Kory Mathewson
Shammie
Designing and Evaluating Dialogue LLMs for Co-Creative Improvised Theatre
May 11, 2024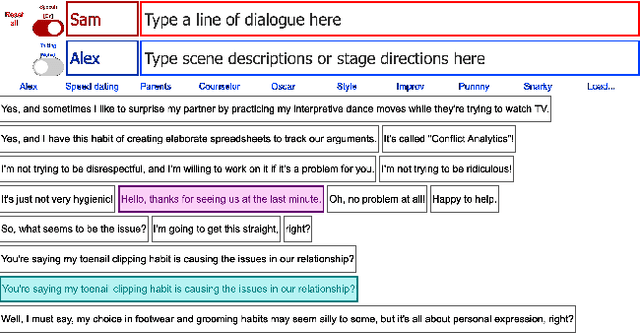
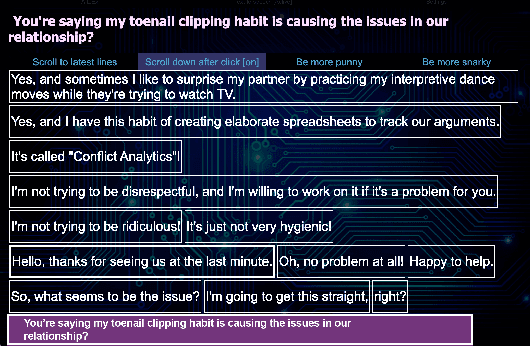

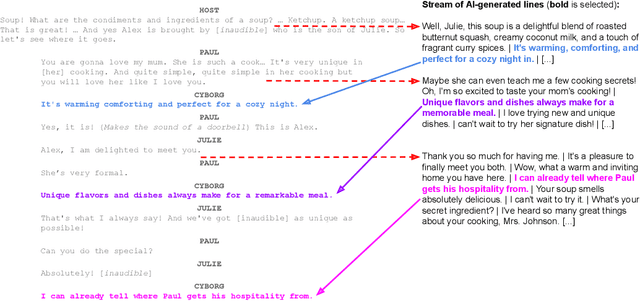
Abstract:Social robotics researchers are increasingly interested in multi-party trained conversational agents. With a growing demand for real-world evaluations, our study presents Large Language Models (LLMs) deployed in a month-long live show at the Edinburgh Festival Fringe. This case study investigates human improvisers co-creating with conversational agents in a professional theatre setting. We explore the technical capabilities and constraints of on-the-spot multi-party dialogue, providing comprehensive insights from both audience and performer experiences with AI on stage. Our human-in-the-loop methodology underlines the challenges of these LLMs in generating context-relevant responses, stressing the user interface's crucial role. Audience feedback indicates an evolving interest for AI-driven live entertainment, direct human-AI interaction, and a diverse range of expectations about AI's conversational competence and utility as a creativity support tool. Human performers express immense enthusiasm, varied satisfaction, and the evolving public opinion highlights mixed emotions about AI's role in arts.
Proceedings of the ICML 2022 Expressive Vocalizations Workshop and Competition: Recognizing, Generating, and Personalizing Vocal Bursts
Jul 14, 2022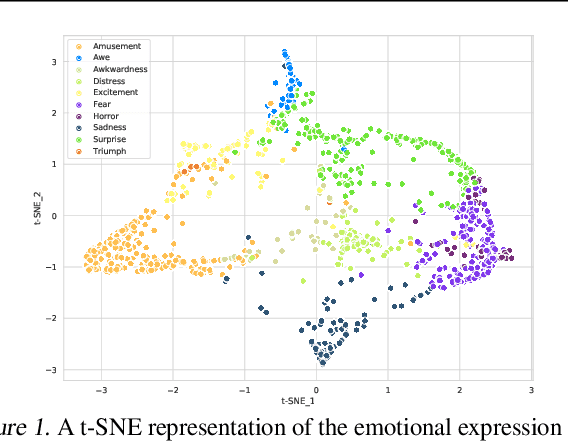
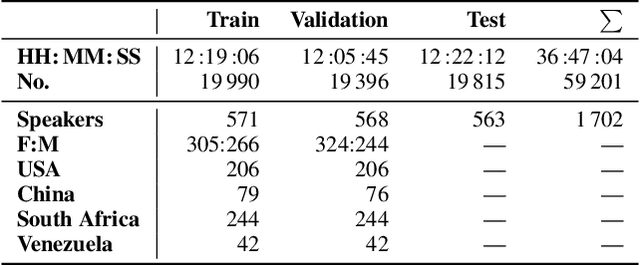
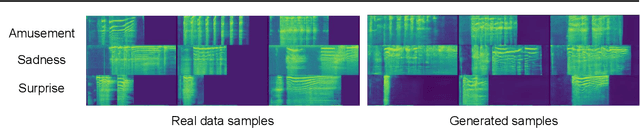
Abstract:This is the Proceedings of the ICML Expressive Vocalization (ExVo) Competition. The ExVo competition focuses on understanding and generating vocal bursts: laughs, gasps, cries, and other non-verbal vocalizations that are central to emotional expression and communication. ExVo 2022, included three competition tracks using a large-scale dataset of 59,201 vocalizations from 1,702 speakers. The first, ExVo-MultiTask, requires participants to train a multi-task model to recognize expressed emotions and demographic traits from vocal bursts. The second, ExVo-Generate, requires participants to train a generative model that produces vocal bursts conveying ten different emotions. The third, ExVo-FewShot, requires participants to leverage few-shot learning incorporating speaker identity to train a model for the recognition of 10 emotions conveyed by vocal bursts.
Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models
Jun 10, 2022Abstract:Language models demonstrate both quantitative improvement and new qualitative capabilities with increasing scale. Despite their potentially transformative impact, these new capabilities are as yet poorly characterized. In order to inform future research, prepare for disruptive new model capabilities, and ameliorate socially harmful effects, it is vital that we understand the present and near-future capabilities and limitations of language models. To address this challenge, we introduce the Beyond the Imitation Game benchmark (BIG-bench). BIG-bench currently consists of 204 tasks, contributed by 442 authors across 132 institutions. Task topics are diverse, drawing problems from linguistics, childhood development, math, common-sense reasoning, biology, physics, social bias, software development, and beyond. BIG-bench focuses on tasks that are believed to be beyond the capabilities of current language models. We evaluate the behavior of OpenAI's GPT models, Google-internal dense transformer architectures, and Switch-style sparse transformers on BIG-bench, across model sizes spanning millions to hundreds of billions of parameters. In addition, a team of human expert raters performed all tasks in order to provide a strong baseline. Findings include: model performance and calibration both improve with scale, but are poor in absolute terms (and when compared with rater performance); performance is remarkably similar across model classes, though with benefits from sparsity; tasks that improve gradually and predictably commonly involve a large knowledge or memorization component, whereas tasks that exhibit "breakthrough" behavior at a critical scale often involve multiple steps or components, or brittle metrics; social bias typically increases with scale in settings with ambiguous context, but this can be improved with prompting.
The ICML 2022 Expressive Vocalizations Workshop and Competition: Recognizing, Generating, and Personalizing Vocal Bursts
May 03, 2022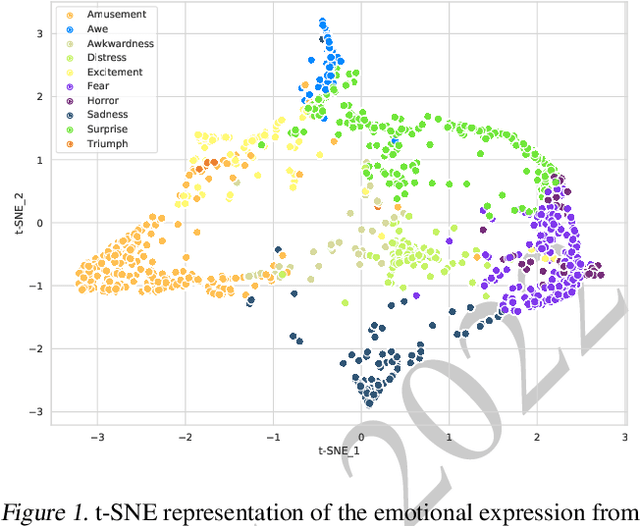
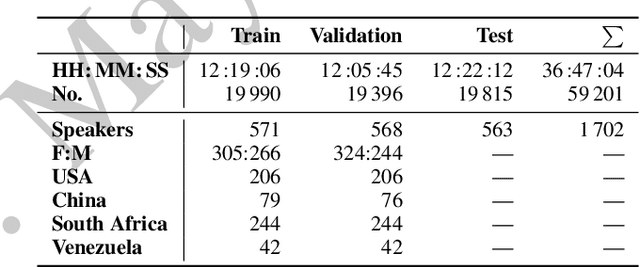
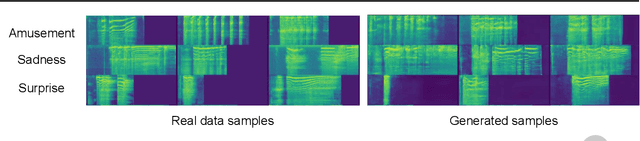
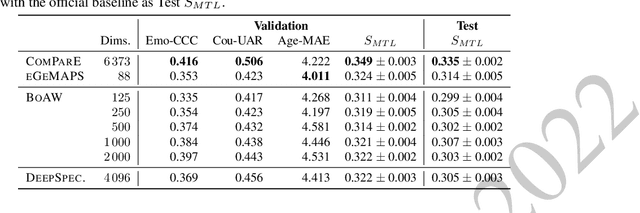
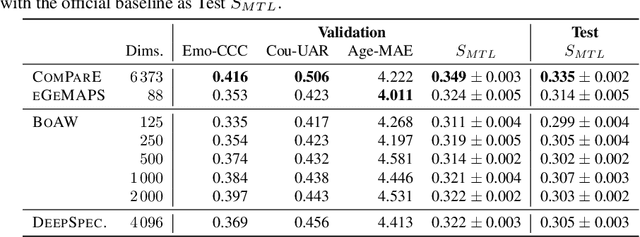
Abstract:The ICML Expressive Vocalization (ExVo) Competition is focused on understanding and generating vocal bursts: laughs, gasps, cries, and other non-verbal vocalizations that are central to emotional expression and communication. ExVo 2022, includes three competition tracks using a large-scale dataset of 59,201 vocalizations from 1,702 speakers. The first, ExVo-MultiTask, requires participants to train a multi-task model to recognize expressed emotions and demographic traits from vocal bursts. The second, ExVo-Generate, requires participants to train a generative model that produces vocal bursts conveying ten different emotions. The third, ExVo-FewShot, requires participants to leverage few-shot learning incorporating speaker identity to train a model for the recognition of 10 emotions conveyed by vocal bursts. This paper describes the three tracks and provides performance measures for baseline models using state-of-the-art machine learning strategies. The baseline for each track is as follows, for ExVo-MultiTask, a combined score, computing the harmonic mean of Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC), Unweighted Average Recall (UAR), and inverted Mean Absolute Error (MAE) ($S_{MTL}$) is at best, 0.335 $S_{MTL}$; for ExVo-Generate, we report Fr\'echet inception distance (FID) scores ranging from 4.81 to 8.27 (depending on the emotion) between the training set and generated samples. We then combine the inverted FID with perceptual ratings of the generated samples ($S_{Gen}$) and obtain 0.174 $S_{Gen}$; and for ExVo-FewShot, a mean CCC of 0.444 is obtained.
Expressivity of Emergent Language is a Trade-off between Contextual Complexity and Unpredictability
Jun 07, 2021



Abstract:Researchers are now using deep learning models to explore the emergence of language in various language games, where simulated agents interact and develop an emergent language to solve a task. Although it is quite intuitive that different types of language games posing different communicative challenges might require emergent languages which encode different levels of information, there is no existing work exploring the expressivity of the emergent languages. In this work, we propose a definition of partial order between expressivity based on the generalisation performance across different language games. We also validate the hypothesis that expressivity of emergent languages is a trade-off between the complexity and unpredictability of the context those languages are used in. Our second novel contribution is introducing contrastive loss into the implementation of referential games. We show that using our contrastive loss alleviates the collapse of message types seen using standard referential loss functions.
Symbolic Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence
Feb 05, 2021Abstract:The ability to use symbols is the pinnacle of human intelligence, but has yet to be fully replicated in machines. Here we argue that the path towards symbolically fluent artificial intelligence (AI) begins with a reinterpretation of what symbols are, how they come to exist, and how a system behaves when it uses them. We begin by offering an interpretation of symbols as entities whose meaning is established by convention. But crucially, something is a symbol only for those who demonstrably and actively participate in this convention. We then outline how this interpretation thematically unifies the behavioural traits humans exhibit when they use symbols. This motivates our proposal that the field place a greater emphasis on symbolic behaviour rather than particular computational mechanisms inspired by more restrictive interpretations of symbols. Finally, we suggest that AI research explore social and cultural engagement as a tool to develop the cognitive machinery necessary for symbolic behaviour to emerge. This approach will allow for AI to interpret something as symbolic on its own rather than simply manipulate things that are only symbols to human onlookers, and thus will ultimately lead to AI with more human-like symbolic fluency.
Imitating Interactive Intelligence
Jan 21, 2021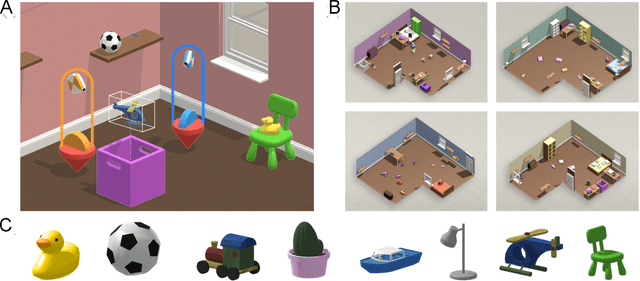
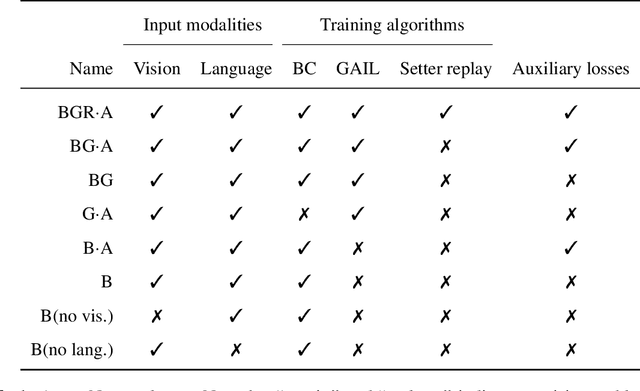
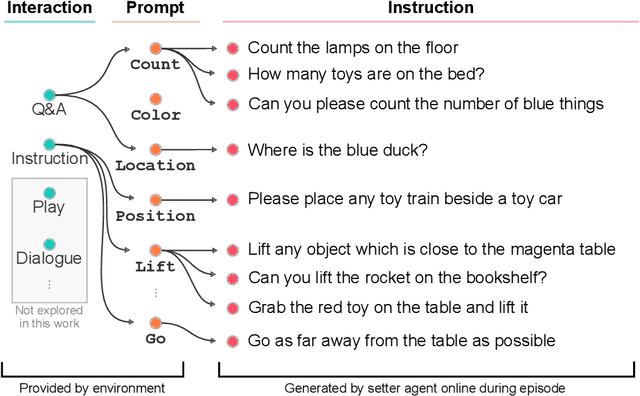
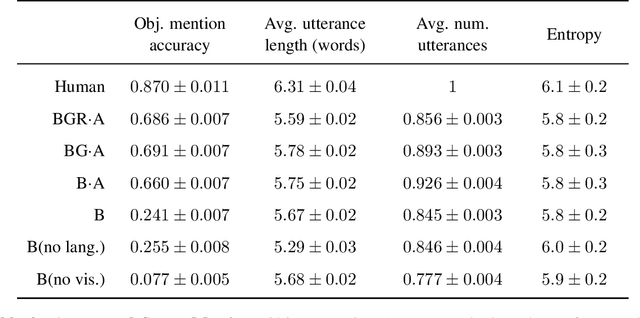
Abstract:A common vision from science fiction is that robots will one day inhabit our physical spaces, sense the world as we do, assist our physical labours, and communicate with us through natural language. Here we study how to design artificial agents that can interact naturally with humans using the simplification of a virtual environment. This setting nevertheless integrates a number of the central challenges of artificial intelligence (AI) research: complex visual perception and goal-directed physical control, grounded language comprehension and production, and multi-agent social interaction. To build agents that can robustly interact with humans, we would ideally train them while they interact with humans. However, this is presently impractical. Therefore, we approximate the role of the human with another learned agent, and use ideas from inverse reinforcement learning to reduce the disparities between human-human and agent-agent interactive behaviour. Rigorously evaluating our agents poses a great challenge, so we develop a variety of behavioural tests, including evaluation by humans who watch videos of agents or interact directly with them. These evaluations convincingly demonstrate that interactive training and auxiliary losses improve agent behaviour beyond what is achieved by supervised learning of actions alone. Further, we demonstrate that agent capabilities generalise beyond literal experiences in the dataset. Finally, we train evaluation models whose ratings of agents agree well with human judgement, thus permitting the evaluation of new agent models without additional effort. Taken together, our results in this virtual environment provide evidence that large-scale human behavioural imitation is a promising tool to create intelligent, interactive agents, and the challenge of reliably evaluating such agents is possible to surmount.
Inductive Bias and Language Expressivity in Emergent Communication
Dec 04, 2020
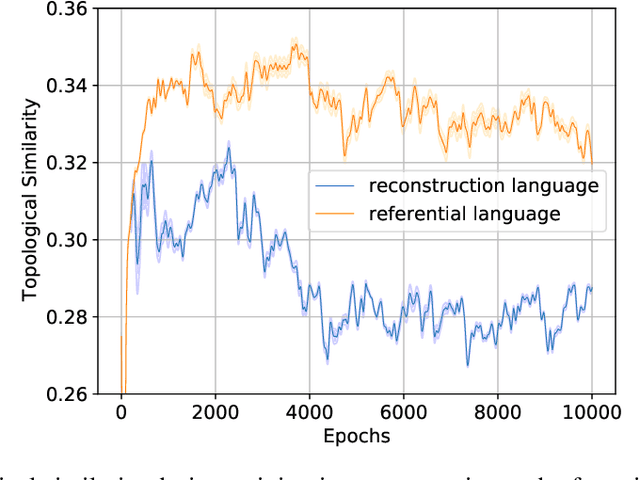

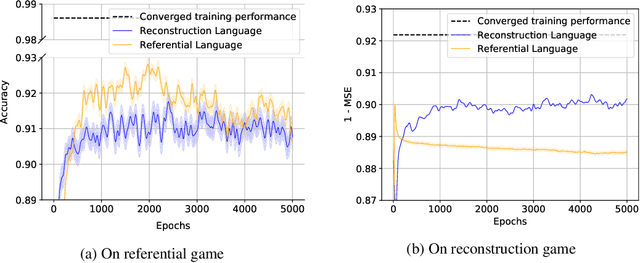
Abstract:Referential games and reconstruction games are the most common game types for studying emergent languages. We investigate how the type of the language game affects the emergent language in terms of: i) language compositionality and ii) transfer of an emergent language to a task different from its origin, which we refer to as language expressivity. With empirical experiments on a handcrafted symbolic dataset, we show that languages emerged from different games have different compositionality and further different expressivity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge