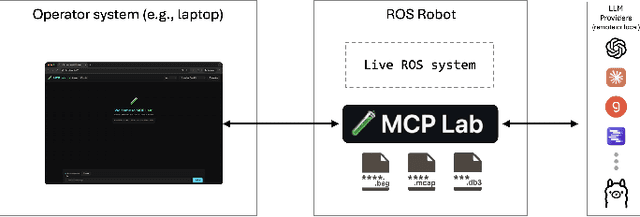
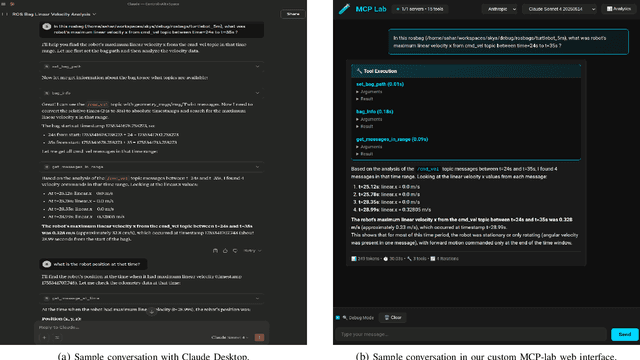
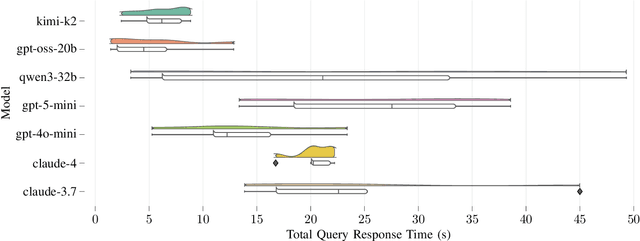
Abstract:Agentic AI systems and Physical or Embodied AI systems have been two key research verticals at the forefront of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, with Model Context Protocol (MCP) increasingly becoming a key component and enabler of agentic applications. However, the literature at the intersection of these verticals, i.e., Agentic Embodied AI, remains scarce. This paper introduces an MCP server for analyzing ROS and ROS 2 bags, allowing for analyzing, visualizing and processing robot data with natural language through LLMs and VLMs. We describe specific tooling built with robotics domain knowledge, with our initial release focused on mobile robotics and supporting natively the analysis of trajectories, laser scan data, transforms, or time series data. This is in addition to providing an interface to standard ROS 2 CLI tools ("ros2 bag list" or "ros2 bag info"), as well as the ability to filter bags with a subset of topics or trimmed in time. Coupled with the MCP server, we provide a lightweight UI that allows the benchmarking of the tooling with different LLMs, both proprietary (Anthropic, OpenAI) and open-source (through Groq). Our experimental results include the analysis of tool calling capabilities of eight different state-of-the-art LLM/VLM models, both proprietary and open-source, large and small. Our experiments indicate that there is a large divide in tool calling capabilities, with Kimi K2 and Claude Sonnet 4 demonstrating clearly superior performance. We also conclude that there are multiple factors affecting the success rates, from the tool description schema to the number of arguments, as well as the number of tools available to the models. The code is available with a permissive license at https://github.com/binabik-ai/mcp-rosbags.
Towards Embodied Agentic AI: Review and Classification of LLM- and VLM-Driven Robot Autonomy and Interaction
Aug 07, 2025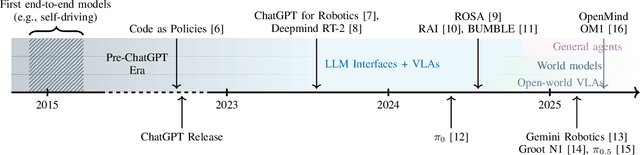
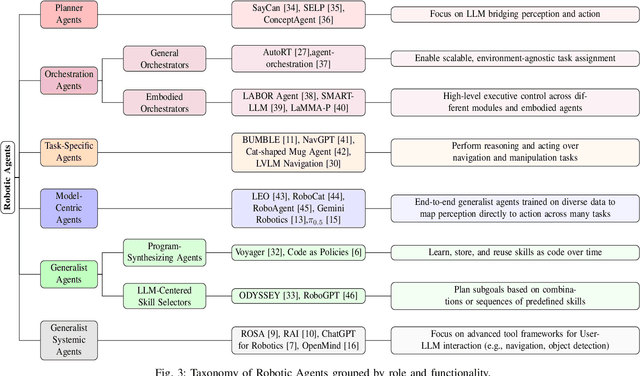
Abstract:Foundation models, including large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), have recently enabled novel approaches to robot autonomy and human-robot interfaces. In parallel, vision-language-action models (VLAs) or large behavior models (BLMs) are increasing the dexterity and capabilities of robotic systems. This survey paper focuses on those words advancing towards agentic applications and architectures. This includes initial efforts exploring GPT-style interfaces to tooling, as well as more complex system where AI agents are coordinators, planners, perception actors, or generalist interfaces. Such agentic architectures allow robots to reason over natural language instructions, invoke APIs, plan task sequences, or assist in operations and diagnostics. In addition to peer-reviewed research, due to the fast-evolving nature of the field, we highlight and include community-driven projects, ROS packages, and industrial frameworks that show emerging trends. We propose a taxonomy for classifying model integration approaches and present a comparative analysis of the role that agents play in different solutions in today's literature.
Hunyuan-TurboS: Advancing Large Language Models through Mamba-Transformer Synergy and Adaptive Chain-of-Thought
May 21, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) rapidly advance, we introduce Hunyuan-TurboS, a novel large hybrid Transformer-Mamba Mixture of Experts (MoE) model. It synergistically combines Mamba's long-sequence processing efficiency with Transformer's superior contextual understanding. Hunyuan-TurboS features an adaptive long-short chain-of-thought (CoT) mechanism, dynamically switching between rapid responses for simple queries and deep "thinking" modes for complex problems, optimizing computational resources. Architecturally, this 56B activated (560B total) parameter model employs 128 layers (Mamba2, Attention, FFN) with an innovative AMF/MF block pattern. Faster Mamba2 ensures linear complexity, Grouped-Query Attention minimizes KV cache, and FFNs use an MoE structure. Pre-trained on 16T high-quality tokens, it supports a 256K context length and is the first industry-deployed large-scale Mamba model. Our comprehensive post-training strategy enhances capabilities via Supervised Fine-Tuning (3M instructions), a novel Adaptive Long-short CoT Fusion method, Multi-round Deliberation Learning for iterative improvement, and a two-stage Large-scale Reinforcement Learning process targeting STEM and general instruction-following. Evaluations show strong performance: overall top 7 rank on LMSYS Chatbot Arena with a score of 1356, outperforming leading models like Gemini-2.0-Flash-001 (1352) and o4-mini-2025-04-16 (1345). TurboS also achieves an average of 77.9% across 23 automated benchmarks. Hunyuan-TurboS balances high performance and efficiency, offering substantial capabilities at lower inference costs than many reasoning models, establishing a new paradigm for efficient large-scale pre-trained models.
Research on Optimizing Real-Time Data Processing in High-Frequency Trading Algorithms using Machine Learning
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:High-frequency trading (HFT) represents a pivotal and intensely competitive domain within the financial markets. The velocity and accuracy of data processing exert a direct influence on profitability, underscoring the significance of this field. The objective of this work is to optimise the real-time processing of data in high-frequency trading algorithms. The dynamic feature selection mechanism is responsible for monitoring and analysing market data in real time through clustering and feature weight analysis, with the objective of automatically selecting the most relevant features. This process employs an adaptive feature extraction method, which enables the system to respond and adjust its feature set in a timely manner when the data input changes, thus ensuring the efficient utilisation of data. The lightweight neural networks are designed in a modular fashion, comprising fast convolutional layers and pruning techniques that facilitate the expeditious completion of data processing and output prediction. In contrast to conventional deep learning models, the neural network architecture has been specifically designed to minimise the number of parameters and computational complexity, thereby markedly reducing the inference time. The experimental results demonstrate that the model is capable of maintaining consistent performance in the context of varying market conditions, thereby illustrating its advantages in terms of processing speed and revenue enhancement.
DataGpt-SQL-7B: An Open-Source Language Model for Text-to-SQL
Sep 24, 2024

Abstract:In addressing the pivotal role of translating natural language queries into SQL commands, we propose a suite of compact, fine-tuned models and self-refine mechanisms to democratize data access and analysis for non-expert users, mitigating risks associated with closed-source Large Language Models. Specifically, we constructed a dataset of over 20K sample for Text-to-SQL as well as the preference dateset, to improve the efficiency in the domain of SQL generation. To further ensure code validity, a code corrector was integrated into the model. Our system, DataGpt-sql, achieved 87.2\% accuracy on the spider-dev, respectively, showcasing the effectiveness of our solution in text-to-SQL conversion tasks. Our code, data, and models are available at \url{https://github.com/CainiaoTechAi/datagpt-sql-7b}
Differentiation of Multi-objective Data-driven Decision Pipeline
Jun 02, 2024Abstract:Real-world scenarios frequently involve multi-objective data-driven optimization problems, characterized by unknown problem coefficients and multiple conflicting objectives. Traditional two-stage methods independently apply a machine learning model to estimate problem coefficients, followed by invoking a solver to tackle the predicted optimization problem. The independent use of optimization solvers and prediction models may lead to suboptimal performance due to mismatches between their objectives. Recent efforts have focused on end-to-end training of predictive models that use decision loss derived from the downstream optimization problem. However, these methods have primarily focused on single-objective optimization problems, thus limiting their applicability. We aim to propose a multi-objective decision-focused approach to address this gap. In order to better align with the inherent properties of multi-objective optimization problems, we propose a set of novel loss functions. These loss functions are designed to capture the discrepancies between predicted and true decision problems, considering solution space, objective space, and decision quality, named landscape loss, Pareto set loss, and decision loss, respectively. Our experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms traditional two-stage methods and most current decision-focused methods.
Benchmarking UWB-Based Infrastructure-Free Positioning and Multi-Robot Relative Localization: Dataset and Characterization
May 15, 2023



Abstract:Ultra-wideband (UWB) positioning has emerged as a low-cost and dependable localization solution for multiple use cases, from mobile robots to asset tracking within the Industrial IoT. The technology is mature and the scientific literature contains multiple datasets and methods for localization based on fixed UWB nodes. At the same time, research in UWB-based relative localization and infrastructure-free localization is gaining traction, further domains. tools and datasets in this domain are scarce. Therefore, we introduce in this paper a novel dataset for benchmarking infrastructure-free relative localization targeting the domain of multi-robot systems. Compared to previous datasets, we analyze the performance of different relative localization approaches for a much wider variety of scenarios with varying numbers of fixed and mobile nodes. A motion capture system provides ground truth data, are multi-modal and include inertial or odometry measurements for benchmarking sensor fusion methods. Additionally, the dataset contains measurements of ranging accuracy based on the relative orientation of antennas and a comprehensive set of measurements for ranging between a single pair of nodes. Our experimental analysis shows that high accuracy can be localization, but the variability of the ranging error is significant across different settings and setups.
Is Alice Really in Wonderland? UWB-Based Proof of Location for UAVs with Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:Remote identification of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) is becoming increasingly important since more UAVs are being widely used for different needs in urban areas. For example, in the US and in the EU, identification and position broadcasting is already a requirement for the use of drones. However, the current solutions do not validate the position of the UAV but its identity, while trusting the given position. Therefore, a more advanced solution enabling the proof of location is needed to avoid spoofing. We propose the combination of a permissioned blockchain managed by public authorities together with UWB-based communication to approach this. Specifically, we leverage the identity management tools from Hyperledger Fabric, an open-source permissioned blockchain framework, and ultra-wideband (UWB) ranging, leading to situated communication (i.e., simultaneous communication and localization). This approach allows us to prove both the UAV identity and also the location it broadcasts through interaction with ground infrastructure in known locations. Our initial experiments show that the proposed approach is viable and UWB transceivers can be used for UAVs to validate both their identity and position with ground infrastructure deployed in known locations.
Event-driven Fabric Blockchain - ROS 2 Interface: Towards Secure and Auditable Teleoperation of Mobile Robots
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:The integration of blockchain technology in robotic systems has been met by the community with a combination of hype and skepticism. The current literature shows that there is indeed potential for more secure and trustable distributed robotic systems. However, it is still unclear in what aspects of robotics beyond high-level decision making can blockchain technology be indeed usable. This paper explores the limits of a permissioned blockchain framework, Hyperledger Fabric, for teleoperation. Remote operation of mobile robots can benefit from the auditability and security properties of a blockchain. We study the potential benefits and the main limitations of such an approach. We introduce a new design and implementation for a event-driven Fabric-ROS 2 bridge that is able to maintain lower latencies at higher network loads than previous solutions. We also show this opens the door to more realistic use cases and applications. Our experiments with small aerial robots show latencies in the hundreds of milliseconds and simultaneous control of both a single and multi-robot system. We analyze the main trade-offs and limitations for real-world near real-time remote teleoperation.
Physics Symbolic Learner for Discovering Ground-Motion Models Via NGA-West2 Database
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:Ground-motion model (GMM) is the basis of many earthquake engineering studies. In this study, a novel physics-informed symbolic learner (PISL) method based on the Nest Generation Attenuation-West2 database is proposed to automatically discover mathematical equation operators as symbols. The sequential threshold ridge regression algorithm is utilized to distill a concise and interpretable explicit characterization of complex systems of ground motions. In addition to the basic variables retrieved from previous GMMs, the current PISL incorporates two a priori physical conditions, namely, distance and amplitude saturation. GMMs developed using the PISL, an empirical regression method (ERM), and an artificial neural network (ANN) are compared in terms of residuals and extrapolation based on obtained data of peak ground acceleration and velocity. The results show that the inter- and intra-event standard deviations of the three methods are similar. The functional form of the PISL is more concise than that of the ERM and ANN. The extrapolation capability of the PISL is more accurate than that of the ANN. The PISL-GMM used in this study provide a new paradigm of regression that considers both physical and data-driven machine learning and can be used to identify the implied physical relationships and prediction equations of ground motion variables in different regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge