Joey Wilson
SLIM-VDB: A Real-Time 3D Probabilistic Semantic Mapping Framework
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces SLIM-VDB, a new lightweight semantic mapping system with probabilistic semantic fusion for closed-set or open-set dictionaries. Advances in data structures from the computer graphics community, such as OpenVDB, have demonstrated significantly improved computational and memory efficiency in volumetric scene representation. Although OpenVDB has been used for geometric mapping in robotics applications, semantic mapping for scene understanding with OpenVDB remains unexplored. In addition, existing semantic mapping systems lack support for integrating both fixed-category and open-language label predictions within a single framework. In this paper, we propose a novel 3D semantic mapping system that leverages the OpenVDB data structure and integrates a unified Bayesian update framework for both closed- and open-set semantic fusion. Our proposed framework, SLIM-VDB, achieves significant reduction in both memory and integration times compared to current state-of-the-art semantic mapping approaches, while maintaining comparable mapping accuracy. An open-source C++ codebase with a Python interface is available at https://github.com/umfieldrobotics/slim-vdb.
These Magic Moments: Differentiable Uncertainty Quantification of Radiance Field Models
Mar 20, 2025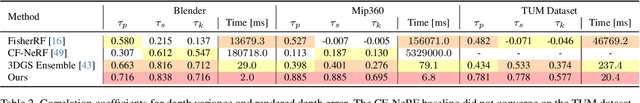
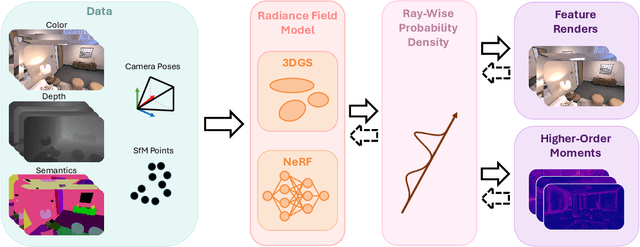
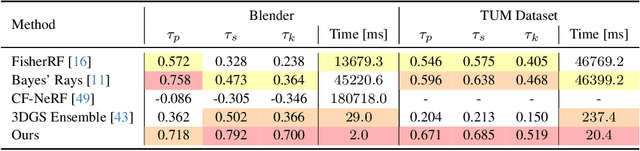
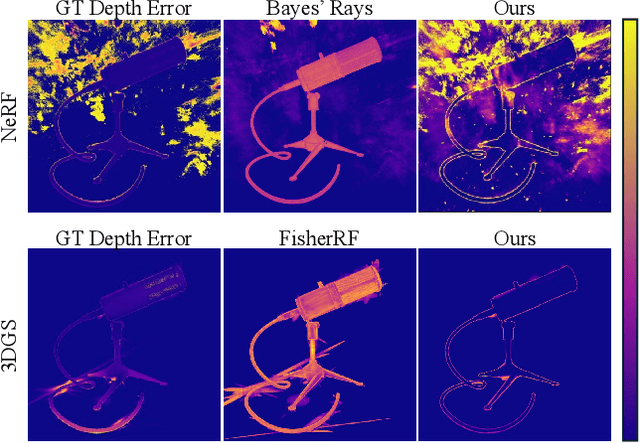
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel approach to uncertainty quantification for radiance fields by leveraging higher-order moments of the rendering equation. Uncertainty quantification is crucial for downstream tasks including view planning and scene understanding, where safety and robustness are paramount. However, the high dimensionality and complexity of radiance fields pose significant challenges for uncertainty quantification, limiting the use of these uncertainty quantification methods in high-speed decision-making. We demonstrate that the probabilistic nature of the rendering process enables efficient and differentiable computation of higher-order moments for radiance field outputs, including color, depth, and semantic predictions. Our method outperforms existing radiance field uncertainty estimation techniques while offering a more direct, computationally efficient, and differentiable formulation without the need for post-processing. Beyond uncertainty quantification, we also illustrate the utility of our approach in downstream applications such as next-best-view (NBV) selection and active ray sampling for neural radiance field training. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world scenes confirm the efficacy of our approach, which achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining simplicity.
POp-GS: Next Best View in 3D-Gaussian Splatting with P-Optimality
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for quantifying uncertainty and information gained within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) through P-Optimality. While 3D-GS has proven to be a useful world model with high-quality rasterizations, it does not natively quantify uncertainty. Quantifying uncertainty in parameters of 3D-GS is necessary to understand the information gained from acquiring new images as in active perception, or identify redundant images which can be removed from memory due to resource constraints in online 3D-GS SLAM. We propose to quantify uncertainty and information gain in 3D-GS by reformulating the problem through the lens of optimal experimental design, which is a classical solution to measuring information gain. By restructuring information quantification of 3D-GS through optimal experimental design, we arrive at multiple solutions, of which T-Optimality and D-Optimality perform the best quantitatively and qualitatively as measured on two popular datasets. Additionally, we propose a block diagonal approximation of the 3D-GS uncertainty, which provides a measure of correlation for computing more accurate information gain, at the expense of a greater computation cost.
Modeling Uncertainty in 3D Gaussian Splatting through Continuous Semantic Splatting
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for probabilistically updating and rasterizing semantic maps within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS). Although previous methods have introduced algorithms which learn to rasterize features in 3D-GS for enhanced scene understanding, 3D-GS can fail without warning which presents a challenge for safety-critical robotic applications. To address this gap, we propose a method which advances the literature of continuous semantic mapping from voxels to ellipsoids, combining the precise structure of 3D-GS with the ability to quantify uncertainty of probabilistic robotic maps. Given a set of images, our algorithm performs a probabilistic semantic update directly on the 3D ellipsoids to obtain an expectation and variance through the use of conjugate priors. We also propose a probabilistic rasterization which returns per-pixel segmentation predictions with quantifiable uncertainty. We compare our method with similar probabilistic voxel-based methods to verify our extension to 3D ellipsoids, and perform ablation studies on uncertainty quantification and temporal smoothing.
Latent BKI: Open-Dictionary Continuous Mapping in Visual-Language Latent Spaces with Quantifiable Uncertainty
Oct 15, 2024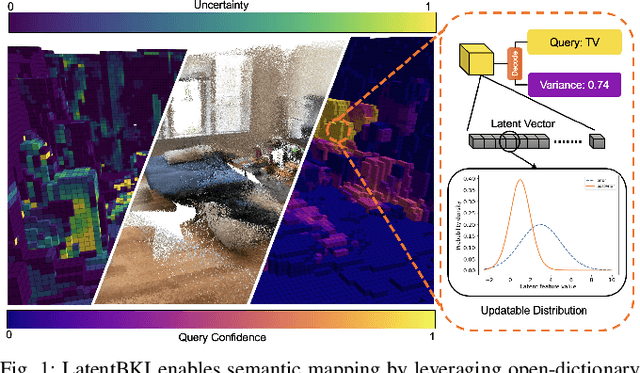



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel probabilistic mapping algorithm, Latent BKI, which enables open-vocabulary mapping with quantifiable uncertainty. Traditionally, semantic mapping algorithms focus on a fixed set of semantic categories which limits their applicability for complex robotic tasks. Vision-Language (VL) models have recently emerged as a technique to jointly model language and visual features in a latent space, enabling semantic recognition beyond a predefined, fixed set of semantic classes. Latent BKI recurrently incorporates neural embeddings from VL models into a voxel map with quantifiable uncertainty, leveraging the spatial correlations of nearby observations through Bayesian Kernel Inference (BKI). Latent BKI is evaluated against similar explicit semantic mapping and VL mapping frameworks on the popular MatterPort-3D and Semantic KITTI data sets, demonstrating that Latent BKI maintains the probabilistic benefits of continuous mapping with the additional benefit of open-dictionary queries. Real-world experiments demonstrate applicability to challenging indoor environments.
MDMP: Multi-modal Diffusion for supervised Motion Predictions with uncertainty
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a Multi-modal Diffusion model for Motion Prediction (MDMP) that integrates and synchronizes skeletal data and textual descriptions of actions to generate refined long-term motion predictions with quantifiable uncertainty. Existing methods for motion forecasting or motion generation rely solely on either prior motions or text prompts, facing limitations with precision or control, particularly over extended durations. The multi-modal nature of our approach enhances the contextual understanding of human motion, while our graph-based transformer framework effectively capture both spatial and temporal motion dynamics. As a result, our model consistently outperforms existing generative techniques in accurately predicting long-term motions. Additionally, by leveraging diffusion models' ability to capture different modes of prediction, we estimate uncertainty, significantly improving spatial awareness in human-robot interactions by incorporating zones of presence with varying confidence levels for each body joint.
ConvBKI: Real-Time Probabilistic Semantic Mapping Network with Quantifiable Uncertainty
Oct 26, 2023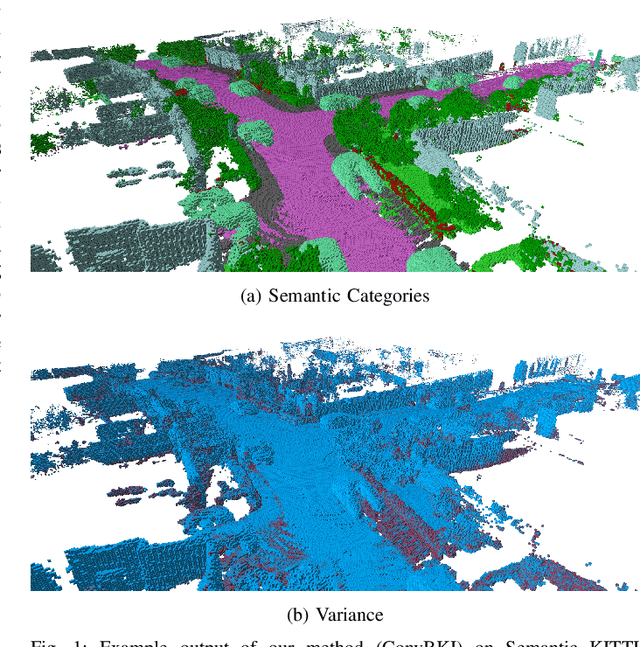
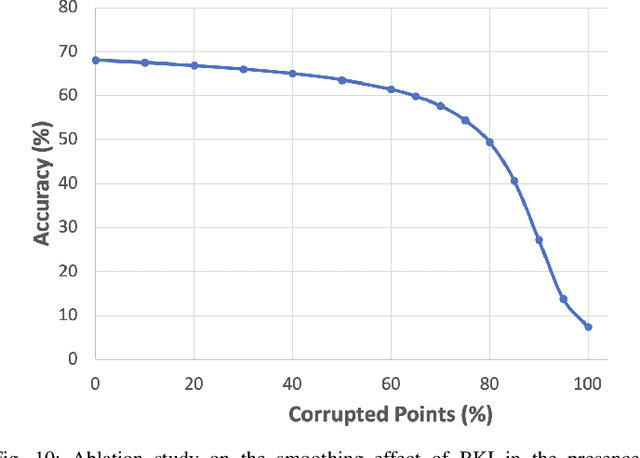
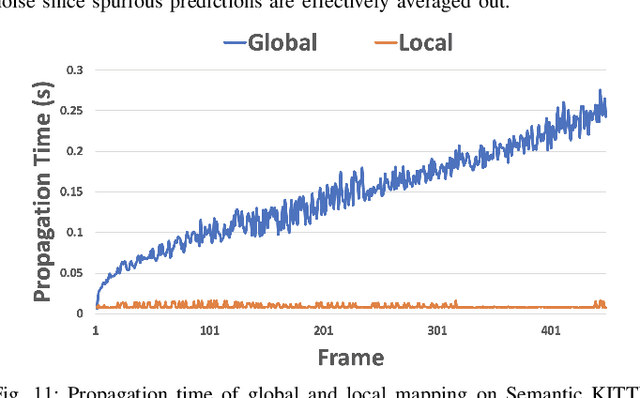

Abstract:In this paper, we develop a modular neural network for real-time semantic mapping in uncertain environments, which explicitly updates per-voxel probabilistic distributions within a neural network layer. Our approach combines the reliability of classical probabilistic algorithms with the performance and efficiency of modern neural networks. Although robotic perception is often divided between modern differentiable methods and classical explicit methods, a union of both is necessary for real-time and trustworthy performance. We introduce a novel Convolutional Bayesian Kernel Inference (ConvBKI) layer which incorporates semantic segmentation predictions online into a 3D map through a depthwise convolution layer by leveraging conjugate priors. We compare ConvBKI against state-of-the-art deep learning approaches and probabilistic algorithms for mapping to evaluate reliability and performance. We also create a Robot Operating System (ROS) package of ConvBKI and test it on real-world perceptually challenging off-road driving data.
Not All Actions Are Created Equal: Bayesian Optimal Experimental Design for Safe and Optimal Nonlinear System Identification
Aug 03, 2023Abstract:Uncertainty in state or model parameters is common in robotics and typically handled by acquiring system measurements that yield information about the uncertain quantities of interest. Inputs to a nonlinear dynamical system yield outcomes that produce varying amounts of information about the underlying uncertain parameters of the system. To maximize information gained with respect to these uncertain parameters we present a Bayesian approach to data collection for system identification called Bayesian Optimal Experimental Design (BOED). The formulation uses parameterized trajectories and cubature to compute maximally informative system trajectories which obtain as much information as possible about unknown system parameters while also ensuring safety under mild assumptions. The proposed method is applicable to non-linear and non-Gaussian systems and is applied to a high-fidelity vehicle model from the literature. It is shown the proposed approach requires orders of magnitude fewer samples compared to state-of-the-art BOED algorithms from the literature while simultaneously providing safety guarantees.
Convolutional Bayesian Kernel Inference for 3D Semantic Mapping
Sep 21, 2022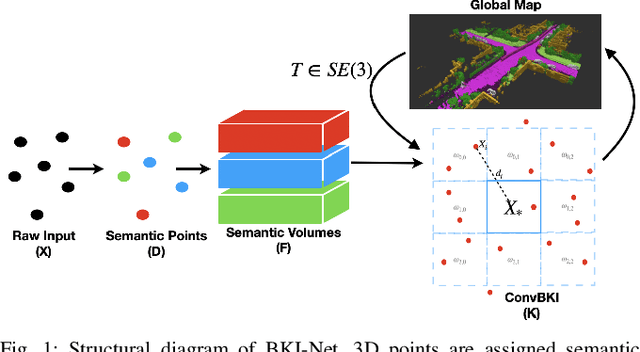
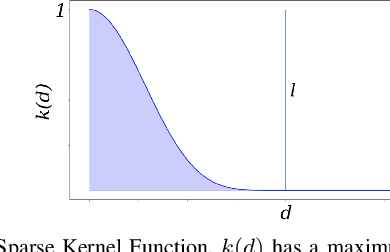
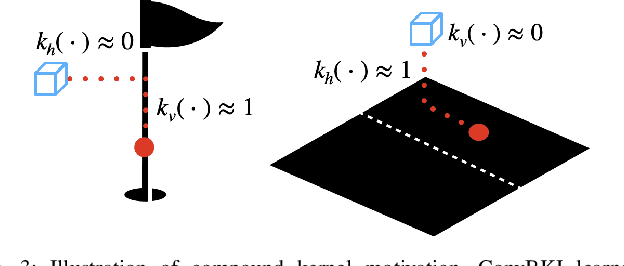
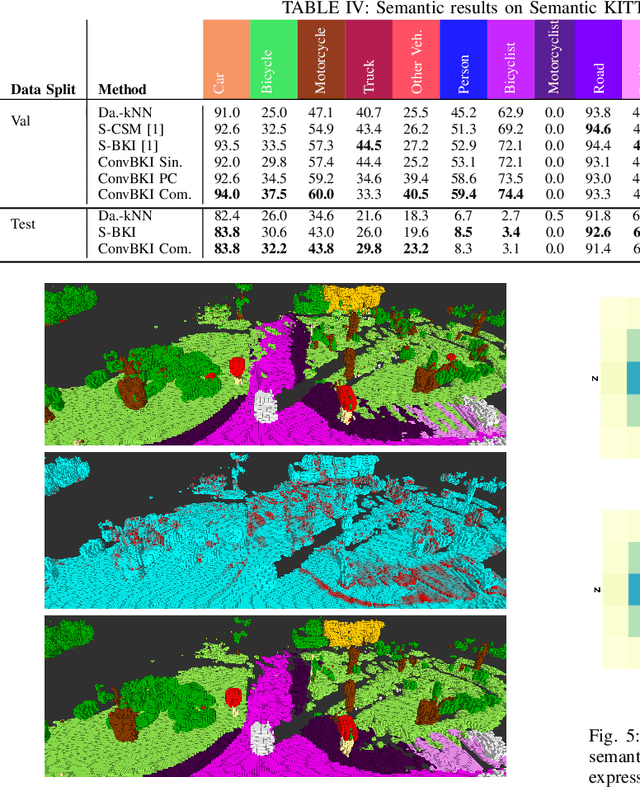
Abstract:Robotic perception is currently at a cross-roads between modern methods which operate in an efficient latent space, and classical methods which are mathematically founded and provide interpretable, trustworthy results. In this paper, we introduce a Convolutional Bayesian Kernel Inference (ConvBKI) layer which explicitly performs Bayesian inference within a depthwise separable convolution layer to simultaneously maximize efficiency while maintaining reliability. We apply our layer to the task of 3D semantic mapping, where we learn semantic-geometric probability distributions for LiDAR sensor information in real time. We evaluate our network against state-of-the-art semantic mapping algorithms on the KITTI data set, and demonstrate improved latency with comparable semantic results.
MotionSC: Data Set and Network for Real-Time Semantic Mapping in Dynamic Environments
Mar 14, 2022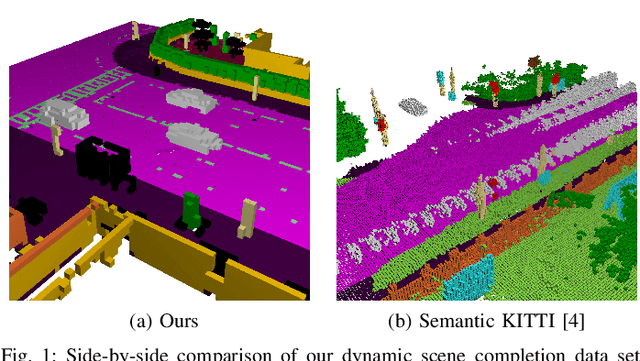
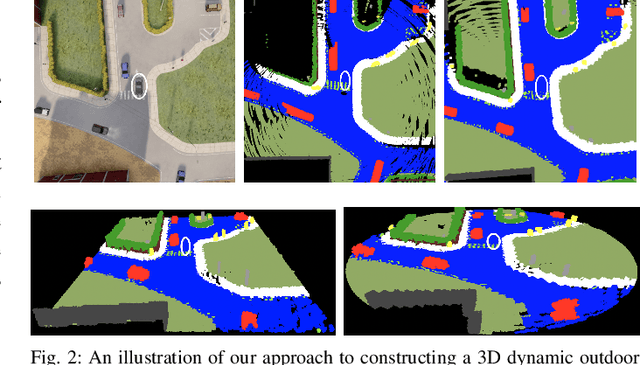
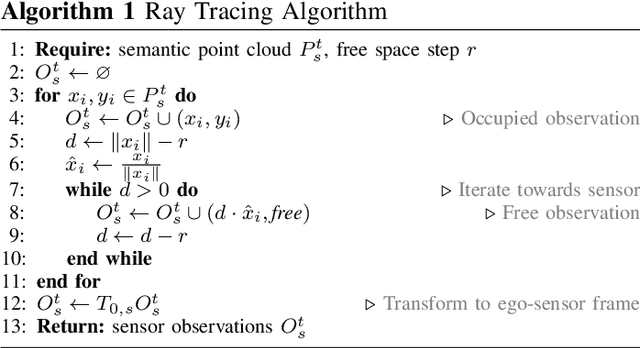
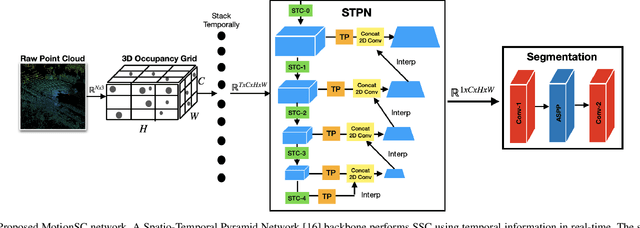
Abstract:This work addresses a gap in semantic scene completion (SSC) data by creating a novel outdoor data set with accurate and complete dynamic scenes. Our data set is formed from randomly sampled views of the world at each time step, which supervises generalizability to complete scenes without occlusions or traces. We create SSC baselines from state-of-the-art open source networks and construct a benchmark real-time dense local semantic mapping algorithm, MotionSC, by leveraging recent 3D deep learning architectures to enhance SSC with temporal information. Our network shows that the proposed data set can quantify and supervise accurate scene completion in the presence of dynamic objects, which can lead to the development of improved dynamic mapping algorithms. All software is available at https://github.com/UMich-CURLY/3DMapping.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge